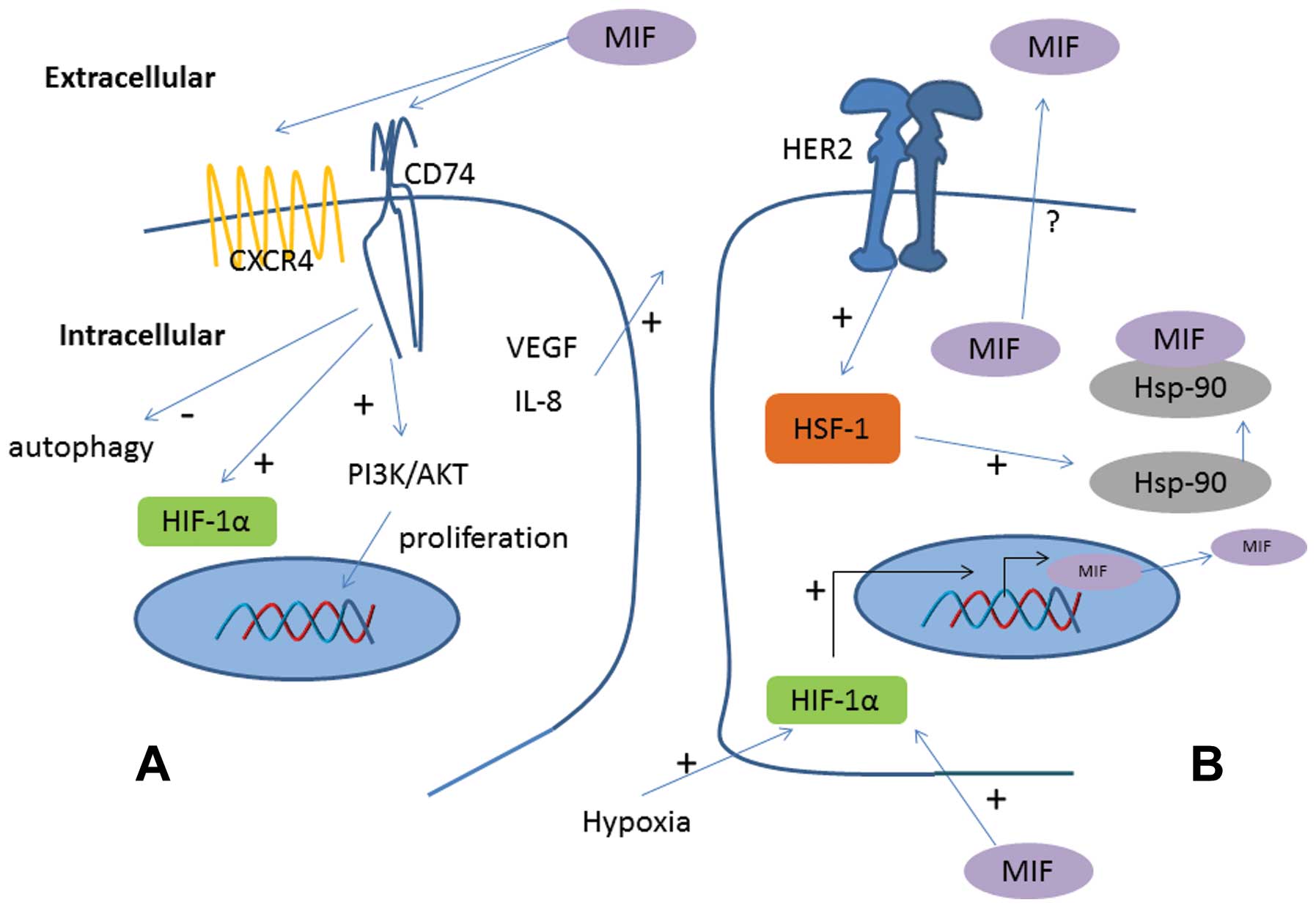
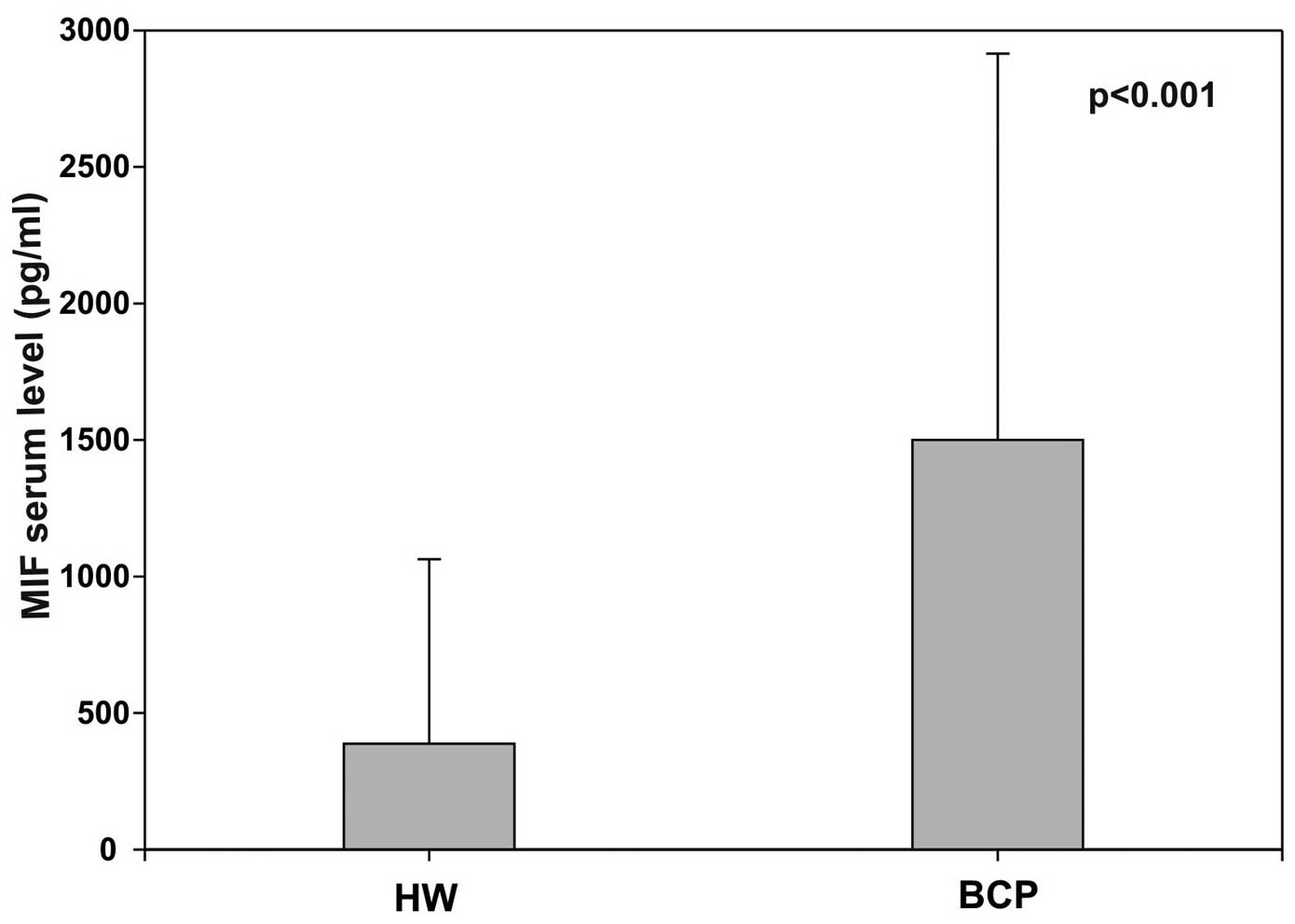
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pietras K and Östman A: Hallmarks of
cancer: Interactions with the tumor stroma. Exp Cell Res.
