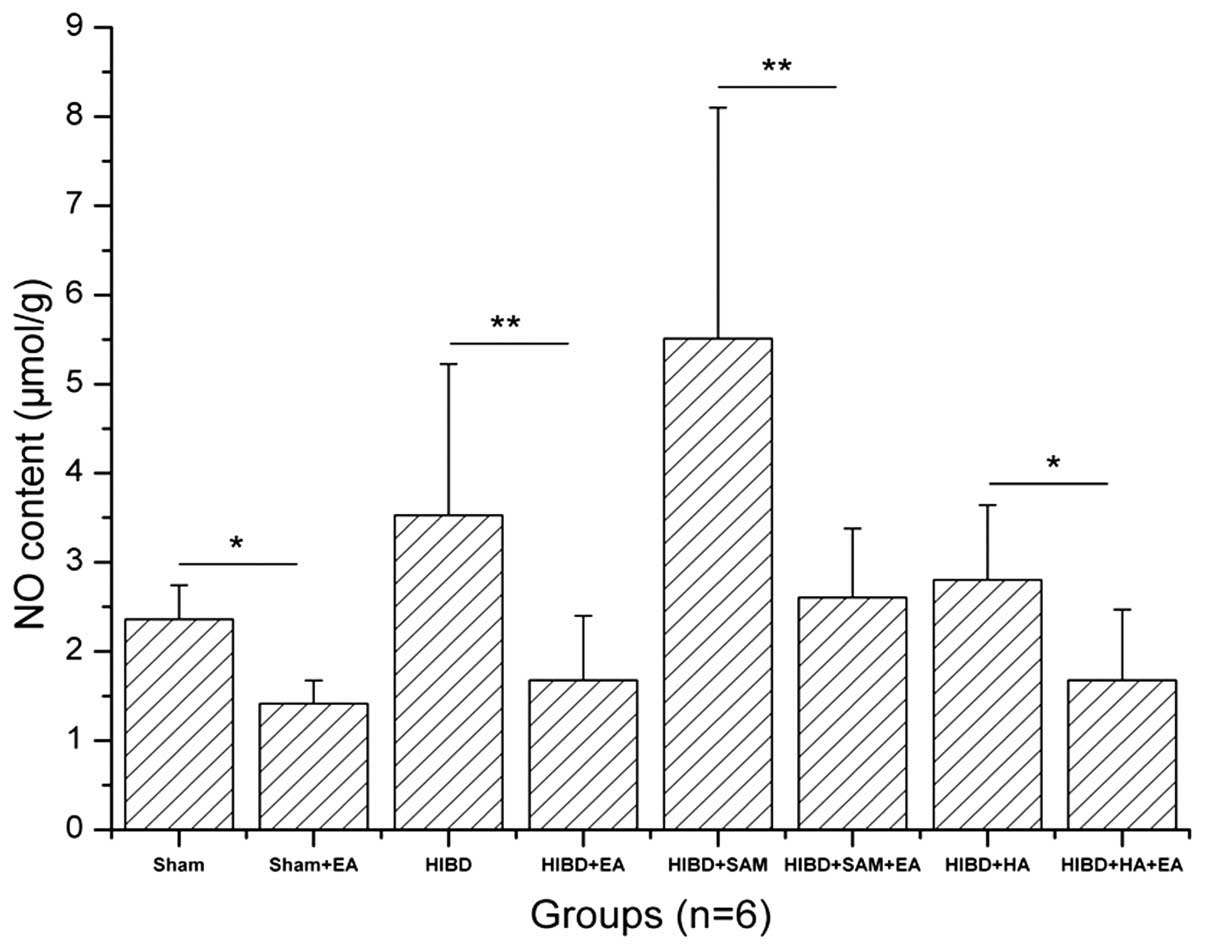
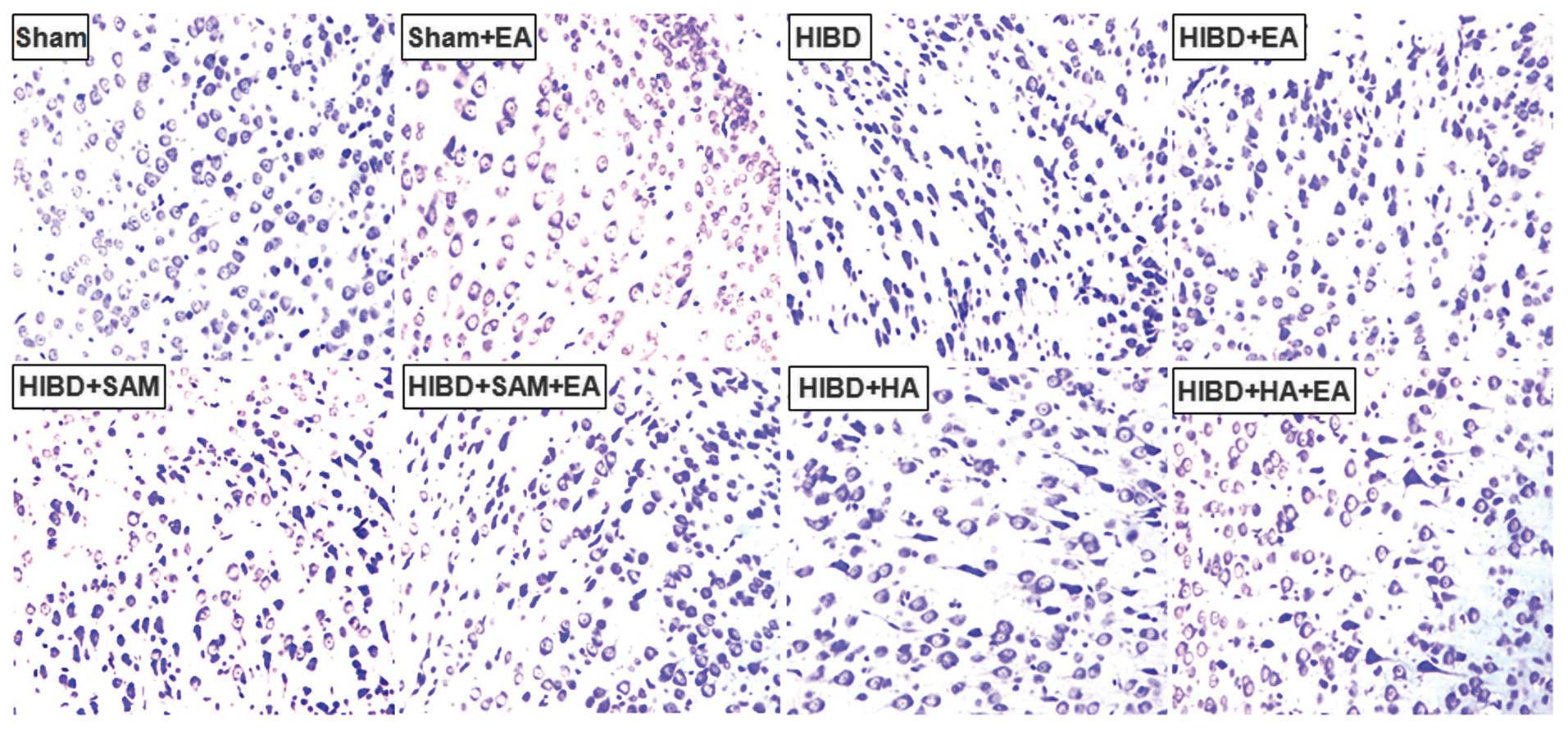
|
1
|
Kajimura M, Nakanishi T, Takenouchi T, et
al: Gas biology: Tiny molecules controlling metabolic systems.
Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 184:139–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Y, Zou LP, Du JB and Wong V:
Electro-acupuncture protects against hypoxic-ischemic brain-damaged
immature rat via hydrogen sulfide as a possible mediator. Neurosci
Lett. 485:74–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He J: Analysis on therapeutic effect of
acupuncture combined with hyperbaric oxygenation on delayed
encephalopathy in the patient of acute carbon monoxide poisoning.
Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 28:30–32. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ha Y, Kim M, Nah J, Suh M and Lee Y:
Measurements of location-dependent nitric oxide levels on skin
surface in relation to acupuncture point. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2012:7814602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ma SX, Li XY, Sakurai T and Pandjaitan M:
Evidence of enhanced non-enzymatic generation of nitric oxide on
the skin surface of acupuncture points: An innovative approach in
humans. Nitric Oxide. 17:60–68. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ignarro LJ, Buga GM, Wood KS, Byrns RE and
Chaudhuri G: Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and
released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 84:9265–9269. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Palmer RM, Ashton DS and Moncada S:
Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from l-arginine.
