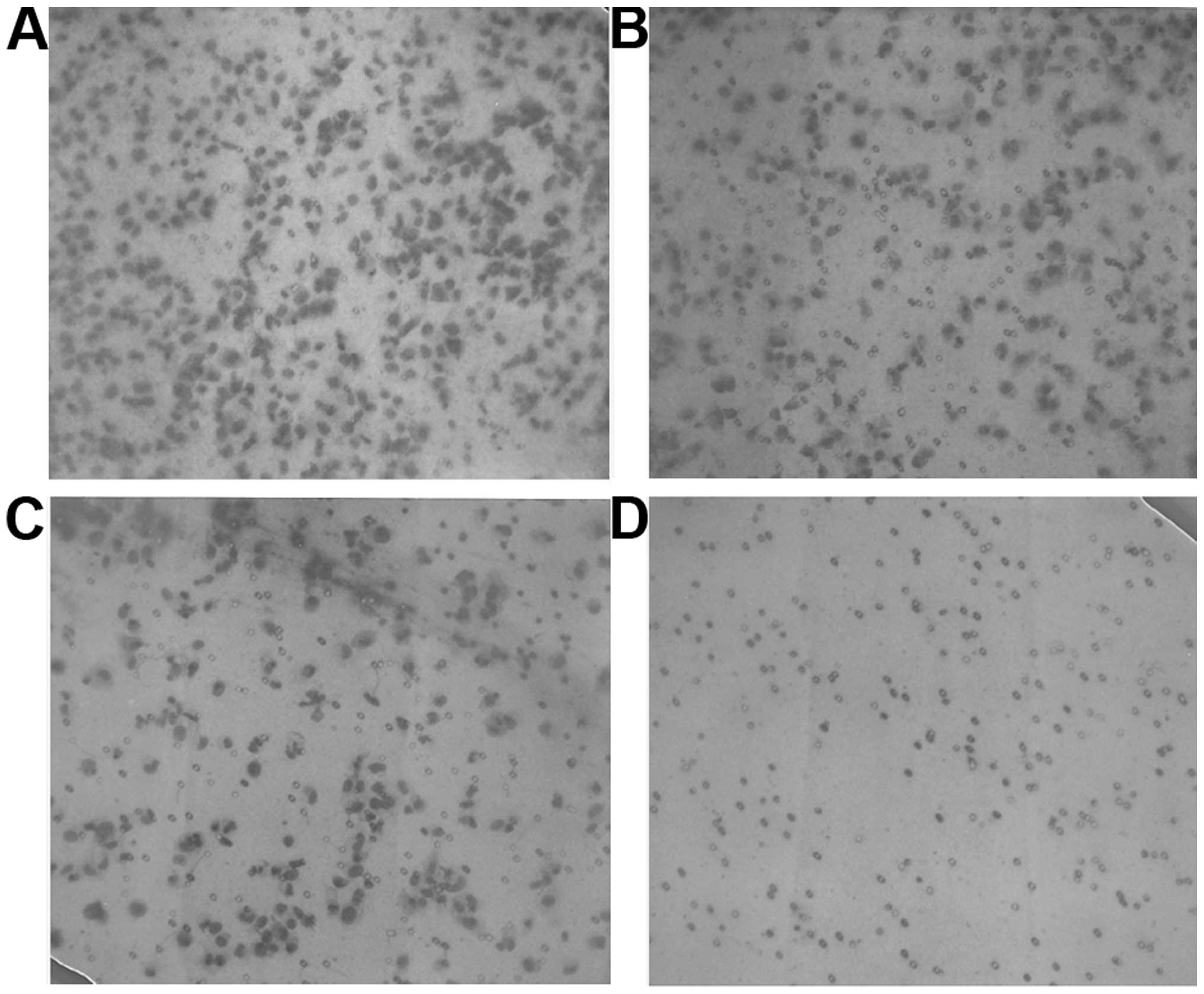
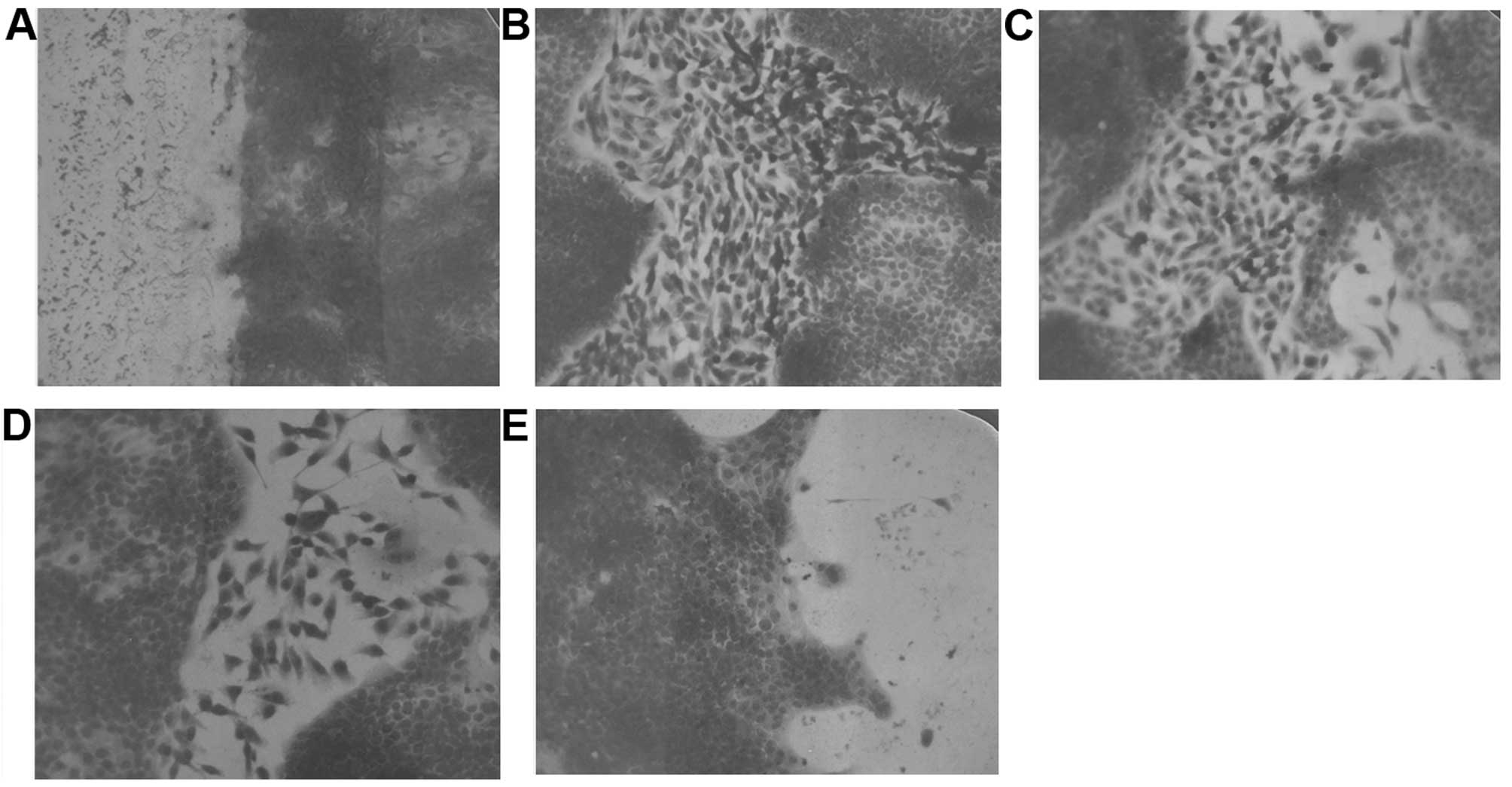
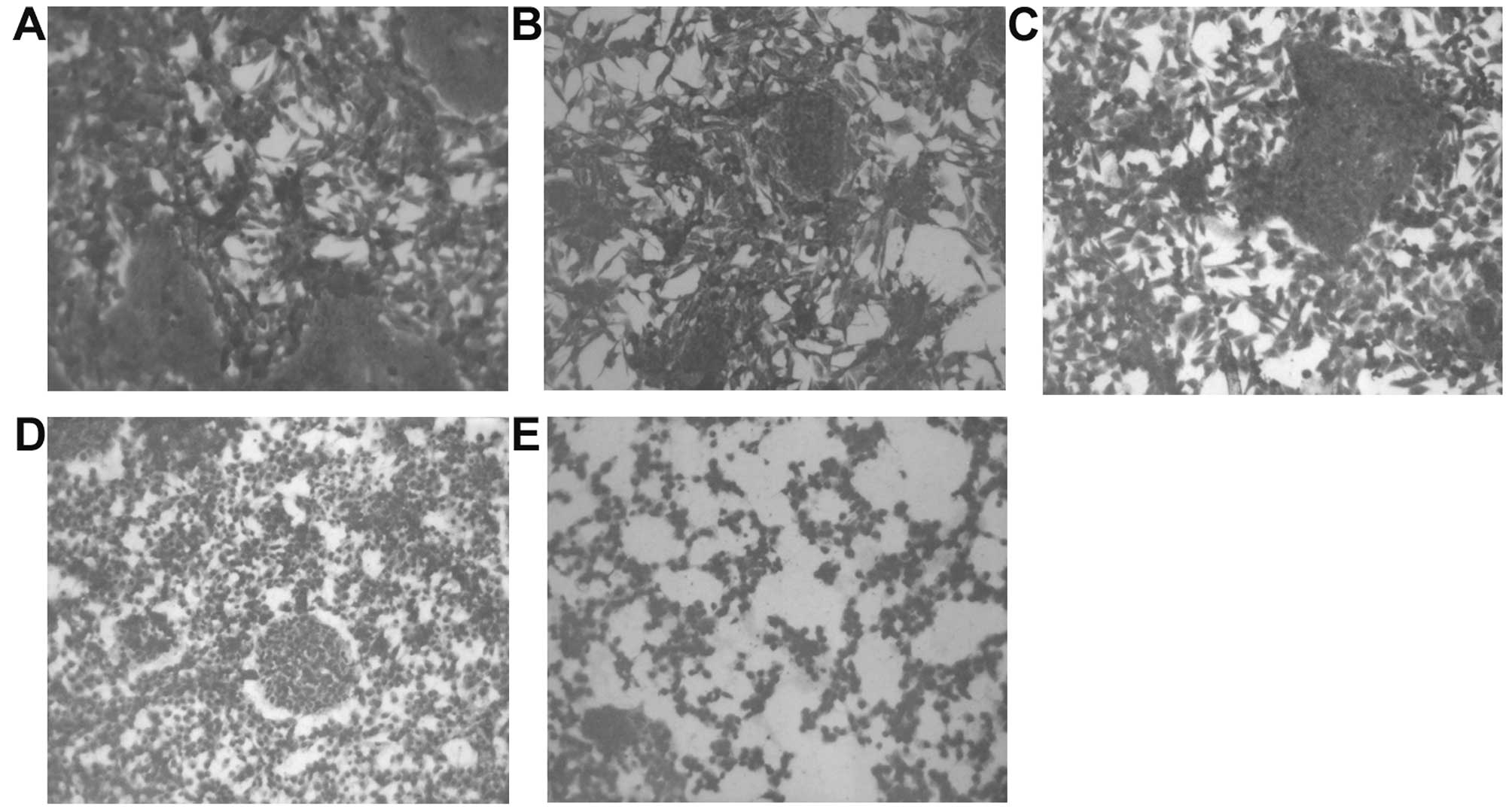
|
1
|
Alter BP, Greene MH, Velazquez I and
Rosenberg PS: Cancer in Fanconi anemia. Blood. 101:2072–2073. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kutler DI, Auerbach AD, Satagopan J,
Giampietro PF, Batish SD, Huvos AG, Goberdhan A, Shah JP and Singh
B: High incidence of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in
patients with Fanconi anemia. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
129:106–112. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh B: Head and neck squamous carcinoma
in Fanconi anemia patients. Fanconi Anemia: Guidelines for
Diagnosis and Management. Eiler ME, Fohnmayer D, Forhnmayer L,
Larsen K and Owen J: 3rd edition. Fanconi Anemia Research Fund,
Inc; 2008
|
|
4
|
Adlercreutz H: Western diet and Western
diseases: Some hormonal and biochemical mechanisms and
associations. Scand J Clin Lab Invest (Suppl). 201:3–23. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Miller AB: Diet and cancer. A review Acta
Oncol. 29:87–95. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Duffy MJ: The role of proteolytic enzymes
in cancer invasion and metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 10:145–155.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kawamata H, Uchida D, Hamano H,
