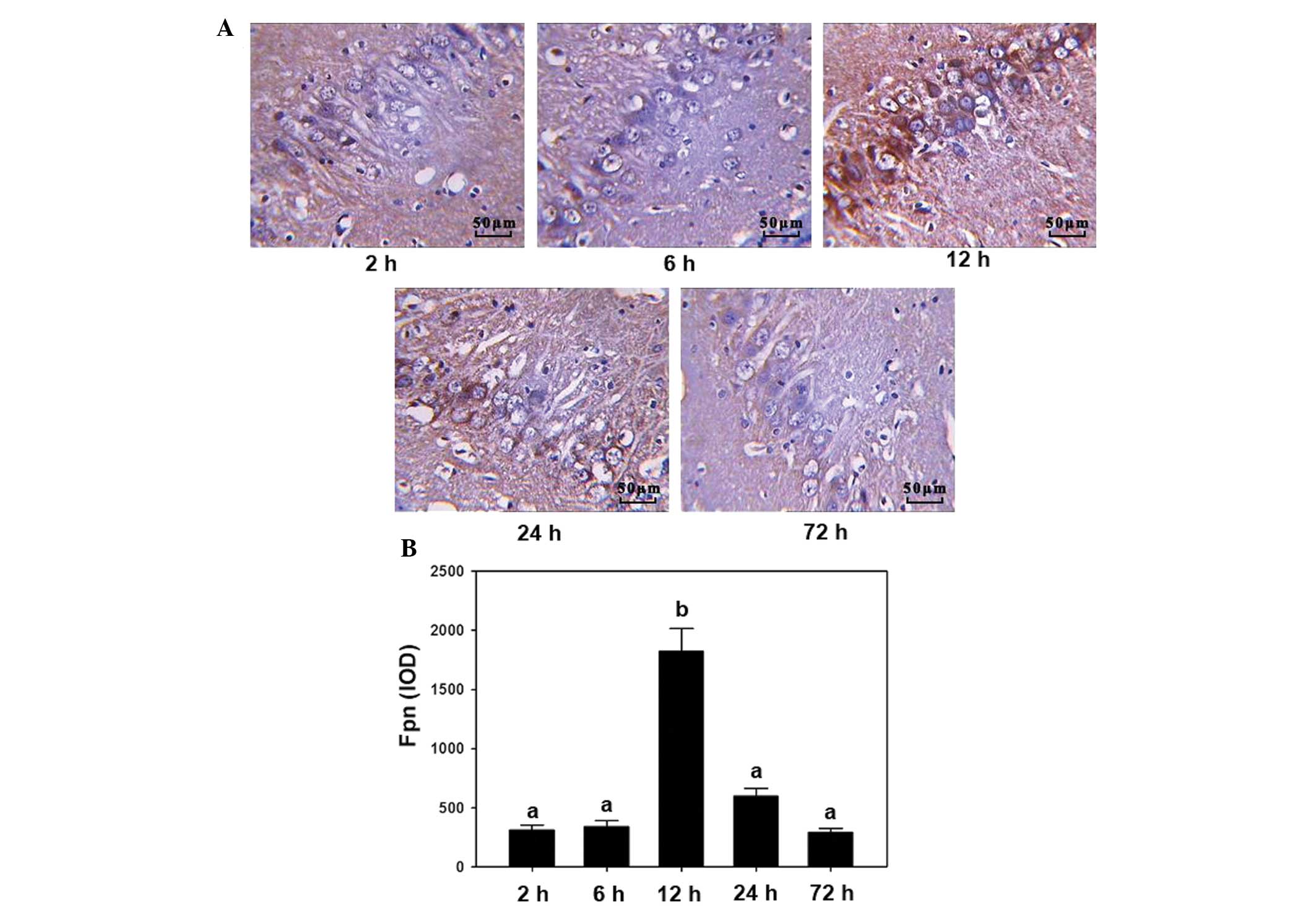
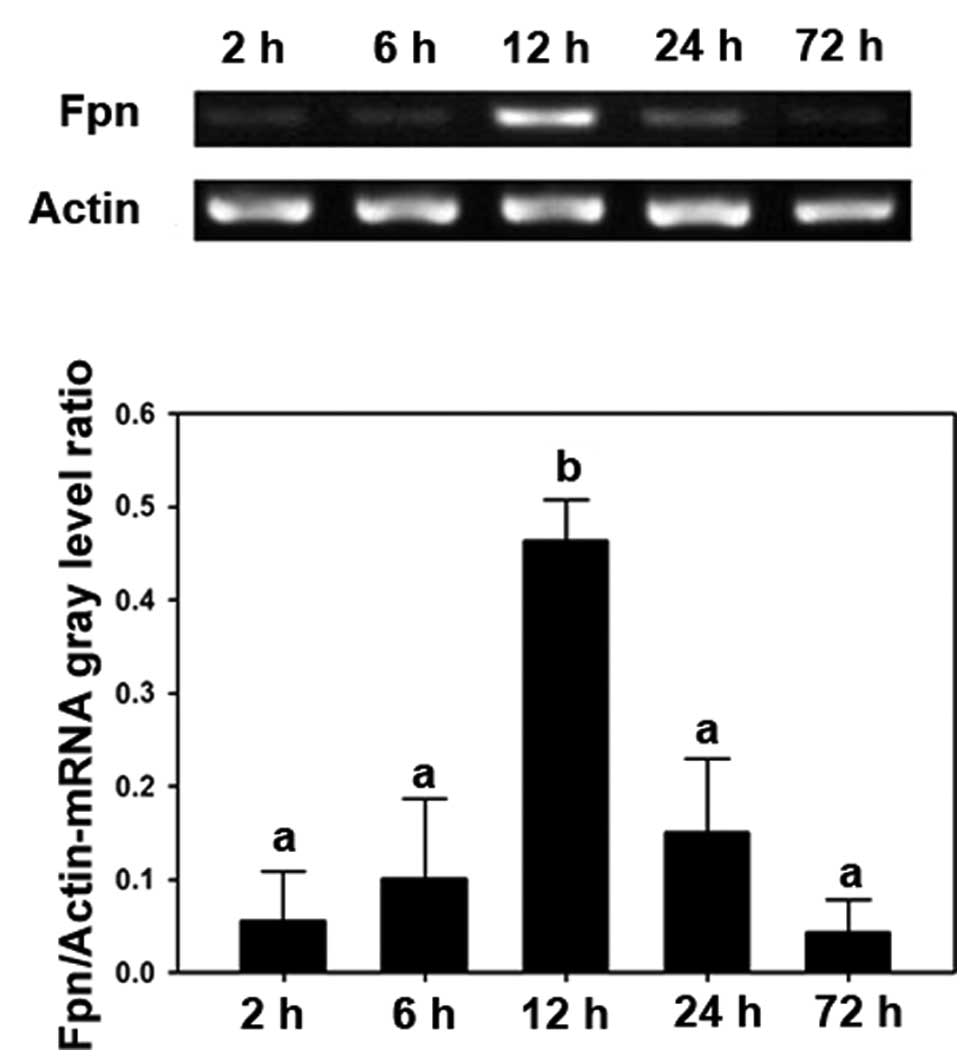
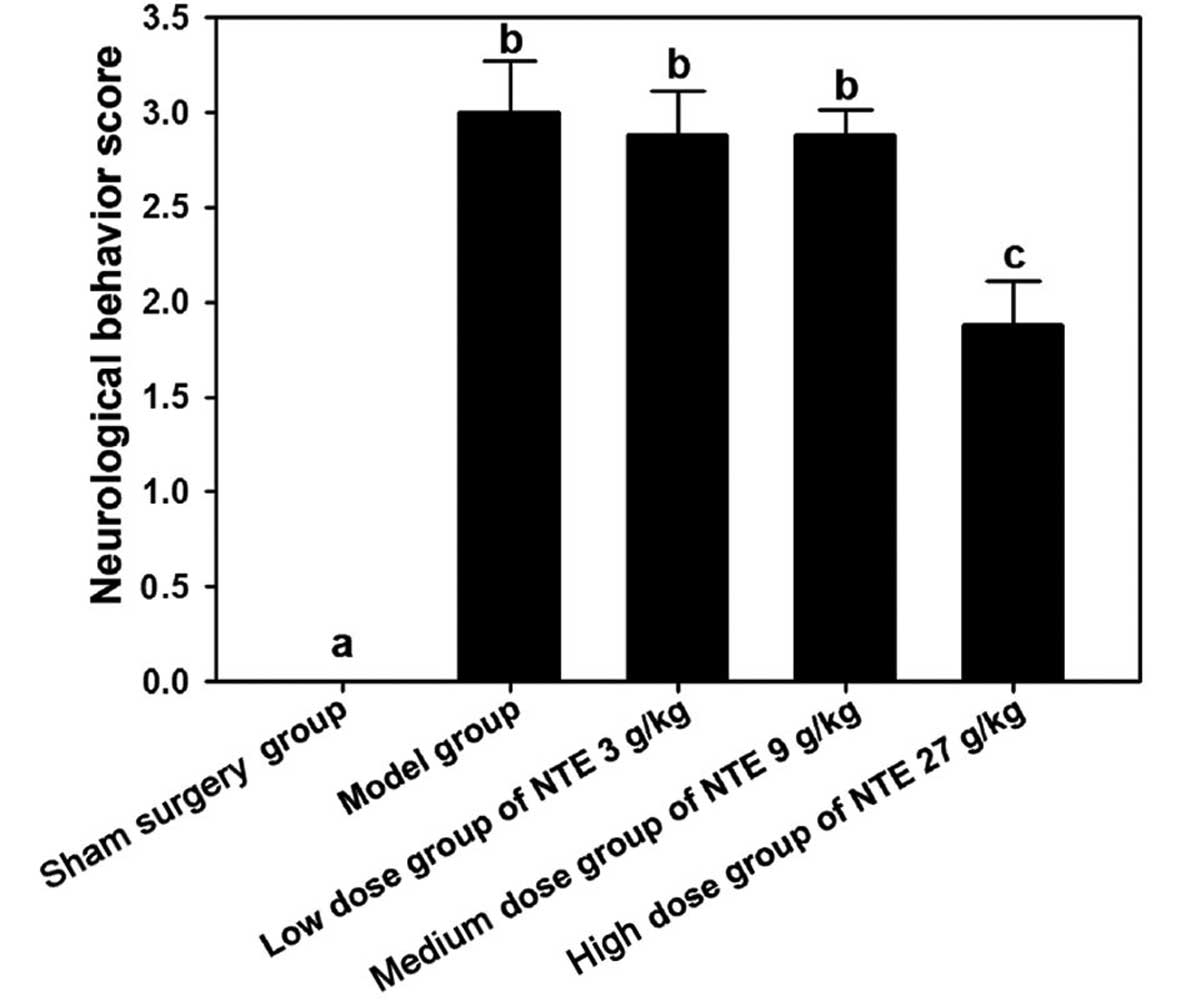
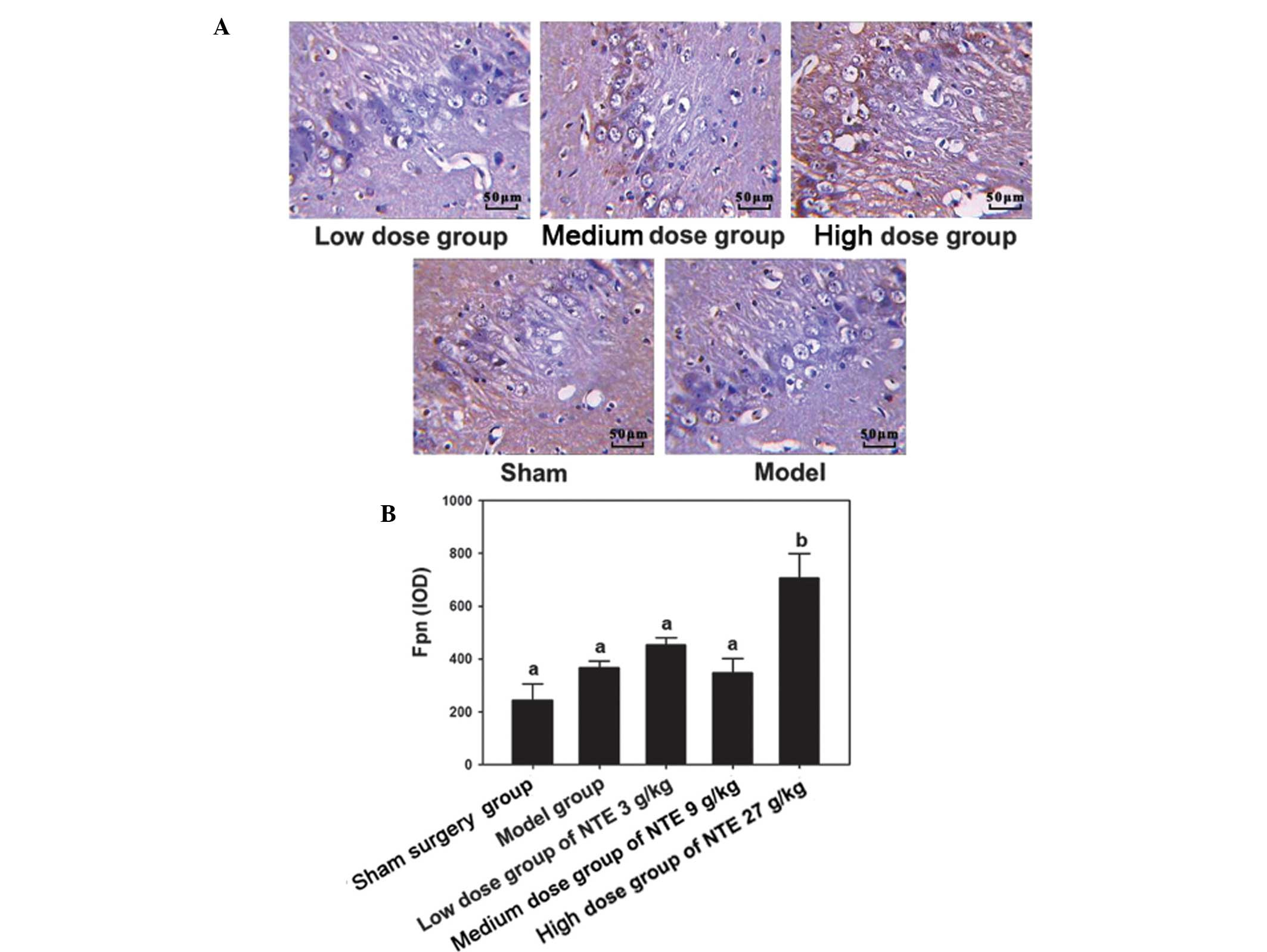
|
1
|
Chu XP and Xiong ZG: Physiological and
pathological functions of acid-sensing ion channels in the central
nervous system. Curr Drug Targets. 13:263–271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Xu M and Zhang HL: Death and survival of
neuronal and astrocytic cells in ischemic brain injury: a role of
autophagy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:1089–1099. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu F, Gu JH and Qin ZH: Neuronal autophagy
in cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Bull. 28:658–666. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Olmez I and Ozyurt H: Reactive oxygen
species and ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Neurochem Int.
60:208–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Belousov AB: Novel model for the
mechanisms of glutamate-dependent excitotoxicity: Role of neuronal
gap junctions. Brain Res. 1487:123–130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giuliani D, Minutoli L, Ottani A, et al:
