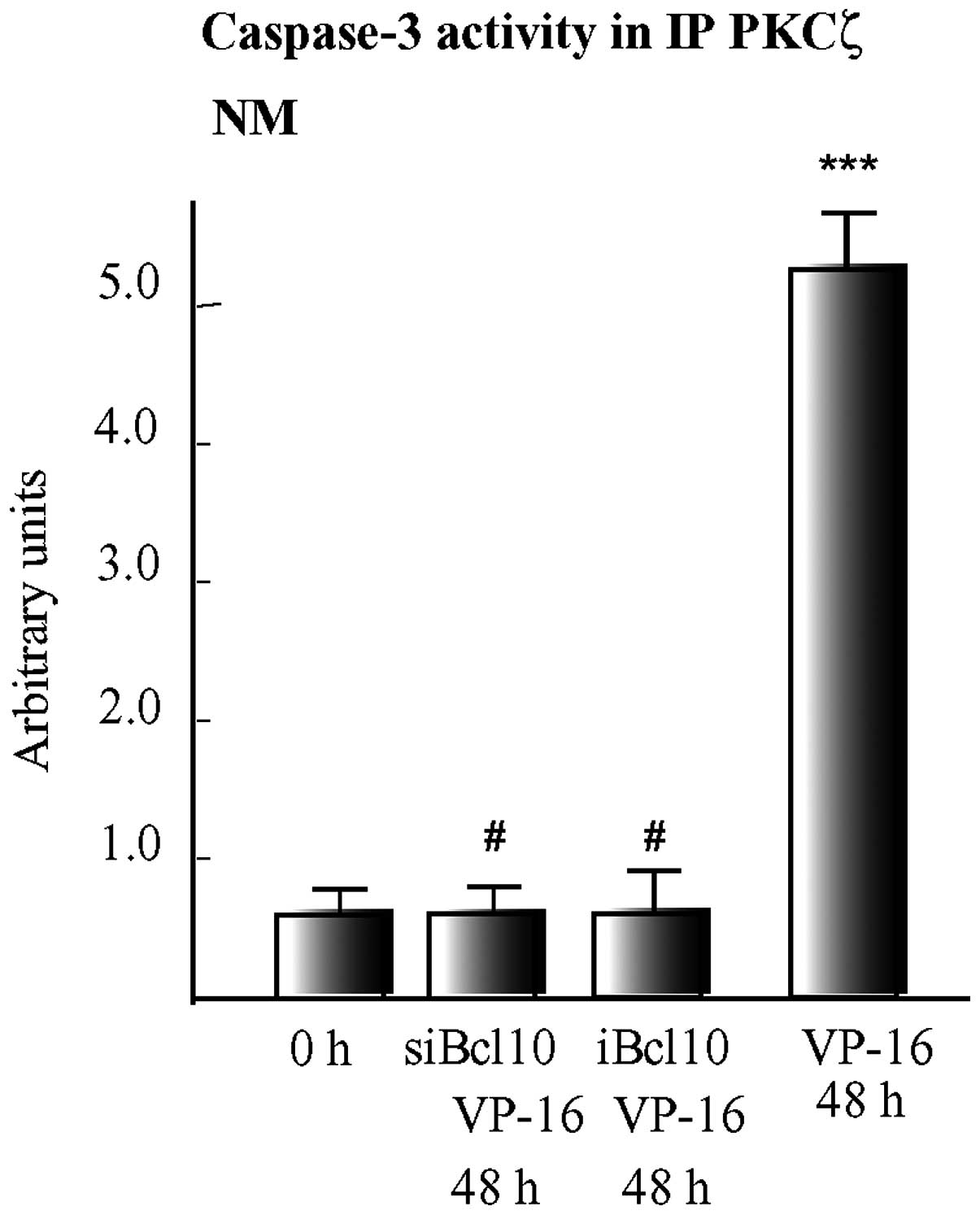
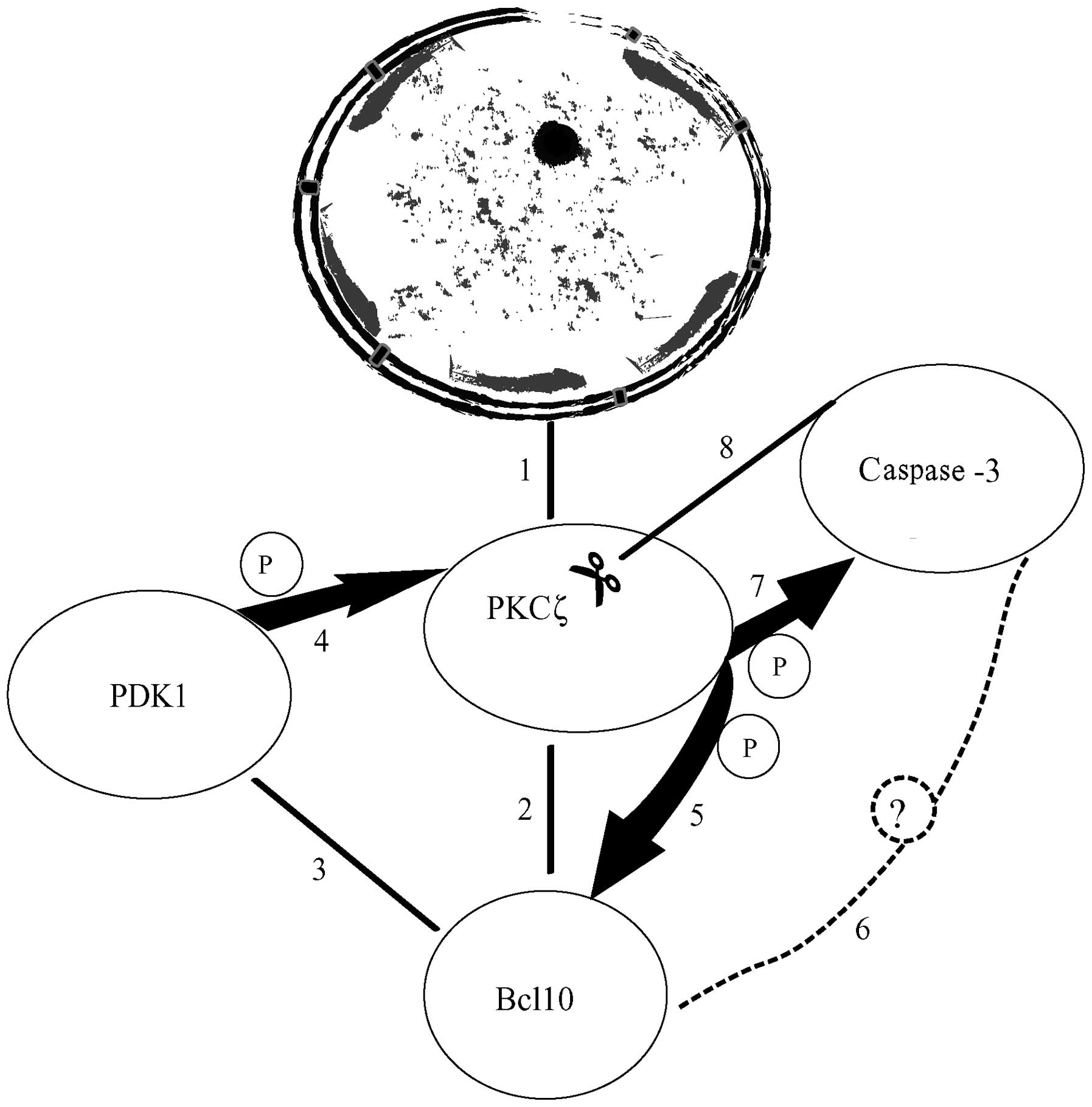
|
1
|
Mukherjee S, Dey S, Bhattacharya RK and
Roy M: Isothiocyanates sensitize the effect of chemotherapeutic
drugs via modulation of protein kinase C and telomerase in cervical
cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 330:9–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Scarinci IC, Garcia FA, Kobetz E,
Partridge EE, Brandt HM, Bell MC, Dignan M, Ma GX, Daye JL and
Castle PE: Cervical cancer prevention: new tools and old barriers.
Cancer. 116:2531–2542. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Molano M, Van den Brule A, Plummer M,
Weiderpass E, Posso H, Arslan A, Meijer CJ, Muñoz N and Franceschi
S; HPV Study Group: Determinants of clearance of human
papillomavirus infections in Colombian women with normal cytology:
a population-based, 5-year follow-up study. Am J Epidemiol.
158:486–494. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Perez-Plasencia C, Duenas-Gonzalez A and
Alatorre-Tavera B: Second hit in cervical carcinogenesis process:
involvement of wnt/beta catenin pathway. Int Arch Med. 1:102008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kwasniewska A, Postawski K,
Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A, Kwasniewski W, Grywalska E, Zdunek M and
Korobowicz E: Estrogen and progesterone receptor expression in
HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical carcinomas. Oncol Rep.
26:153–160. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu X, Lv J, Yu L, Zhu X, Wu J, Zou S and
Jiang S: Proteomic identification of differentially-expressed
proteins in squamous cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 112:248–256.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Higareda-Almaraz JC, Enríquez-Gasca MR,
Hernández-Ortiz M, Resendis-Antonio O and Encarnación-Guevara S:
Proteomic patterns of cervical cancer cell lines, a network
perspective. BMC Syst Biol. 5:962011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carlson MW, Iyer VR and Marcotte EM:
Quantitative gene expression assessment identifies appropriate cell
line models for individual cervical cancer pathways. BMC Genomics.
