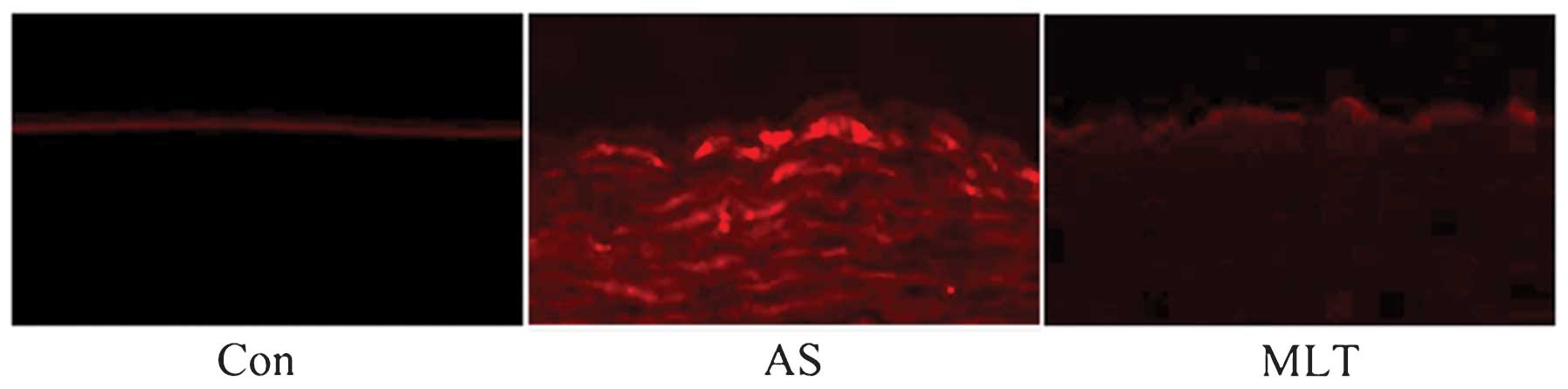
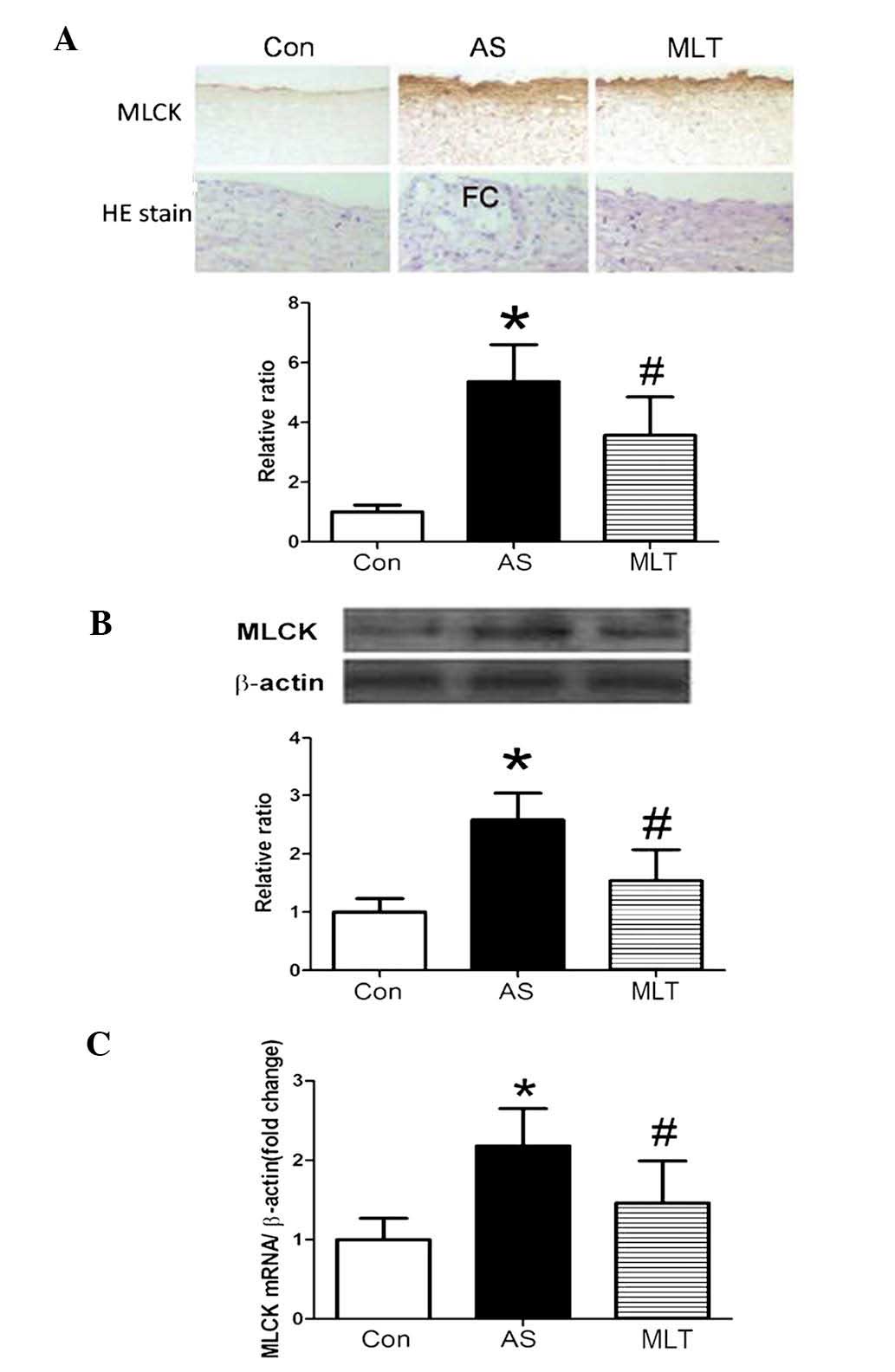
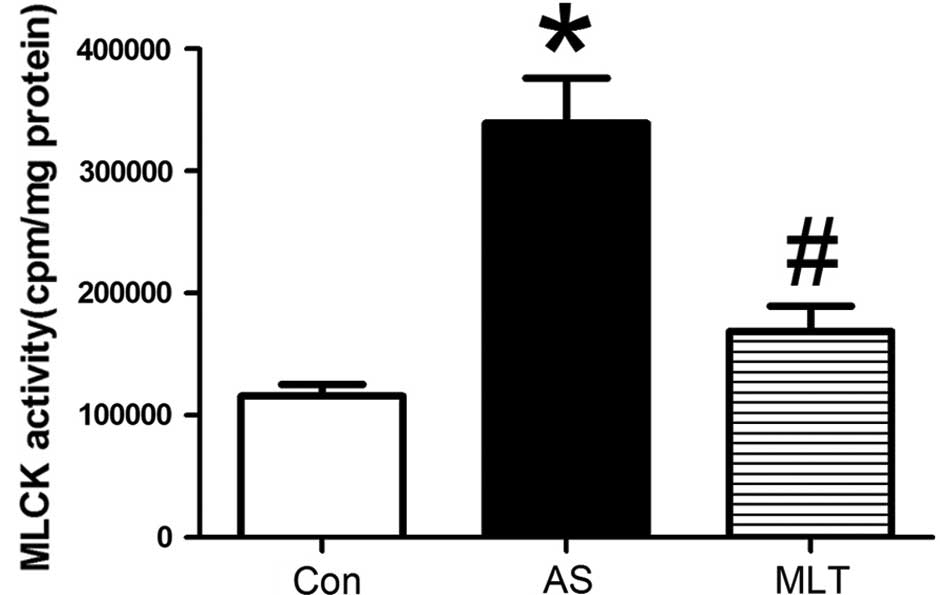
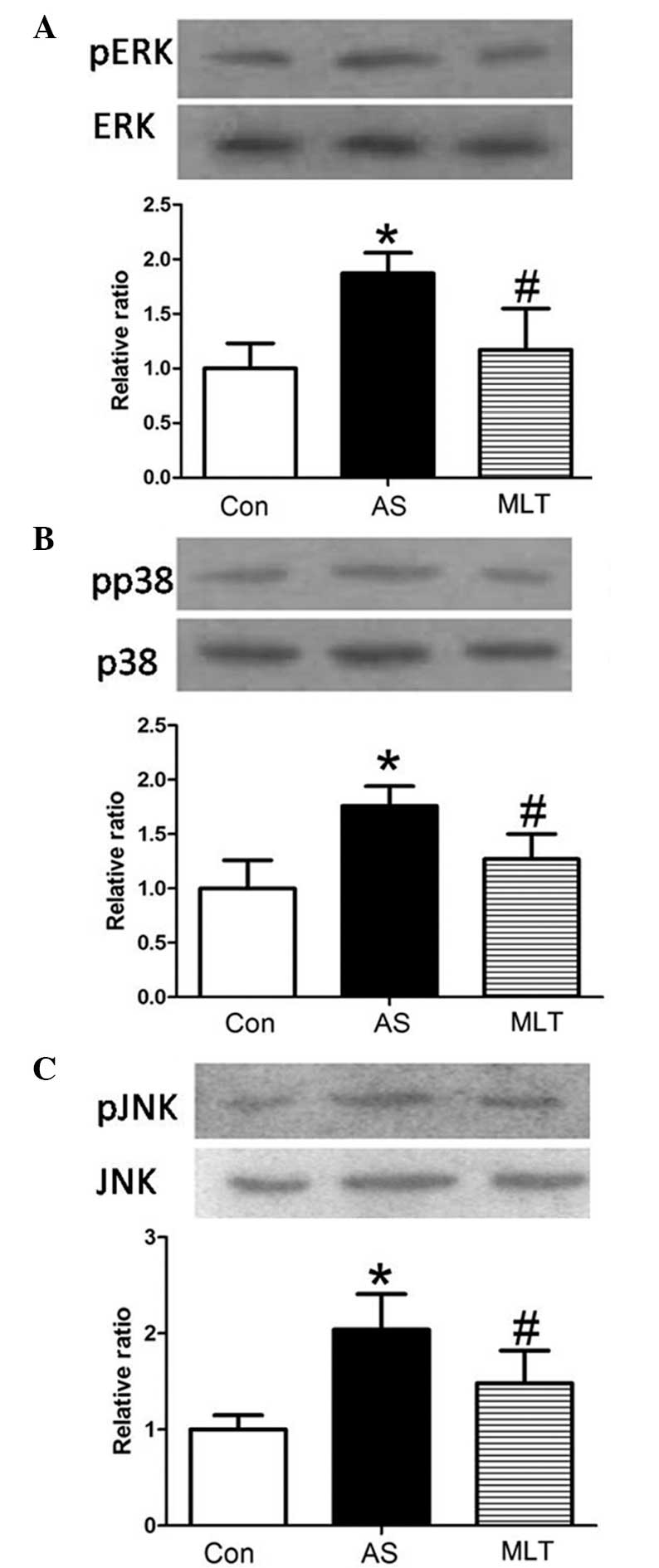
|
1
|
Daffu G, del Pozo CH, O’Shea KM, et al:
Radical roles for RAGE in the pathogenesis of oxidative stress in
cardiovascular diseases and beyond. Int J Mol Sci. 14:19891–19910.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tengattini S, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, et al:
Cardiovascular diseases: protective effects of melatonin. J Pineal
Res. 44:16–25. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liao JK: Linking endothelial dysfunction
with endothelial cell activation. J Clin Invest. 123:540–541. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Liu X, et al:
Mitochondria and chloroplasts as the original sites of melatonin
synthesis: a hypothesis related to melatonin’s primary function and
evolution in eukaryotes. J Pineal Res. 54:127–138. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen HI, Huang YC, Su WH and Jen CJ:
Endothelial calcium signaling in rabbit arteries and its local
alterations in early-stage atherosclerosis. J Biomed Sci.
14:145–153. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nausch LW, Bonev AD, Heppner TJ, et al:
Sympathetic nerve stimulation induces local endothelial
Ca2+ signals to oppose vasoconstriction of mouse
mesenteric arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
302:H594–H602. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Turner JR, Angle JM, Black ED, et al:
PKC-dependent regulation of transepithelial resistance: roles of
MLC and MLC kinase. Am J Physiol. 277(3 Pt 1): C554–C562.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan SY: Protein kinase signaling in the
modulation of microvascular permeability. Vascul Pharmacol.
