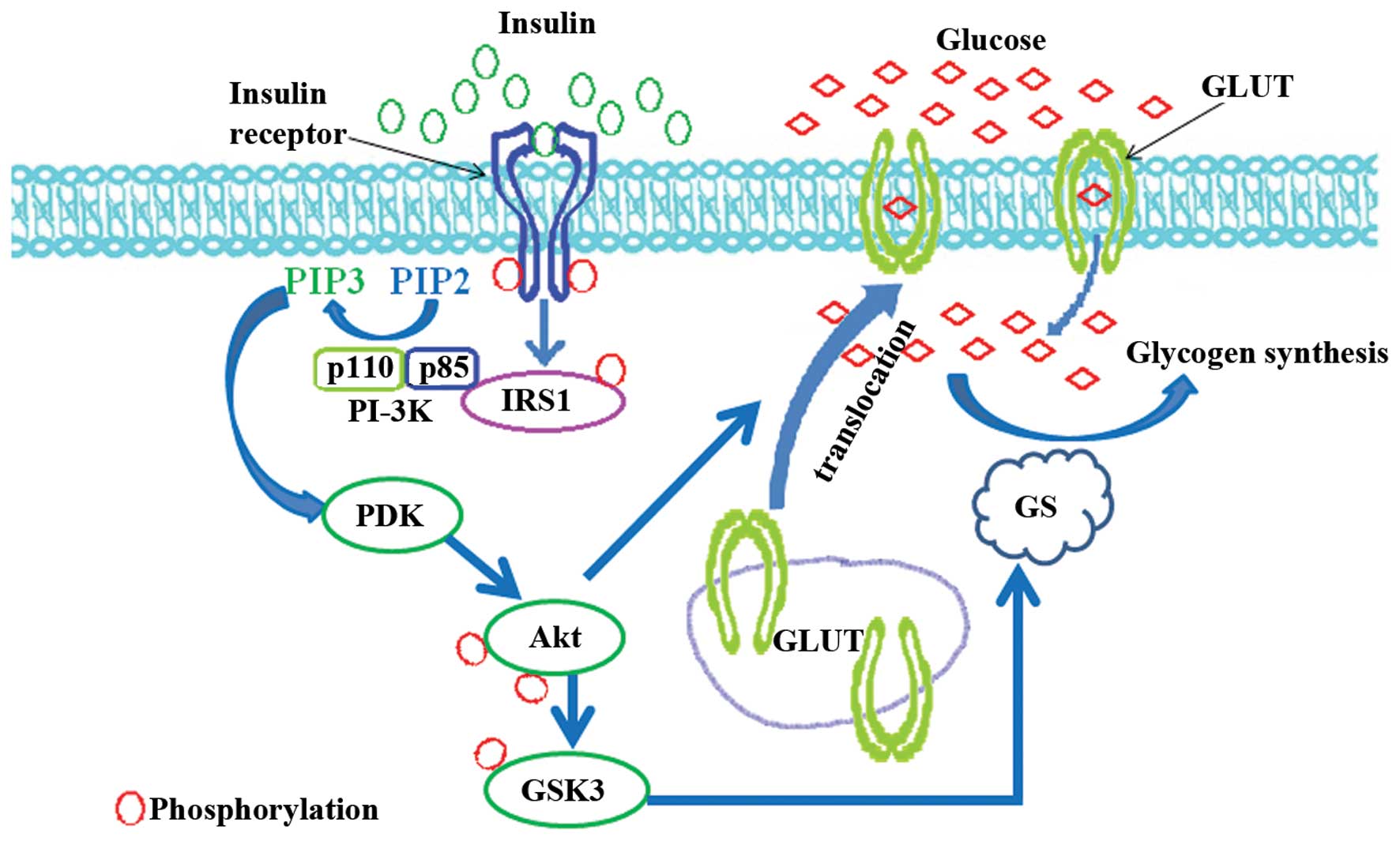
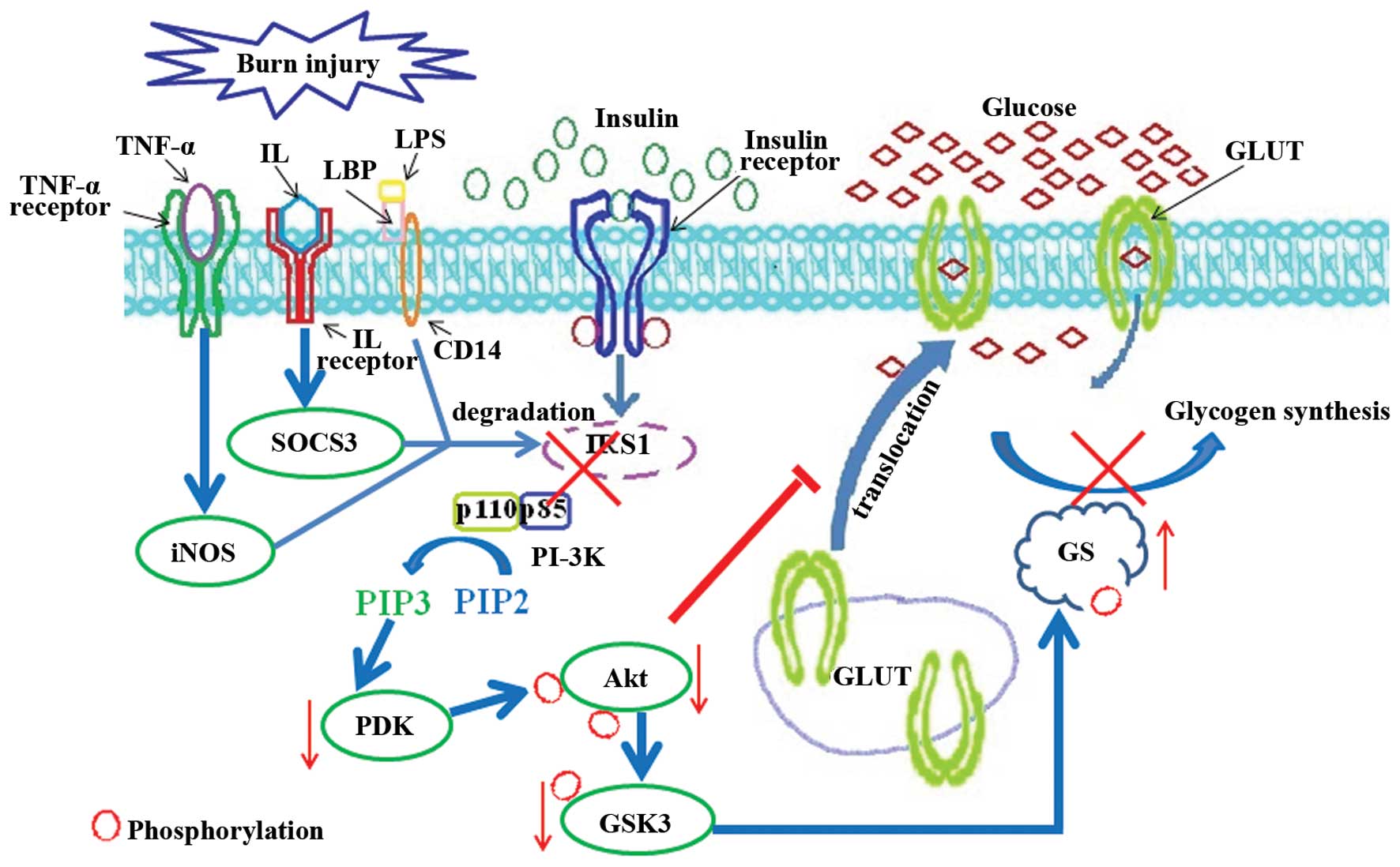
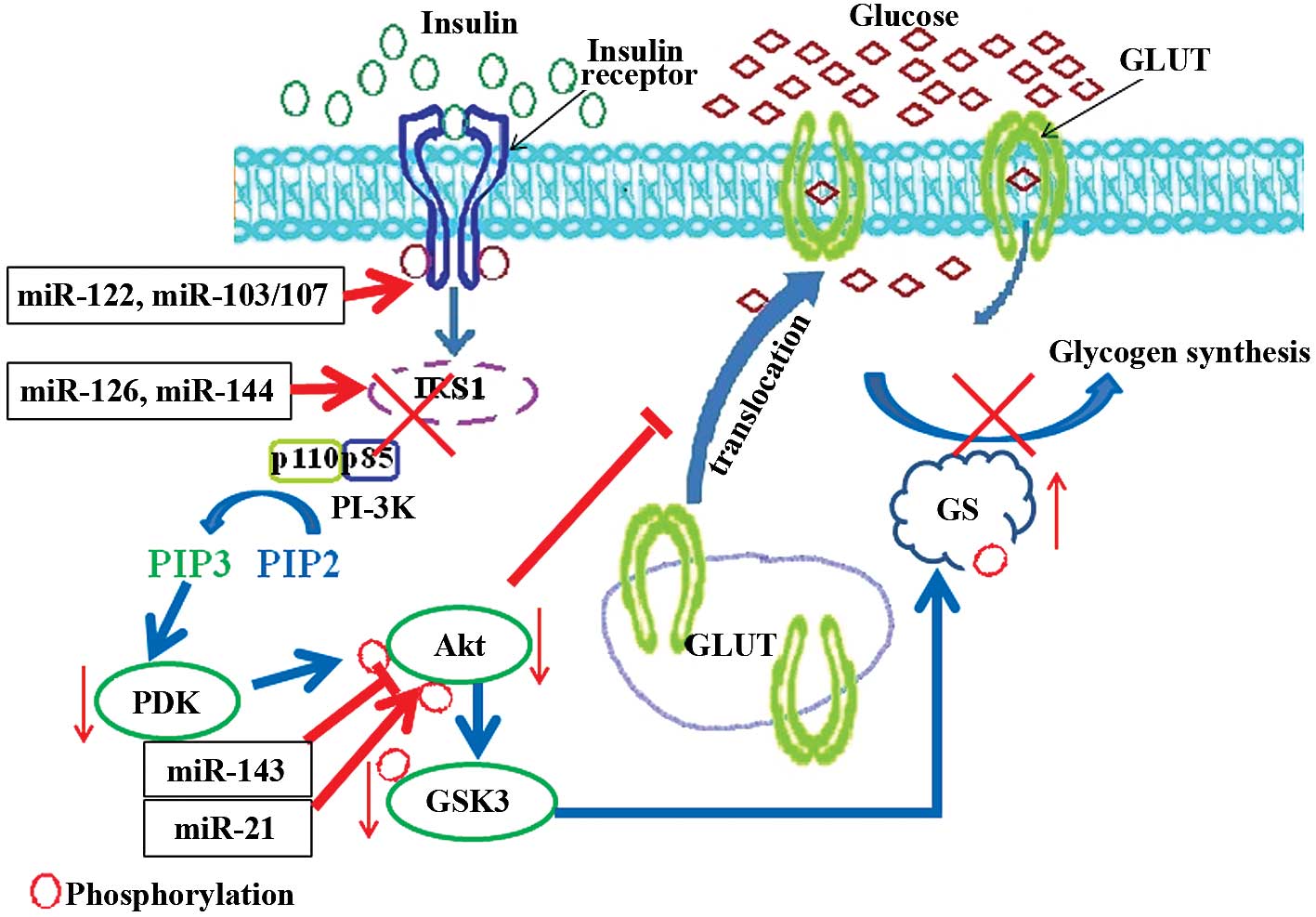
|
1
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, et al: MicroRNA genes
are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 23:4051–4060. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zeng Y and Cullen BR: Efficient processing
of primary microRNA hairpins by Drosha requires flanking
nonstructured RNA sequences. J Biol Chem. 280:27595–27603. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Andl T, Murchison EP, Liu F, et al: The
miRNA-processing enzyme dicer is essential for the morphogenesis
and maintenance of hair follicles. Curr Biol. 16:1041–1049. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Visone R and Croce CM: MiRNAs and cancer.
