|
1
|
Lai EC: Micro RNAs are complementary to 3′
UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional
regulation. Nat Genet. 30:363–364. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ and
Dahiya R: MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with
complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:1608–1613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B and
Rigoutsos I: MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions
modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature.
455:1124–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang S, Johnston RJ Jr, Frøkjaer-Jensen
C, Lockery S and Hobert O: MicroRNAs act sequentially and
asymmetrically to control chemosensory laterality in the nematode.
Nature. 430:785–789. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lands WE: Biochemistry and physiology of
n-3 fatty acids. FASEB J. 6:2530–2536. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Simopoulos AP: The importance of the ratio
of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed Pharmacother.
56:365–379. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Visioli F, Giordano E, Nicod NM and
Dávalos A: Molecular targets of omega 3 and conjugated linoleic
Fatty acids - ‘micromanaging’ cellular response. Front Physiol.
3:422012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ross SA and Davis CD: MicroRNA, nutrition,
and cancer prevention. Adv Nutr. 2:472–485. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
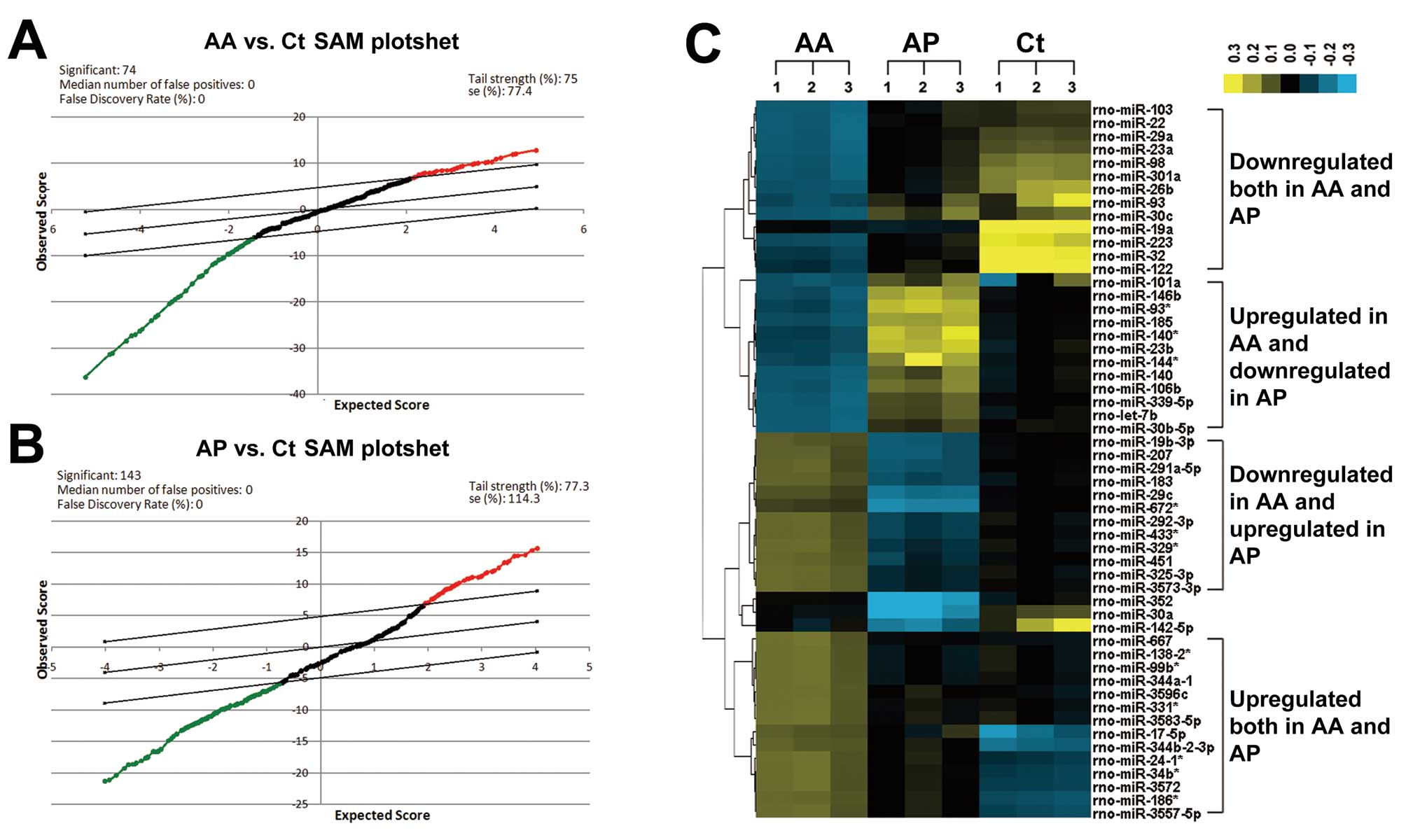
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R and Chu G:
Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing
radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:5116–5121. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li J and Tibshirani R: Finding consistent
patterns: a nonparametric approach for identifying differential
expression in RNA-Seq data. Stat Methods Med Res. 22:519–536. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
de Hoon MJ, Imoto S, Nolan J and Miyano S:
Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics. 20:1453–1454.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Saldanha AJ: Java Treeview - extensible
visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics. 20:3246–3248.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison
and statistical analysis of relative expression results in
real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk - database: prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jayaswal V, Lutherborrow M, Ma DD and Yang
YH: Identification of microRNA-mRNA modules using microarray data.
