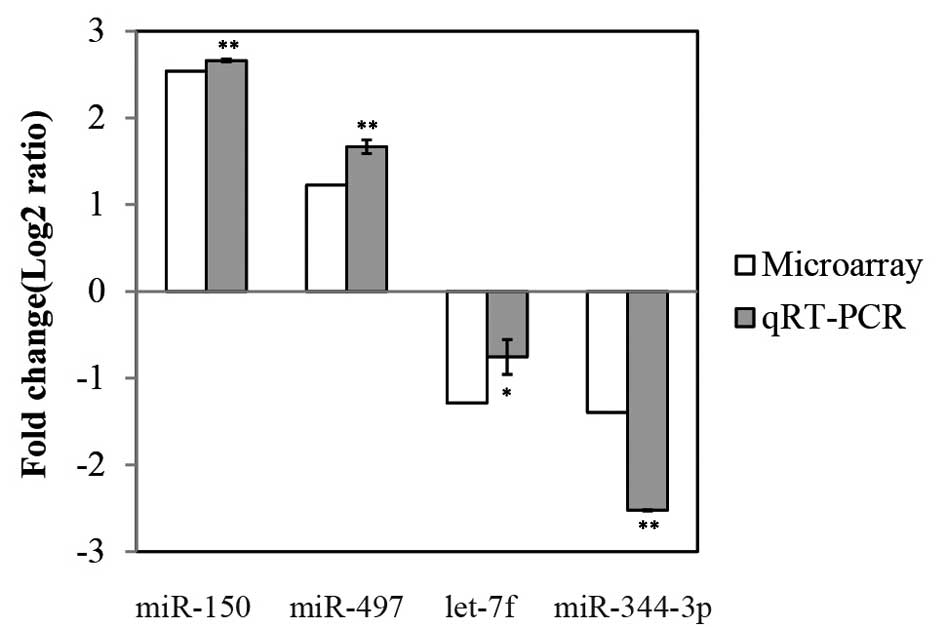
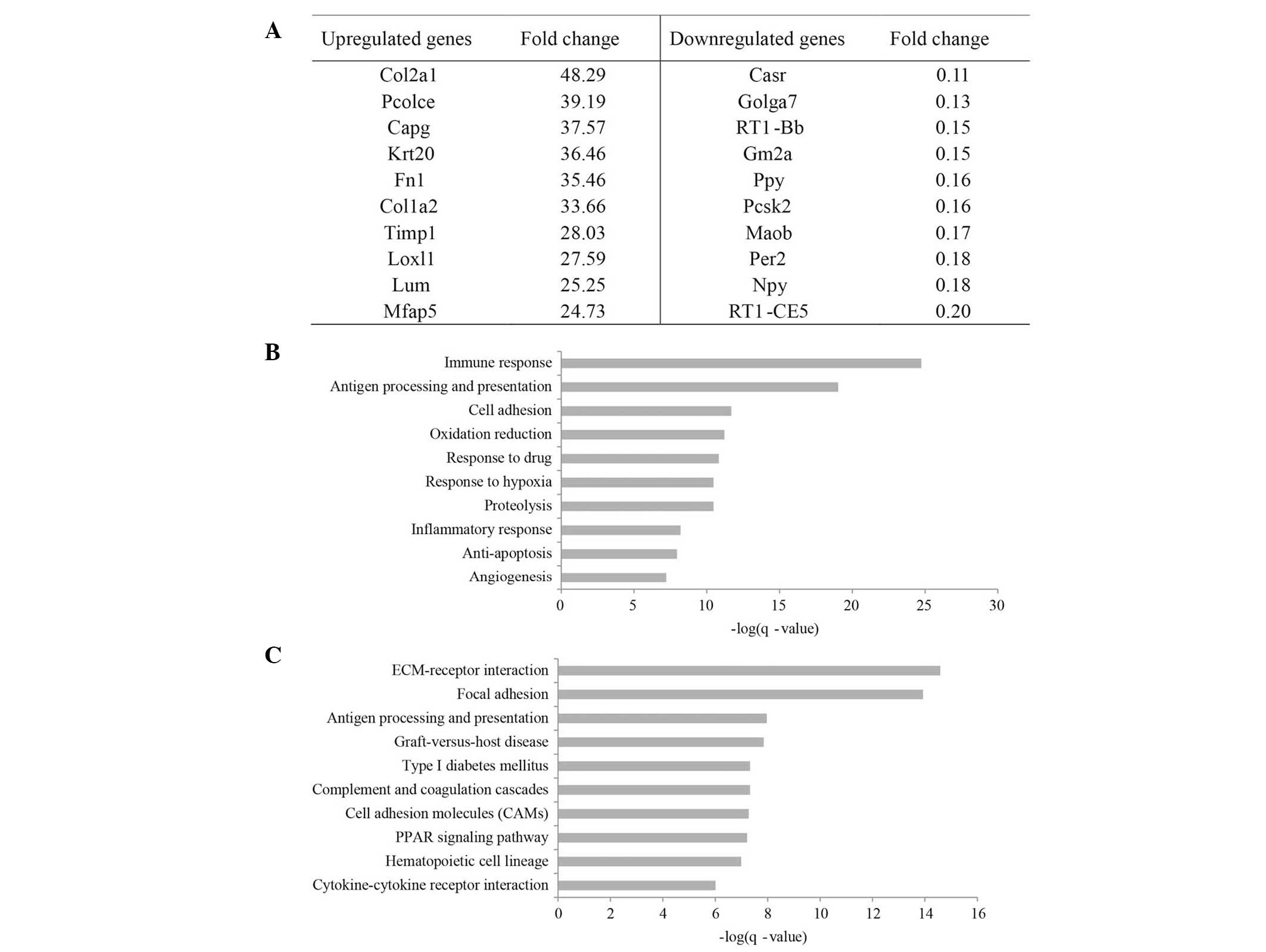
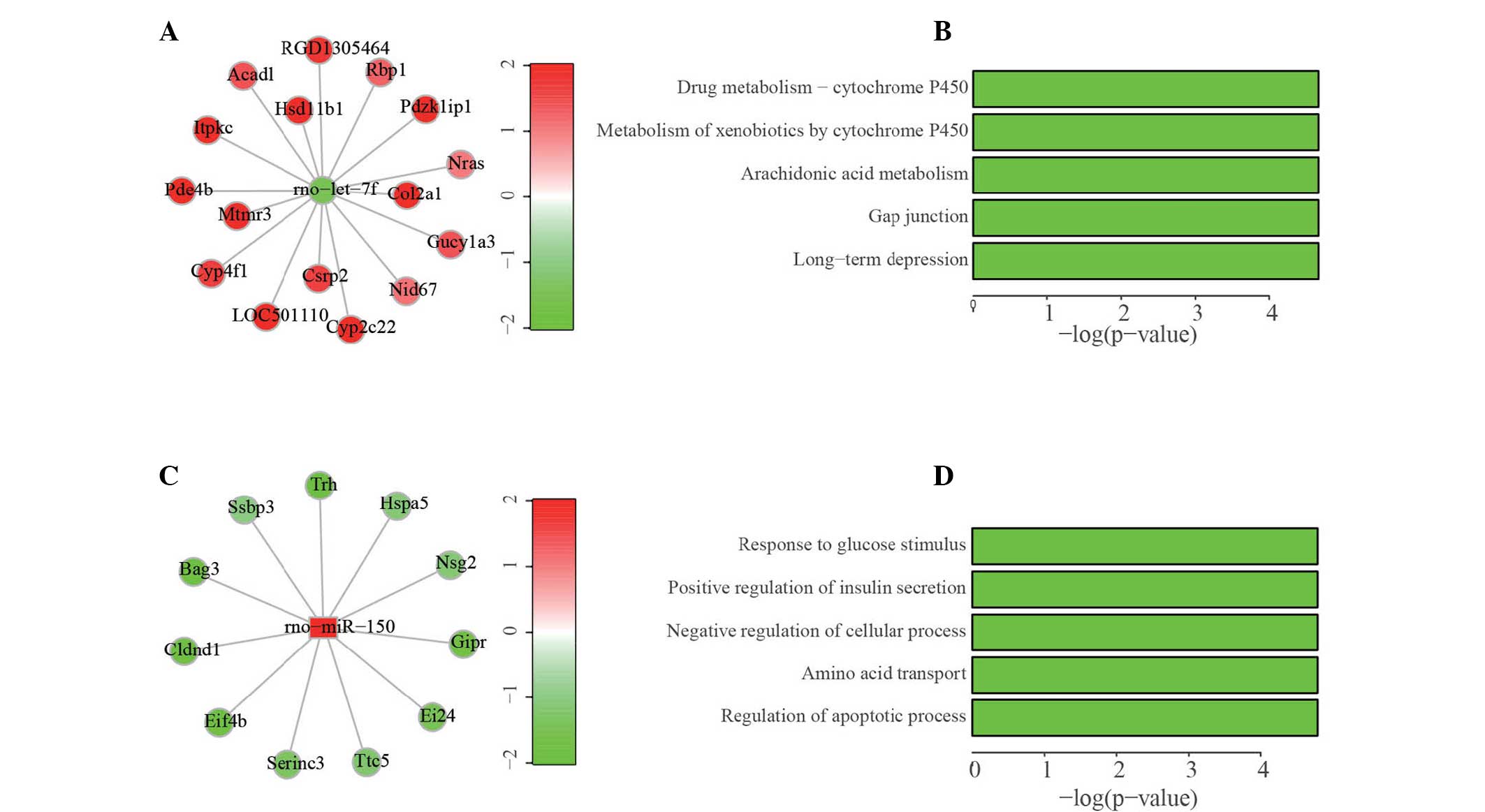
|
1
|
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R and
King H: Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000
and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 27:1047–1053.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin Y and Sun Z: Current views on type 2
diabetes. J Endocrinol. 204:1–11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McCarthy MI and Zeggini E: Genome-wide
association studies in type 2 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 9:164–171.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qin W, Dong P, Ma C, et al: MicroRNA-133b
is a key promoter of cervical carcinoma development through the
activation of the ERK and AKT1 pathways. Oncogene. 31:4067–4075.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tan X, Qin W, Zhang L, et al: A 5-microRNA
signature for lung squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis and hsa-miR-31
for prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6802–6811. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo H, Liu H, Mitchelson K, et al:
MicroRNAs-372/373 promote the expression of hepatitis B virus
through the targeting of nuclear factor I/B. Hepatology.
54:808–819. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Olsson AH, Yang BT, Hall E, et al:
Decreased expression of genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation
in human pancreatic islets from patients with type 2 diabetes. Eur
J Endocrinol. 165:589–595. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sreekumar R, Halvatsiotis P, Schimke JC
and Nair KS: Gene expression profile in skeletal muscle of type 2
diabetes and the effect of insulin treatment. Diabetes.
51:1913–1920. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen Z, Zhang S, Zou CC, Gu WZ and Shang
SQ: DNA microarray analysis of the gene expression profile of
kidney tissue in a type 2 diabetic rat model. Mol Med Report.