316:1324–1331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mitchell RA and Yaddanapudi K:
Stromal-dependent tumor promotion by MIF family members. Cell
Signal. 26:2969–2978. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Conroy H, Mawhinney L and Donnelly SC:
Inflammation and cancer: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor
(MIF) - the potential missing link. QJM. 103:831–836. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Donn RP and Ray DW: Macrophage migration
inhibitory factor: Molecular, cellular and genetic aspects of a key
neuroendocrine molecule. J Endocrinol. 182:1–9. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Swope M, Sun HW, Blake PR and Lolis E:
Direct link between cytokine activity and a catalytic site for
macrophage migration inhibitory factor. EMBO J. 17:3534–3541. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li XJ, Luo Y and Yi YF: P115 promotes
growth of gastric cancer through interaction with macrophage
migration inhibitory factor. World J Gastroenterol. 19:8619–8629.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Zernecke A, Bernhagen J and Weber C:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in cardiovascular disease.
Circulation. 117:1594–1602. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim H, Lee S, Kim HJ, Kong MH, Kim YR,
Kang SH, Lee K, Leng L, Lee B, Park CG, et al: Elevated levels of
macrophage migration inhibitory factor in women with metabolic
syndrome. Horm Metab Res. 43:642–645. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kindt N, Preillon J, Kaltner H, Gabius HJ,
Chevalier D, Rodriguez A, Johnson BD, Megalizzi V, Decaestecker C,
Laurent G, et al: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Clinical and experimental
studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 139:727–737. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang D, Luo L, Chen W, Chen LZ, Zeng WT,
Li W and Huang XH: Significance of the vascular endothelial growth
factor and the macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the
progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 31:1199–1204.
2014.
|
|
12
|
Krockenberger M, Kranke P, Häusler S,
Engel JB, Horn E, Nürnberger K, Wischhusen J, Dietl J and Hönig A:
Macrophage migration-inhibitory factor levels in serum of patients
with ovarian cancer correlates with poor prognosis. Anticancer Res.
32:5233–5238. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tan L, Ye X, Zhou Y, Yu M, Fu Z, Chen R,
Zhuang B, Zeng B, Ye H, Gao W, et al: Macrophage migration
inhibitory factor is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and
impairs insulin secretion function of β-cell. J Transl Med.
12:922014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
He XX, Yang J, Ding YW, Liu W, Shen QY and
Xia HH: Increased epithelial and serum expression of macrophage
migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in gastric cancer: Potential role
of MIF in gastric carcinogenesis. Gut. 55:797–802. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi X, Leng L, Wang T, Wang W, Du X, Li J,
McDonald C, Chen Z, Murphy JW, Lolis E, et al: CD44 is the
signaling component of the macrophage migration inhibitory
factor-CD74 receptor complex. Immunity. 25:595–606. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee CY, Su MJ, Huang CY, Chen MY, Hsu HC,
Lin CY and Tang CH: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor
increases cell motility and up-regulates αvβ3 integrin in human
chondrosar-coma cells. J Cell Biochem. 113:1590–1598. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Mitchell RA: Mechanisms and effectors of
MIF-dependent promotion of tumourigenesis. Cell Signal. 16:13–19.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xin D, Rendon BE, Zhao M, Winner M, McGhee
Coleman A and Mitchell RA: The MIF homologue D-dopachrome
tautomerase promotes COX-2 expression through β-catenin-dependent
and -independent mechanisms. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1601–1609. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meyer-Siegler K: COX-2 specific inhibitor,
NS-398, increases macrophage migration inhibitory factor expression
and induces neuroendocrine differentiation in C4-2b prostate cancer
cells. Mol Med. 7:850–860. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Xia HH, Zhang ST, Lam SK, Lin MC, Kung HF
and Wong BC: Expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and effects of bile acids and
NSAIDs. Carcinogenesis. 26:11–15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ristimäki A, Sivula A, Lundin J, Lundin M,
Salminen T, Haglund C, Joensuu H and Isola J: Prognostic
