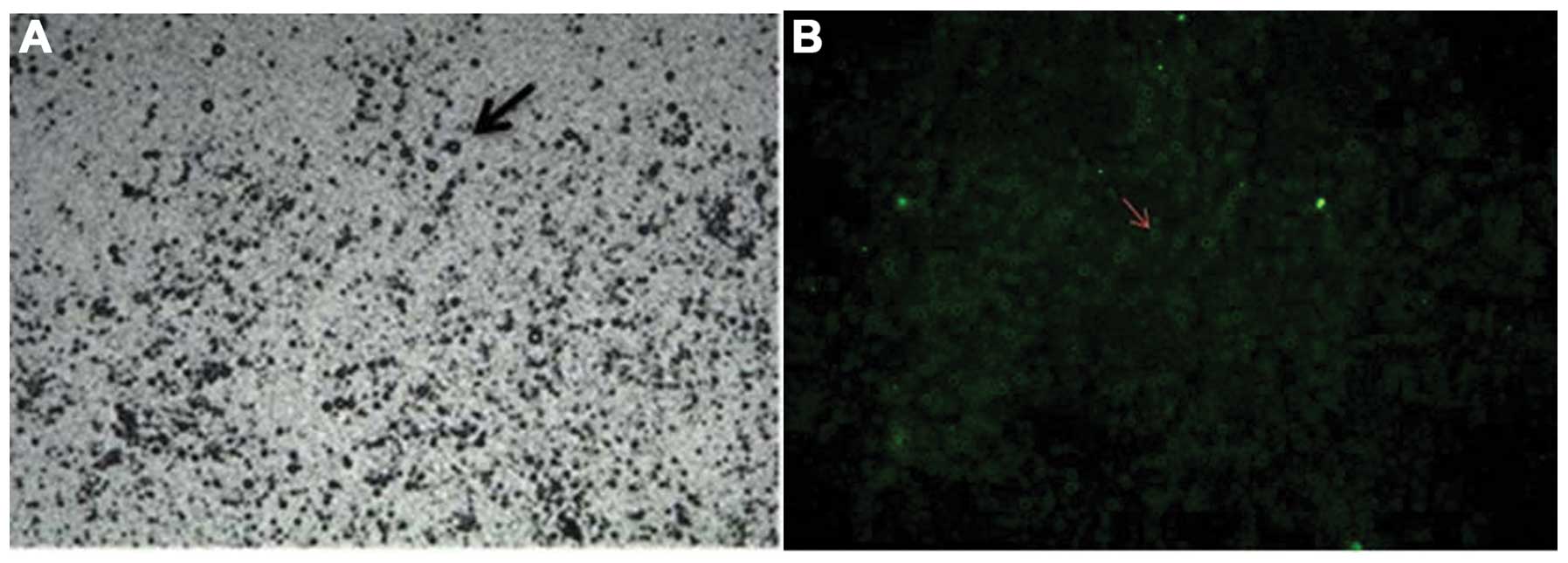
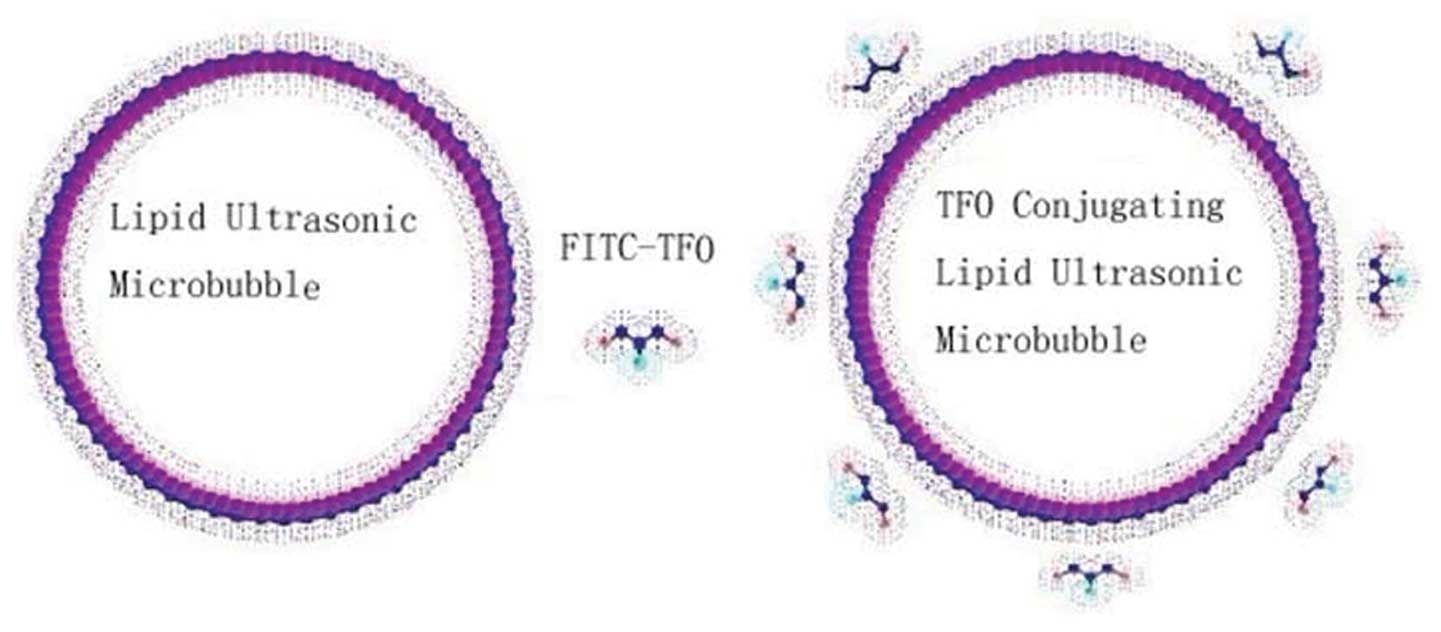
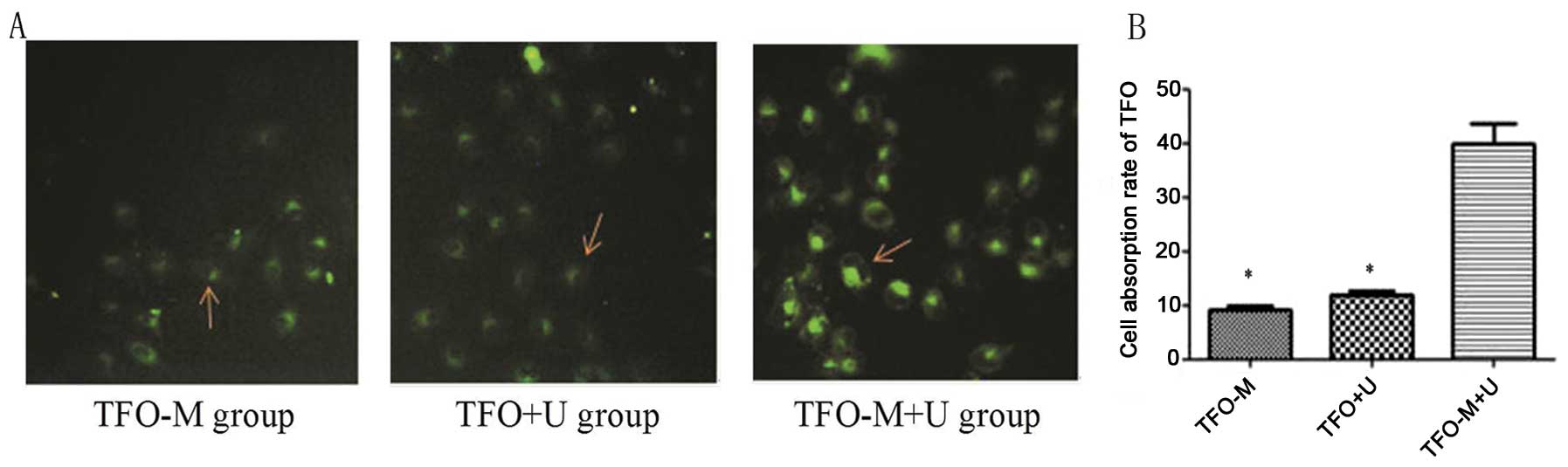
