|
1
|
Angulo P: Nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. N Engl J Med. 346:1221–1231. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Clark JM, Brancati FL and Diehl AM:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 122:1649–1657.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Falck-Ytter Y, Younossi ZM, Marchesini G
and McCullough AJ: Clinical features and natural history of
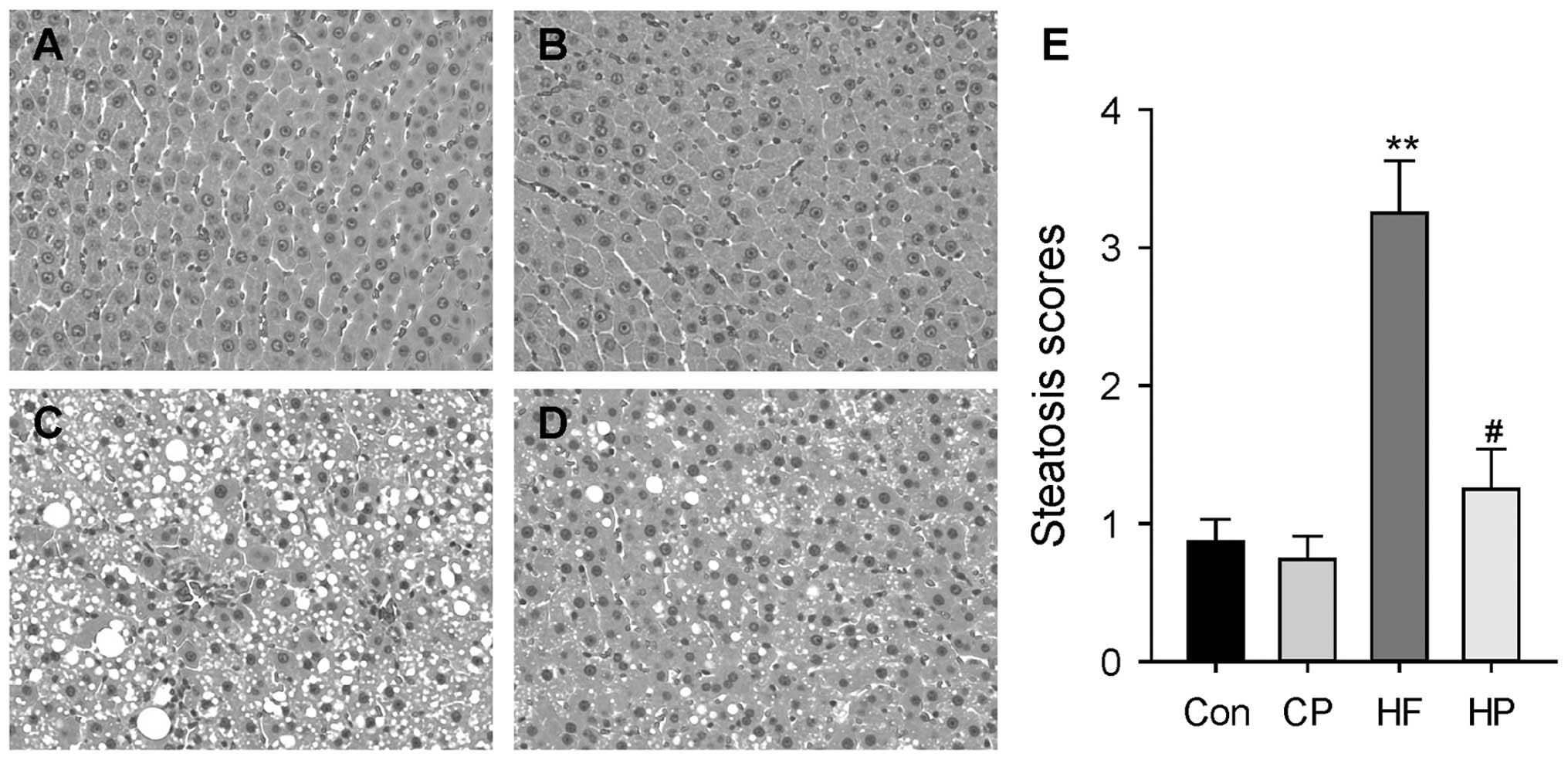
nonalcoholic steatosis syndromes. Semin Liver Dis. 21:17–26. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
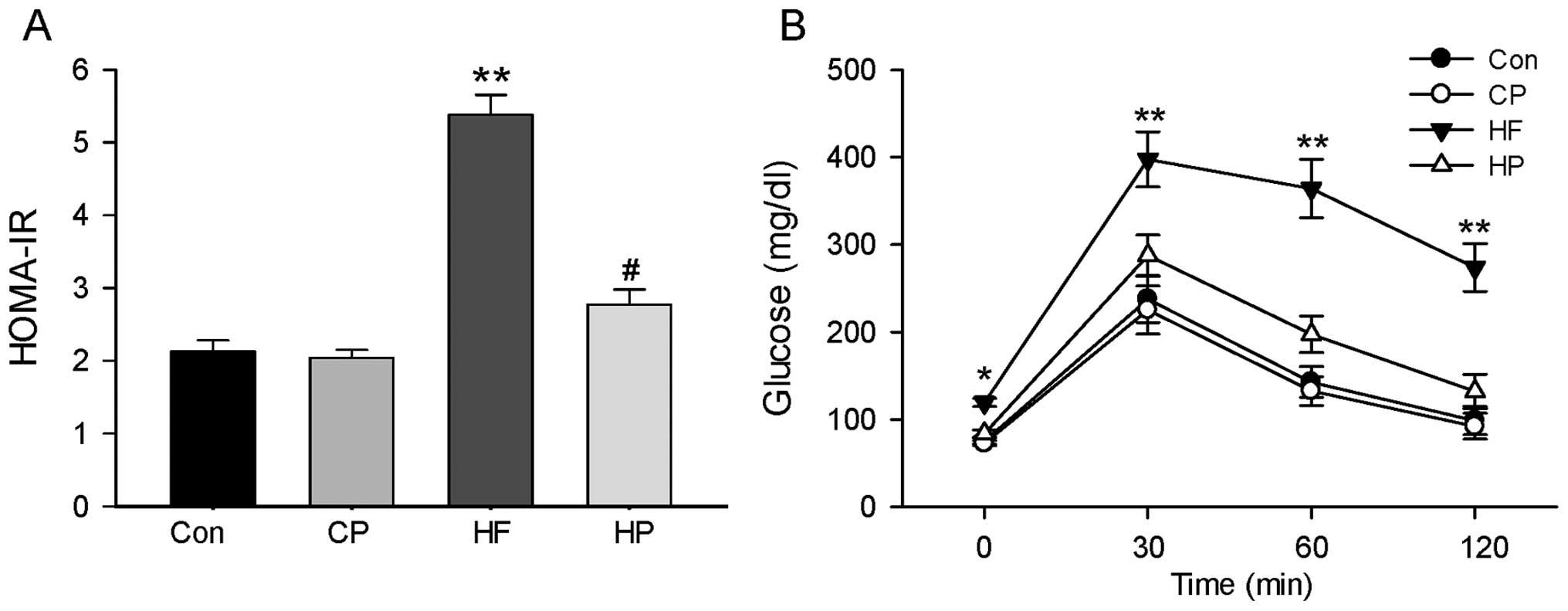
|
4
|
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V and
Czech MP: Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 9:367–377.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
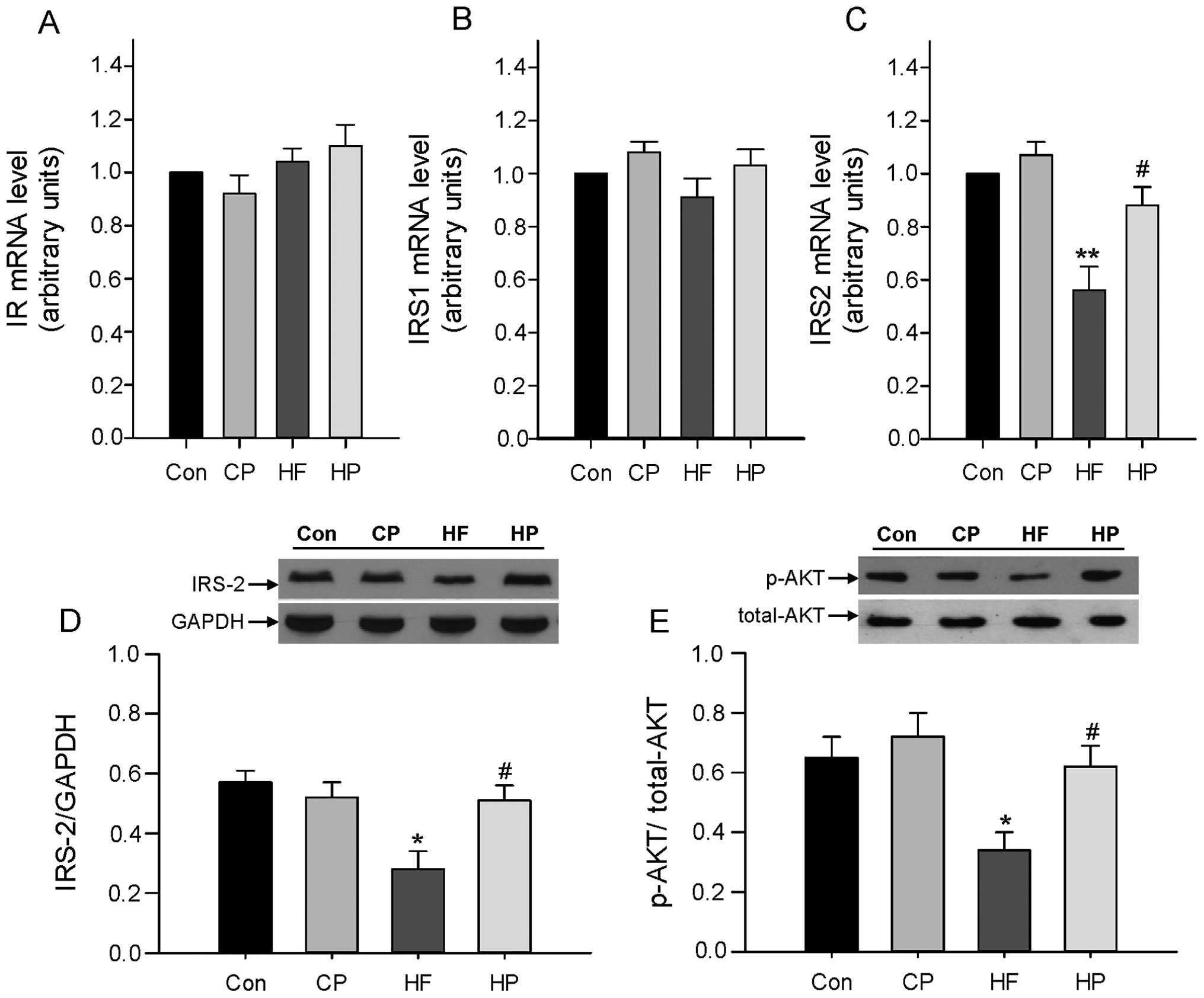
