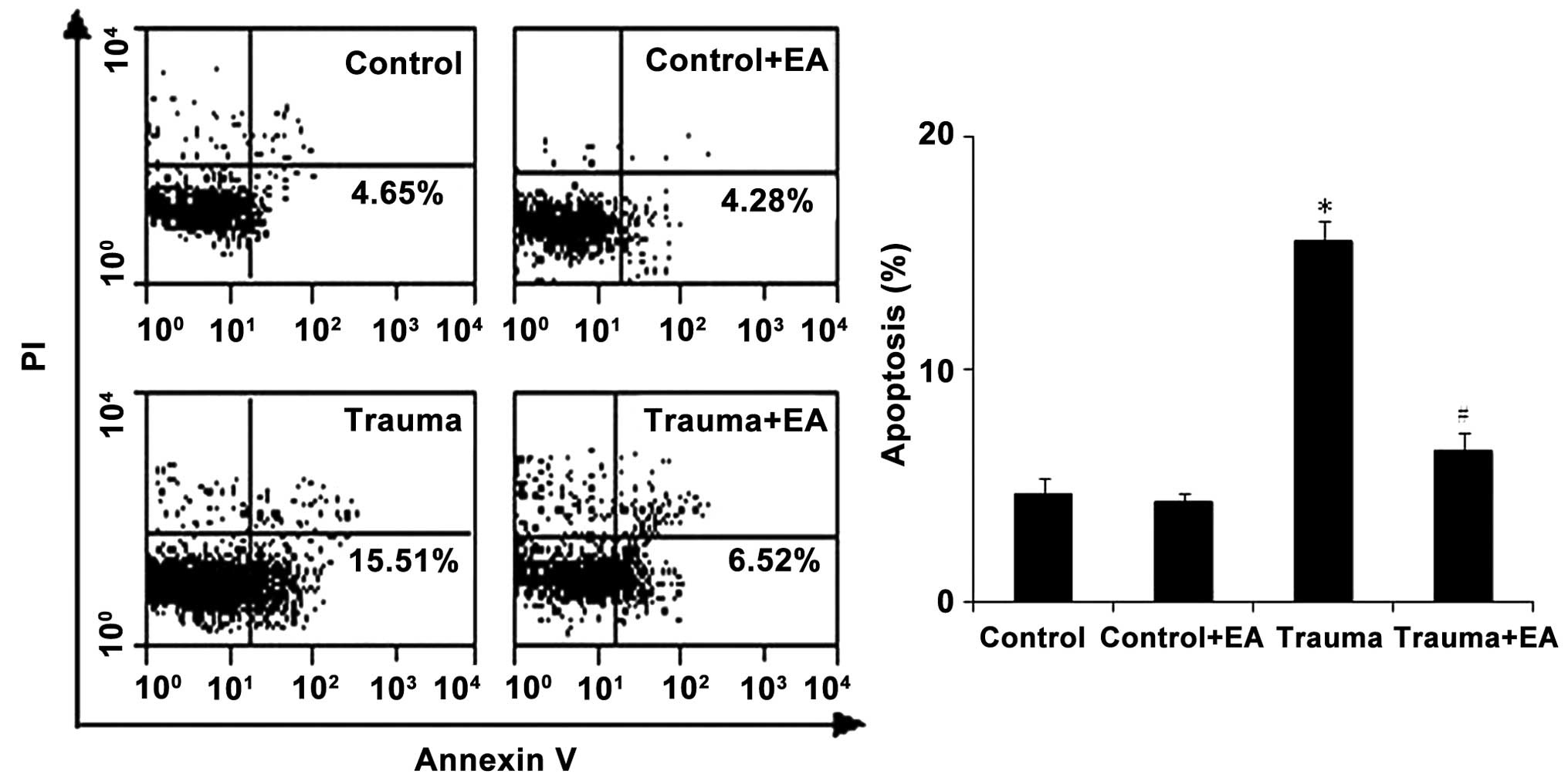
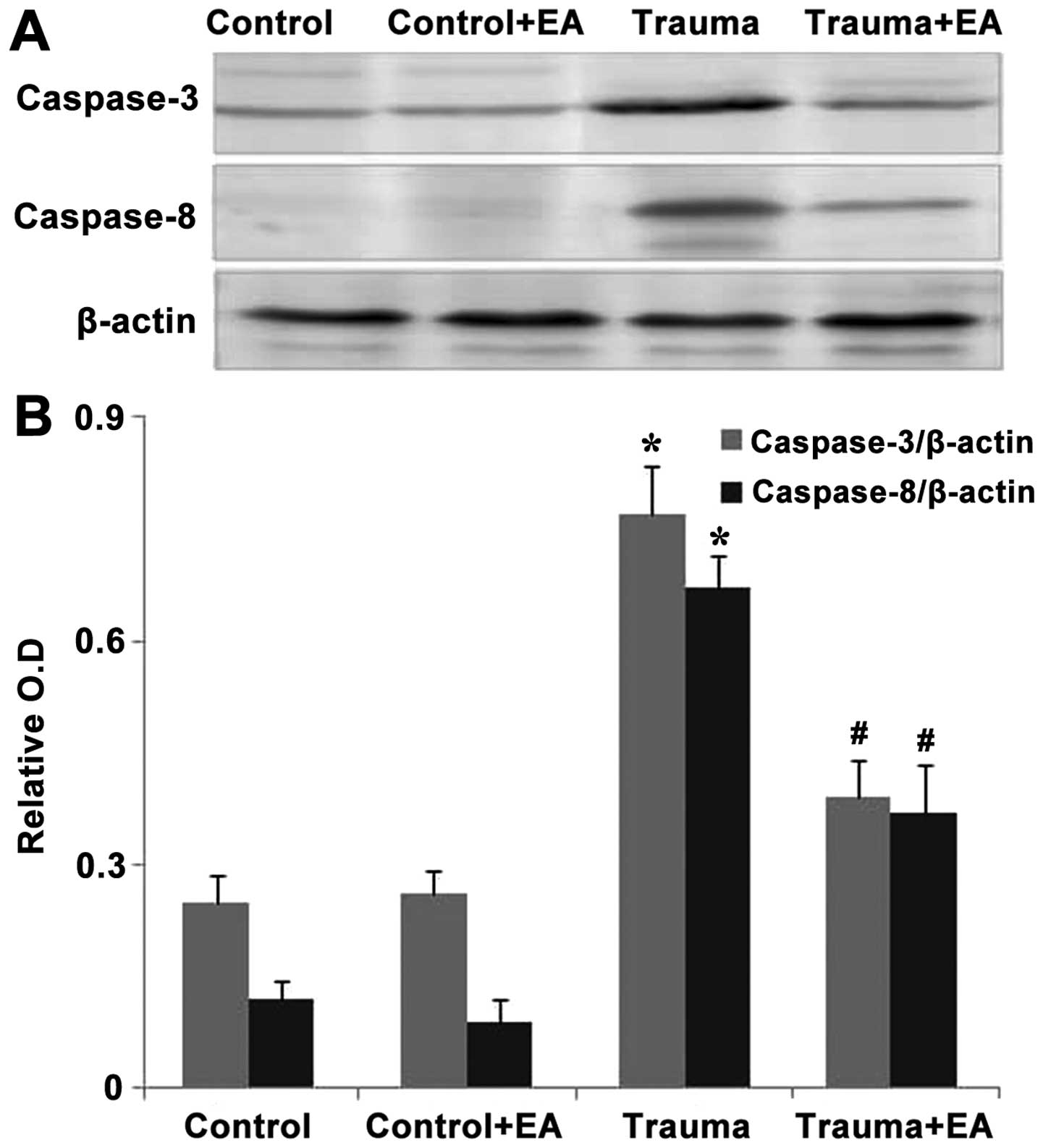
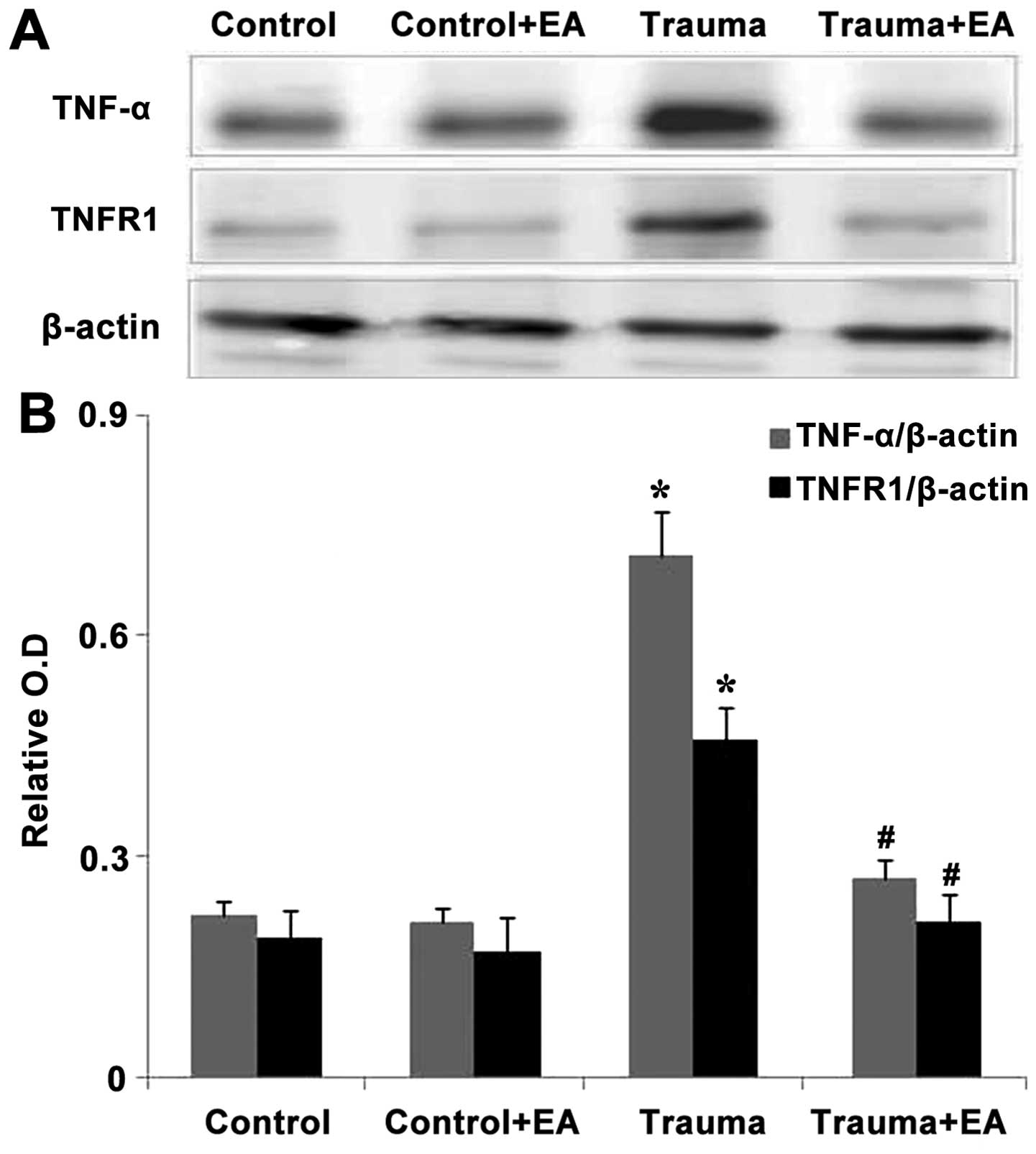
|
1
|
Kimura F, Shimizu H, Yoshidome H, Ohtsuka
M and Miyazaki M: Immunosuppression following surgical and
traumatic injury. Surg Today. 40:793–808. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Choudhry MA, Bland KI and Chaudry IH:
Trauma and immune response - effect of gender differences. Injury.
38:1382–1391. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang J, Wang YQ, Yu J, Cao XD and Wu GC:
Electroacupuncture suppresses surgical trauma stress-induced
lymphocyte apoptosis in rats. Neurosci Lett. 383:68–72. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Angele MK and Chaudry IH: Surgical trauma
and immunosuppression: pathophysiology and potential
immunomodulatory approaches. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 390:333–341.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang YS, Jiang JW, Cao XD and Wu GC:
Melatonin enhances lymphocyte proliferation and decreases the
release of pituitary pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides in
surgically traumatized rats. Neurosci Lett. 343:109–112. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang G, Weng Y, Ishiguro Y, Sakamoto H and
Morita S: The effect of tramadol on serum cytokine response in
patients undergoing pulmonary lobectomy. J Clin Anesth. 17:444–450.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiangyang L, Qian L, Xiaohong W, et al:
Changes of spleen dendritic cells in the terminal stage of multiple
organ dysfunction syndrome. Acta Biomed. 82:146–153.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun Y, Gan TJ, Dubose JW and Habib AS:
Acupuncture and related techniques for postoperative pain: a
systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Br J Anaesth.