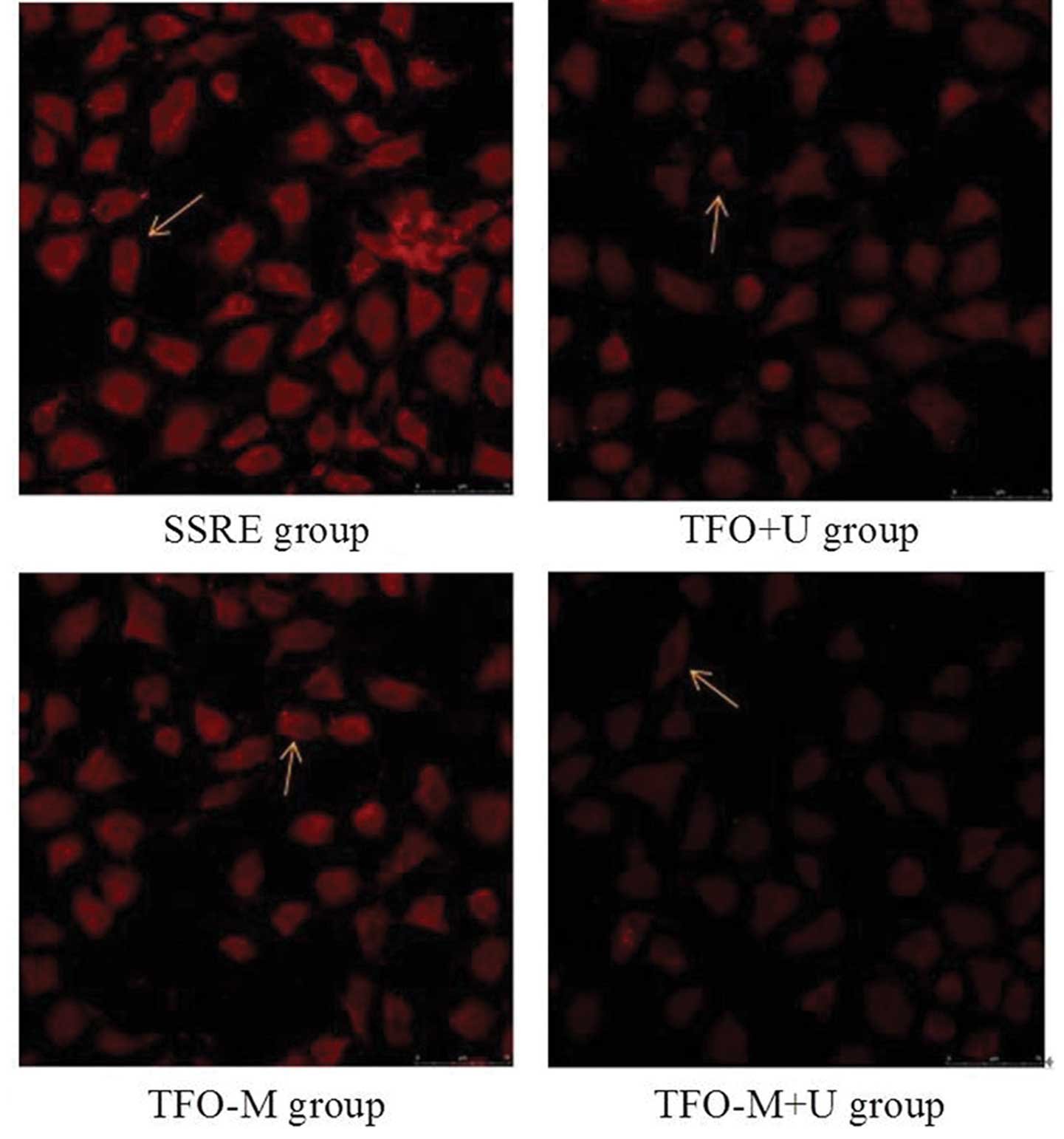
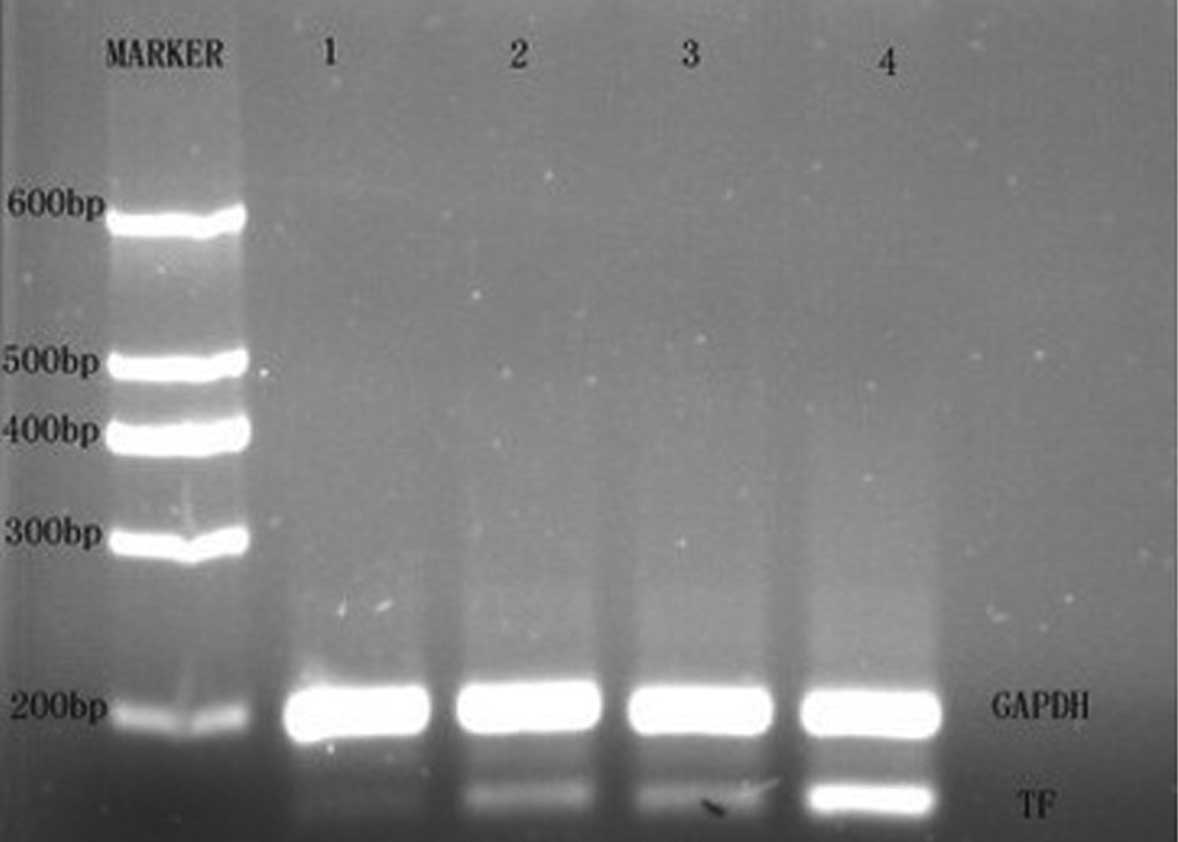
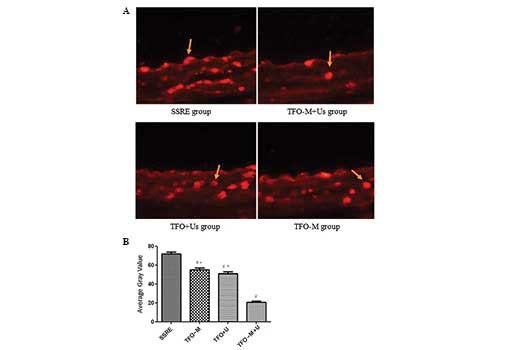
|
1
|
Yang N, Singh S and Mahato RI: Targeted
TFO delivery to hepatic stellate cells. J Control Release.
155:326–330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mukherjee A and Vasquez KM: Triplex
technology in studies of DNA damage, DNA repair, and mutagenesis.