Melanocortins as potential therapeutic agents in severe hypoxic
conditions. Front Neuroendocrinol. 33:179–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rathnasamy G, Ling EA and Kaur C: Iron and
iron regulatory proteins in amoeboid microglial cells are linked to
oligodendrocyte death in hypoxic neonatal rat periventricular white
matter through production of proinflammatory cytokines and reactive
oxygen/nitrogen species. J Neurosci. 31:17982–17995. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gebril OH, Simpson JE, Kirby J, Brayne C
and Ince PG: Brain iron dysregulation and the risk of ageing white
matter lesions. Neuromolecular Med. 13:289–299. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Muñoz P and Humeres A: Iron deficiency on
neuronal function. Biometals. 25:825–835. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Khan AA and Quigley JG: Heme and
FLVCR-related transporter families SLC48 and SLC49. Mol Aspects
Med. 34:669–682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Garrick MD and Garrick LM: Cellular iron
transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1790:309–325. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ferraro S, Mozzi R and Panteghini M:
Revaluating serum ferritin as a marker of body iron stores in the
traceability era. Clin Chem Lab Med. 50:1911–1916. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vermeulen E and Vermeersch P: Hepcidin as
a biomarker for the diagnosis of iron metabolism disorders: a
review. Acta Clin Belg. 67:190–197. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fellman V: GRACILE syndrome-a severe
neonatal mitochondrial disorder. Duodecim. 128:1560–1567. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Chu WC, Au WY and Lam WW: MRI of cardiac
iron overload. J Magn Reson Imaging. 36:1052–1059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shander A, Berth U, Betta J and Javidroozi
M: Iron overload and toxicity: implications for anesthesiologists.
J Clin Anesth. 24:419–425. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Elborai Y, Uwumugambi A and Lehmann L:
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for thalassemia.
Immunotherapy. 4:947–956. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Valenti L, Dongiovanni P and Fargion S:
Diagnostic and therapeutic implications of the association between
ferritin level and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
World J Gastroenterol. 18:3782–3786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
González-Ramos R, Defrère S and Devoto L:
Nuclear factor-kappaB: a main regulator of inflammation and cell
survival in endometriosis pathophysiology. Fertil Steril.
98:520–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Annaloro C, Airaghi L, Saporiti G, Onida
F, Cortelezzi A and Deliliers GL: Metabolic syndrome in patients
with hematological diseases. Expert Rev Hematol. 5:439–458. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Theil EC: Iron homeostasis and nutritional
iron deficiency. J Nutr. 141:724S–728S. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J and Enns CA: Hereditary
hemochromatosis and transferrin receptor 2. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1820:256–263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Graham RM, Chua AC, Herbison CE, Olynyk JK
and Trinder D: Liver iron transport. World J Gastroenterol.