Nature. 333:664–666. 1988. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmidl D, Boltz A, Kaya S, et al: Role of
nitric oxide in optic nerve head blood flow regulation during
isometric exercise in healthy humans. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
54:1964–1970. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guarini G, Ohanyan VA, Kmetz JG, et al:
Disruption of trpv1-mediated coupling of coronary blood flow to
cardiac metabolism in diabetic mice: Role of nitric oxide and bk
channels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 303:H216–H223. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Phattanarudee S, Towiwat P, Maher TJ and
Ally A: Effects of medullary administration of a nitric oxide
precursor on cardiovascular responses and neurotransmission during
static exercise following ischemic stroke. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
91:510–520. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ito E, Matsuo R and Okada R: Involvement
of nitric oxide in memory formation in microbrains. Neurosci Lett.
541:1–3. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Martin LJ, Adams NA, Pan Y, Price A and
Wong M: The mitochondrial permeability transition pore regulates
nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis of neurons induced by target
deprivation. J Neurosci. 31:359–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsuji M, Higuchi Y, Shiraishi K, Kume T,
Akaike A and Hattori H: Protective effect of aminoguanidine on
hypoxic-ischemic brain damage and temporal profile of brain nitric
oxide in neonatal rat. Pediatr Res. 47:79–83. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fabian RH, Perez-Polo JR and Kent TA:
Perivascular nitric oxide and superoxide in neonatal cerebral
hypoxia-ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1809–H1814.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Zou LP and Du JB: Nitric
oxide-mediated neuronal functional recovery in hypoxic-ischemic
brain damaged rats subjected to electrical stimulation. Brain Res.
1383:324–328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gong QH, Shi XR, Hong ZY, Pan LL, Liu XH
and Zhu YZ: A new hope for neurodegeneration: Possible role of
hydrogen sulfide. J Alzheimers Dis. 24:173–182. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abe K and Kimura H: The possible role of
hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci.
16:1066–1071. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Edwards G, Félétou M and Weston AH:
Hydrogen sulfide as an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor
in rodent mesenteric arteries. Circ Res. 110:e13–e14. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mustafa AK, Sikka G, Gazi SK, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor
sulfhydrates potassium channels. Circ Res. 109:1259–1268. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu C, Gu X and Zhu YZ: Synthesis and
biological evaluation of novel leonurine-sprc conjugate as
cardioprotective agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 20:6942–6946. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu LF, Wong PT, Moore PK and Bian JS:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation
by inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in microglia.
J Neurochem. 100:1121–1128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim KM, Pae HO, Zhung M, et al:
Involvement of anti-inflammatory heme oxygenase-1 in the inhibitory
effect of curcumin on the expression of pro-inflammatory inducible
nitric oxide synthase in raw264.7 macrophages. Biomed Pharmacother.
62:630–636. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yanagimoto T, Toyota T, Matsuki N, Makino
Y, Uchiyama S and Ohwada T: Transnitrosation of thiols from
aliphatic n-nitrosamines: S-nitrosation and indirect generation of
nitric oxide. J Am Chem Soc. 129:736–737. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kovacs I and Lindermayr C: Nitric
oxide-based protein modification: Formation and site-specificity of
protein s-nitrosylation. Front Plant Sci. 4:1372013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Avolio A and Grassi G: Haemoglobin: Subtle
scavenger of nitric oxide and modulator of retinal blood flow. J
Hypertens. 31:661–662. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Badn W and Siesjö P: The dual role of
nitric oxide in glioma. Curr Pharm Des. 16:428–430. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang R, Huang ZN and Cheng JS:
Anticonvulsion effect of acupuncture might be related to the
decrease of neuronal and inducible nitric oxide synthases. Acupunct
Electrother Res. 25:137–143. 2000.
|
|
28
|
Jou NT and Ma SX: Responses of nitric
oxide-cgmp release in acupuncture point to electroacupuncture in
human skin in vivo using dermal microdialysis. Microcirculation.
16:434–443. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang XY, Li XJ, Li DL, Wang CR and Guo XP:
Progesterone exerts neuroprotective effect on hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy-induced brain damage via inhibition expression of
inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide production.
Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 28:253–254. 2622012.(In
Chinese).
|