39:213–223. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rashid G, Bernheim J, Green J and
Benchetrit S: Parathyroid hormone stimulates endothelial expression
of atherosclerotic parameters through protein kinase pathways. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 292:F1215–F1218. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shen Q, Rigor RR, Pivetti CD, et al:
Myosin light chain kinase in microvascular endothelial barrier
function. Cardiovasc Res. 87:272–280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hong T and Grabel LB: Migration of F9
parietal endoderm cells is regulated by the ERK pathway. J Cell
Biochem. 97:1339–1349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu P, Lai D, Lu P, et al: ERK and Akt
signaling pathways are involved in advanced glycation end
product-induced autophagy in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Int
J Mol Med. 29:613–618. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peng YS, Lin YT, Chen Y, et al: Effects of
indoxyl sulfate on adherens junctions of endothelial cells and the
underlying signaling mechanism. J Cell Biochem. 113:1034–1043.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Korkmaz A, Tamura H, Manchester LC, et al:
Combination of melatonin and a peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma agonist induces apoptosis in a breast cancer cell
line. J Pineal Res. 46:115–116. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu C, Wu A, Zhu H, et al: Melatonin is
involved in the apoptosis and necrosis of pancreatic cancer cell
line SW-1990 via modulating of Bcl-2/Bax balance. Biomed
Pharmacother. 67:133–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reiter RJ and Korkmaz A: Clinical aspects
of melatonin. Saudi Med J. 29:1537–1547. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Wilhelm EA, Jesse CR, Bortolatto CF and
Nogueira CW: Correlations between behavioural and oxidative
parameters in a rat quinolinic acid model of Huntington’s disease:
protective effect of melatonin. Eur J Pharmacol. 701:65–72.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Galano A, Tan DX and Reiter RJ: Melatonin
as a natural ally against oxidative stress: a physicochemical
examination. J Pineal Res. 51:1–16. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Broncel M, Koziróg-Kołacińska M and
Chojnowska-Jezierska J: Melatonin in the treatment of
atherosclerosis. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 23:124–127. 2007.(In
Polish).
|
|
20
|
Rodella LF, Favero G, Foglio E, et al:
Vascular endothelial cells and dysfunctions: role of melatonin.
Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 5:119–129. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maldonado MD, Murillo-Cabezas F, Terron
MP, et al: The potential of melatonin in reducing
morbidity-mortality after craniocerebral trauma. J Pineal Res.
42:1–11. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu HQ, Cheng XW, Xiao LL, et al:
Melatonin prevents oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
increase of myosin light chain kinase activation and expression in
HUVEC through ERK/MAPK signal transduction. J Pineal Res.
45:328–334. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang N, Liang J, Tian Y, et al: A novel
testis-specific GTPase serves as a link to proteasome biogenesis:
functional characterization of RhoS/RSA-14–44 in spermatogenesis.
Mol Biol Cell. 21:4312–4324. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hirase T and Node K: Endothelial
dysfunction as a cellular mechanism for vascular failure. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302:H499–H505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rossi JL, Ralay Ranaivo H, Patel F, et al:
Albumin causes increased myosin light chain kinase expression in
astrocytes via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Neurosci
Res. 89:852–861. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tinsley JH, Teasdale NR and Yuan SY:
Myosin light chain phosphorylation and pulmonary endothelial cell
hyperpermeability in burns. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
286:L841–L847. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Anssari-Benam A and Korakianitis T:
Atherosclerotic plaques:is endothelial shear stress the only
factor? Med Hypotheses. 81:235–239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takahashi M: Inflammatory cytokines in the
pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Nihon Rinsho. 69:30–33. 2011.(In
Japanese).
|
|
29
|
You JZ, Wang HB, Yang ZW, et al: Signal
transduction pathways involved in promotion of proliferation and
migration via p-ERK in high metastasis potential breast cancer
cells. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol. 22:1007–1013. 2006.
|
|
30
|
Costantini TW, Peterson CY, Kroll L, et
al: Role of p38 MAPK in burn-induced intestinal barrier breakdown.
J Surg Res. 156:64–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sewwrynek E: Melatonin and the
cardiovascular system. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 23:79–83. 2002.
|