|
5
|
Gariani K, Philippe J and Jornayvaz FR:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance: from
bench to bedside. Diabetes Metab. 39:16–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
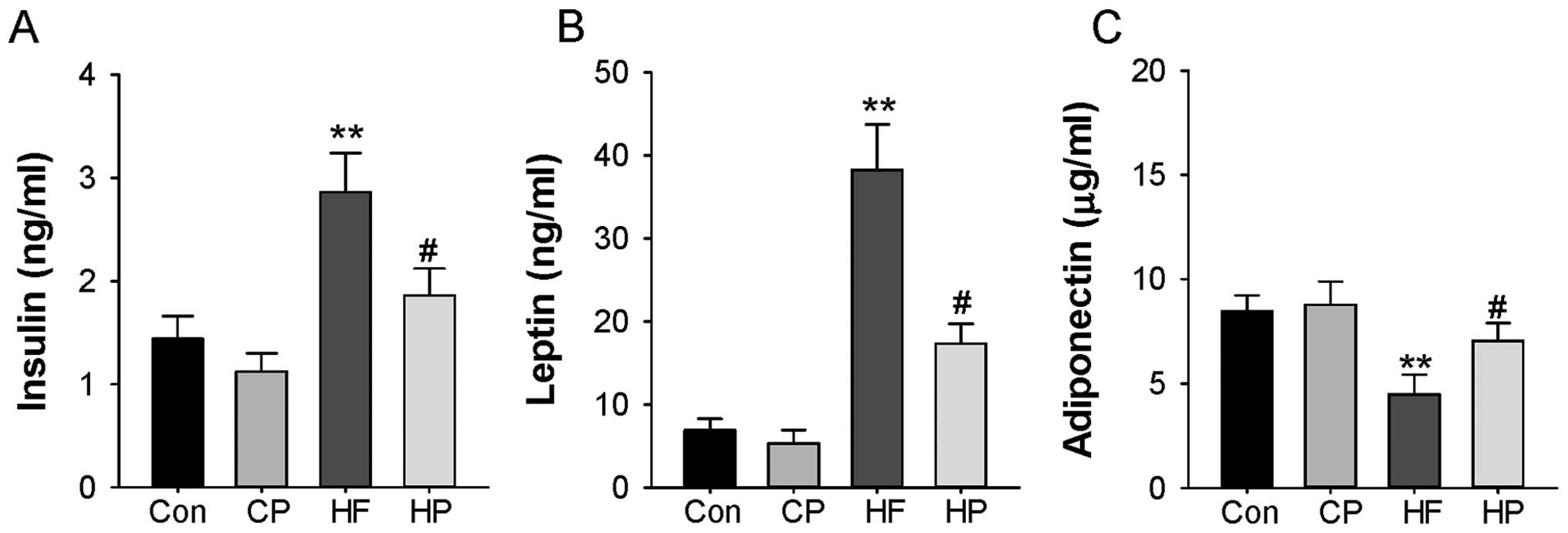
|
Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, Forlani G, et
al: Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic
syndrome. Hepatology. 37:917–923. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jou J, Choi SS and Diehl AM: Mechanisms of
disease progre ssion in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Semin
Liver Dis. 28:370–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tilg H and Moschen AR: Insulin resistance,
inflammation, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 19:371–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kimura Y: Pharmacological studies on
