Article
Sann-Joong-Kuey-Jian-Tang decreases the protein expression of mammalian target of rapamycin but increases microtubule associated protein II light chain 3 expression to inhibit human BxPC‑3 pancreatic carcinoma cells
- Authors:
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Tumor Research Center of Integrative Medicine, Changhua Christian Hospital, Changhua, Taiwan 50006, R.O.C.
-
Pages:
3160-3166
|
Published online on:
December 15, 2014
https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.3090
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
Sann‑Joong‑Kuey‑Jian‑Tang (SJKJT), a Traditional Chinese Medicinal prescription, has been used for the treatment of lymphadenopathy and solid tumors, and has shown therapeutic potential in a number of human malignant tumor cell lines, such as Hep‑G2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Previous mechanistic studies demonstrated that SJKJT inhibited the proliferation of BxPC‑3 pancreatic carcinoma cells through the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways in vitro. SJKJT was also shown to be cytotoxic to colo 205 colon cancer cells by inducing autophagy in vitro. The present study therefore investigated molecular mechanisms of autophagy in human BxPC‑3 pancreatic cancer cells treated with SJKJT. The cytotoxic effects of SJKJT on BxPC‑3 human pancreatic carcinoma cells were evaluated using an MTT assay. Furthermore, the expression of autophagy‑associated proteins, including mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), beclin‑1, autophagocytosis‑associated protein (Atg)3, Atg7, Atg5‑Atg12 and microtubule‑associated protein II light chain 3 (LC3‑II), was assessed using western blot analysis. The results demonstrated that BxPC‑3 cells treated with SJKJT exhibited decreased expression levels of mTOR and increased expression of LC3‑II protein. In addition, the expression of the beclin‑1, Atg3, Atg7 and Atg5‑Atg12 proteins was increased during the first 24 h, but decreased from 48 to 72 h. The results showed that SJKJT inhibited the proliferation of human BxPC‑3 pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. A possible underlying molecular mechanism may be the induction of autophagy. Further investigation into the therapeutic potential of SJKJT in human pancreatic cancer is required.
View Figures |
Figure 1
|
 |
Figure 2
|
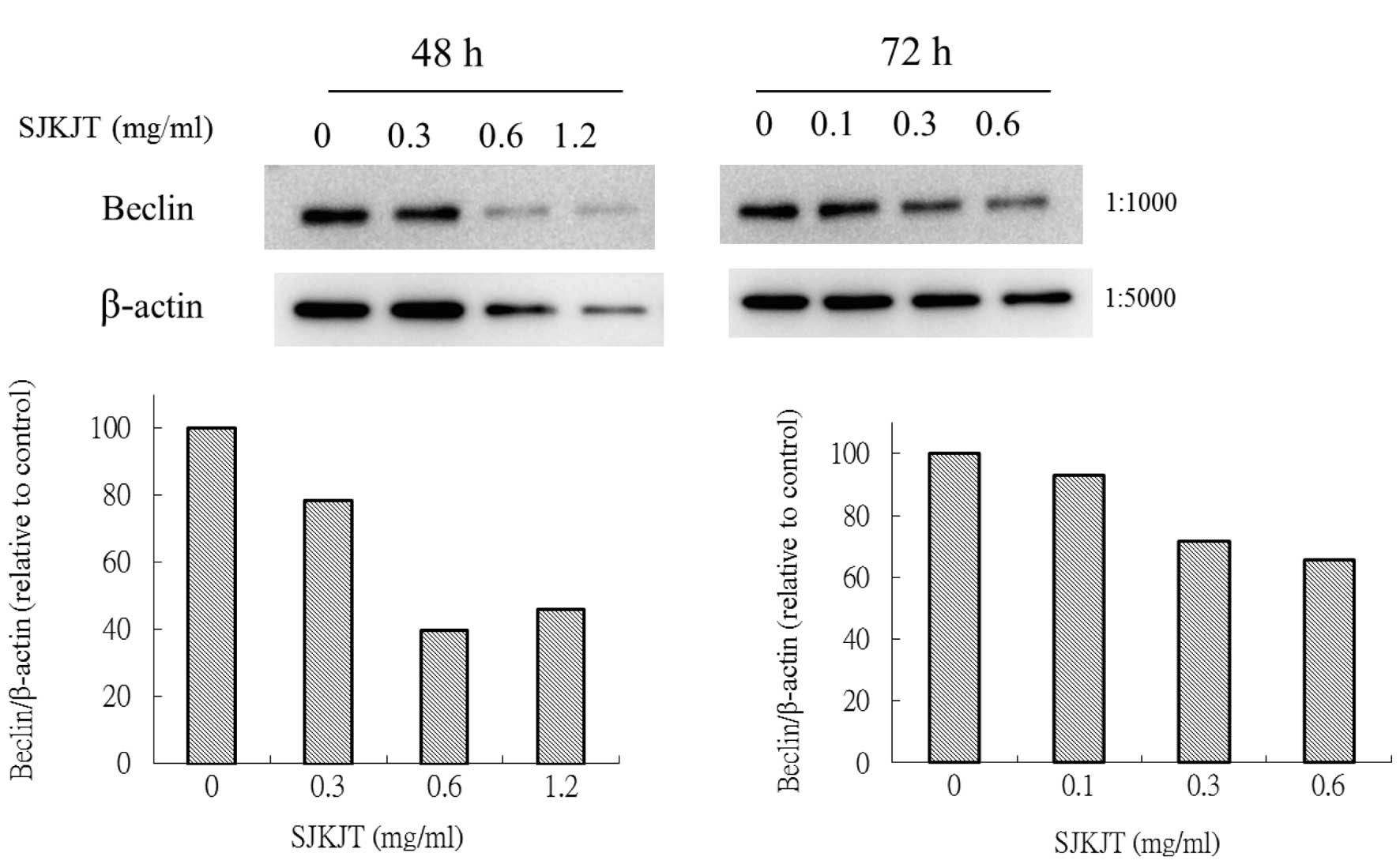 |
Figure 3
|
 |
Figure 4
|
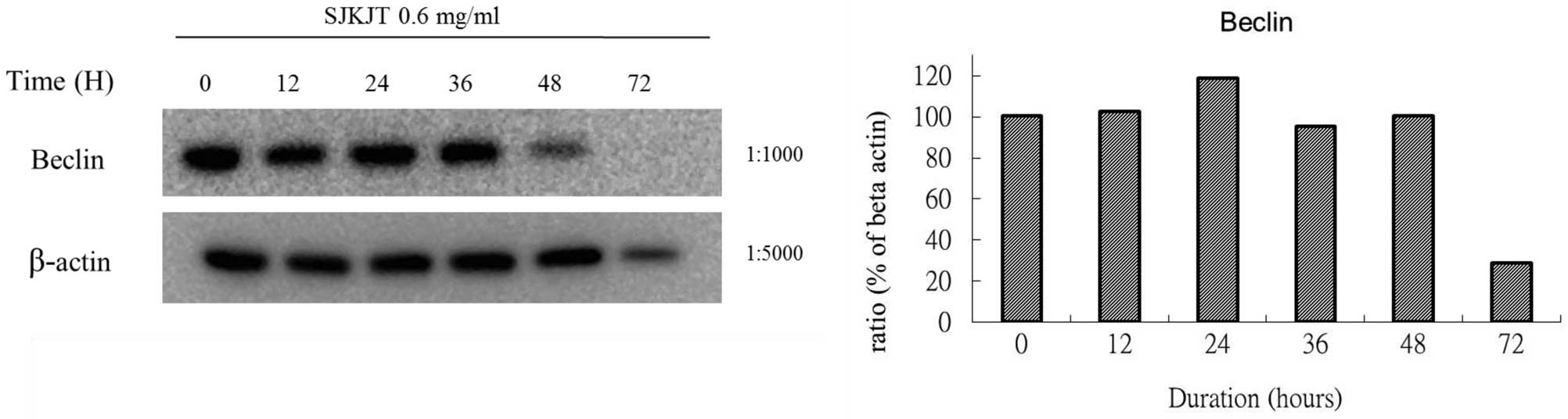 |
Figure 5
|
 |
Figure 6
|
 |
Figure 7
|
 |
Figure 8
|
 |
Figure 9
|
 |
Figure 10
|
View References
|
1
|
Yang CH and Craise LM: Development of
human epithelial cell systems for radiation risk assessment. Adv
Space Res. 14:115–120. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cheng CY, Lin YH and Su CC:
Sann-Joong-Kuey-Jian-Tang up-regulates the protein expression of
Fas and TNF-α in colo 205 cells in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