13:4725–4736. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kasvosve I: Effect of ferroportin
polymorphism on iron homeostasis and infection. Clin Chim Acta.
416:20–25. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng W and Monnot AD: Regulation of brain
iron and copper homeostasis by brain barrier systems: implication
in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 133:177–188. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Boserup MW, Lichota J, Haile D and Moos T:
Heterogenous distribution of ferroportin-containing neurons in
mouse brain. Biometals. 24:357–375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pietrangelo A, Caleffi A and Corradini E:
Non-HFE hepatic iron overload. Semin Liver Dis. 31:302–318. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schulz K, Kroner A and David S: Iron
efflux from astrocytes plays a role in remyelination. J Neurosci.
32:4841–4847. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Urrutia P, Aguirre P, Esparza A, et al:
Inflammation alters the expression of DMT1, FPN1 and hepcidin, and
it causes iron accumulation in central nervous system cells. J
Neurochem. 126:541–549. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang HW, Liou KT, Wang YH, et al:
Deciphering the neuroprotective mechanisms of Bu-yang Huan-wu
decoction by an integrative neurofunctional and genomic approach in
ischemic stroke mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 138:22–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Loh KP, Qi J, Tan BK, Liu XH, Wei BG and
Zhu YZ: Leonurine protects middle cerebral artery occluded rats
through antioxidant effect and regulation of mitochondrial
function. Stroke. 41:2661–2668. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Koh PO: Ferulic acid modulates nitric
oxide synthase expression in focal cerebral ischemia. Lab Anim Res.
28:273–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yunhe H, Jinwen G and Zhanying C: Effect
of Naotaifang on TXB 2, 6-Keto-PGF 1α in plasma and TNF-α in serum
of patients with cerebral infarction with deficiency of Qi and
blood stasis. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese
Medicine. 4:16–17. 2002.
|
|
34
|
Garcia JH: A reliable method to occlude a
middle cerebral in wistar rats. Stroke. 24:14231993.
|
|
35
|
González-Delgado M and Bogousslavsky J:
Superficial middle cerebral artery territory infarction. Front
Neurol Neurosci. 30:111–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eisenstein RS: Iron regulatory proteins
and the molecular control of mammalian iron metabolism. Annu Rev
Nutr. 20:627–662. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bandyopadhyay U, Das D and Banerjee RK:
Reactive oxygen species: oxidative damage and pathogenesis. Curr
Sci. 77:658–666. 1999.
|
|
39
|
Jinwen G, Song C and Huibin Z: Effect of
naotaifang extract on functional changes of coagulation and
fibrinolysis of human umbilical veins endothelial cell induced by
recombined human tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Trad Chin Med U
Hun. 6:4–6. 2005.
|
|
40
|
Zhang Q, Gao WY, Zhang Y, et al:
Protective effects of astragalus extract against intermittent
hypoxia-induced hippocampal neurons impairment in rats. Chin Med J
(Engl). 126:1551–1554. 2013.
|
|
41
|
Yin YY, Zhu FF and Wu GC: Protective
effect of astragalosides on anoxia/reoxygenation injury of
hippocampal neuron. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
30:1173–1177. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
42
|
Li SL, Chan SS, Lin G, et al: Simultaneous
analysis of seventeen chemical ingredients of Ligusticum chuanxiong
by online high performance liquid chromatography-diode array
detector-mass spectrometry. Planta Med. 69:445–451. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Qiu F, Liu Y, Zhang PB, et al: Effects of
ligustrazine on hippocampal dentate gyrus cell proliferation after
focal cerebral ischemia in adult rats. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue
Bao. 26:1400–1403. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cheng CY, Su SY, Tang NY, et al: Ferulic
acid inhibits nitric oxide-induced apoptosis by enhancing GABA(Bl)
receptor expression in transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:889–899. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
He YH, Hao XY, Ge JW, et al: Clinical
studies on naotaifang in treating patients with cerebral infarction
with deficiency of qi and blood stasis in TCM. J Emerg Trad Chin
Med. 10:319–320. 2001.
|
|
46
|
Zhu HB, Chen Y, Tan H and Ge JW: Effects
of Naotai recipe extracts on cerebral CD34 expression in rats with
focal cerebral ischemia. Trad Chin Drug Res Clin Pharma.
22:141–144. 2011.
|