Am J Pathol. 174:1131–1138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Argyropoulos C, Wang K, McClarty S, et al:
Urinary microRNA profiling in the nephropathy of type 1 diabetes.
PLoS One. 8:e546622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van de Bunt M, Gaulton KJ, Parts L, et al:
The miRNA profile of human pancreatic islets and beta-cells and
relationship to type 2 diabetes pathogenesis. PLoS One.
8:e552722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McMichael AJ, Borrow P, Tomaras GD,
Goonetilleke N and Haynes BF: The immune response during acute
HIV-1 infection: clues for vaccine development. Nat Rev Immunol.
10:11–23. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ono K, Kuwabara Y and Han J: MicroRNAs and
cardiovascular diseases. FEBS J. 278:1619–1633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Evers LH, Bhavsar D and Mailander P: The
biology of burn injury. Exp Dermatol. 19:777–783. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duan H, Chai J, Sheng Z, et al: Effect of
burn injury on apoptosis and expression of apoptosis-related
genes/proteins in skeletal muscles of rats. Apoptosis. 14:52–65.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nishimura T, Nishiura T, deSerres S,
Nakagawa T, Brenner DA and Meyer AA: Impact of burn injury on
hepatic TGF-beta1 expression and plasma TGF-beta1 levels. J Trauma.
48:39–44. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kowal-Vern A, Walenga JM, Hoppensteadt D,
Sharp-Pucci M and Gamelli RL: Interleukin-2 and interleukin-6 in
relation to burn wound size in the acute phase of thermal injury. J
Am Coll Surg. 178:357–362. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Soejima K, Traber LD, Schmalstieg FC, et
al: Role of nitric oxide in vascular permeability after combined
burns and smoke inhalation injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
163:745–752. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cree MG, Zwetsloot JJ, Herndon DN, et al:
Insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial function are improved in
children with burn injury during a randomized controlled trial of
fenofibrate. Ann Surg. 245:214–221. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cree MG, Aarsland A, Herndon DN and Wolfe
RR: Role of fat metabolism in burn trauma-induced skeletal muscle
insulin resistance. Crit Care Med. 35:S476–S483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sharp A and Clark J: Diabetes and its
effects on wound healing. Nurs Stand. 25:41–47. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lima MH, Caricilli AM, de Abreu LL, et al:
Topical insulin accelerates wound healing in diabetes by enhancing
the AKT and ERK pathways: a double-blind placebo-controlled
clinical trial. PLoS One. 7:e369742012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ryu HS, Park SY, Ma D, Zhang J and Lee W:
The induction of microRNA targeting IRS-1 is involved in the
development of insulin resistance under conditions of mitochondrial
dysfunction in hepatocytes. PLoS One. 6:e173432011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karolina DS, Armugam A, Tavintharan S, et
al: MicroRNA 144 impairs insulin signaling by inhibiting the
expression of insulin receptor substrate 1 in type 2 diabetes
mellitus. PLoS One. 6:e228392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frayn KN: Effects of burn injury on
insulin secretion and on sensitivity to insulin in the rat in vivo.
Eur J Clin Invest. 5:331–337. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jeschke MG, Kulp GA, Kraft R, et al:
Intensive insulin therapy in severely burned pediatric patients: a
prospective randomized trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
182:351–359. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gauglitz GG, Herndon DN, Kulp GA, Meyer WJ
III and Jeschke MG: Abnormal insulin sensitivity persists up to
three years in pediatric patients post-burn. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 94:1656–1664. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kokubun E, Hirabara SM, Fiamoncini J, Curi
R and Haebisch H: Changes of glycogen content in liver, skeletal
muscle, and heart from fasted rats. Cell Biochem Funct. 27:488–495.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chari-Bitron A, Lepkovsky S, Lemmon RM and
Dimick MK: Conversion of glucose to glycogen after ingestion of a
high-carbohydrate diet. Am J Physiol. 198:787–792. 1960.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bell GI, Kayano T, Buse JB, et al:
Molecular biology of mammalian glucose transporters. Diabetes Care.