3:63–67. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen YL, Yan MY, Chien SY, Kuo SJ, Chen
DR, Cheng CY and Su CC: Sann-Joong-Kuey-Jian-Tang inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma Hep-G2 cell proliferation by increasing
TNF-α, Caspase-8, Caspase-3 and Bax but by decreasing TCTP and
Mcl-1 expression in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 7:1487–1493.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mujumdar N, Mackenzie TN, Dudeja V, et al:
Triptolide induces cell death in pancreatic cancer cells by
apoptotic and autophagic pathways. Gastroenterology. 139:598–608.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Verhoef MJ, Balneaves LG, Boon HS and
Vroegindewey A: Reasons for and characteristics associated with
complementary and alternative medicine use among adult cancer
patients: a systematic review. Integr Cancer Ther. 4:274–286. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chien SY, Kuo SJ, Chen DR and Su CC:
Sann-Joong-Kuey-Jian-Tang decreases the protein expression of Mcl-1
and TCTP and increases that of TNF-α and Bax in BxPC-3 pancreatic
carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 32:85–92. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dalby KN, Tekedereli I, Lopez-Berestein G
and Ozpolat B: Targeting the prodeath and prosurvival functions of
autophagy as novel therapeutic strategies in cancer. Autophagy.
6:322–329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fujii S, Mitsunaga S, Yamazaki M, et al:
Autophagy is activated in pancreatic cancer cells and correlates
with poor patient outcome. Cancer Sci. 99:1813–1819.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang S, Wang X, Contino G, et al:
Pancreatic cancers require autophagy for tumor growth. Genes Dev.
25:717–729. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng CY, Lin YH and Su CC:
Sann-Joong-Kuey-Jian-Tang increases the protein expression of
microtubule-associated protein II light chain 3 in human colon
cancer colo 205 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2:707–711. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Clarke PG: Developmental cell death:
morphological diversity and multiple mechanisms. Anat Embryol
(Berl). 181:195–213. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang YP, Liang ZQ, Gu ZL and Qin ZH:
Molecular mechanism and regulation of autophagy. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 26:1421–1434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Konado Y and Kondo S: Autophagy and cancer
therapy. Autophagy. 2:85–90. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Moretti L, Yang ES, Kim KW and Lu B:
Autophagy signaling in cancer and its potential as novel target to
improve anticancer therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 10:135–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
