Biochimie. 93:1197–1208. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chin JY and Glazer PM: Repair of DNA
lesions associated with triplex-forming oligonucleotides. Mol
Carcinog. 48:389–399. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Duca M, Vekhoff P, Oussedik K, Halby L and
Arimondo PB: The triple helix: 50 years later, the outcome. Nucleic
Acids Res. 36:5123–5138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seidman MM, Puri N, Majumdar A, et al: The
development of bioactive triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1058:119–127. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Guntaka RV, Varma BR and Weber KT:
Triplex-forming oligonucleotides as modulators of gene expression.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 35:22–31. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mahato RI, Cheng K and Guntaka RV:
Modulation of gene expression by antisense and antigene
oligodeoxynucleotides and small interfering RNA. Expert Opin Drug
Deliv. 2:3–28. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hernot S and Klibanov AL: Microbubbles in
ultrasound-triggered drug and gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
60:1153–1166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaneko OF and Willmann JK: Ultrasound for
molecular imaging and therapy in cancer. Quant Imaging Med Surg.
2:87–97. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Newman CM and Bettinger T: Gene therapy
progress and prospects: ultrasound for gene transfer. Gene Ther.
14:465–475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen ZY, Lin Y, Yang F, Jiang L and Ge Sp:
Gene therapy for cardiovascular disease mediated by ultrasound and
microbubbles. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 11:112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang HD, Tang J and Halliwell M:
Sonoporation, drug delivery, and gene therapy. Proc Inst Mech Eng
H. 224:343–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sboros V: Response of contrast agents to
ultrasound. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 60:1117–1136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van Wamel A, Kooiman K, Harteveld M, et
al: Vibrating microbubbles poking individual cells: drug transfer
into cells via sonoporation. J Control Release. 112:149–155. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sirsi SR and Borden MA: Advances in
ultrasound mediated gene therapy using microbubble contrast agents.
Theranostics. 2:1208–1222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tachibana K and Tachibana S: Albumin
microbubble echo-contrast material as an enhancer for ultrasound
accelerated thrombolysis. Circulation. 92:1148–1150. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Molina CA, Ribo M, Rubiera M, et al:
Microbubble administration accelerates clot lysis during continuous
2-MHz ultrasound monitoring in stroke patients treated with
intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke. 37:425–429. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Corti R and Fuster V: New understanding,
diagnosis, and prognosis of atherothrombosis and the role of
imaging. Am J Cardiol. 91:17A–26A. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taillefer R: Radiolabeled peptides in the
detection of deep venous thrombosis. Semin Nucl Med. 31:102–123.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leung K: Anti-ligand-induced binding sites
(LIBS) single-chain antibody conjugated to microbubbles. Molecular
Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) Bethesda (MD): National
Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013
|
|
21
|
Owens AP III and Mackman N: Tissue factor
and thrombosis: The clot starts here. Thromb Haemost. 104:432–439.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Malý MA, Tomasov P, Hájek P, et al: The
role of tisue factor in thrombosis and hemostasis. Physiol Res.
56:685–695. 2007.
|
|
23
|
Mackman N, Tilley RE and Key NS: Role of
the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation in hemostasis and
thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 27:1687–1693. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Resnick N, Yahav H, Khachigian LM, et al:
Endothelial gene regulation by laminar shear stress. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 430:155–164. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brooks AR, Lelkes PI and Rubanyi GM: Gene
expression profiling of vascular endothelial cells exposed to fluid
mechanical forces: relevance for focal susceptibility to
atherosclerosis. Endothelium. 11:45–57. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen BP, Li YS, Zhao Y, et al: DNA
microarray analysis of gene expression in endothelial cells in
response to 24-h shear stress. Physiol Genomics. 7:55–63. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
García-Cardeña G, Comander JI, Blackman
BR, Anderson KR and Gimbrone MA: Mechanosensitive endothelial gene
expression profiles: scripts for the role of hemodynamics in
atherogenesis? Ann NY Acad Sci. 947:1–6. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
McCormick SM, Eskin SG, McIntire LV, et
al: DNA microarray reveals changes in gene expression of shear
stressed human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 98:8955–8960. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dai G, Vaughn S, Zhang Y, et al:
Biomechanical forces in atherosclerosis-resistant vascular regions
regulate endothelial redox balance via phosphoinositol
3-kinase/Akt-dependent activation of Nrf2. Circ Res. 101:723–733.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McCormick SM, Frye SR, Eskin SG, et al:
Microarray analysis of shear stressed endothelial cells.