13:198–208. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kasuga M, Zick Y, Blithe DL, Crettaz M and
Kahn CR: Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin
receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 298:667–669. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Boura-Halfon S and Zick Y: Phosphorylation
of IRS proteins, insulin action, and insulin resistance. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 296:E581–E591. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Metz HE and Houghton AM: Insulin receptor
substrate regulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Clin Cancer Res.
17:206–211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bhaskar PT and Hay N: The two TORCs and
Akt. Dev Cell. 12:487–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Thorell A, Hirshman MF, Nygren J, et al:
Exercise and insulin cause GLUT-4 translocation in human skeletal
muscle. Am J Physiol. 277:E733–E741. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Browner MF, Nakano K, Bang AG and
Fletterick RJ: Human muscle glycogen synthase cDNA sequence: a
negatively charged protein with an asymmetric charge distribution.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:1443–1447. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bai G, Zhang ZJ, Werner R, Nuttall FQ, Tan
AW and Lee EY: The primary structure of rat liver glycogen synthase
deduced by cDNA cloning. Absence of phosphorylation sites 1a and
1b. J Biol Chem. 265:7843–7848. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hojlund K, Birk JB, Klein DK, et al:
Dysregulation of glycogen synthase COOH- and
NH2-terminal phosphorylation by insulin in obesity and
type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:4547–4556.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich
M and Hemmings BA: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by
insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 378:785–789. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fang X, Yu SX, Lu Y, Bast RC Jr, Woodgett
JR and Mills GB: Phosphorylation and inactivation of glycogen
synthase kinase 3 by protein kinase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:11960–11965. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bouskila M, Hirshman MF, Jensen J,
Goodyear LJ and Sakamoto K: Insulin promotes glycogen synthesis in
the absence of GSK3 phosphorylation in skeletal muscle. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 294:E28–E35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Villar-Palasi C and Guinovart JJ: The role
of glucose 6-phosphate in the control of glycogen synthase. FASEB
J. 11:544–558. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ikezu T, Okamoto T, Yonezawa K, Tompkins
RG and Martyn JA: Analysis of thermal injury-induced insulin
resistance in rodents. Implication of postreceptor mechanisms. J
Biol Chem. 272:25289–25295. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pilon G, Charbonneau A, White PJ, et al:
Endotoxin mediated-iNOS induction causes insulin resistance via
ONOO− induced tyrosine nitration of IRS-1 in skeletal
muscle. PLoS One. 5:e159122010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sugita H, Kaneki M, Tokunaga E, et al:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase plays a role in LPS-induced
hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 282:E386–E394. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sugita H, Fujimoto M, Yasukawa T, et al:
Inducible nitric-oxide synthase and NO donor induce insulin
receptor substrate-1 degradation in skeletal muscle cells. J Biol
Chem. 280:14203–14211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sugita M, Sugita H, Kim M, et al:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase deficiency ameliorates skeletal
muscle insulin resistance but does not alter unexpected lower blood
glucose levels after burn injury in C57BL/6 mice. Metabolism.
61:127–136. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Hotamisligil GS, Murray DL, Choy LN and
Spiegelman BM: Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits signaling from
the insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:4854–4858. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pederson TM, Kramer DL and Rondinone CM:
Serine/threonine phosphorylation of IRS-1 triggers its degradation:
possible regulation by tyrosine phosphorylation. Diabetes.
50:24–31. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Q, Carter EA, Ma BY, White M,
Fischman AJ and Tompkins RG: Molecular mechanism(s) of burn-induced
insulin resistance in murine skeletal muscle: role of IRS
phosphorylation. Life Sci. 77:3068–3077. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rui L, Aguirre V, Kim JK, et al:
Insulin/IGF-1 and TNF-α stimulate phosphorylation of IRS-1 at
inhibitory Ser307 via distinct pathways. J Clin Invest.
