|
1
|
Sentinelli F, Minicocci I, Montali A, et
al: Association of RXR-Gamma gene variants with Familial combined
hyper-lipidemia: Genotype and haplotype analysis. J Lipids.
2013:5179432013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wojciechowski AP, Farrall M, Cullen P, et
al: Familial combined hyperlipidaemia linked to the apolipoprotein
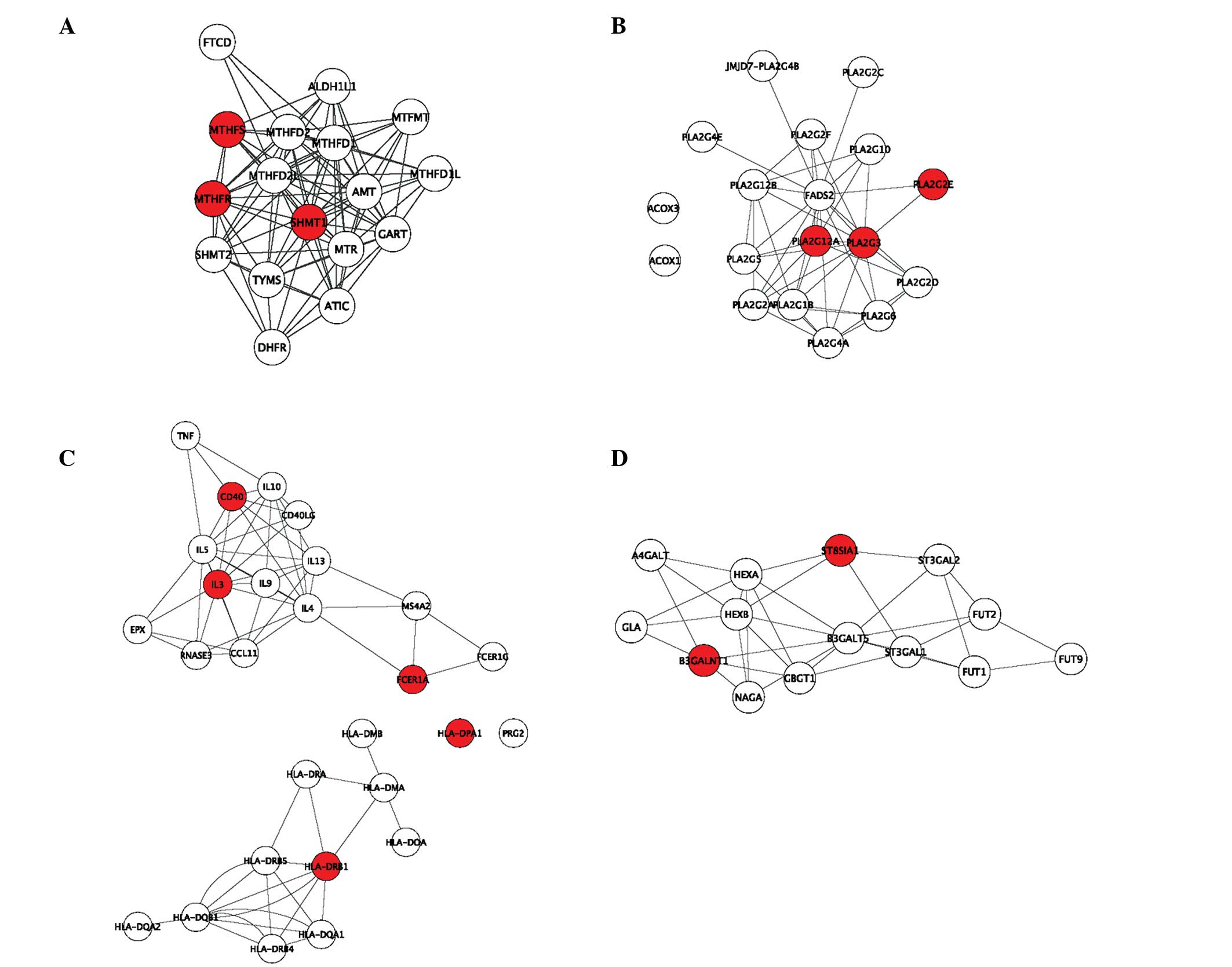
AI-CIII-AIV gene cluster on chromosome 11q23q-q24. Nature.
