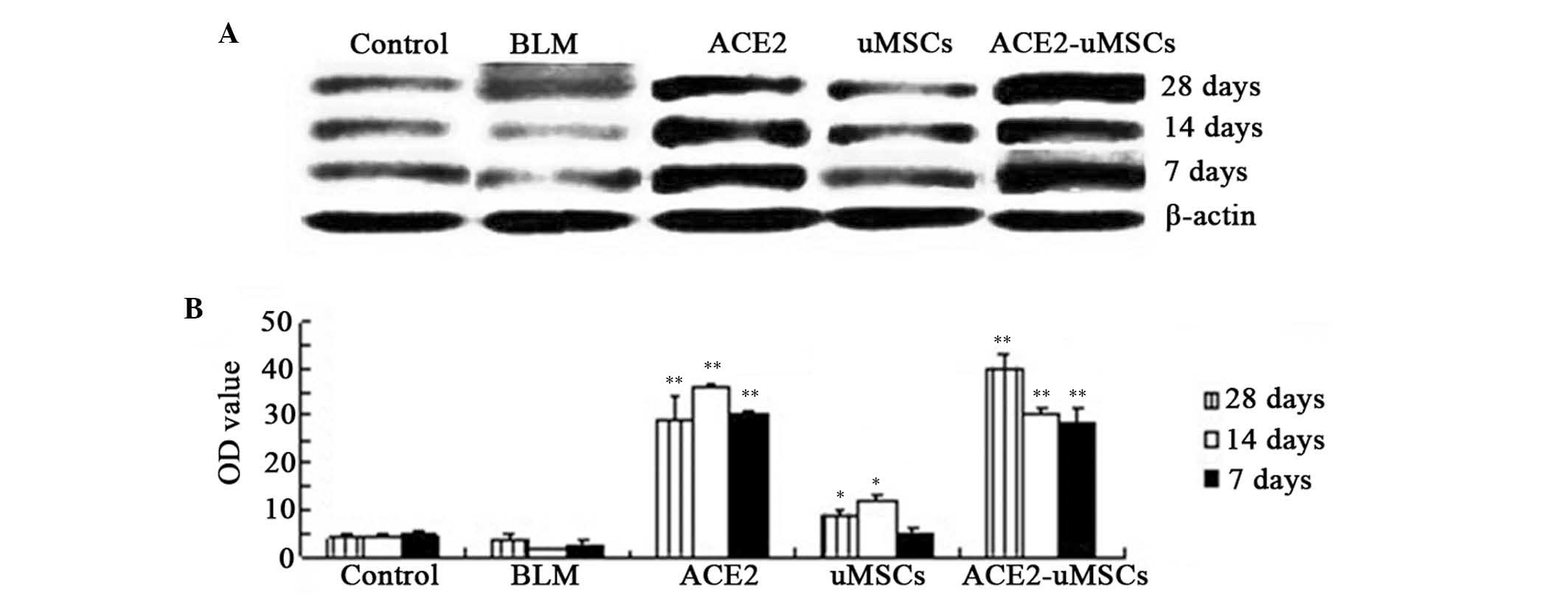
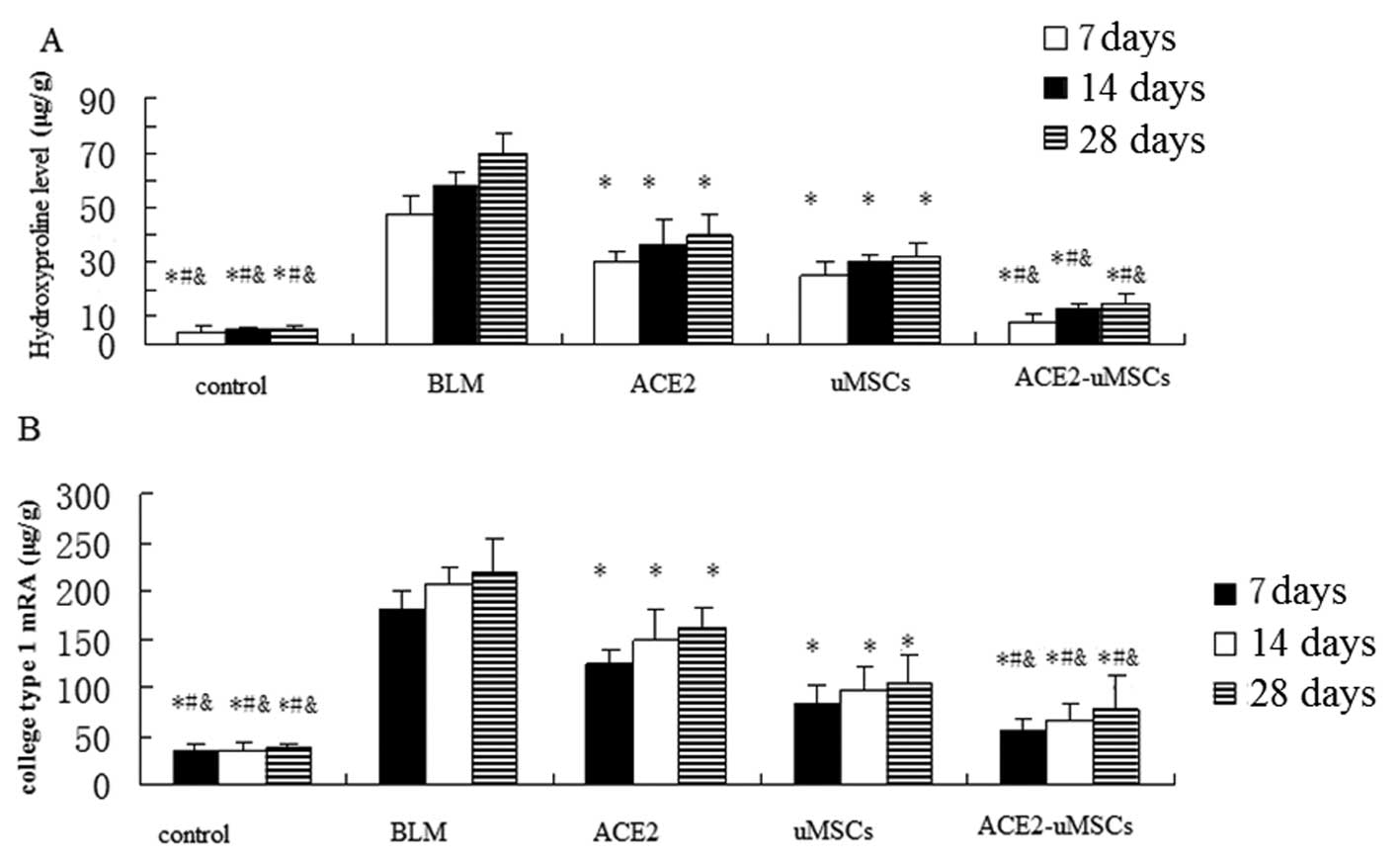
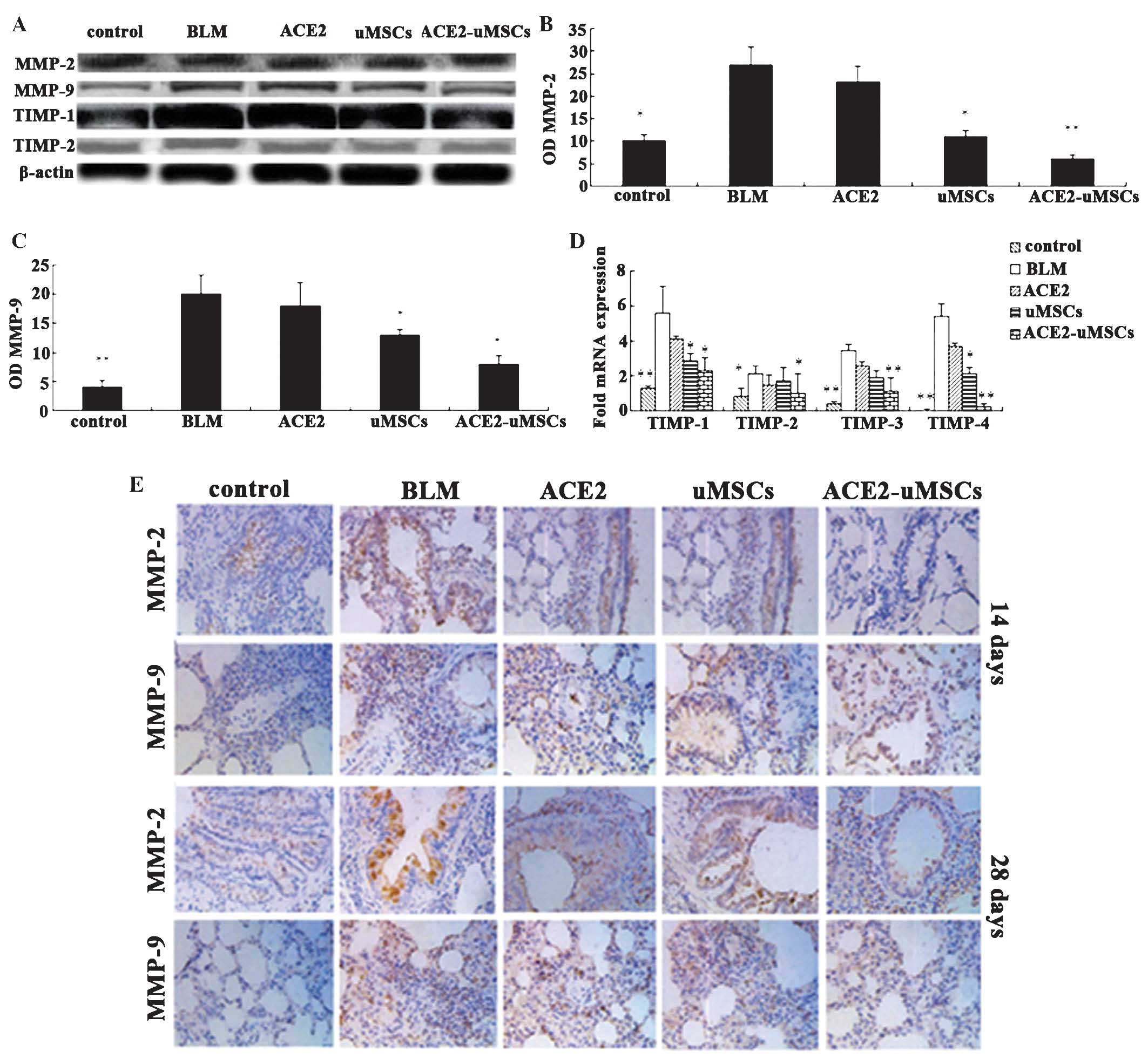
|
1
|
Bakowitz M, Bruns B and McCunn M: Acute
lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome in the
injured patient. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 20:542012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wada T, Jesmin S, Gando S, et al: The role
of angiogenic factors and their soluble receptors in acute lung
injury (ALI)/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) associated
with critical illness. J Inflamm (Lond). 10:62013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hayes M, Curley G, Ansari B and Laffey JG:
Clinical review: Stem cell therapies for acute lung injury/acute
respiratory distress syndrome - hope or hype? Crit Care.
16:2052012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Walkey AJ, Summer R, Ho V and Alkana P:
Acute respiratory distress syndrome: epidemiology and management