107:181–189. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Senn JJ, Klover PJ, Nowak IA and Mooney
RA: Interleukin-6 induces cellular insulin resistance in
hepatocytes. Diabetes. 51:3391–3399. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rotter V, Nagaev I and Smith U:
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) induces insulin resistance in 3T3-L1
adipocytes and is, like IL-8 and tumor necrosis factor-α,
overexpressed in human fat cells from insulin-resistant subjects. J
Biol Chem. 278:45777–45784. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang L, Du J, Hu Z, et al: IL-6 and serum
amyloid A synergy mediates angiotensin II-induced muscle wasting. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 20:604–612. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jager J, Gremeaux T, Cormont M, Le
Marchand-Brustel Y and Tanti JF: Interleukin-1beta-induced insulin
resistance in adipocytes through down-regulation of insulin
receptor substrate-1 expression. Endocrinology. 148:241–251. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
54
|
Sugita H, Kaneki M, Sugita M, Yasukawa T,
Yasuhara S and Martyn JA: Burn injury impairs insulin-stimulated
Akt/PKB activation in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 288:E585–E591. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Fang CH, Li B, James JH, et al: GSK-3β
activity is increased in skeletal muscle after burn injury in rats.
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 293:R1545–R1551. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Beilharz TH, Humphreys DT, Clancy JL, et
al: microRNA-mediated messenger RNA deadenylation contributes to
translational repression in mammalian cells. PLoS One. 4:e67832009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J, Doerks T,
Stark A, Bork P and Izaurralde E: mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping
complexes. Genes Dev. 20:1885–1898. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mathonnet G, Fabian MR, Svitkin YV, et al:
MicroRNA inhibition of translation initiation in vitro by targeting
the cap-binding complex eIF4F. Science. 317:1764–1767. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Jordan SD, Kruger M, Willmes DM, et al:
Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits
insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism.
Nat Cell Biol. 13:434–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Frost RJ and Olson EN: Control of glucose
homeostasis and insulin sensitivity by the Let-7 family of
microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:21075–21080. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang YM, Seo SY, Kim TH and Kim SG:
Decrease of microRNA-122 causes hepatic insulin resistance by
inducing protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, which is reversed by
licorice flavonoid. Hepatology. 56:2209–2220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Trajkovski M, Hausser J, Soutschek J, et
al: MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature.
474:649–653. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang JG, Wang JJ, Zhao F, Liu Q, Jiang K
and Yang GH: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN
and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta. 411:846–852. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ling HY, Hu B, Hu XB, et al: MiRNA-21
reverses high glucose and high insulin induced insulin resistance
in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through targeting phosphatase and tensin
homologue. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 120:553–559. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Horie T, Ono K, Nishi H, et al:
MicroRNA-133 regulates the expression of GLUT4 by targeting KLF15
and is involved in metabolic control in cardiac myocytes. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 389:315–320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lu H, Buchan RJ and Cook SA: MicroRNA-223
regulates Glut4 expression and cardiomyocyte glucose metabolism.
Cardiovasc Res. 86:410–420. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chen YH, Heneidi S, Lee JM, et al:
miRNA-93 inhibits GLUT4 and is overexpressed in adipose tissue of
polycystic ovary syndrome patients and women with insulin
resistance. Diabetes. 62:2278–2286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Liang P, Lv C, Jiang B, et al: MicroRNA
profiling in denatured dermis of deep burn patients. Burns.
38:534–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, et al: The
microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis
by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wiggins JF, Ruffino L, Kelnar K, et al:
Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor
suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res. 70:5923–5930. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Callis TE, Pandya K, Seok HY, et al:
MicroRNA-208a is a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and conduction
in mice. J Clin Invest. 119:2772–2786. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Henke JI, Goergen D, Zheng J, et al:
microRNA-122 stimulates translation of hepatitis C virus RNA. EMBO
J. 27:3300–3310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Janssen HL, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, et al:
Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N Engl J Med.
368:1685–1694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|