349:161–164. 1991. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
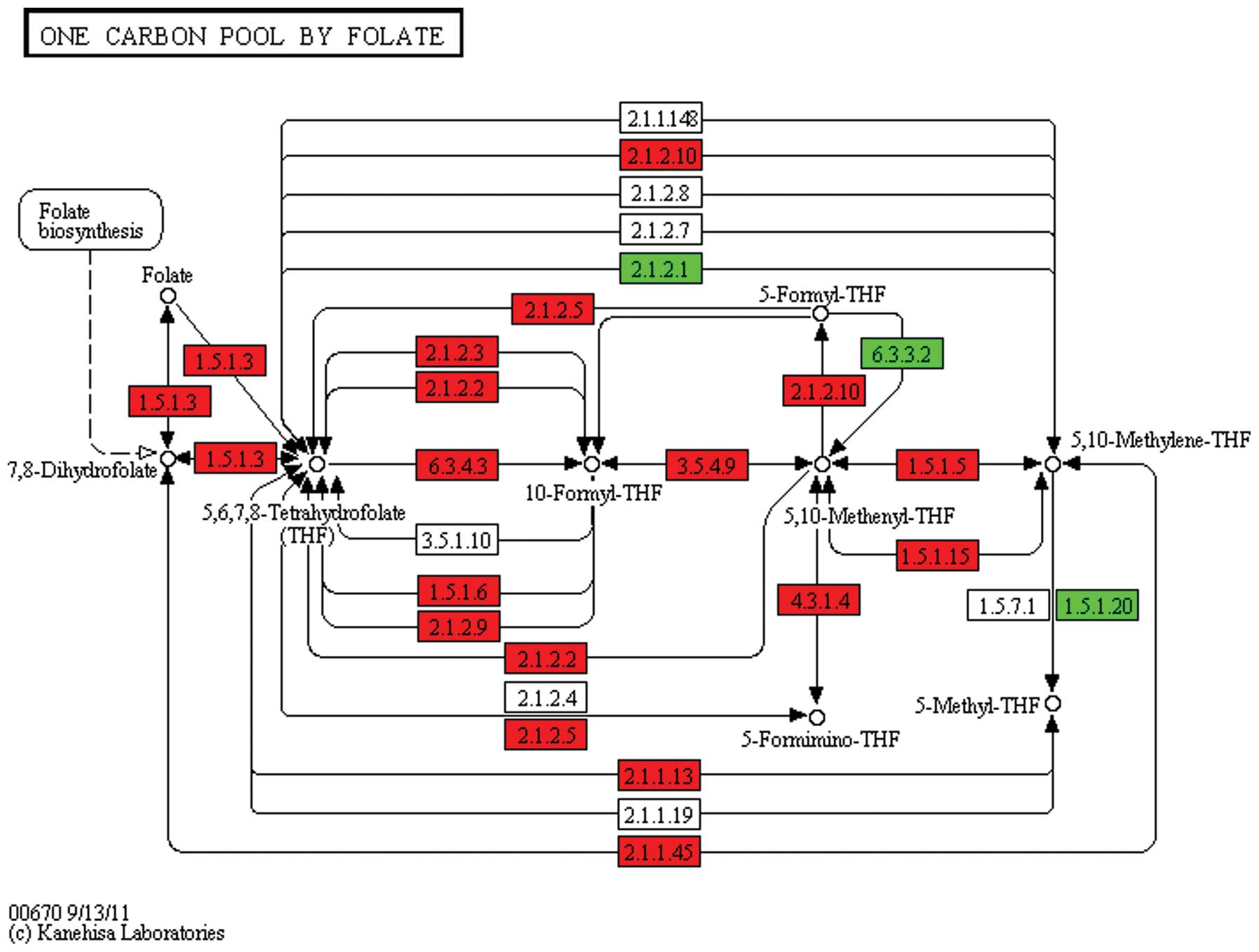
|
Ayyobi AF, McGladdery SH, McNeely MJ,
Austin MA, Motulsky AG and Brunzell JD: Small, dense LDL and
elevated apolipoprotein B are the common characteristics for the
three major lipid phenotypes of familial combined hyperlipidemia.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:1289–1294. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sniderman A and Ribalta J: How should FCHL
be defined and how should we think about its metabolic bases? Nutr
Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 11:259–273. 2001.