significance of elevated cyclooxygenase-2 expression in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 62:632–635. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Pedro M, Baeza S, Escudero MT,
Dierssen-Sotos T, Gómez-Acebo I, Pollán M and Llorca J: Effect of
COX-2 inhibitors and other non-steroidal inflammatory drugs on
breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
149:525–536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tarnowski M, Grymula K, Liu R, Tarnowska
J, Drukala J, Ratajczak J, Mitchell RA, Ratajczak MS and Kucia M:
Human Rhabdomyosarcomas secrete MIF that modulates metastatic
behavior of tumor cells and inhibits recruitment of cancer
associated fibroblasts. Mol Cancer Res. 8:1328–1343. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Martinez LM, Vallone VBF, Labovsky V, Choi
H, Hofer EL, Feldman L, Bordenave RH, Batagelj E, Dimase F,
Villafañe AR, et al: Changes in the peripheral blood and bone
marrow from untreated advanced breast cancer patients that are
associated with the establishment of bone metastases. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 31:213–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Verjans E, Noetzel E, Bektas N, Schûtz AK,
Lue H, Lennartz B, Hartmann A, Dahl E and Bernhagen J: Dual role of
macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in human breast
cancer. BMC Cancer. 9:2302009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schulz R, Streller F, Scheel AH, Rüschoff
J, Reinert MC, Dobbelstein M, Marchenko ND and Moll UM: HER2/ErbB2
activates HSF1 and thereby controls HSP90 clients including MIF in
HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 5:e9802014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bando H, Toi M, Kitada K and Koike M:
Genes commonly upregulated by hypoxia in human breast cancer cells
MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. Biomed Pharmacother. 57:333–340. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Larsen M, Tazzyman S, Lund EL, Junker N,
Lewis CE, Kristjansen PE and Murdoch C: Hypoxia-induced secretion
of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor from MCF-7 breast cancer
cells is regulated in a hypoxia-inducible factor-independent
manner. Cancer Lett. 265:239–249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lue H, Dewor M, Leng L, Bucala R and
Bernhagen J: Activation of the JNK signalling pathway by macrophage
migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and dependence on CXCR4 and CD74.
Cell Signal. 23:135–144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dewan MZ, Ahmed S, Iwasaki Y, Ohba K, Toi
M and Yamamoto N: Stromal cell-derived factor-1 and CXCR4 receptor
interaction in tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 60:273–276. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lue H, Thiele M, Franz J, Dahl E,
Speckgens S, Leng L, Fingerle-Rowson G, Bucala R, Lüscher B and
Bernhagen J: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) promotes
cell survival by activation of the Akt pathway and role for
CSN5/JAB1 in the control of autocrine MIF activity. Oncogene.
26:5046–5059. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Simpson KD, Templeton DJ and Cross JV:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes tumor growth and
metastasis by inducing myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the
tumor microenvironment. J Immunol. 189:5533–5540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lim S, Choong LY, Kuan CP, Yunhao C and
Lim YP: Regulation of macrophage inhibitory factor (MIF) by
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in the MCF10AT model of
breast cancer progression. J Proteome Res. 8:4062–4076. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Drews-Elger K, Iorns E, Dias A, Miller P,
Ward TM, Dean S, Clarke J, Campion-Flora A, Rodrigues DN,
Reis-Filho JS, et al: Infiltrating S100A8+ myeloid cells
promote metastatic spread of human breast cancer and predict poor
clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 148:41–59. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu X, Wang B, Ye C, Yao C, Lin Y, Huang X,
Zhang Y and Wang S: Overexpression of macrophage migration
inhibitory factor induces angiogenesis in human breast cancer.
Cancer Lett. 261:147–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oda S, Oda T, Nishi K, Takabuchi S,
Wakamatsu T, Tanaka T, Adachi T, Fukuda K, Semenza GL and Hirota K:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor activates hypoxia-inducible
factor in a p53-dependent manner. PLoS One. 3:e22152008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu MY, Fu J, Xu J, O'Malley BWO and Wu RC:
Steroid receptor coactivator 3 regulates autophagy in breast cancer
cells through macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Cell Res.