resveratrol. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 25:297–310. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xue L: Progress in the pharmacological
study of Chinese herbal drug: Polygonum cuspidatum. Zhongguo
Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 25:651–653. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Luper S: A review of plants used in the
treatment of liver disease: part two. Altern Med Rev. 4:178–188.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang H, Dou C and Gu F: Advances in the
study on pharmacological actions of Polygonum cuspidatum
Sieb. et Zucc.: clearing heat and detoxication. Zhong Yao Cai.
26:606–610. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Zhang H, Yu CH, Jiang YP, et al:
Protective effects of polydatin from Polygonum cuspidatum
against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. PLoS
One. 7:e465742012.
|
|
14
|
Ji H, Zhang X, Du Y, Liu H, Li S and Li L:
Polydatin modulates inflammation by decreasing NF-κB activation and
oxidative stress by increasing Gli1, Ptch1, SOD1 expression and
ameliorates blood-brain barrier permeability for its
neuroprotective effect in pMCAO rat brain. Brain Res Bull.
87:50–59. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Du J, Sun LN, Xing WW, et al:
Lipid-lowering effects of polydatin from Polygonum
cuspidatum in hyperlipidemic hamsters. Phytomedicine.
16:652–658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xing WW, Wu JZ, Jia M, Du J, Zhang H and
Qin LP: Effects of polydatin from Polygonum cuspidatum on
lipid profile in hyperlipidemic rabbits. Biomed Pharmacother.
