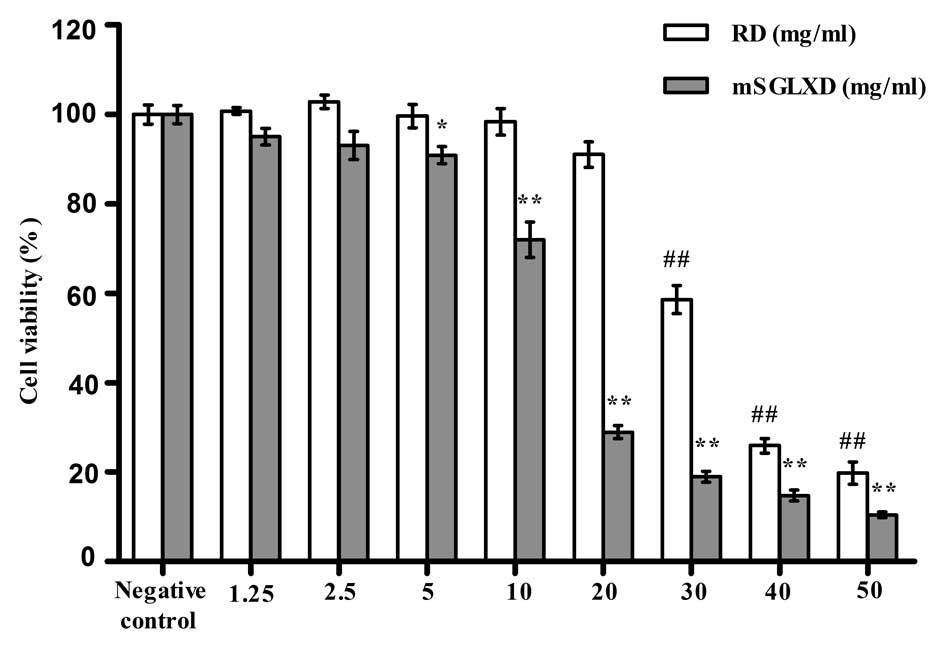
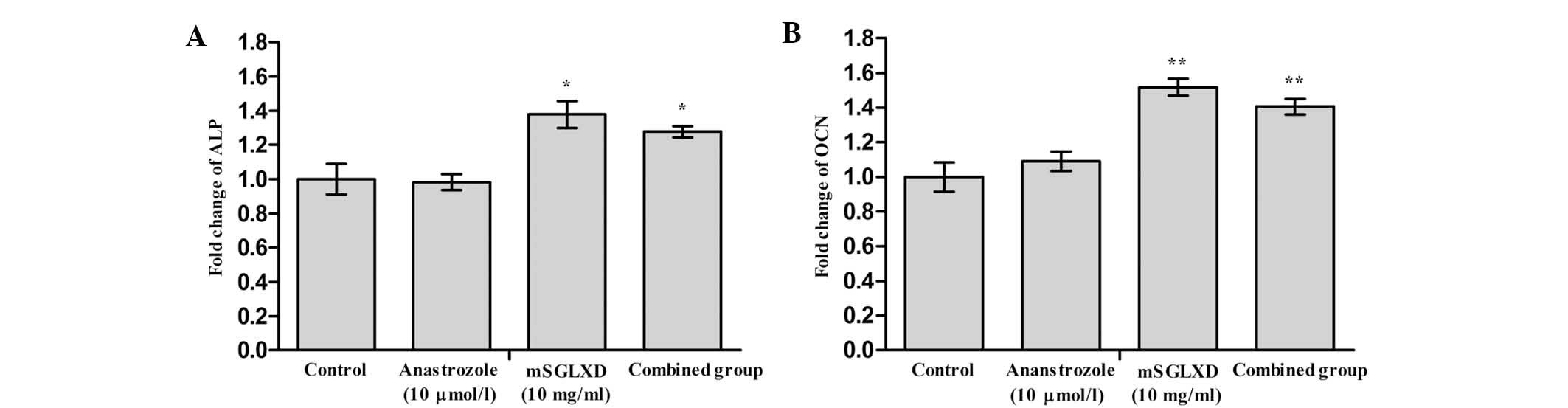
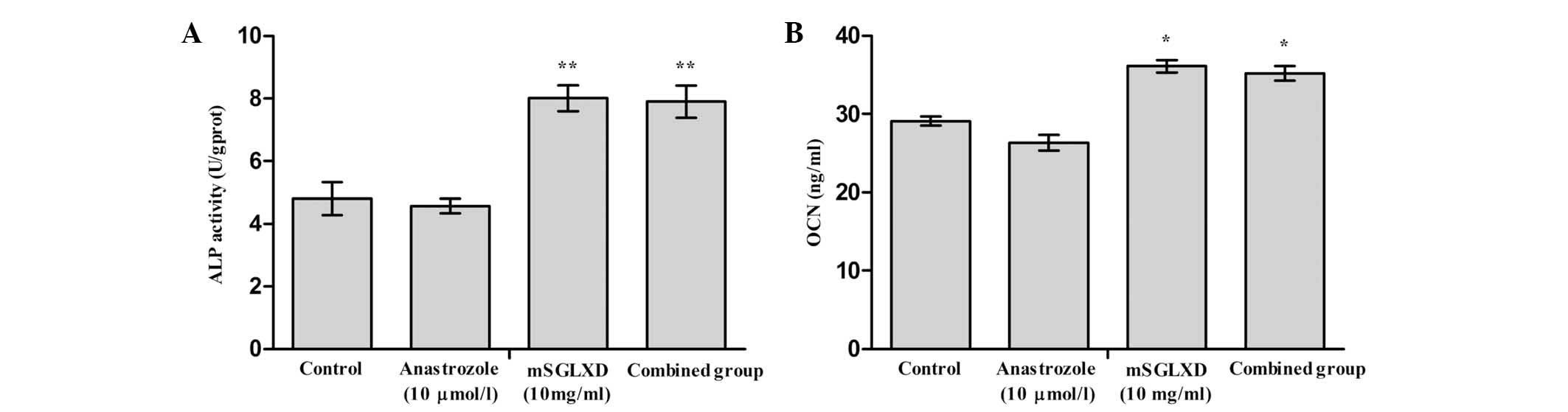
|
1
|
Kwong A, Cheung PS, Wong Y, et al: The
acceptance and feasibility of breast cancer screening in the East.