BMC Genomics. 12:1382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al:
Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of
biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, et al:
Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome
Res. 19:1639–1645. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
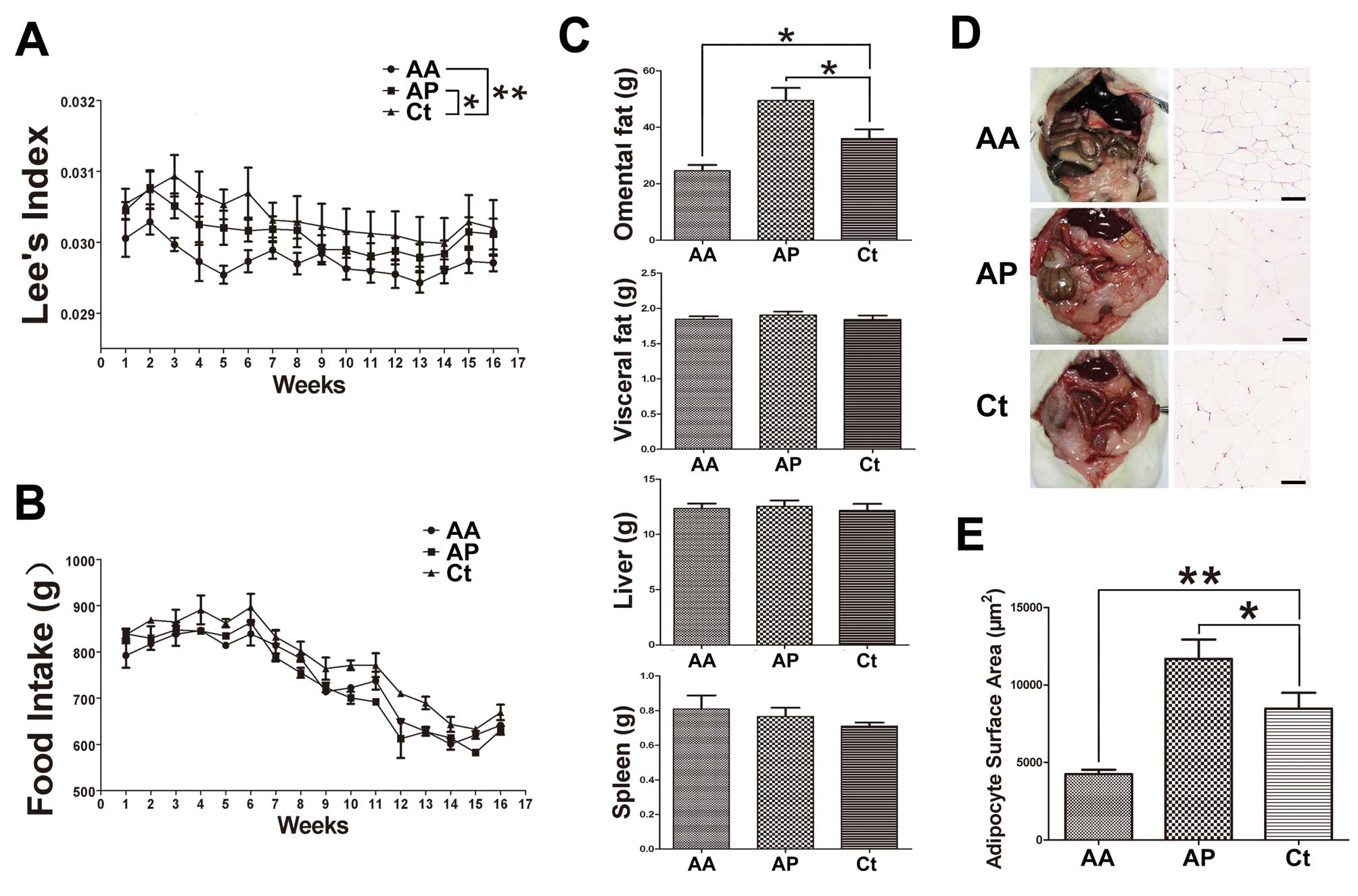
Rogers P and Webb GP: Estimation of body
fat in normal and obese mice. Br J Nutr. 43:83–86. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
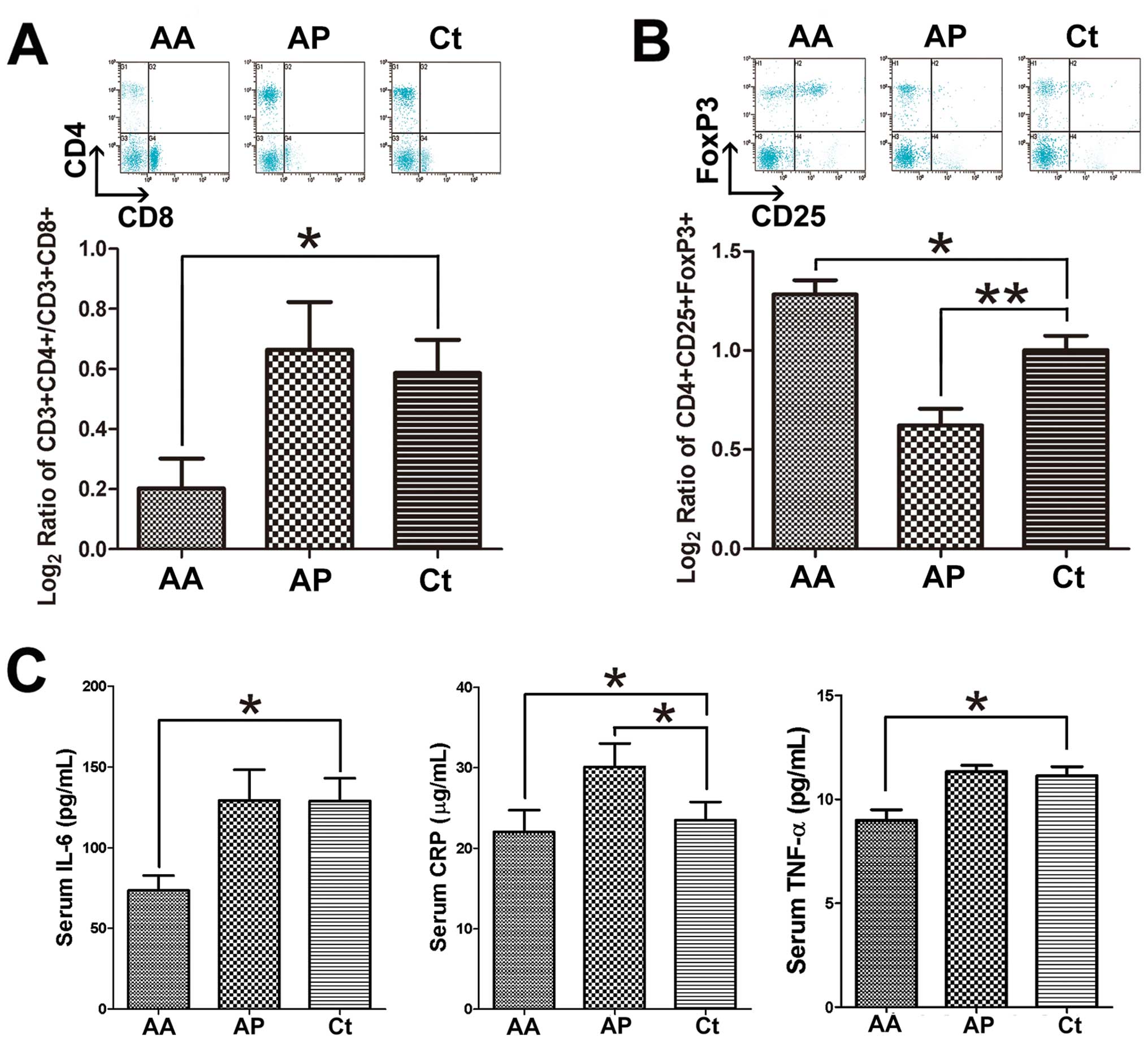
Jiang H and Chess L: An integrated view of
suppressor T cell subsets in immunoregulation. J Clin Invest.