approaches. Clin Epidemiol. 4:159–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kumar P, Goldstraw P, Yamada K, et al:
Pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer: risk and benefit analysis of
pulmonary resection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surq. 125:1231–1237.
2003.
|
|
6
|
Perkins GD, Gao F and Thickett DR: In vivo
and in vitro effects of salbutamol on alveolar epithelial repair in
acute lung injury. Thorax. 63:215–220. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Corbel M, Belleguic E, Biochot V and
Lagente V: Involvement of gelatinases (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in the
development of airway inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis. Cell
Biol Toxicol. 18:51–61. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hayes M, Curley G and Laffey JG:
Mesenchymal stem cells - a promising therapy for acute respiratory
distress syndrome. F1000 Med Rep. 4:22012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krause DS, Theise ND, Collector MI, et al:
Multi-organ, multi-lineage engraftment by a single bone
marrow-derived stem cell. Cell. 105:369–377. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Li D, Liu X, Tang S and Wei F: Human
umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce systemic inflammation
and attenuate LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. J Inflamm
(Lond). 9:332012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fong CY, Gauthaman K, Cheyyatraivendran S,
Lin HD, Biswas A and Bongso A: Human umbilical cord Wharto’s jelly
stem cells and its conditioned medium support hematopoietic stem
cell expansion ex vivo. J Cell Biochem. 113:658–668. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, et al: A
novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2)
converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ Res. 87:E1–E9.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tikellis C and Thomas M:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a key modulator of the
renin angiotensin system in health and disease. Int J Pept.