22:1003–1021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schulz R, Marchenko ND, Holembowski L,
Fingerle-Rowson G, Pesic M, Zender L, Dobbelstein M and Moll UM:
Inhibiting the HSP90 chaperone destabilizes macrophage migration
inhibitory factor and thereby inhibits breast tumor progression. J
Exp Med. 209:275–289. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fujita Y, Islam R, Sakai K, Kaneda H, Kudo
K, Tamura D, Aomatsu K, Nagai T, Kimura H, Matsumoto K, et al:
Aza-derivatives of resveratrol are potent macrophage migration
inhibitory factor inhibitors. Invest New Drugs. 30:1878–1886. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sprouse AA and Herbert BS: Resveratrol
augments paclitaxel treatment in MDA-MB-231 and
paclitaxel-resistant MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Anticancer
Res. 34:5363–5374. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bando H, Matsumoto G, Bando M, Muta M,
Ogawa T, Funata N, Nishihira J, Koike M and Toi M: Expression of
macrophage migration inhibitory factor in human breast cancer:
Association with nodal spread. Jpn J Cancer Res. 93:389–396. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Richard V, Kindt N, Decaestecker C, Gabius
HJ, Laurent G, Noël JC and Saussez S: Involvement of macrophage
migration inhibitory factor and its receptor (CD74) in human breast
cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:523–529. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fersching DM, Nagel D, Siegele B, Salat C,
Heinemann V, Holdenrieder S and Stoetzer OJ: Apoptosis-related
biomarkers sFAS, MIF, ICAM-1 and PAI-1 in serum of breast cancer
patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Anticancer Res.
32:2047–2058. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jesneck JL, Mukherjee S, Yurkovetsky Z,
Clyde M, Marks JR, Lokshin AE and Lo JY: Do serum biomarkers really
measure breast cancer? BMC Cancer. 9:1642009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Opstal-van Winden AW, Rodenburg W,
Pennings JLA, van Oostrom CTM, Beijnen JH, Peeters PHM, van Gils CH
and de Vries A: A bead-based multiplexed immunoassay to evaluate
breast cancer biomarkers for early detection in pre-diagnostic
serum. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13587–13604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Choi J, Jung WH and Koo JS:
Metabolism-related proteins are differentially expressed according
to the molecular subtype of invasive breast cancer defined by
surrogate immunohistochemistry. Pathobiology. 80:41–52. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Catteau X, Simon P, Vanhaeverbeek M and
Noël JC: Variable stromal periductular expression of CD34 and
smooth muscle actin (SMA) in intraductal carcinoma of the breast.
PLoS One. 8:e577732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Catteau X, Simon P and Noël JC:
Myofibroblastic stromal reaction and lymph node status in invasive
breast carcinoma: possible role of the TGF-β1/TGF-βR1 pathway. BMC
Cancer. 4:4992014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Catteau X, Simon P and Noël JC:
Myofibroblastic reaction is a common event in metastatic disease of
breast carcinoma: A descriptive study. Diagn Pathol. 9:1962014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S, Sirtaine
N, Klauschen F, Pruneri G, Wienert S, Van den Eynden G, Baehner FL,
Penault-Llorca F, et al: The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an
International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann Oncol. 26:259–271. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Jhaveri K, Chandarlapaty S, Lake D,
Gilewski T, Robson M, Goldfarb S, Drullinsky P, Sugarman S,
Wasserheit-Leiblich C, Fasano J, et al: A phase II open-label study
of ganetespib, a novel heat shock protein 90 inhibitor for patients
with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 14:154–160.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Baxalta US Inc. (sponsor). Phase I Study
of anti-Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor antibody in solid
Tumors. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01765790. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01765790.
|
|
53
|
Berkova Z, Tao RH and Samaniego F:
Milatuzumab - a promising new immunotherapeutic agent. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 19:141–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Howe LR: Inflammation and breast cancer.
Cyclooxygenase/ prostaglandin signaling and breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 9:2102007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Majumder M, Xin X, Liu L, Girish GV and
Lala PK: Prostaglandin E2 receptor EP4 as the common target on
cancer cells and macrophages to abolish angiogenesis,
lymphangiogenesis, metastasis, and stem-like cell functions. Cancer
Sci. 105:1142–1151. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|