8:117–129. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dempsey EC, Newton AC, Mochly-Rosen D,
Fields AP, Reyland ME, Insel PA and Messing RO: Protein kinase C
isozymes and the regulation of diverse cell responses. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 279:L429–L438. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reyland ME: Protein kinase C isoforms:
multi-functional regulators of cell life and death. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 14:2386–2399. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Breitkreutz D, Braiman-Wiksman L, Daum N,
Denning MF and Tennenbaum T: Protein kinase C family: on the
crossroads of cell signaling in skin and tumor epithelium. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 133:793–808. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Diaz-Meco MT, Dominguez I, Sanz L, Dent P,
Lozano J, Municio MM, Berra E, Hay RT, Sturgill TW and Moscat J:
zeta PKC induces phosphorylation and inactivation of I kappa
B-alpha in vitro. EMBO J. 13:2842–2848. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Filomenko R, Poirson-Bichat F, Billerey C,
Belon JP, Garrido C, Solary E and Bettaieb A: Atypical protein
kinase C zeta as a target for chemosensitization of tumor cells.
Cancer Res. 62:1815–1821. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Malhas AN and Vaux DJ: The nuclear
envelope and its involvement in cellular stress responses. Biochem
Soc Trans. 39:1795–1798. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dal Pra I, Whitfield JF, Chiarini A and
Armato U: Changes in nuclear protein kinase C-delta holoenzyme, its
catalytic fragments, and its activity in polyomavirus-transformed
pyF111 rat fibroblasts while proliferating and following exposure
to apoptogenic topoisomerase-II inhibitors. Exp Cell Res.
249:147–160. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chiarini A, Whitfield JF, Armato U and Dal
Pra I: Protein kinase C-beta II Is an apoptotic lamin kinase in
polyomavirus-transformed, etoposide-treated pyF111 rat fibroblasts.
J Biol Chem. 277:18827–18839. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chiarini A, Whitfield JF, Armato U and Dal
Pra I: VP-16 (etoposide) and calphostin C trigger different nuclear
but akin cytoplasmic patterns of changes in the distribution and
activity of protein kinase C-betaI in polyomavirus-transformed
pyF111 rat fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 17:111–120. 2006.
|
|
18
|
Chiarini A, Whitfield JF, Pacchiana R,
Armato U and Dal Pra I: Photoexcited calphostin C selectively
destroys nuclear lamin B1 in neoplastic human and rat cells - a
novel mechanism of action of a photodynamic tumor therapy agent.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1783:1642–1653. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Watanabe Y, Hoshiai H, Nakanishi T,
Kawamura N, Tanaka N, Isaka K, Kamiura S, Ohmichi M, Hatae M and
Ochiai K: Evaluation of oral etoposide in combination with
cisplatin for patients with recurrent cervical cancer: long-term
follow-up results of a Japanese multicenter study. Anticancer Res.
31:3063–3067. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chiarini A, Marconi M, Pacchiana R, Dal
Prà I, Wu J and Armato U: Role-shifting PKCζ fosters its own
proapoptotic destruction by complexing with Bcl10 at the nuclear
envelope of human cervical carcinoma cells: a proteomic and
biochemical study. J Proteome Res. 11:3996–4012. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Willis TG, Jadayel DM, Du M-Q, Peng H,
Perry AR, Abdul-Rauf M, Price H, Karran L, Majekodunmi O, Wlodarska
I, et al: Bcl10 is involved in t(1;14)(p22;q32) of MALT B cell
lymphoma and mutated in multiple tumor types. Cell. 96:35–45. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen M, Li LY and Qi Y-P: Bcl10 protein
can act as a transcription activator in yeast. Mol Cell Biochem.
246:97–103. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Y, Dong W, Chen L, Zhang P and Qi Y:
Characterization of Bcl10 as a potential transcriptional activator
that interacts with general transcription factor TFIIB. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 320:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thome M and Weil R: Post-translational
modifications regulate distinct functions of CARMA1 and BCL10.
Trends Immunol. 28:281–288. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ruland J, Duncan GS, Elia A, del Barco
Barrantes I, Nguyen L, Plyte S, Millar DG, Bouchard D, Wakeham A,
Ohashi PS and Mak TW: Bcl10 is a positive regulator of antigen
receptor-induced activation of NF-kappaB and neural tube closure.