114:1198–1208. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maloy KJ, Salaun L, Cahill R, Dougan G,
Saunders NJ and Powrie F: CD4+CD25+ T(R)
cells suppress innate immune pathology through cytokine-dependent
mechanisms. J Exp Med. 197:111–119. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
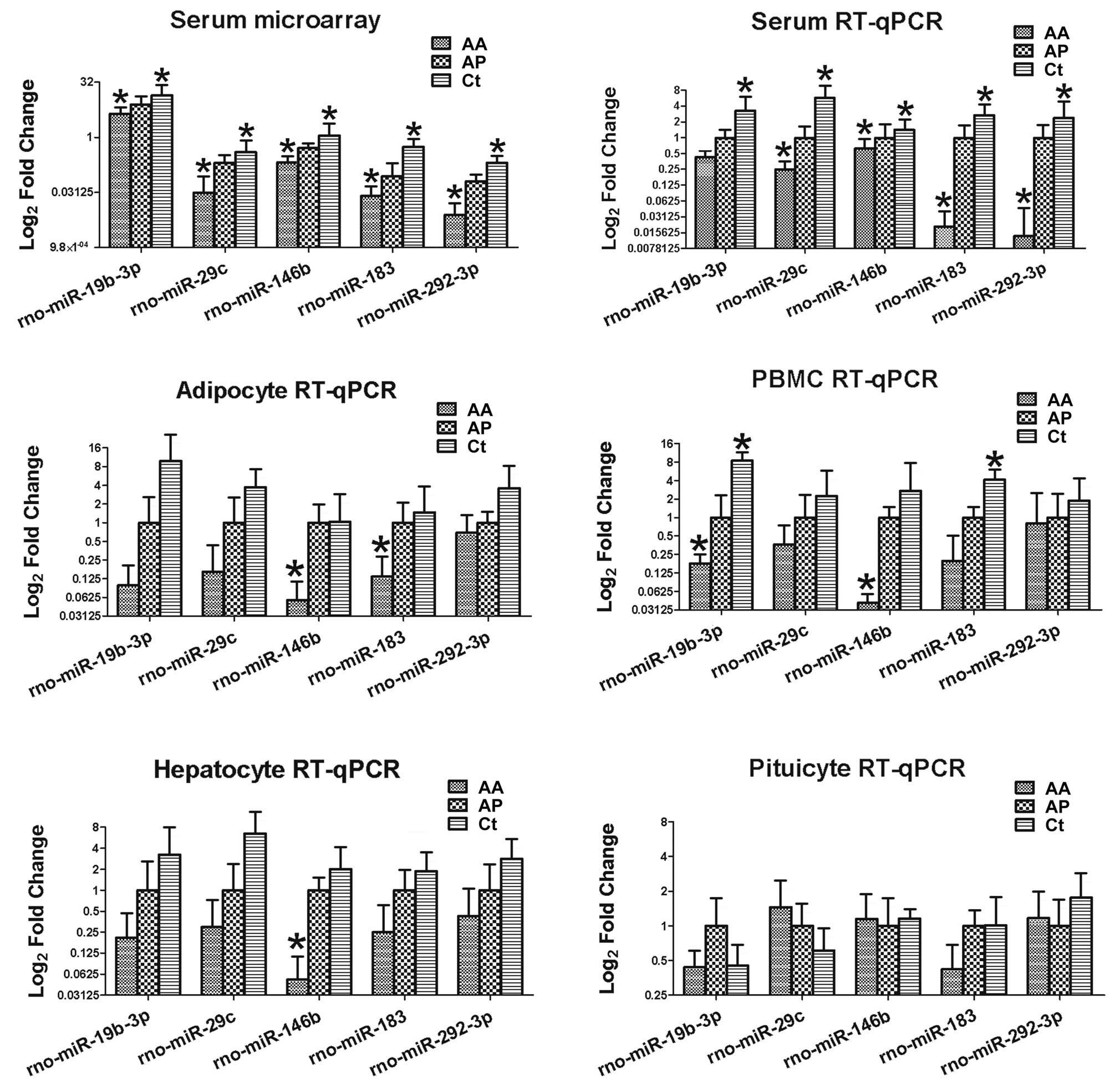
Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, et al: Serum
microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS One. 3:e31482008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang X: miRDB: a microRNA target
prediction and functional annotation database with a wiki
interface. RNA. 14:1012–1017. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nat Genet. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Raza Shaikh S: Diet-induced
docosahexaenoic acid non-raft domains and lymphocyte function.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 82:159–164. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Richard D, Bausero P, Schneider C and
Visioli F: Polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular disease.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:3277–3288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kang JX and Weylandt KH: Modulation of
inflammatory cytokines by omega-3 fatty acids. Subcell Biochem.