101:151–160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pavão TS, Vianna P, Pillat MM, Machado AB
and Bauer ME: Acupuncture is effective to attenuate stress and
stimulate lymphocyte proliferation in the elderly. Neurosci Lett.
484:47–50. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SK and Bae H: Acupuncture and immune
modulation. Auton Neurosci. 157:38–41. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng XD, Wu GC, Jiang JW, Du LN and Cao
XD: Dynamic observation on regulation on spleen lymphocyte from the
traumatized rats in vitro of continued electroacupuncture. Chung
Kuo Mien I Hsueh Tsa Chih. 13:68–70. 1997.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Cheng XD, Wu GC, He QZ and Cao XD: Effect
of continued electroacupuncture on induction of interleukin-2
production of spleen lymphocytes from the injured rats. Acupunct
Electrother Res. 22:1–8. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang K, Wu H, Wang G, Li M, Zhang Z and Gu
G: The effects of electroacupuncture on TH1/TH2 cytokine mRNA
expression and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways
in the splenic T cells of traumatized rats. Anesth Analg.
109:1666–1673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Engel D, Peshock R, Armstong RC,
Sivasubramanian N and Mann DL: Cardiac myocyte apoptosis provokes
adverse cardiac remodeling in transgenic mice with targeted TNF
overexpression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 287:H1303–H1311.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen CC, Young JL, Monzon RI, Chen N,
Todorović V and Lau LF: Cytotoxicity of TNFalpha is regulated by
integrin-mediated matrix signaling. EMBO J. 26:1257–1267. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shen HM and Pervaiz S: TNF receptor
superfamily-induced cell death: redox-dependent execution. FASEB J.
20:1589–1598. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu J and Lin A: Role of JNK activation in
apoptosis: a double-edged sword. Cell Res. 15:36–42. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Varfolomeev EE and Ashkenazi A: Tumor
necrosis factor: an apoptosis JuNKie? Cell. 116:491–497. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rui T and Kvietys PR: NFkappaB and AP-1
differentially contribute to the induction of Mn-SOD and eNOS
during the development of oxidant tolerance. FASEB J. 19:1908–1910.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Batistaki C, Kostopanagiotou G,
Myrianthefs P, et al: Effect of exogenous catecholamines on tumor
necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, interleukin-10 and
beta-endorphin levels following severe trauma. Vascul Pharmacol.
48:85–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kawasaki T, Choudhry MA, Schwacha MG, et
al: Trauma-hemorrhage inhibits splenic dendritic cell
proinflammatory cytokine production via a mitogen-activated protein
kinase process. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 294:C754–C764. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kawasaki T, Suzuki T, Choudhry MA, Bland
KI and Chaudry IH: Salutary effects of 17beta-estradiol on Peyer’s
patch T cell functions following trauma-hemorrhage. Cytokine.
51:166–172. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Du L, Wu G and Cao X:
Electro-acupuncture (EA) induced attenuation of immunosuppression
appearing after epidural or intrathecal injection of morphine in
patients and rats. Acupunct Electrother Res. 21:177–186.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Delogu G, Moretti S, Antonucci A, et al:
Apoptosis and surgical trauma: dysregulated expression of death and
survival factors on peripheral lymphocytes. Arch Surg.
135:1141–1147. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oka M, Hirazawa K, Yamamoto K, et al:
Induction of Fas-mediated apoptosis on circulating lymphocytes by
surgical stress. Ann Surg. 223:434–440. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rogers PA, Schoen AM and Limehouse J:
Acupuncture for immune-mediated disorders. Literature review and
clinical applications. Probl Vet Med. 4:162–193. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding WX and Yin XM: Dissection of the
multiple mechanisms of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in liver injury.
J Cell Mol Med. 8:445–454. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sandur SK, Ahn KS, Ichikawa H, et al:
Zyflamend, a polyherbal preparation, inhibits invasion, suppresses
osteoclastogenesis, and potentiates apoptosis through
down-regulation of NF-kappa B activation and NF-kappa B-regulated
gene products. Nutr Cancer. 57:78–87. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Batistaki C, Kostopanagiotou G,
Myrianthefs P, et al: Effect of exogenous catecholamines on tumor
necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, interleukin-10 and
beta-endorphin levels following severe trauma. Vascul Pharmacol.
48:85–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|