Kimura-Yanagawa T, Nakashiro KI, Hino S, Omotehara F, Yoshida H and
Sato M: Active-MMP2 in cancer cell nests of oral cancer patients:
Correlation with lymph node metastasis. Int J Oncol. 13:699–704.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Patel BP, Shah SV, Shukla SN, Shah PM and
Patel PS: Clinical significance of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in patients with
oral cancer. Head Neck. 29:564–572. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Katayama A, Bandoh N, Kishibe K, Takahara
M, Ogino T, Nonaka S and Harabuchi Y: Expressions of matrix
metal-loproteinases in early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma as
predictive indicators for tumor metastases and prognosis. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:634–640. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Riedel F, Götte K, Schwalb J, Bergler W
and Hörmann K: Expression of 92-kDa type IV collagenase correlates
with angiogenic markers and poor survival in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 17:1099–1105. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kurahara S, Shinohara M, Ikebe T, Nakamura
S, Beppu M, Hiraki A, Takeuchi H and Shirasuna K: Expression of
MMPS, MT-MMP, and TIMPs in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral
cavity: Correlations with tumor invasion and metastasis. Head Neck.
21:627–638. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anand P, Sundaram C, Jhurani S,
Kunnumakkara AB and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin and cancer: An ‘old-age’
disease with an ‘age-old’ solution. Cancer Lett. 267:133–164. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Keck AS and Finley JW: Cruciferous
vegetables: Cancer protective mechanisms of glucosinolate
hydrolysis products and selenium. Integr Cancer Ther. 3:5–12. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Valcic S, Timmermann BN, Alberts DS,
Wächter GA, Krutzsch M, Wymer J and Guillén JM: Inhibitory effect
of six green tea catechins and caffeine on the growth of four
selected human tumor cell lines. Anticancer Drugs. 7:461–468. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mukhtar H and Ahmad N: Tea polyphenols:
Prevention of cancer and optimizing health. Am J Clin Nutr.
71(Suppl 6): S1698–S1702; discussion S1703–S1704. 2000.
|
|
16
|
Yang GY, Liao J, Kim K, Yurkow EJ and Yang
CS: Inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis in human cancer
cell lines by tea polyphenols. Carcinogenesis. 19:611–616. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Taniguchi S, Fujiki H, Kobayashi H, Go H,
Miyado K, Sadano H and Shimokawa R: Effect of (-)-epigallocatechin
gallate, the main constituent of green tea, on lung metastasis with
mouse B16 melanoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 65:51–54. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hara Y: Green tea: Health Benefits and
Applications. Marcel Dekker, Inc; New York, Basel: 2001, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Harakeh S, Abu-El-Ardat K, Diab-Assaf M,
Niedzwiecki A, El-Sabban M and Rath M: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in HTLV-1-positive and
-negative leukemia cells. Med Oncol. 25:30–39. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cal C, Garban H, Jazirehi A, Yeh C,
Mizutani Y and Bonavida B: Resveratrol and cancer: Chemoprevention,
apoptosis, and chemo-immunosensitizing activities. Curr Med Chem
Anticancer Agents. 3:77–93. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bishayee A: Cancer prevention and
treatment with resveratrol: From rodent studies to clinical trials.
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2:409–418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gibellini L, Pinti M, Nasi M, Montagna JP,
De Biasi S, Roat E, Bertoncelli L, Cooper EL and Cossarizza A:
Quercetin and cancer chemoprevention. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2011:5913562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|