49:133–143. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Spalding KL, Arner E, Westermark PO, et
al: Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature. 453:783–787.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, et al: Chronic
inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of
obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 112:1821–1830.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim KD, Zhao J, Auh S, et al: Adaptive
immune cells temper initial innate responses. Nat Med.
13:1248–1252. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lu L, Werneck MB and Cantor H: The
immunoregulatory effects of Qa-1. Immunol Rev. 212:51–59. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vinciguerra M, Sgroi A, Veyrat-Durebex C,
Rubbia-Brandt L, Buhler LH and Foti M: Unsaturated fatty acids
inhibit the expression of tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin
homolog (PTEN) via microRNA-21 up-regulation in hepatocytes.
Hepatology. 49:1176–1184. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Vinciguerra M and Foti M: PTEN at the
crossroad of metabolic diseases and cancer in the liver. Ann
Hepatol. 7:192–199. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bannenberg G and Serhan CN: Specialized
pro-resolving lipid mediators in the inflammatory response: An
update. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1801:1260–1273. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Recchiuti A, Krishnamoorthy S, Fredman G,
Chiang N and Serhan CN: MicroRNAs in resolution of acute
inflammation: identification of novel resolvin D1-miRNA circuits.
FASEB J. 25:544–560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Davidson LA, Wang N, Shah MS, Lupton JR,
Ivanov I and Chapkin RS: n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids modulate
carcinogen-directed non-coding microRNA signatures in rat colon.
Carcinogenesis. 30:2077–2084. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Leaver HA, Bell HS, Rizzo MT, et al:
Antitumour and pro-apoptotic actions of highly unsaturated fatty
acids in glioma. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids.
66:19–29. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Faragó N, Fehér LZ, Kitajka K, Das UN and
Puskás LG: MicroRNA profile of polyunsaturated fatty acid treated
glioma cells reveal apoptosis-specific expression changes. Lipids
Health Dis. 10:1732011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou X and Su Z: EasyGO: Gene
Ontology-based annotation and functional enrichment analysis tool
for agronomical species. BMC Genomics. 8:2462007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li C, Li X, Miao Y, et al:
SubpathwayMiner: a software package for flexible identification of
pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:e1312009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kawai T and Akira S: TLR signaling. Cell
Death Differ. 13:816–825. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Inohara, Chamaillard, McDonald C and Nuñez
G: NOD-LRR proteins: role in host-microbial interactions and
inflammatory disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 74:355–383. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Meylan E and Tschopp J: Toll-like
receptors and RNA helicases: two parallel ways to trigger antiviral
responses. Mol Cell. 22:561–569. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shi Y and Massague J: Mechanisms of
TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell.
113:685–700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Weiss A and Littman DR: Signal
transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell. 76:263–274.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chang CL, Au LC, Huang SW, Fai Kwok C, Ho
LT and Juan CC: Insulin up-regulates heme oxygenase-1 expression in
3T3-L1 adipocytes via PI3-kinase- and PKC-dependent pathways and
heme oxygenase-1-associated microRNA downregulation. Endocrinology.
152:384–393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Li J, Fu H, Xu C, et al: miR-183 inhibits
TGF-beta1-induced apoptosis by downregulation of PDCD4 expression
in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 10:3542010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Goeppert B, Schmezer P, Dutruel C, et al:
Down-regulation of tumor suppressor A kinase anchor protein 12 in
human hepatocarcinogenesis by epigenetic mechanisms. Hepatology.
52:2023–2033. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Merkerova M, Vasikova A, Belickova M and
Bruchova H: MicroRNA expression profiles in umbilical cord blood
cell lineages. Stem Cells Dev. 19:17–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Serhan CN: Systems approach to
inflammation resolution: identification of novel anti-inflammatory
and pro-resolving mediators. J Thromb Haemost. 7(Suppl 1): S44–S48.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|