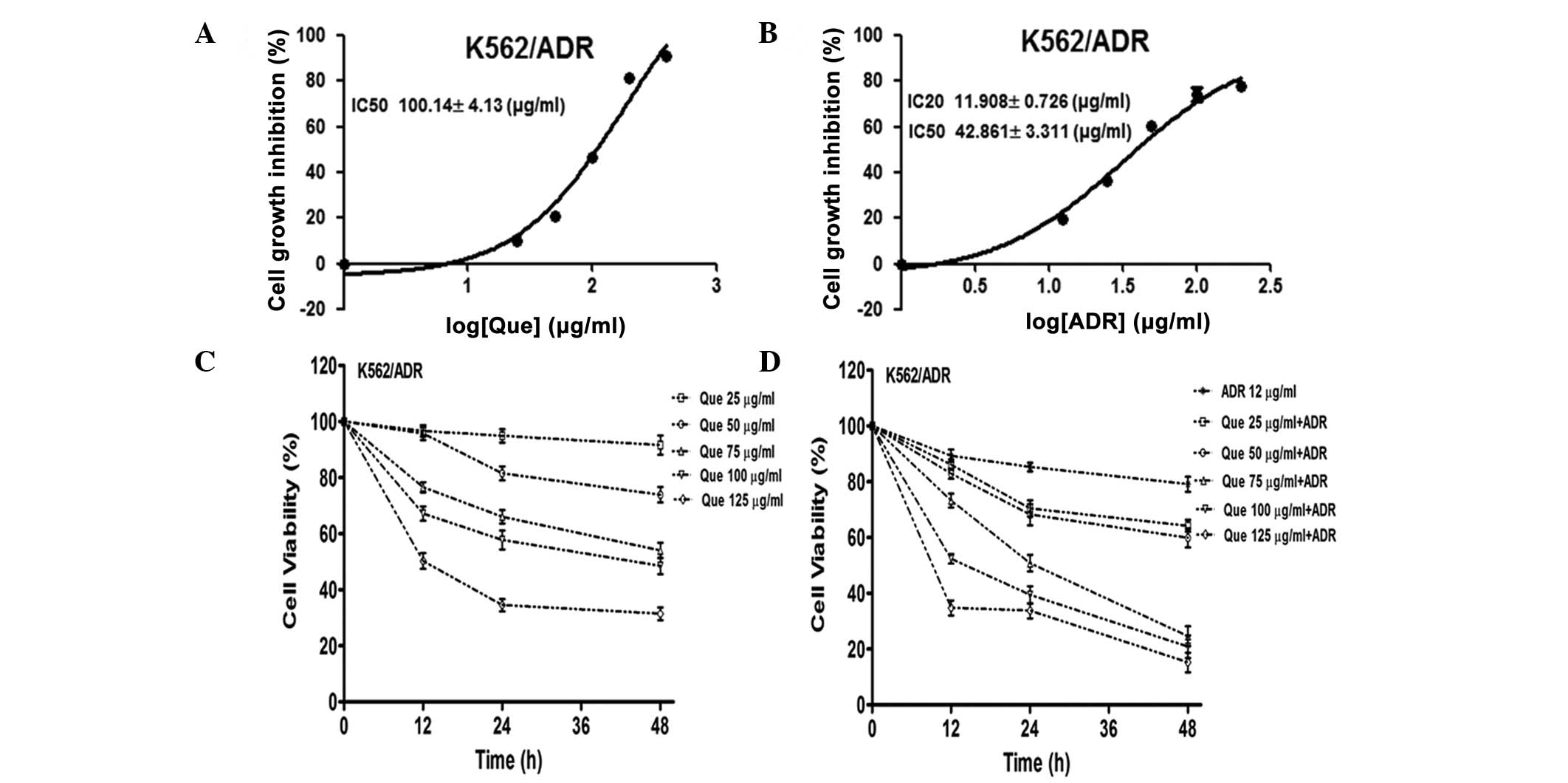
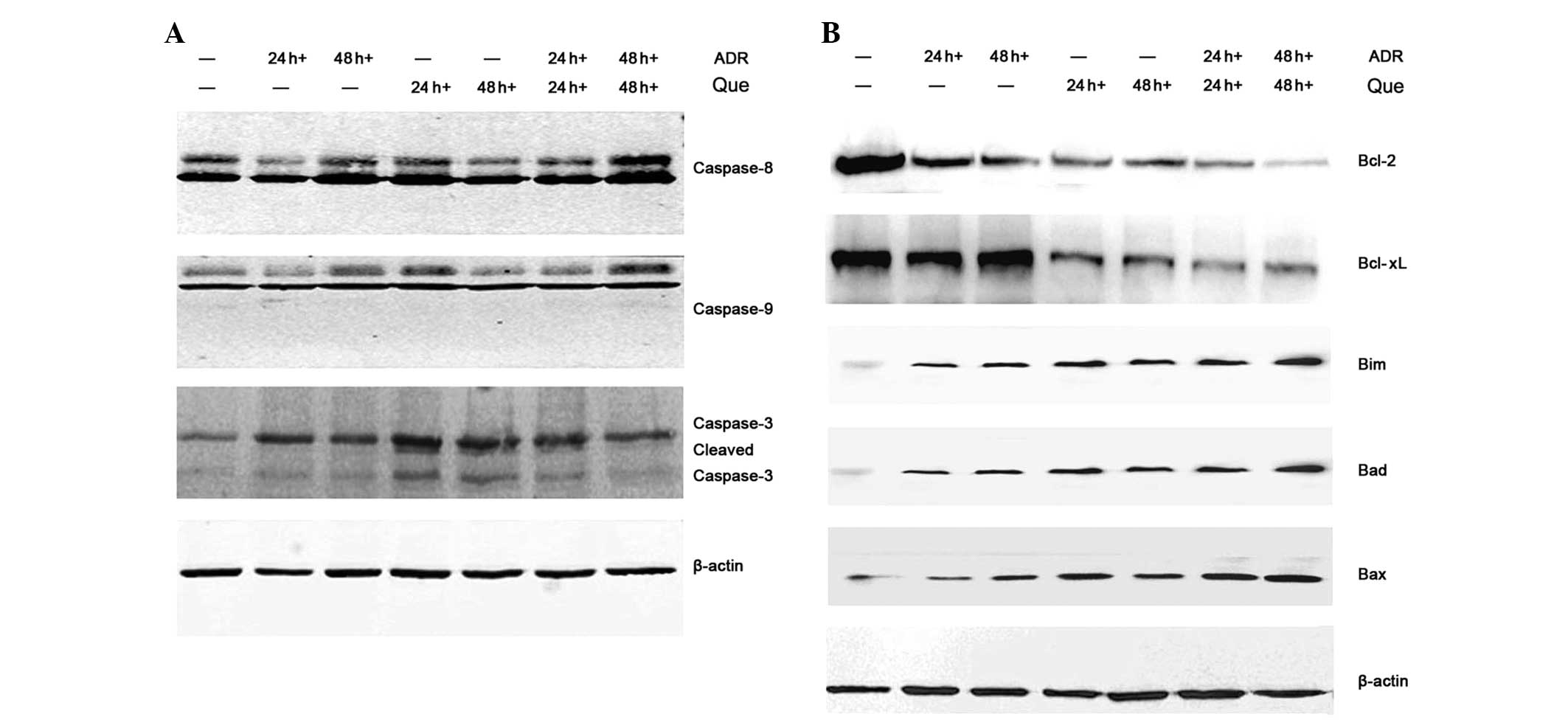
|
1
|
Fang S, Zhu W, Zhang Y, Shu Y and Liu P:
Paeoniflorin modulates multidrug resistance of a human gastric
cancer cell line via the inhibition of NF-κB activation. Mol Med
Rep. 5:351–356. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cho S, Lu M, He X, et al: Notch1 regulates
the expression of the multidrug resistance gene ABCC1/MRP1 in
cultured cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:20778–20783.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stępień KM, Tomaszewski M, Tomaszewska J
and Czuczwar SJ: The multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein in
pharmacoresistance to antiepileptic drugs. Pharmacol Rep.
64:1011–1019. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Assef Y, Rubio F, Coló G, del Mónaco S,
Costas MA and Kotsias BA: Imatinib resistance in
multidrug-resistant K562 human leukemic cells. Leuk Res.