|
|
5
|
Hsieh C, Pei D, Hung Y and Hsiao F:
Association between retinoid-X receptor-gamma genetic polymorphisms
and diabetic retinopathy. Genet Mol Res. 10:3545–3551. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pushpakom SP, Owen A, Back DJ and
Pirmohamed M: RXRγ gene variants are associated with HIV
lipodystrophy. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 23:438–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Xue F, Liu L and He Z: Pathway
analysis detect potential mechanism for familial combined
hyperlipidemia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:1909–1915.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pajukanta P, Lilja HE, Sinsheimer JS, et
al: Familial combined hyperlipidemia is associated with upstream
transcription factor 1 (USF1). Nat Genet. 36:371–376. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Coon H, Myers RH, Borecki IB, et al:
Replication of linkage of Familial combined hyperlipidemia to
chromosome 1q with additional heterogeneous effect of
apolipoprotein AI/C-III/A-IV locus The NHLBI Family Heart Study.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:2275–2280. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Smyth GK: Limma: Linear Models for
Microarray Data. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
Using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey V, Huber W, Irizarry R
and Dudoit S: Springer; New York, NY: pp. 397–420. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ritchie ME, Silver J, Oshlack A, et al: A
comparison of background correction methods for two-colour
microarrays. Bioinformatics. 23:2700–2707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smyth GK: Linear models and empirical
bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray
experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 3:32004.
|
|
13
|
Glaab E, Baudot A, Krasnogor N, Schneider
R and Valencia A: EnrichNet: network-based gene set enrichment
analysis. Bioinformatics. 28:i451–i457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jensen LJ, Kuhn M, Stark M, et al: STRING
8-a global view on proteins and their functional interactions in
630 organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:D412–D416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al:
Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of
biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nepusz T, Yu H and Paccanaro A: Detecting
overlapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction
networks. Nat Methods. 9:471–472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, et al:
DAVID: database for annotation, visualization and integrated
discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hunter S, Jones P, Mitchell A, et al:
InterPro in 2011: new developments in the family and domain
prediction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D306–D312. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Locasale JW: Serine, glycine and
one-carbon units: cancer metabolism in full circle. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:572–583. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Almario RU, Vonghavaravat V, Wong R and
Kasim-Karakas SE: Effects of walnut consumption on plasma fatty
acids and lipoproteins in combined hyperlipidemia. Am J Clin Nutr.
74:72–79. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alessandri C, Pignatelli P, Loffredo L, et
al: Alpha-linolenic acid-rich wheat germ oil decreases oxidative
stress and CD40 ligand in patients with mild hypercholesterolemia.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:2577–2578. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao G, Etherton TD, Martin KR, West SG,
Gillies PJ and Kris-Etherton PM: Dietary α-linolenic acid reduces
inflammatory and lipid cardiovascular risk factors in
hypercholesterolemic men and women. J Nutr. 134:2991–2997.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Al-Shawwa B, Al-Huniti N, Titus G and
Abu-Hasan M: Hypercholesterolemia is a potential risk factor for
asthma. J Asthma. 43:231–233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nakou E, Babageorgakas P, Bouchliou I, et
al: Statin-induced immunomodulation alters peripheral invariant
natural killer T-cell prevalence in hyperlipidemic patients.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 26:293–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bietrix F, Lombardo E, van Roomen CP, et
al: Inhibition of glycosphingolipid synthesis induces a profound
reduction of plasma cholesterol and inhibits atherosclerosis
development in APOE*3 Leiden and low-density lipoprotein
receptor−/−mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:931–937. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hara A and Taketomi T: Characterization
and changes of glycosphingolipids in the aorta of the Watanabe
hereditable hyperlipidemic rabbit. J Biochem. 109:904–908.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parhami F: Possible role of oxidized
lipids in osteoporosis: could hyperlipidemia be a risk factor?
Prostaglandins, leukotrienes and essential fatty acids. 68:373–378.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Solomon DH, Avorn J, Canning CF and Wang
PS: Lipid levels and bone mineral density. Am J Med. 118:14142005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Schmiedl A, Schwille P, Bonucci E, Erben
R, Grayczyk A and Sharma V: Nephrocalcinosis and hyperlipidemia in
rats fed a cholesterol-and fat-rich diet: association with
hyperoxaluria, altered kidney and bone minerals and renal tissue
phospholipid-calcium interaction. Urol Res. 28:404–415. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rosenbaum DM, Cherezov V, Hanson MA, et
al: GPCR engineering yields high-resolution structural insights
into β2-adrenergic receptor function. Science. 318:1266–1273. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liao J, Chen X, Li Y, et al: Transfer of
bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells influences vascular
remodeling and calcification after balloon injury in hyperlipidemic
rats. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:1652962012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Baldán Á, Pei L, Lee R, et al: Impaired
development of atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic Ldlr−/− and
ApoE−/− mice transplanted with Abcg1−/−bone marrow. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 26:2301–2307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Drechsler M, Megens RT, van Zandvoort M,
Weber C and Soehnlein O: Hyperlipidemia-triggered neutrophilia
promotes early atherosclerosis. Circulation. 122:1837–1845. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|