3:947–952. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou H, Saito S, Piao G, et al: Network
screening of Goto-Kakizaki rat liver microarray data during
diabetic progression. BMC Syst Biol. 5(Suppl 1): S162011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang YL, Xiang RL, Yang C, et al: Gene
expression profile of human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue of
Chinese Han patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed Environ
Sci. 22:359–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Quan W, Jo EK and Lee MS: Role of
pancreatic β-cell death and inflammation in diabetes. Diabetes Obes
Metab. 15(Suppl 3): 141–51. 2013.
|
|
18
|
Van der Auwera I, Limame R, van Dam P,
Vermeulen PB, Dirix LY and Van Laere SJ: Integrated miRNA and mRNA
expression profiling of the inflammatory breast cancer subtype. Br
J Cancer. 103:532–541. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fu J, Tang W, Du P, et al: Identifying
microRNA-mRNA regulatory network in colorectal cancer by a
combination of expression profile and bioinformatics analysis. BMC
Syst Biol. 6:682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nunez-Iglesias J, Liu CC, Morgan TE, Finch
CE and Zhou XJ: Joint genome-wide profiling of miRNA and mRNA
expression in Alzheimer’s disease cortex reveals altered miRNA
regulation. PLoS One. 5:e88982010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin J, Cheng Y, Zhang Y, et al:
Interrogation of brain miRNA and mRNA expression profiles reveals a
molecular regulatory network that is perturbed by mutant
huntingtin. J Neurochem. 123:477–490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steuerwald NM, Parsons JC, Bennett K,
Bates TC and Bonkovsky HL: Parallel microRNA and mRNA expression
profiling of (genotype 1b) human hepatoma cells expressing
hepatitis C virus. Liver Int. 30:1490–1504. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He A, Zhu L, Gupta N, Chang Y and Fang F:
Overexpression of micro ribonucleic acid 29, highly up-regulated in
diabetic rats, leads to insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Mol Endocrinol. 21:2785–2794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Frost RJ and Olson EN: Control of glucose
homeostasis and insulin sensitivity by the Let-7 family of
microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:21075–21080. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nieto M, Hevia P, Garcia E, et al:
Antisense miR-7 impairs insulin expression in developing pancreas
and in cultured pancreatic buds. Cell Transplant. 21:1761–1774.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang XH, Qian RZ, Zhang W, Chen SF, Jin HM
and Hu RM: MicroRNA-320 expression in myocardial microvascular
endothelial cells and its relationship with insulin-like growth
factor-1 in type 2 diabetic rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
36:181–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu JH, Gao Y, Ren AJ, et al: Altered
microRNA expression profiles in retinas with diabetic retinopathy.
Ophthalmic Res. 47:195–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mallone R and van Endert P: T cells in the
pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 8:101–106. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shoelson SE, Lee J and Goldfine AB:
Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 116:1793–1801.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ehses JA, Perren A, Eppler E, et al:
Increased number of islet-associated macrophages in type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 56:2356–2370. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Donath MY and Shoelson SE: Type 2 diabetes
as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:98–107. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eguchi K, Manabe I, Oishi-Tanaka Y, et al:
Saturated fatty acid and TLR signaling link β cell dysfunction and
islet inflammation. Cell Metab. 15:518–533. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Thrailkill KM, Clay Bunn R and Fowlkes JL:
Matrix metalloproteinases: their potential role in the pathogenesis
of diabetic nephropathy. Endocrine. 35:1–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Khalfaoui T, Lizard G and Ouertani-Meddeb
A: Adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) and diabetic retinopathy
in type 2 diabetes. J Mol Histol. 39:243–249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Condorelli G, Vigliotta G, Iavarone C, et
al: PED/PEA-15 gene controls glucose transport and is overexpressed
in type 2 diabetes mellitus. EMBO J. 17:3858–3866. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Makino H, Mukoyama M, Sugawara A, et al:
Roles of connective tissue growth factor and prostanoids in early
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat kidney: the effect of aspirin
treatment. Clin Exp Nephrol. 7:33–40. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Danda RS, Habiba NM, Rincon-Choles H, et
al: Kidney involvement in a nongenetic rat model of type 2
diabetes. Kidney Int. 68:2562–2571. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Laybutt DR, Preston AM, Akerfeldt MC, et
al: Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to beta cell apoptosis
in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 50:752–763. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu X, Wang J, Cui X, et al: The effect of
insulin on expression of genes and biochemical pathways in human
skeletal muscle. Endocrine. 31:5–17. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|