Application of a cervical low incision in the functional neck dissection of thyroid papillary carcinoma
- Authors:
- Published online on: January 27, 2016 https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2016.745
- Pages: 477-482
-
Copyright: © Xu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of Creative Commons Attribution License.
Metrics: Total
Views: 0 (Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics: )
Total PDF Downloads: 0 (Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics: )
Abstract
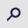
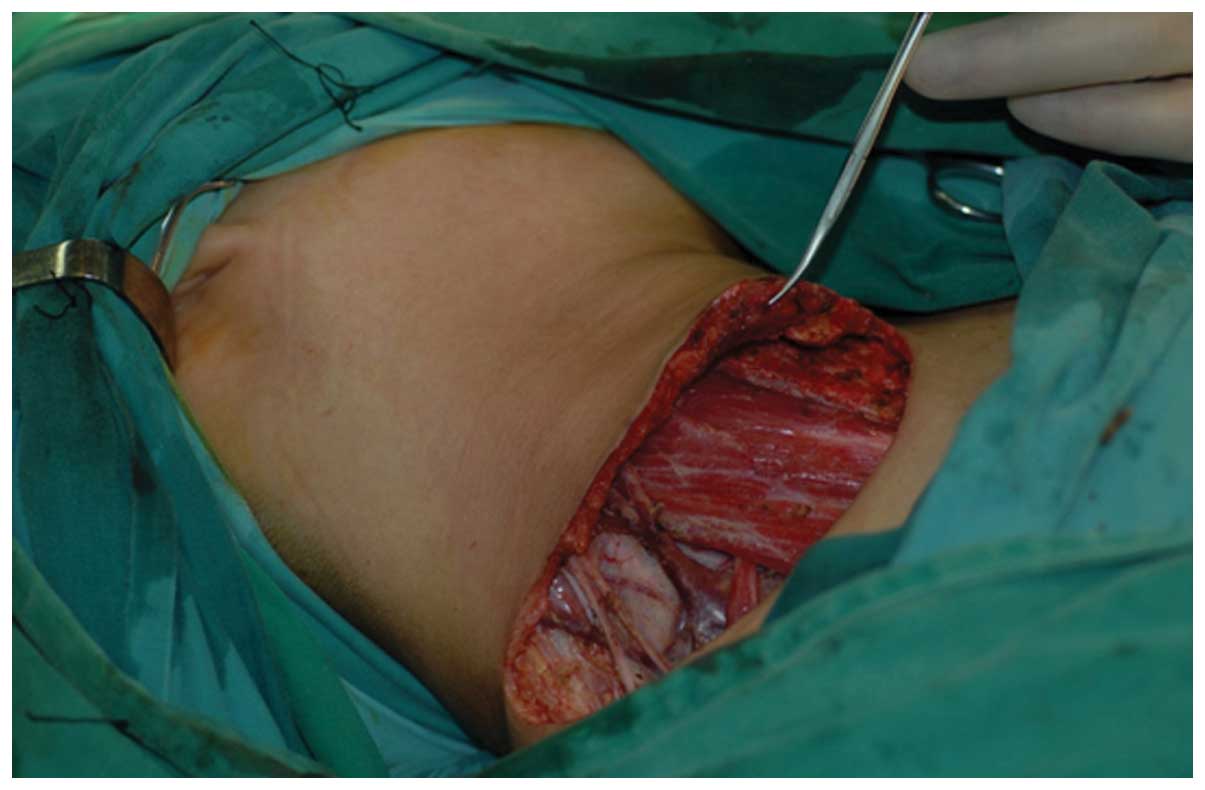
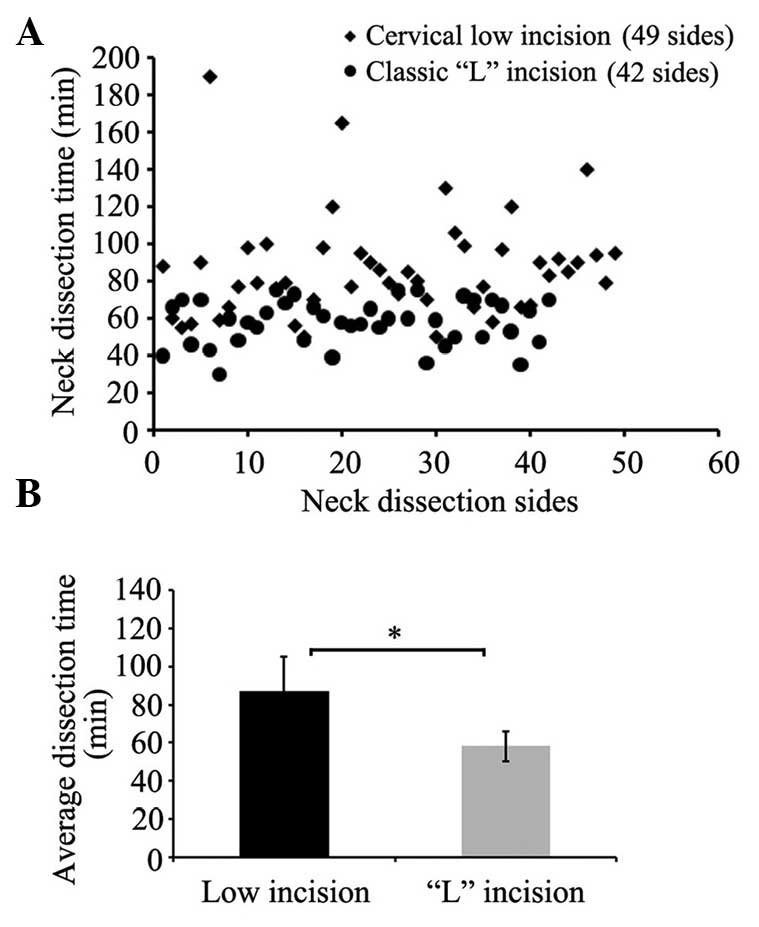