63:457–462. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Tan Y, Yao F and Zhang Q:
Polydatin alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats by
inhibiting the expression of TNF-α and SREBP-1c. Mol Med Rep.
6:815–820. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brunt EM, Janney CG and Di Bisceglie AM:
Neuschwander-Tetri BA and Bacon BR: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a
proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J
Gastroenterol. 94:2467–2474. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Folch J, Lees M and Sloane Starley GH: A
simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides
from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 226:497–509. 1957.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Zhang DB and Sun LJ:
Effect of Sinai san decoction on the development of non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 11:1392–1395. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS,
Naylor BA, Treacher DF and Turner RC: Homeostasis model assessment:
insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma
glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia.
28:412–419. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang Q, Yao F, Raizada MK, O’Rourke ST
and Sun C: Apelin gene transfer into the rostral ventrolateral
medulla induces chronic blood pressure elevation in normotensive
rats. Circ Res. 104:1421–1428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bugianesi E, McCullough AJ and Marchesini
G: Insulin resistance: a metabolic pathway to chronic liver
disease. Hepatology. 42:987–1000. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saltiel AR and Kahn CR: Insulin signalling
and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature.
414:799–806. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Youngren JF: Regulation of insulin
receptor function. Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:873–891. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Khan AH and Pessin JE: Insulin regulation
of glucose uptake: a complex interplay of intracellular signalling
pathways. Diabetologia. 45:1475–1483. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Le Roith D and Zick Y: Recent advances in
our understanding of insulin action and insulin resistance.
Diabetes Care. 24:588–597. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Q, Somwar R, Bilan PJ, et al: Protein
kinase B/Akt participates in GLUT4 translocation by insulin in L6
myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 19:4008–4018. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Boura-Halfon S and Zick Y: Phosphorylation
of IRS proteins, insulin action, and insulin resistance. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 296:E581–E591. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kerouz NJ, Hörsch D, Pons S and Kahn CR:
Differential regulation of insulin receptor substrates-1 and -2
(IRS-1 and IRS-2) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase isoforms in
liver and muscle of the obese diabetic (ob/ob) mouse. J Clin
Invest. 100:3164–3172. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shimomura I, Matsuda M, Hammer RE, et al:
Decreased IRS-2 and increased SREBP-1c lead to mixed insulin
resistance and sensitivity in livers of lipodystrophic and ob/ob
mice. Mol Cell. 6:77–86. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Previs SF, Withers DJ, Ren JM, White MF
and Shulman GI: Contrasting effects of IRS-1 versus IRS-2 gene
disruption on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in vivo. J Biol
Chem. 275:38990–38994. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Withers DJ, Gutierrez JS, Towery H, et al:
Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature.
391:900–904. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rother KI, Imai Y, Caruso M, Beguinot F,
Formisano P and Accili D: Evidence that IRS-2 phosphorylation is
required for insulin action in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem.
273:17491–17497. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kido Y, Burks DJ, Withers D, et al:
Tissue-specific insulin resistance in mice with mutations in the
insulin receptor, IRS-1, and IRS-2. J Clin Invest. 105:199–205.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Valverde AM, Burks DJ, Fabregat I, et al:
Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance in IRS-2-deficient
hepatocytes. Diabetes. 52:2239–2248. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Farrell GC and Larter CZ: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology.
43:S99–S112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Musso G, Gambino R, Durazzo M, et al:
Adipokines in NASH: postprandial lipid metabolism as a link between
adiponectin and liver disease. Hepatology. 42:1175–1183. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gambino R, Cassader M, Pagano G, Durazzo M
and Musso G: Polymorphism in microsomal triglyceride transfer
protein: a link between liver disease and atherogenic postprandial
lipid profile in NASH? Hepatology. 45:1097–1107. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang Z, Yao T, Pini M, Zhou Z, Fantuzzi G
and Song Z: Betaine improved adipose tissue function in mice fed a
high-fat diet: a mechanism for hepatoprotective effect of betaine
in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 298:G634–G642. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|