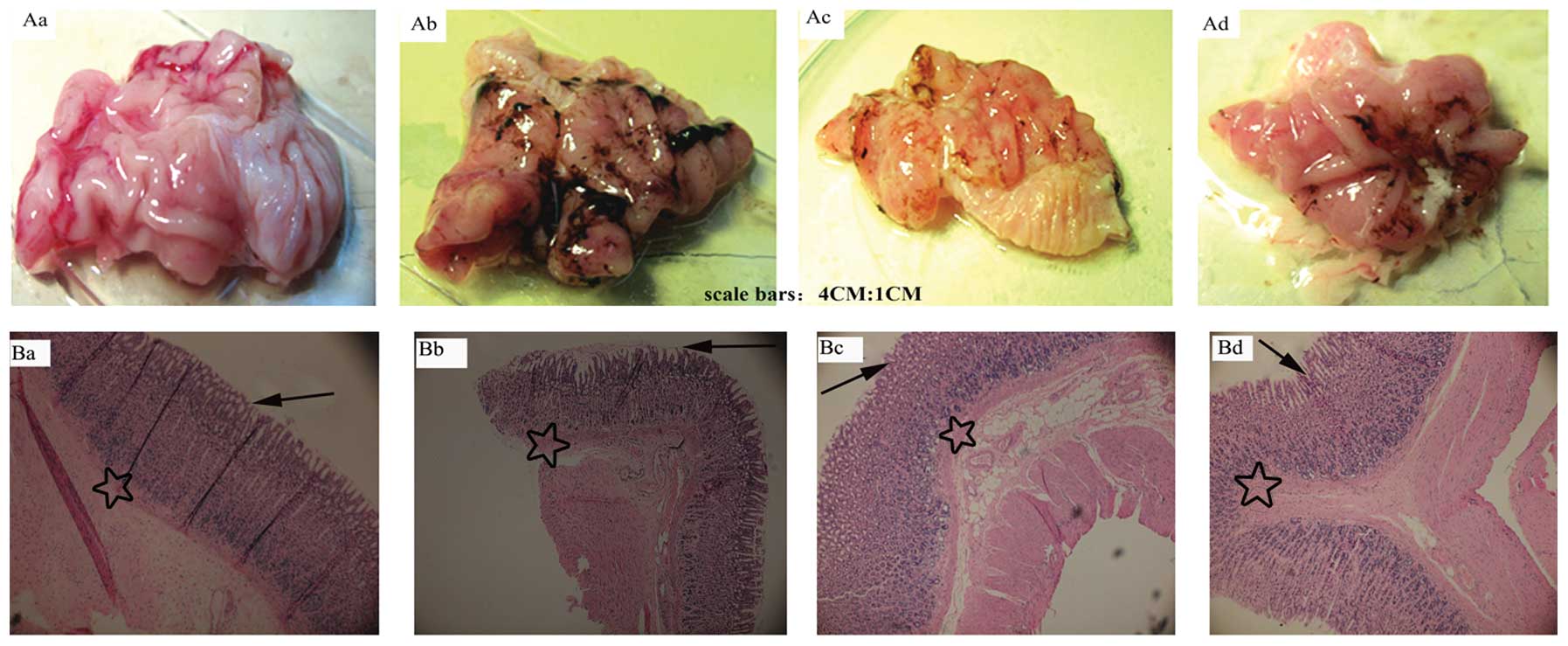
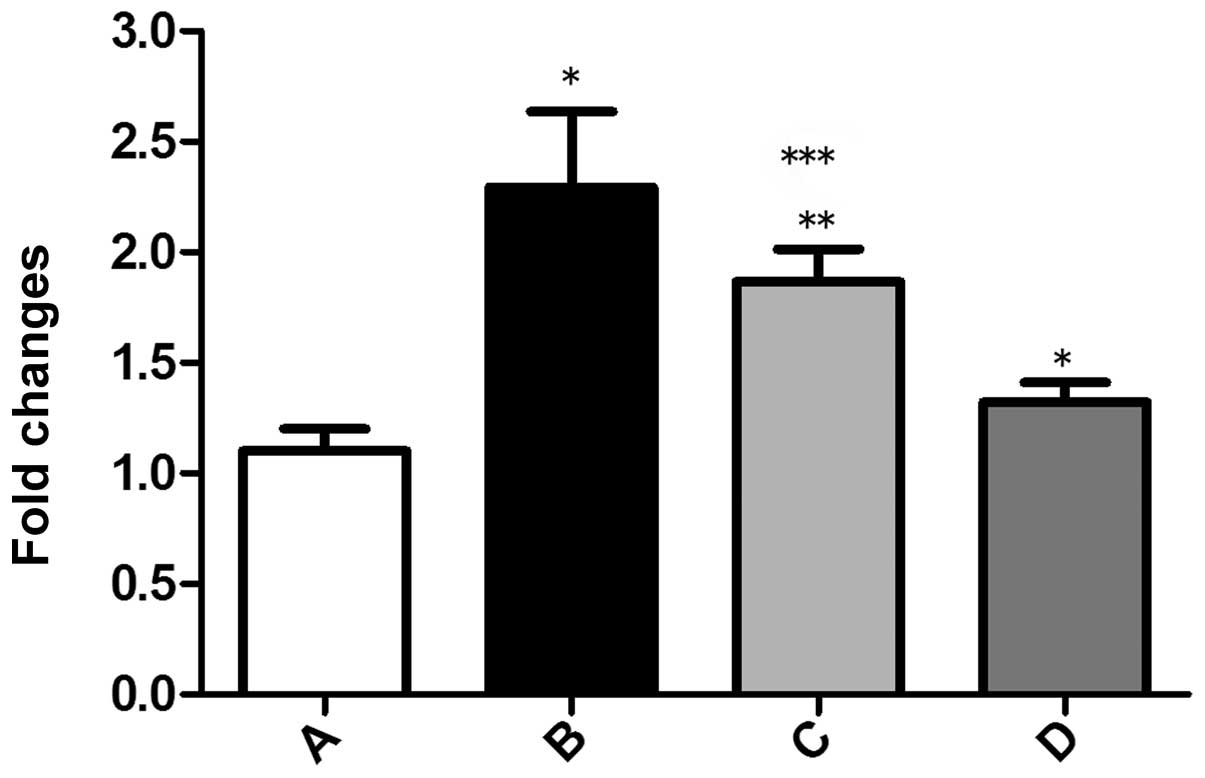
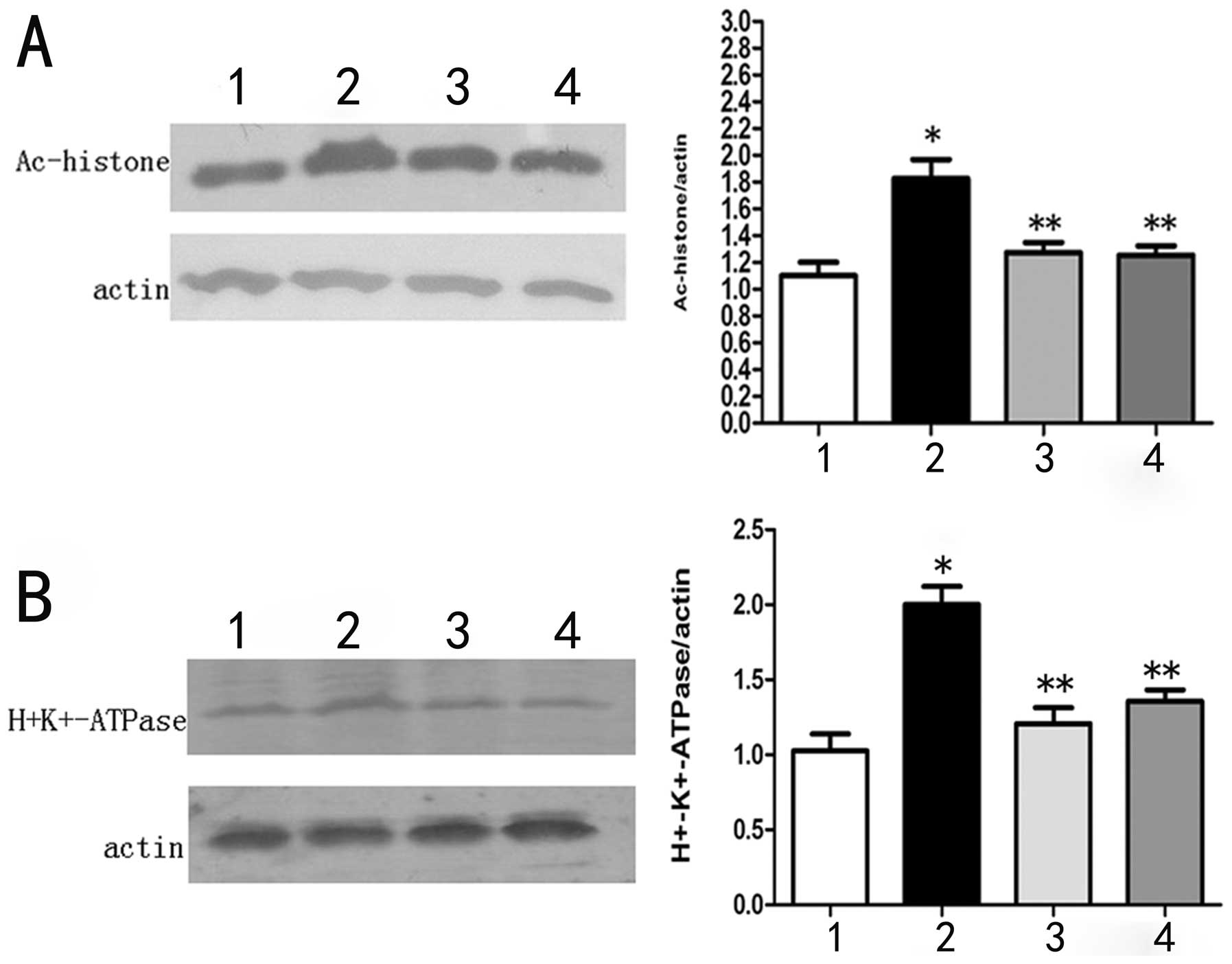
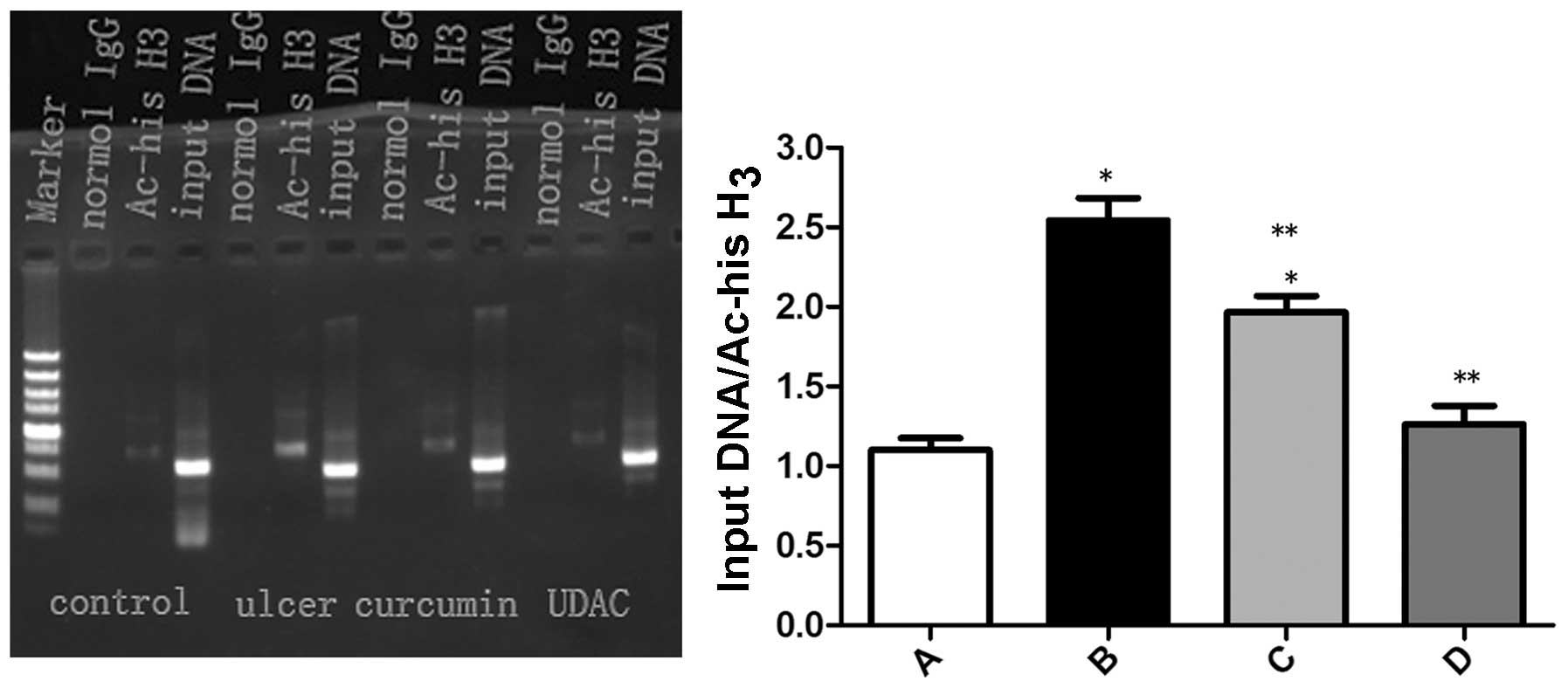
|
1
|
Gold BD, Colletti RB, Abbott M, et al:
Helicobacter pylori infection in children: recommendations for
diagnosis and treatment. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 31:490–497.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
McCullough P and Benson D:
Acid-suppressive medication and hospital-acquired pneumonia. JAMA.
302:1415–1417. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ali T, Roberts DN and Tierney WM:
Long-term safety concerns with proton pump inhibitors. Am J Med.
122:896–903. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hassall E, Owen D, Kerr W, et al: Gastric
histology in children treated with proton pump inhibitors long
term, with emphasis on enterochromaffin cell-like hyperplasia.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 33:829–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thong-Ngam D, Choochuai S, Patumraj S,
Chayanupatkul M and Klaikeaw N: Curcumin prevents
indomethacin-induced gastropathy in rats. World J Gastroenterol.
18:1479–1484. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma AV, Ganguly K, Paul S, Maulik N and
Swarnakar S: Curcumin heals indomethacin-induced gastric ulceration
by stimulation of angiogenesis and restitution of collagen fibers
via VEGF and MMP-2 mediated signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal.
16:351–362. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu L, Sun L, Wu Q, et al: Curcumin loaded
polymeric micelles inhibit breast tumor growth and spontaneous
pulmonary metastasis. Int J Pharm. 443:175–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shehzad A, Rehman G and Lee YS: Curcumin
in inflammatory diseases. Biofactors. 39:69–77. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Villaflores OB, Chen YJ, Chen CP, Yeh JM
and Wu TY: Effects of curcumin and demethoxycurcumin on amyloid-β
precursor and tau proteins through the internal ribosome entry
sites: a potential therapeutic for Alzheimer’s disease. Taiwan J
Obstet Gynecol. 51:554–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mahattanadul S, Nakamura T,
Panichayupakaranant P, et al: Comparative antiulcer effect of
bisdemethoxycurcumin and curcumin in a gastric ulcer model system.