Biorheology. 40:5–11. 2003.
|
|
31
|
Passerini AG, Polacek DC, Shi C, et al:
Coexisting proin-flammatory and antioxidative endothelial
transcription profiles in a disturbed flow region of the adult
porcine aorta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:2482–2487. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hademenos GJ and Massoud TF: Biophysical
mechanisms of stroke. Stroke. 28:2067–2077. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Houston P, Dickson MC, Ludbrook V, et al:
Fluid shear stress induction of the tissue factor promoter in vitro
and in vivo is mediated by Egr-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
19:281–289. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Davies PF: Hemodynamic shear stress and
the endothelium in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Nat Clin Pract
Cardiovasc Med. 6:16–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chien S and Shyy JY: Effects of
hemodynamic forces on gene expression and signal transduction in
endothelial cells. Biol Bull. 194:390–391. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gimbrone MA Jr, Topper JN, Nagel T,
Anderson KR and Garcia-Cardeña G: Endothelial dysfunction,
hemodynamic forces, and atherogenesis. Ann NY Acad Sci.
902:230–239. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Resnick N, Yahav H, Shay-Salit A, et al:
Fluid shear stress and the vascular endothelium: for better and for
worse. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 81:177–199. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chiu JJ, Usami S and Chien S: Vascular
endothelial responses to altered shear stress: pathologic
implications for atherosclerosis. Ann Med. 41:19–28. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chien S: Role of shear stress direction in
endothelial mechanotransduction. Mol Cell Biomech. 5:1–8.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
García-Cardeña G and Gimbrone MA Jr:
Biomechanical modulation of endothelial phenotype: implications for
health and disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 176:79–95. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li QN, Yin DJ, Dai GM and Zheng J: The
affinity study of phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. Modern
Rehabilitation. 6:46–47. 49:2002
|
|
42
|
Li Q, Ying D, Dai G and Zheng J: Synthesis
of a triple helix-forming phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides
and its effects on coagulation activity of tissue factor (TF) and
TF gene expression in endothelial cells. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng
Xue Za Zhi. 20:71–75. 902003.(In Chinese).
|
|
43
|
Yang YM, Li QN, Ying DJ, et al:
Triplex-forming oligonucleotide inhibits the expression of tissue
factor gene in endothelial cells induced by the blood flow shear
stress in rats. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 41:808–813. 2006.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin MC, Almus-Jacobs F, Chen HH, et al:
Shear stress induction of the tissue factor gene. J Clin Invest.
99:737–744. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Silberman M, Barac YD, Yahav H, et al:
Shear stress-induced transcriptional regulation via hybrid
promoters as a potential tool for promoting angiogenesis.
Angiogenesis. 12:231–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ali MH and Schumacker PT: Endothelial
responses to mechanical stress: where is the mechanosensor? Crit
Care Med. 30(Suppl 5): S198–S206. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Davies PF, Polacek DC, Shi C and Helmke
BP: The convergence of haemodynamics, genomics, and endothelial
structure in studies of the focal origin of atherosclerosis.
Biorheology. 39:299–306. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Helmke BP and Davies PF: The cytoskeleton
under external fluid mechanical forces: hemodynamic forces acting
on the endothelium. Ann Biomed Eng. 30:284–296. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Khachigian LM, Anderson KR, Halnon NJ, et
al: Egr-1 is activated in endothelial cells exposed to fluid shear
stress and interacts with a novel shear-stress-response element in
the PDGF A-chain promoter. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
17:2280–2286. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Urbich C, Stein M, Reisinger K, et al:
Fluid shear stress-induced transcriptional activation of the
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 gene requires
Sp1-dependent DNA binding. FEBS Lett. 535:87–93. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Houston P, White BP, Campbell CJ and
Braddock M: Delivery and expression of fluid shear stress-inducible
promoters to the vessel wall: applications for cardiovascular gene
therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 10:3031–3044. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Castle J, Butts M, Healey A, et al:
Ultrasound-mediated targeted drug delivery: recent success and
remaining challenges. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
304:H350–H357. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Brooks AR, Lelkes PI and Rubanyi GM: Gene
expression profiling of vascular endothelial cells exposed to fluid
mechanical forces: relevance for focal susceptibility to
atherosclerosis. Endothelium. 11:45–57. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|