2012:2562942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uhal BD, Li X, Xue A, Gao X and
Abdul-Hafez A: Regulation of alveolar epithelial cell survival by
the ACE-2/angiotensin 1–7/Mas axis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 301:L269–L274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oudit GY, Kassiri Z, Patel MP, et al:
Angiotensin II-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation mediate
the age-dependent cardiomyopathy in ACE2 null mice. Cardiovasc Res.
75:29–39. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, et al:
Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 confers endothelial protection and
attenuates atherosclerosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
295:H1377–H1384. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Treml B, Neu N, Kleinsasser A, et al:
Recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 improves pulmonary
blood flow and oxygenation in lipopolysaccharide-induced lung
injury in piglets. Crit Care Med. 38:596–601. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Imai Y, Kuba K, Rao S, et al:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung
failure. Nature. 436:112–116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ashcroft T, Simpson JM and Timbrell V:
Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a
numerical scale. J Clin Pathol. 41:467–470. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baker MA, Cerniglia GJ and Zaman A:
Microtiter plate assayfor the measurement of glutathione and
glutathione disulfide in large numbers of biological samples. Anal
Biochem. 190:360–365. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shimoda-Matsubayashi S, Hattori T,
Matsumine H, et al: Mn SOD activity and protein in a patient with
chromosome 6-linked autosomal recessive parkinsonism in comparison
with Parkinson’s disease and control. Neurology. 49:1257–1262.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cohnheim J: Ueber die endigung der
sensiblen nerven in der hornhaut. Virchows Arch. 38:343–386. 1867.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK and
Gerasimov UV: Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: in vitro
cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers. Cell Tissue
Kinet. 20:263–272. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Secco M, Zucconi E, Vieira NM, et al:
Multipotent stem cells from umbilical cord: cord is richer than
blood! Stem Cells. 26:146–150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Imai Y, Kuba K and Penninger JM:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:2006–2012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamamoto K, Ohishi M, Katsuya T, et al:
Deletion of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 accelerates pressure
overload-induced cardiac dysfunction by increasing local
angiotensin II. Hypertension. 47:718–726. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li X, Molina-Molina M, Abdul-Hafez A, Uhal
V, Xaubet A and Uhal BD: Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 is
protective but downregulated in human and experimental lung
fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 295:L178–L185. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zisman LS, Keller RS, Weaver B, et al:
Increased angiotensin-1–7-forming activity in failing human heart
ventricles: evidence for upregulation of the angiotensin-converting
enzyme homologue ACE2. Circulation. 108:1707–1712. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rey-Parra GJ, Vadivel A, Coltan L, et al:
Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 abrogates bleomycin-induced lung
injury. J Mol Med (Berl). 90:637–647. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Horwitz EM, Prockop DJ, Fitzpatrick LA, et
al: Transplantability and therapeutic effects of bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal cells in children with osteogenesis
imperfecta. Nat Med. 5:309–313. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moodley Y, Atienza D, Manuelpillai U, et
al: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce fibrosis of
bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Pathol. 175:303–313. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Verrecchia F and Mauviel A: Transforming
growth factor-beta and fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol.
13:3056–3062. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Parks WC: Matrix metalloproteinases in
lung repair. Eur Respir J. Suppl 44:36s–38s. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell engraftment in lung is enhanced in response
to bleomycin exposure and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8407–8411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yaguchi T, Fukuda Y, Ishizaki M and
Yamanaka N: Immunohistochemical and gelatin zymography studies for
matrix metalloproteinases in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.
Pathol Int. 48:954–963. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Oggionni T, Morbini P, Inghilleri S, et
al: Time course of matrix metalloproteases and tissue inhibitors in
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Eur J Histochem. 50:317–325.
2006.
|