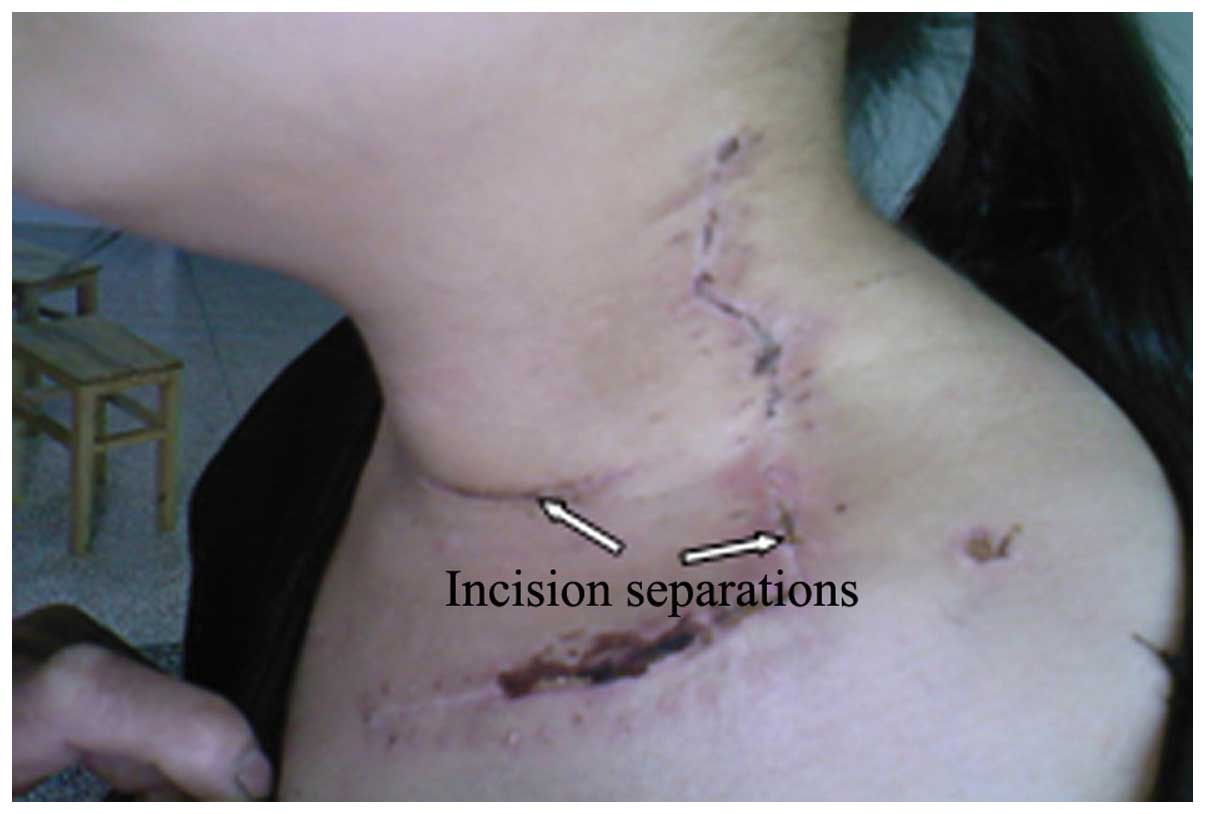
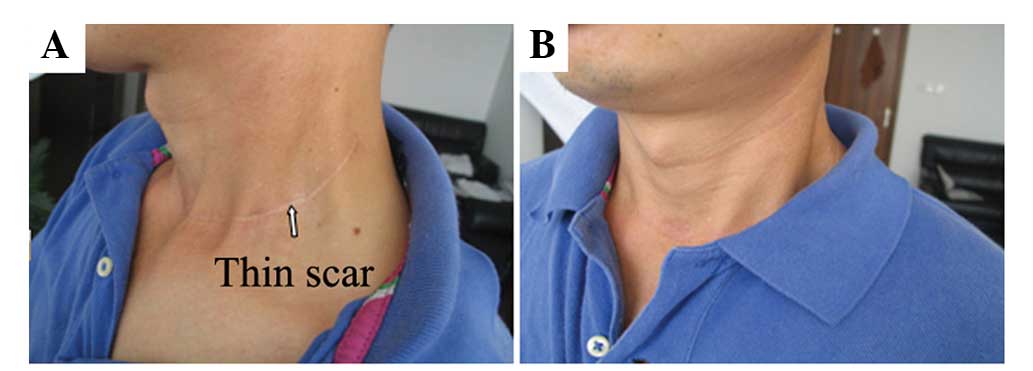
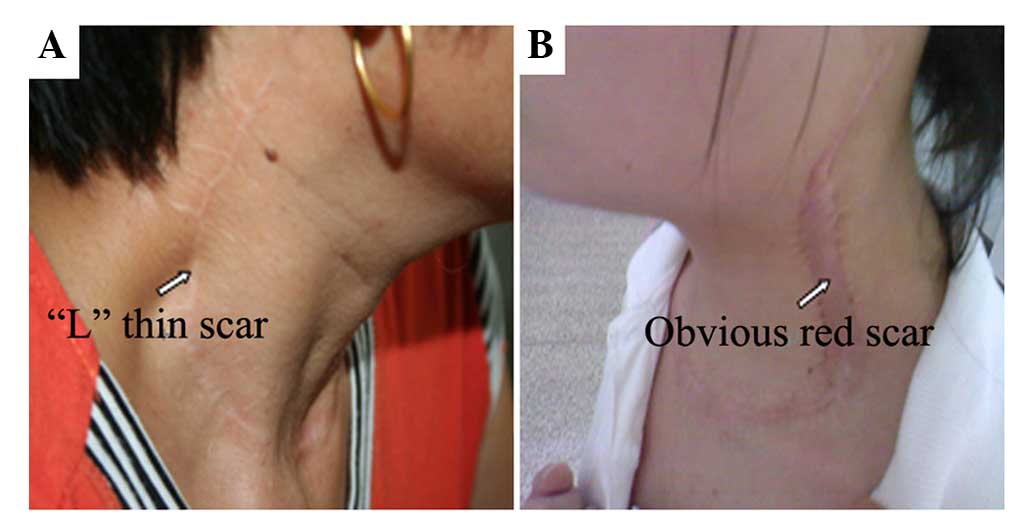
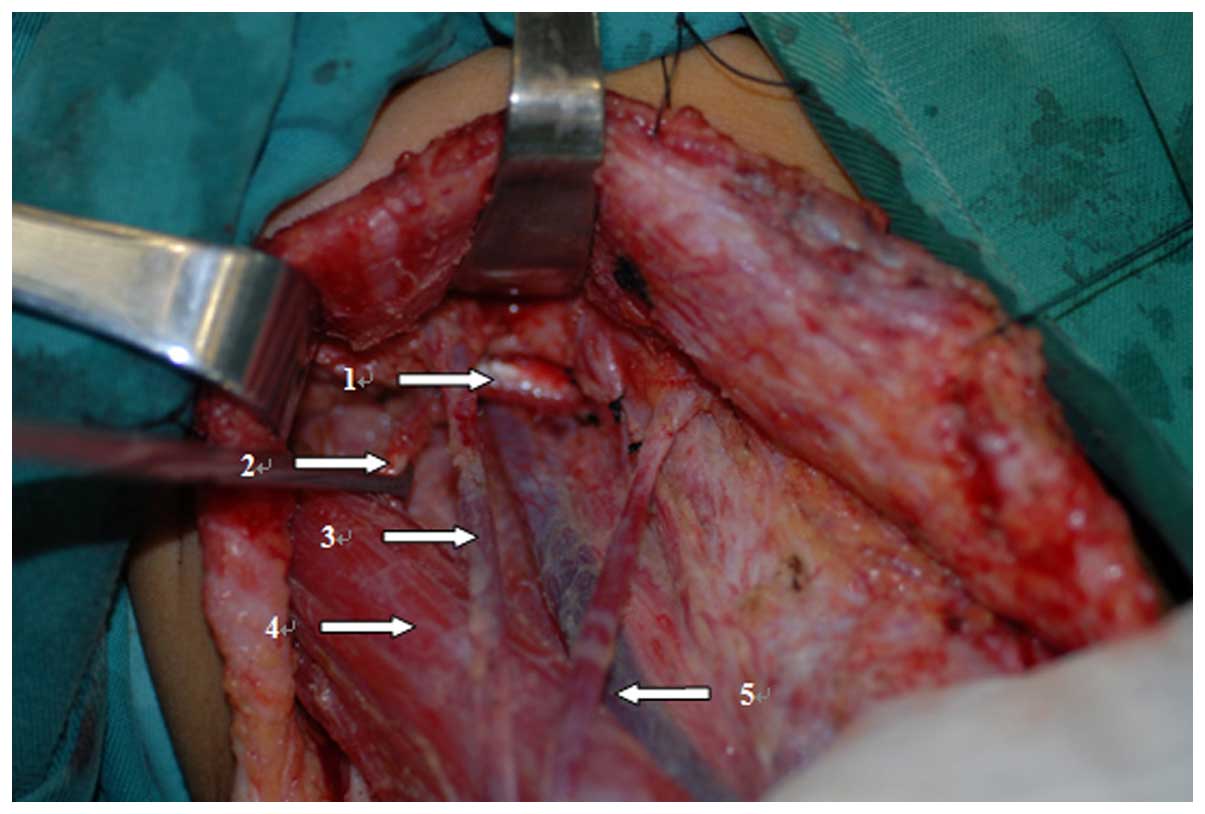
The present study aimed to discuss the advantage of the application of a cervical low incision for functional neck dissection in patients with thyroid papillary carcinoma. The study was a retrospective analysis of 87 thyroid papillary carcinoma patients; cervical low incision in the functional neck dissection was applied for 47 cases and the classic ʻLʼ incision was applied for 40 cases. The different integrity, surgical time, blood loss and the aesthetic property of the incision were compared between the cervical low incision and the classic ʻLʼ incision for lateral neck dissection of thyroid cancer. The postoperative pathological diagnosis was that the average total amount and the region II lymph nodes of the unilateral neck dissection were 33 and 10 for the cervical low incision group, and 32 and 11 for the classic ʻLʼ incision group, respectively (P>0.05). The average unilateral neck dissection times were 87 and 58 min for the cervical low incision group and the classic ʻLʼ incision group, respectively (P<0.05). The blood loss of the cervical low incision group was 67 ml, while the loss for the classic ʻLʼ incision group was 61 ml (P>0.05). The postoperative incision of the cervical low incision group was smaller and more concealing. Additionally, the cosmetic deformities were milder for an inconspicuous cervical scar, and the sensation was improved for the patients in comparison with the classic ʻLʼ incision group. These results suggest that the application of cervical low incision for functional neck dissection in thyroid papillary carcinoma patients aids in reducing postoperative complications, without increasing recurrence rates. Therefore, the classic ʻLʼ incision can be replaced by the cervical low incision.