33:710–716. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Higgins CF: Multiple molecular mechanisms
for multidrug resistance transporters. Nature. 446:749–757. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tai DJ, Jin WS, Wu CS, et al: Changes in
intracellular redox status influence multidrug resistance in
gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Exp Ther Med. 4:291–296.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun L, Chen W, Qu L, Wu J and Si J:
Icaritin reverses multidrug resistance of HepG2/ADR human hepatoma
cells via downregulation of MDR1 and P-glycoprotein expression. Mol
Med Rep. 8:1883–1887. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Limtrakul P, Anuchapreeda S and Buddhasukh
D: Modulation of human multidrug-resistance MDR-1 gene by natural
curcuminoids. BMC Cancer. 4:132004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Maeda J, Roybal EJ, Brents CA, Uesaka M,
Aizawa Y and Kato TA: Natural and glucosyl flavonoids inhibit
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase activity and induce synthetic lethality
in BRCA mutant cells. Oncol Rep. 31:551–556. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kawai Y, Nishikawa T, Shiba Y, et al:
Macrophage as a target of quercetin glucuronides in human
atherosclerotic arteries: implication in the anti-atherosclerotic
mechanism of dietary flavonoids. J Biol Chem. 283:9424–9434. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hu QF, Zhou B, Huang JM, et al: Cytotoxic
oxepinochromenone and flavonoids from the flower buds of Rosa
rugosa. J Nat Prod. 76:1866–1871. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Umathe SN, Dixit PV, Kumar V, Bansod KU
and Wanjari MM: Quercetin pretreatment increases the
bioavailability of pioglitazone in rats: involvement of CYP3A
inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 75:1670–1676. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Punithavathi VR and Prince PS:
Pretreatment with a combination of quercetin and alpha-tocopherol
ameliorates adenosine triphosphatases and lysosomal enzymes in
myocardial infarcted rats. Life Sci. 86:178–184. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Gee JM, Hara H and Johnson IT: Suppression
of intestinal crypt cell proliferation and aberrant crypt foci by
dietary quercetin in rats. Nutr Cancer. 43:193–201. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duo J, Ying GG, Wang GW and Zhang L:
Quercetin inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation and
induces apoptosis via Bcl-2 and Bax regulation. Mol Med Rep.
5:1453–1456. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu YM, Xia XY, Pan LJ, et al: Evaluation
of sperm mitochondrial function using Rh123/PI dual fluorescent
staining. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 12:803–806. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Sun c, Guo XX, Zhu D, et al: Apoptosis is
induced in cancer cells via the mitochondrial pathway by the novel
xylocydine-derived compound JRS-15. Int J, Mol Sci. 41:850–870.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li T, Kon N, Jiang L, et al: Tumor
suppression in the absence of p53-mediated cell-cycle arrest,
apoptosis, and senescence. Cell. 149:1269–1283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Ren X, Alt E, et al:
Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer by targeting APC-deficient
cells for apoptosis. Nature. 464:1058–1061. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tassi E, Zanon M, Vegetti C, et al: Role
of Apollon in human melanoma resistance to antitumor agents that
activate the intrinsic or the extrinsic apoptosis pathways. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:3316–3327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Franklin EE and Robertson JD: Requirement
of Apaf-1 for mitochondrial events and the cleavage or activation
of all procaspases during genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis.
Biochem J. 405:115–122. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Tsuruma K, Nakagawa T, Morimoto N, et al:
Glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 binds to
initiator procaspases and inhibits ischemia-induced apoptosis and
neuronal injury. J Biol Chem. 281:11397–11404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li J, Li PF, Dietz R and von Harsdorf R:
Intracellular superoxide induces apoptosis in VSMCs: role of
mitochondrial membrane potential, cytochrome C and caspases.
Apoptosis. 7:511–517. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu CY, Chiang RL, Chang TH, Liao CL and
Lin YL: The interferon stimulator mitochondrial antiviral signaling
protein facilitates cell death by disrupting the mitochondrial
membrane potential and by activating caspases. J Virol.
84:2421–2431. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kumar A, Byun HS, Bittman R and Saba JD:
The sphingolipid degradation product trans-2-hexadecenal induces
cytoskeletal reorganization and apoptosis in a JNK-dependent
manner. Cell Signal. 23:1144–1152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lei K and Davis RJ: JNK phosphorylation of
Bim-related members of the Bcl2 family induces Bax-dependent
apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:2432–2437. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ha Thi HT, Lim HS, Kim J, Kim YM, Kim HY
and Hong S: Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of
Bim is essential for TGF-β and TNF-α-induced apoptosis of gastric
cancer cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:3584–3592. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Pathological roles of
MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:396–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Platanias LC: Map kinase signaling
pathways and hematologic malignancies. Blood. 101:4667–4679. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Niedermeier M, Hennessy BT, Knight ZA, et
al: Isoform-selective phosphoinositide 3′-kinase inhibitors inhibit
CXCR4 signaling and overcome stromal cell-mediated drug resistance
in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a novel therapeutic approach.
Blood. 113:5549–5557. 2009.
|
|
31
|
Ebert SP, Wetzel B, Myette RL, et al:
Chalcogenopyrylium compounds as modulators of the ATP-binding
cassette transporters P-glycoprotein (P-gp/ABCB1) and multidrug
resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1). J Med Chem. 55:4683–4699. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|