Phytomedicine. 16:342–351. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Siddaraju MN and Dharmesh SM: Inhibition
of gastric H(+), K(+)-ATPase and Helicobacter pylori growth by
phenolic antioxidants of Curcuma amada. J Agric Food Chem.
55:7377–7386. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang W and Kone BC: NF-kappaB inhibits
transcription of the H(+)-K(+)-ATPase alpha(2)-subunit gene: role
of histone deacetylases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 283:F904–F911.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Sun H, Pan B, et al: Inhibition of
histone acetylation by curcumin reduces alcohol-induced expression
of heart development-related transcription factors in cardiac
progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 424:593–596. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Puglia C, Frasca G, Musumeci T, et al:
Curcumin loaded NLC induces histone hypoacetylation in the CNS
after intraperitoneal administration in mice. Eur J Pharm Biopharm.
81:288–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li-jun J, Zhi-feng L, Mei Li, et al:
Preventive and therapeutic effects of curcumin on gastric ulcer in
rats with stress. Journal of Applied Clinical Pediatrics.
6:451–453. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Guth PH and Paulsen G: Aspirin-induced
gastric injury in the rat: histologic changes and sucralfate
cytoprotection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 184:423–428. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Spicer Z, Miller ML, Andringa A, et al:
Stomachs of mice lacking the gastric H,K-ATPase alpha-subunit have
achlorhydria, abnormal parietal cells, and ciliated metaplasia. J
Biol Chem. 275:21555–21565. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jackson SJ, Murphy LL, Venema RC,
Singletary KW and Young AJ: Curcumin binds tubulin, induces mitotic
catastrophe, and impedes normal endothelial cell proliferation.
Food Chem Toxicol. 60:431–438. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun J, Han J, Zhao Y, Zhu Q and Hu J:
Curcumin induces apoptosis in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-treated
HaCaT cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 13:170–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mahattanadul S, Reanmongkol W, Yano S, et
al: Preventive and curative effects of curcumin on the development
of gastric inflammatory diseases in rats. J Nat Med. 60:191–197.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li YM, Lu GM, Zou XP, et al: Dynamic
functional and ultrastructural changes of gastric parietal cells
induced by water immersion-restraint stress in rats. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:3368–3372. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tuorkey M and Karolin K: Anti-ulcer
activity of curcumin on experimental gastric ulcer in rats and its
effect on oxidative stress/antioxidant, IL-6 and enzyme activities.
Biomed Environ Sci. 22:488–495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Huang J, Plass C and Gerhauser C: Cancer
chemoprevention by targeting the epigenome. Curr Drug Targets.
12:1925–1956. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kotb MA: Molecular mechanisms of
ursodeoxycholic acid toxicity & side effects: ursodeoxycholic
acid freezes regeneration & induces hibernation mode. Int J Mol
Sci. 13:8882–8914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Balasubramanyam K, Varier RA, Altaf M, et
al: Curcumin, a novel p300/CREB-binding protein-specific inhibitor
of acetyltransferase, represses the acetylation of
histone/nonhistone proteins and histone acetyltransferase-dependent
chromatin transcription. J Biol Chem. 279:51163–51171. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mei X, Xu D and Xu S, Zheng Y and Xu S:
Novel role of Zn(II)-curcumin in enhancing cell proliferation and
adjusting proinflammatory cytokine-mediated oxidative damage of
ethanol-induced acute gastric ulcers. Chem-Biol Interact.
197:31–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Icardi L, De Bosscher K and Tavernier J:
The HAT/HDAC interplay: multilevel control of STAT signaling.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 23:283–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang J, Plass C and Gerhauser C: Cancer
chemoprevention by targeting the epigenome. Curr Drug Targets.
12:1925–1956. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Buro LJ, Shah S and Henriksen MA:
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to assay dynamic histone
modification in activated gene expression in human cells. J Vis
Exp. 29:20532010.
|
|
30
|
Pillai S and Chellappan SP: ChIP on chip
assays: genome-wide analysis of transcription factor binding and
histone modifications. Methods Mol Biol. 523:341–366. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|