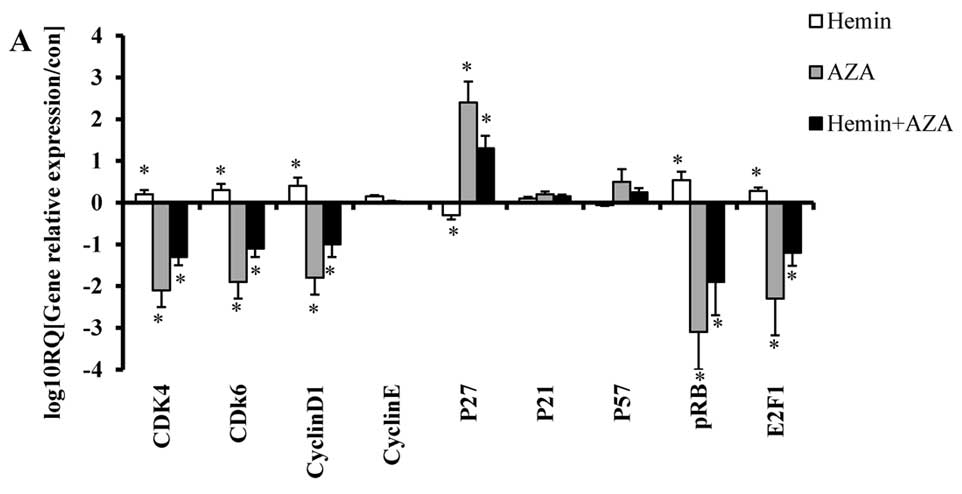
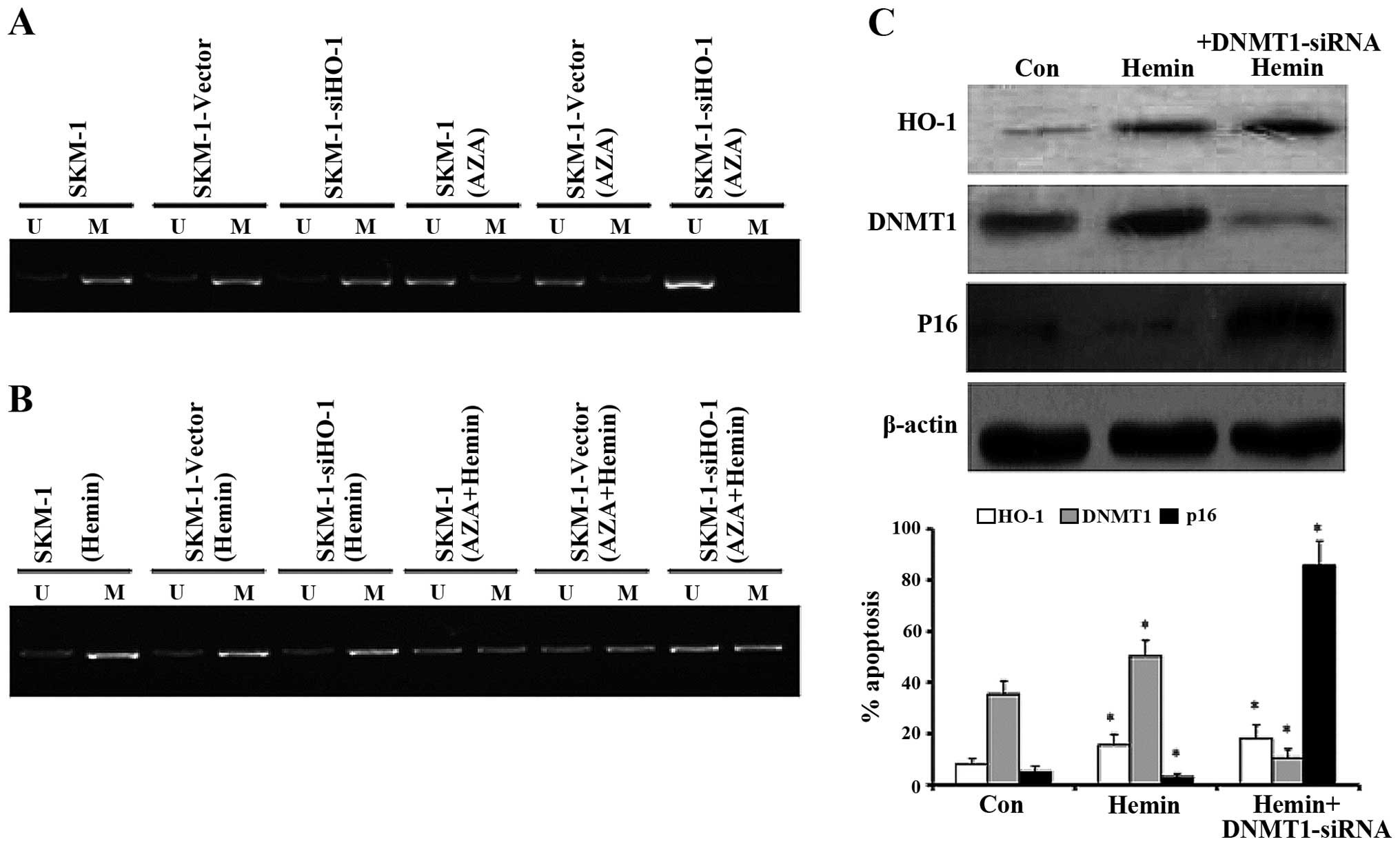
|
1
|
Sekeres MA and Cutler C: How we treat
higher-risk myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 123:829–836. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jiang Y, Dunbar A, Gondek LP, et al:
Aberrant DNA methylation is a dominant mechanism in MDS progression
to AML. Blood. 113:1315–1325. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Stintzing S, Kemmerling R, Kiesslich T,
Alinger B, Ocker M and Neureiter D: Myelodysplastic syndrome and
histone deacetylase inhibitors: ‘to be or not to be acetylated’? J
Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:2141432011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fenaux P, Mufti GJ, Hellstrom-Lindberg E,
et al: Efficacy of azacitidine compared with that of conventional
care regimens in the treatment of higher-risk myelodysplastic
syndromes: a randomised, open-label, phase III study. Lancet Oncol.
10:223–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kimura S, Kuramoto K, Homan J, et al:
Antiproliferative and antitumor effects of azacitidine against the
human myelodysplastic syndrome cell line SKM-1. Anticancer Res.
32:795–798. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Figueroa ME, Skrabanek L, Li Y, et al: MDS
and secondary AML display unique patterns and abundance of aberrant
DNA methylation. Blood. 114:3448–3458. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ades L and Santini V: Hypomethylating
agents and chemotherapy in MDS. Best Pract Res Cl Ha. 26:411–419.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Khan C, Pathe N, Fazal S, Lister J and
Rossetti JM: Azacitidine in the management of patients with
myelodysplastic syndromes. Ther Adv Hematol. 3:355–373. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jozkowicz A, Was H and Dulak J: Heme
oxygenase-1 in tumors: is it a false friend? Antioxid Redox Sign.
9:2099–2117. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rushworth SA, Zaitseva L, Langa S, Bowles
KM and MacEwan DJ: FLIP regulation of HO-1 and TNF signalling in
human acute myeloid leukemia provides a unique secondary
anti-apoptotic mechanism. Oncotarget. 1:359–366. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Rushworth SA and MacEwan DJ: HO-1
underlies resistance of AML cells to TNF-induced apoptosis. Blood.