Breast. 17:42–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Clemons M and Goss P: Estrogen and the
risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 344:276–285. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brueggemeier RW, Hackett JC and Diaz-Cruz
ES: Aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of breast cancer. Endocr
Rev. 26:331–345. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smith IE and Dowsett M: Aromatase
inhibitors in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 348:2431–2442. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Geisler J, Haynes B, Anker G, Dowsett M
and Lønning PE: Influence of letrozole and anastrozole on total
body aromatization and plasma estrogen levels in postmenopausal
breast cancer patients evaluated in a randomized, cross-over study.
J Clin Oncol. 20:751–757. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geisler J, King N, Anker G, Ornati G, Di
Salle E, Lønning PE and Dowsett M: In vivo inhibition of
aromatization by exemestane, a novel irreversible aromatase
inhibitor, in postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer
Res. 4:2089–2093. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miller WR and Dixon JM: Local endocrine
effects of aromatase inhibitors within the breast. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 79:93–102. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Coombes RC, Hall E, Gibson LJ, et al:
Intergroup Exemestane Study: A randomized trial of exemestane after
two to three years of tamoxifen therapy in postmenopausal women
with primary breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 350:1081–1092. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cuzick J, Sestak I, Baum M, Buzdar A,
Howell A, Dowsett M and Forbes JF: ATAC/LATTE investigators: Effect
of anastrozole and tamoxifen as adjuvant treatment for early-stage
breast cancer: 10-year analysis of the ATAC trial. Lancet Oncol.
11:1135–1141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thürlimann B, Keshaviah A, Coates AS, et
al: Breast International Group (BIG) 1–98 Collaborative Group: A
comparison of letrozole and tamoxifen in postmenopausal women with
early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:2747–2757. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Coates AS, Keshaviah A, Thürlimann B, et
al: Five years of letrozole compared with tamoxifen as initial
adjuvant therapy for postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive
early breast cancer: update of study BIG 1–98. J Clin Oncol.
25:486–492. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nabholtz JM, Bonneterre J, Buzdar A,
Robertson JF and Thürlimann B: Anastrozole (Arimidex) versus
tamoxifen as first-line therapy for advanced breast cancer in
postmenopausal women: survival analysis and updated safety results.
Eur J Cancer. 39:1684–1689. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perez EA: Safety profiles of tamoxifen and
the aromatase inhibitors in adjuvant therapy of hormone-responsive
early breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 18(Suppl 8): viii26–viii35. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ettinger B, Pressman A, Sklarin P, Bauer
DC, Cauley JA and Cummings SR: Associations between low levels of
serum estradiol, bone density, and fractures among elderly women:
the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
83:2239–2243. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kenny AM and Raisz LG: Mechanisms of bone
remodeling: implications for clinical practice. J Reprod Med. 47(1
Suppl): 63–70. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ernst M, Schmid C and Froesch ER: Enhanced
osteoblast proliferation and collagen gene expression by estradiol.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:2307–2310. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kameda T, Mano H, Yuasa T, et al: Estrogen
inhibits bone resorption by directly inducing apoptosis of the
bone-resorbing osteoclasts. J Exp Med. 186:489–495. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pant S and Shapiro CL: Aromatase
inhibitor-associated bone loss: clinical considerations. Drugs.