Cell. 104:33–42. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Q, Siebert R, Yan M, Hinzmann B, Cui
X, Xue L, Rakestraw KM, Naeve CW, Beckmann G, Weisenburger DD, et
al: Inactivating mutations and overexpression of BCL10, a caspase
recruitment domain-containing gene, in MALT lymphoma with
t(1;14)(p22;q32). Nat Genet. 22:63–68. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lambers AR, Gumbs C, Ali S, Marks JR,
Iglehart JD, Berchuck A and Futreal PA: Bcl10 is not a target for
frequent mutation in human carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 80:1575–1576.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan M, Lee J, Schilbach S, Goddard A and
Dixit V: mE10, a novel caspase recruitment domain-containing
proapoptotic molecule. J Biol Chem. 274:10287–10292. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koseki T, Inohara N, Chen S, Carrio R,
Merino J, Hottiger MO, Nabel GJ and Núñez G: CIPER, a novel NF
kappaB-activating protein containing a caspase recruitment domain
with homology to Herpesvirus-2 protein E10. J Biol Chem.
274:9955–9961. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yui D, Yoneda T, Oono K, Katayama T,
Imaizumi K and Tohyama M: Interchangeable binding of Bcl10 to TRAF2
and cIAPs regulates apoptosis signaling. Oncogene. 20:4317–4323.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pacchiana R, Abbate M, Armato U, Dal Prà I
and Chiarini A: Combining immunofluorescence with in situ proximity
ligation assay: a novel imaging approach to monitor protein-protein
interactions in relation to subcellular localization. Histochem
Cell Biol. 142:593–600. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bayascas JR: Dissecting the role of the
3-phosphoinosi-tide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) signalling
pathways. Cell Cycle. 7:2978–2982. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Casamayor A, Morrice NA and Alessi DR:
Phosphorylation of Ser-241 is essential for the activity of
3-phosphoin-ositide-dependent protein kinase-1: identification of
five sites of phosphorylation in vivo. Biochem J. 342:287–292.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kikani CK, Dong LQ and Liu F: 'New̓-clear
functions of PDK1: beyond a master kinase in the cytosol? J Cell
Biochem. 96:1157–1162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sephton CF, Zhang D, Lehmann TM,
Pennington PR, Scheid MP and Mousseau DD: The nuclear localization
of 3′-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 is dependent on its
association with the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Cell
Signal. 21:1634–1644. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee KY, D'Acquisto F, Hayden MS, Shim JH
and Ghosh S: PDK1 nucleates T cell receptor-induced signaling
complex for NF-kappaB activation. Science. 308:114–118. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hodgkinson CP and Sale GJ: Regulation of
both PDK1 and the phosphorylation of PKC-zeta and -delta by a
C-terminal PRK2 fragment. Biochemistry. 41:561–569. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu LR, Lv JQ, Jin LY, Ding SD, Ma XY, Wang
JJ and Zhu XQ: Over-expression of protein kinase C isoforms (α, δ,
θ and ζ) in squamous cervical cancer. Neoplasma. 58:491–498.
2011.
|
|
39
|
Hirai T and Chida K: Protein kinase Czeta
(PKCzeta): Activation mechanisms and cellular functions. J Biochem.
133:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xin M, Gao F, May WS, Flagg T and Deng X:
Protein kinase Czeta abrogates the proapoptotic function of Bax
through phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 282:21268–21277. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nazarenko I, Jenny M, Keil J, Gieseler C,
Weisshaupt K, Sehouli J, Legewie S, Herbst L, Weichert W,
Darb-Esfahani S, et al: Atypical protein kinase C zeta exhibits a
proapoptotic function in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 8:919–934.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yoneda T, Imaizumi K, Maeda M, Yui D,
Manabe T, Katayama T, Sato N, Gomi F, Morihara T, Mori Y, et al:
Regulatory mechanisms of TRAF2-mediated signal transduction by
Bcl10, a MALT lymphoma-associated protein. J Biol Chem.
275:11114–11120. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Rosebeck S, Rehman AO, Lucas PC and
McAllister-Lucas LM: From MALT lymphoma to the CBM signalosome:
three decades of discovery. Cell Cycle. 10:2485–2496. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yeh PY, Kuo S-H, Yeh K-H, Chuang SE, Hsu
C-H, Chang WC, Lin H-I, Gao M and Cheng A-L: A pathway for tumor
necrosis factor-alpha-induced Bcl10 nuclear translocation. Bcl10 is
up-regulated by NF-kappaB and phosphorylated by Akt1 and then
complexes with Bcl3 to enter the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 281:167–175.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kuo SH, Chou CH, Cheng AL, Wang CW, Chen
YH and Chen RJ: Expression of BCL10 in cervical cancer has a role
in the regulation of cell growth through the activation of
NF-κB-dependent cyclin D1 signaling. Gynecol Oncol. 126:245–251.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Parrish AB, Freel CD and Kornbluth S:
Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 5:a0086722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kurokawa M and Kornbluth S: Caspases and
kinases in a death grip. Cell. 138:838–854. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Voss OH, Kim S, Wewers MD and Doseff AI:
Regulation of monocyte apoptosis by the protein kinase
Cdelta-dependent phosphorylation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem.
280:17371–17379. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|