111:3793–3801. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma D, Fang Q, Li Y, et al: Crucial role of
heme oxygenase-1 in the sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cell
line Kasumi-1 to ursolic acid. Anti-cancer Drug. 25:406–414. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Su ZY, Shu L, Khor TO, Lee JH, Fuentes F
and Kong AN: A perspective on dietary phytochemicals and cancer
chemoprevention: oxidative stress, nrf2, and epigenomics. Topics
Curr Chem. 329:133–162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kang KA, Piao MJ, Kim KC, et al:
Epigenetic modification of Nrf2 in 5-fluorouracil-resistant colon
cancer cells: involvement of TET-dependent DNA demethylation. Cell
Death Dis. 5:e11832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang LF, Qi J, Zuo G, et al:
Osteoblast-secreted factors promote proliferation and osteogenic
differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells via
VEGF/heme-oxygenase-1 pathway. PLoS One. 9:e999462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wegiel B, Hedblom A, Li M, et al: Heme
oxygenase-1 derived carbon monoxide permits maturation of myeloid
cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parker JE, Mufti GJ, Rasool F, Mijovic A,
Devereux S and Pagliuca A: The role of apoptosis, proliferation,
and the Bcl-2-related proteins in the myelodysplastic syndromes and
acute myeloid leukemia secondary to MDS. Blood. 96:3932–3938.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Issa JP: The myelodysplastic syndrome as a
prototypical epigenetic disease. Blood. 121:3811–3817. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Curik N, Burda P, Vargova K, et al:
5-azacitidine in aggressive myelodysplastic syndromes regulates
chromatin structure at PU.1 gene and cell differentiation capacity.
Leukemia. 26:1804–1811. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumode T, Fukui A, Eguchi G, Yamaguchi T
and Maeda Y: A case of secondary leukemia subsequent to
myelodysplastic syndromes successfully treated with azacitidine.
Case Rep Med. 2014:7939282014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jasielec J, Saloura V and Godley LA: The
mechanistic role of DNA methylation in myeloid leukemogenesis.
Leukemia. 28:1765–1773. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Heasman SA, Zaitseva L, Bowles KM,
Rushworth SA and Macewan DJ: Protection of acute myeloid leukaemia
cells from apoptosis induced by front-line chemotherapeutics is
mediated by haem oxygenase-1. Oncotarget. 2:658–668.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cazzola M, Della Porta mg and Malcovati L:
The genetic basis of myelodysplasia and its clinical relevance.
Blood. 122:4021–4034. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bogenberger JM, Kornblau SM, Pierceall WE,
et al: BCL-2 family proteins as 5-Azacytidine-sensitizing targets
and determinants of response in myeloid malignancies. Leukemia.
28:1657–1665. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cluzeau T, Robert G, Mounier N, et al:
BCL2L10 is a predictive factor for resistance to azacitidine in MDS
and AML patients. Oncotarget. 3:490–501. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karlic H, Herrmann H, Varga F, et al: The
role of epigenetics in the regulation of apoptosis in
myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Crit Rev
Oncol Hemat. 90:1–16. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang YY, Cen JN, He J, et al: Accelerated
cellular senescence in myelodysplastic syndrome. Exp Hematol.
37:1310–1317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ausserlechner MJ, Obexer P, Geley S and
Kofler R: G1 arrest by p16INK4A uncouples growth from cell cycle
progression in leukemia cells with deregulated cyclin E and c-Myc
expression. Leukemia. 19:1051–1057. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim JK, Noh JH, Eun JW, et al: Targeted
inactivation of HDAC2 restores p16INK4a activity and exerts
antitumor effects on human gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
11:62–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ng KP, Ebrahem Q, Negrotto S, et al: p53
independent epigenetic-differentiation treatment in xenotransplant
models of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 25:1739–1750. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Soberanes S, Gonzalez A, Urich D, et al:
Particulate matter Air Pollution induces hypermethylation of the
p16 promoter Via a mitochondrial ROS-JNK-DNMT1 pathway. Sci Rep-UK.
2:2752012.
|
|
32
|
Khan R, Schmidt-Mende J, Karimi M, et al:
Hypomethylation and apoptosis in 5-azacytidine-treated myeloid
cells. Exp Hematol. 36:149–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|