68:2591–2600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McCloskey E: Effects of third-generation
aromatase inhibitors on bone. Eur J Cancer. 42:1044–1051. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lester JE, Dodwell D, Purohit OP, et al:
Prevention of anastrozole-induced bone loss with monthly oral
ibandronate during adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6336–6342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brufsky AM, Bosserman LD, Caradonna RR, et
al: Zoledronic acid effectively prevents aromatase
inhibitor–associated bone loss in postmenopausal women with early
breast cancer receiving adjuvant letrozole: Z-FAST study 36-month
follow-up results. Clin Breast Cancer. 9:77–85. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eidtmann H, de Boer R, Bundred N, et al:
Efficacy of zoledronic acid in postmenopausal women with early
breast cancer receiving adjuvant letrozole: 36-month results of the
ZO-FAST Study. Ann Oncol. 21:2188–2194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Llombart A, Frassoldati A, Paija O, et al:
Immediate administration of zoledronic acid reduces aromatase
inhibitor-associated bone loss in postmenopausal women with early
breast cancer: 12-month analysis of the E-ZO-FAST trial. Clin
Breast Cancer. 12:40–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ruggiero SL, Mehrotra B, Rosenberg TJ and
Engroff SL: Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with the use of
bisphosphonates: a review of 63 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
62:527–534. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bamias A, Kastritis E, Bamia C, et al:
Osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer after treatment with
bisphosphonates: incidence and risk factors. J Clin Oncol.
23:8580–8587. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee SH, Chang SS, Lee M, Chan RC and Lee
CC: Risk of osteonecrosis in patients taking bisphosphonates for
prevention of osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Osteoporos Int. 25:1131–1139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xue D, Sun H and Li PP: Long-term chinese
herbs decoction administration for management of hot flashes
associated with endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients. Chin J
Cancer Res. 23:74–78. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu CX and Li PP: Anti-tumor effect of
Shu-Gan-Liang-Xue decoction combined with tamoxifen on
estrogen-dependent breast cancer. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae.
14:31–34. 2008.
|
|
29
|
Zhang Y and Li PP: Evaluation of
estrogenic potential of Shu-Gan-Liang-Xue Decoction by
dual-luciferase reporter based bioluminescent measurements in
vitro. J Ethnopharmacol. 126:345–349. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Zhang S, Lu X, Zheng S, Li F and
Xiong Z: Metabonomic study on the anti-osteoporosis effect of
Rhizoma Drynariae and its action mechanism using ultra-performance
liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Ethnopharmacol.
139:311–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wong RW, Rabie B, Bendeus M and Hägg U:
The effects of Rhizoma Curculiginis and Rhizoma Drynariae extracts
on bones. Chin Med. 2:132007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pang WY, Wang XL, Wong KC, Leung PC, Yao
XS and Wong MS: Total flavonoid fraction of Rhizoma Drynaria
improves bone properties in ovariectomized mice and exerts
estrogen-like activities in rat osteoblast-like (UMR-106) cells.
JFood Drug Anal. 20:265–269. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Chang EJ, Lee WJ, Cho SH and Choi SW:
Proliferative effects of flavan-3-ols and propelargonidins from
rhizomes of Drynaria fortunei on MCF-7 and osteoblastic cells. Arch
Pharm Res. 26:620–630. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Quarles LD, Yohay DA, Lever LW, Caton R
and Wenstrup RJ: Distinct proliferative and differentiated stages
of murine MC3T3-E1 cells in culture: An in vitro model of
osteoblast development. J Bone Miner Res. 7:683–692. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kim EJ, Bu SY, Sung MK and Choi MK:
Effects of silicon on osteoblast activity and bone mineralization
of MC3T3-E1 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 152:105–112. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Peeters PH, Keinan-Boker L, van der Schouw
YT and Grobbee DE: Phytoestrogens and breast cancer risk. Review of
the epidemiological evidence. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 77:171–183.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adlercreutz H: Phyto-oestrogens and
cancer. Lancet Oncol. 3:364–373. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Keinan-Boker L, van Der Schouw YT, Grobbee
DE and Peeters PH: Dietary phytoestrogens and breast cancer risk.
Am J Clin Nutr. 79:282–288. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Trock BJ, Hilakivi-Clarke L and Clarke R:
Meta-analysis of soy intake and breast cancer risk. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 98:459–471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Christenson RH: Biochemical markers of
bone metabolism: an overview. Clin Biochem. 30:573–593. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hlaing TT and Compston JE: Biochemical
markers of bone turnover - uses and limitations. Ann Clin Biochem.
51(Pt 2): 189–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Speirs V, Walton DS, Hall MC and Atkin SL:
In vivo and in vitro expression of steroid-converting enzymes in
human breast tumours: associations with interleukin-6. Br J Cancer.
81:690–695. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fu XS and Li PP: Shu-Gan-Liang-Xue
decoction simultaneously down-regulates expressions of aromatase
and steroid sulfatase in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer
cells. Chin J Cancer Res. 23:208–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Seeman E and Delmas PD: Bone quality - the
material and structural basis of bone strength and fragility. N
Engl J Med. 354:2250–2261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|