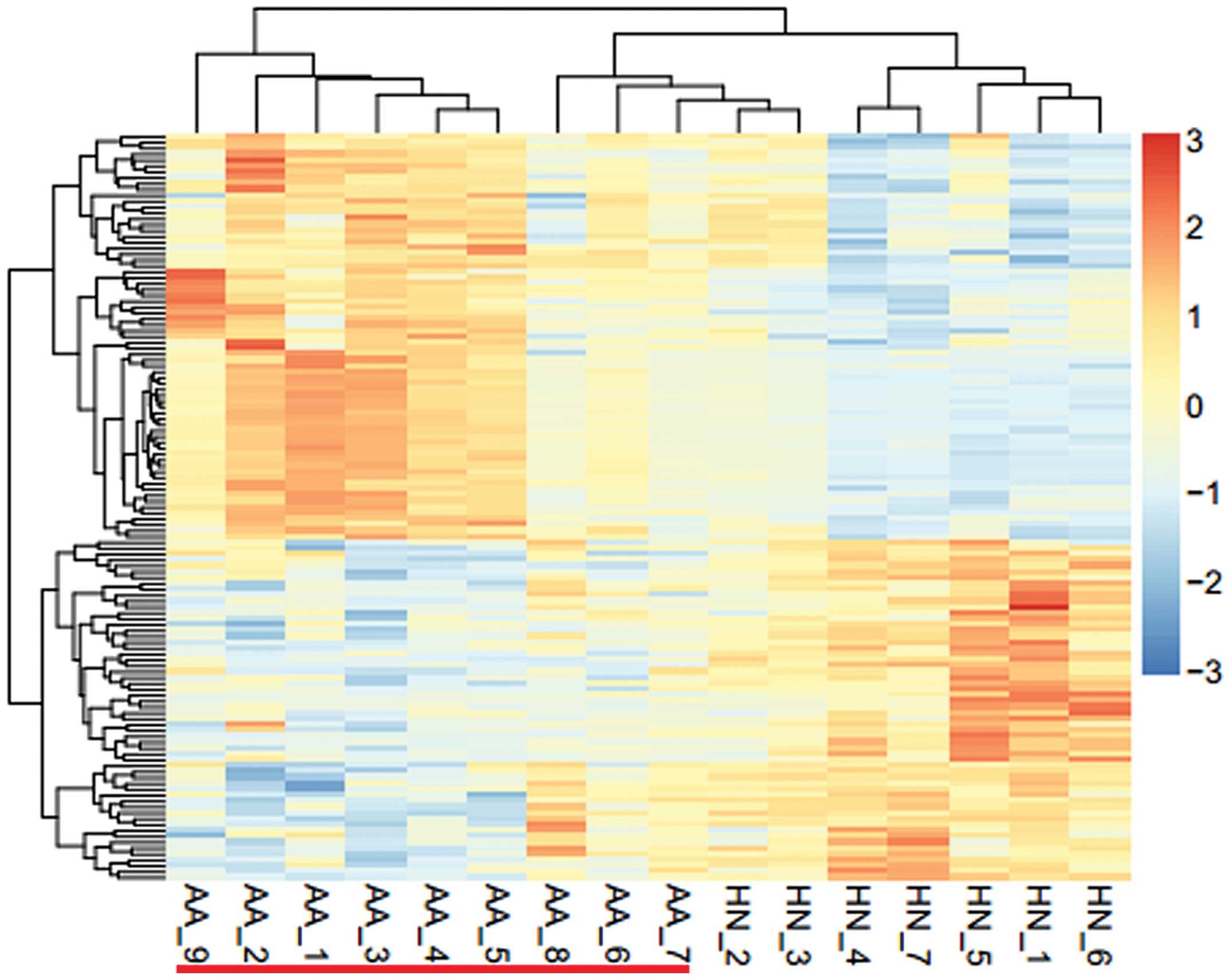
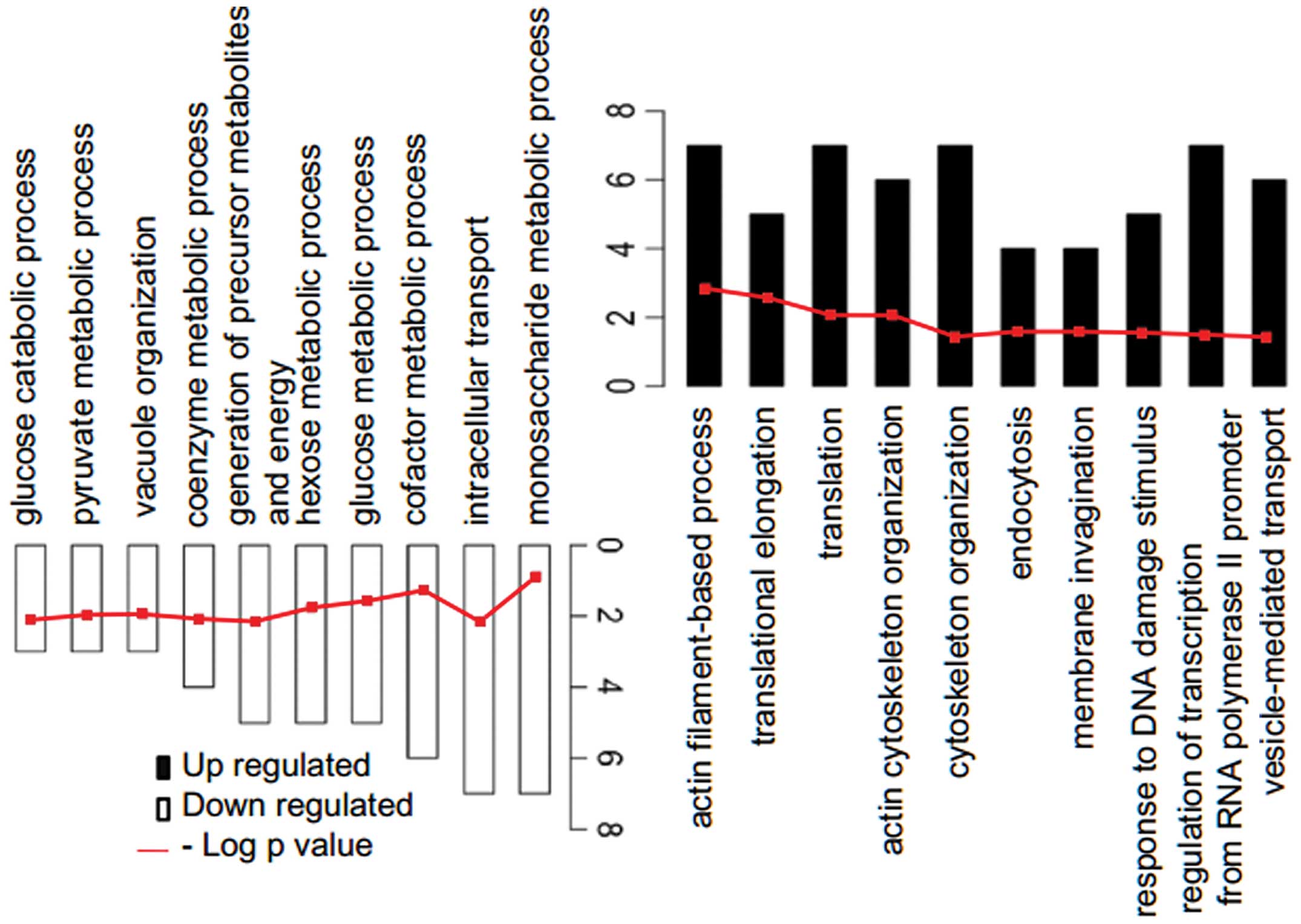
|
1
|
Tomita Y, Tomida S, Hasegawa Y, et al:
Artificial neural network approach for selection of susceptible
single nucleotide polymorphisms and construction of prediction
model on childhood allergic asthma. BMC Bioinformatics. 5:1202004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mannino DM, Homa DM, Akinbami LJ, Moorman
JE, Gwynn C and Redd SC: Surveillance for asthma - United States,
1980–1999. MMWR Surveill Summ. 51:1–13. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dietert RR and Zelikoff JT: Early-life
environment, developmental immunotoxicology, and the risk of
pediatric allergic disease including asthma. Birth Defects Res B
Dev Reprod Toxicol. 83:547–560. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schmid-Ott G, Jaeger B, Adamek C, et al:
Levels of circulating CD8(+) T lymphocytes, natural killer cells,
and eosinophils increase upon acute psychosocial stress in patients
with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 107:171–177. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang XQ, Wang XM, Zhou TF and Dong LQ:
Screening of differentially expressed genes and small molecule
drugs of pediatric allergic asthma with DNA microarray. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 16:1961–1966. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bender B, Milgrom H and Rand C:
Nonadherence in asthmatic patients: is there a solution to the
problem? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 79:177–185. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Milgrom H, Bender B, Ackerson L, Bowry P,
Smith B and Rand C: Noncompliance and treatment failure in children
with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 98:1051–1057. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Laird PW: Principles and challenges of
genomewide DNA methylation analysis. Nat Rev Genet. 11:191–203.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Creer TL and Wigal JK: Self-efficacy.
CHEST. 103:1316–1317. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Heller MJ: DNA microarray technology:
devices, systems, and applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 4:129–153.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kicic A, Hallstrand TS, Sutanto EN, et al:
Decreased fibronectin production significantly contributes to
dysregulated repair of asthmatic epithelium. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 181:889–898. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fujita A, Sato JR, Rodrigues LO, Ferreira
CE and Sogayar MC: Evaluating different methods of microarray data
normalization. BMC Bioinformatics. 7:4692006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Smyth GK: limma: Linear models for
microarray data. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
Using R and Bioconductor Statistics for Biology and Health.
Gentleman R, Carey VJ, Huber W, Irizarry RA and Dudoit S: Springer;
New York: pp. 397–420. 2005, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol. 57:289–300.
1995.
|
|
15
|
Deza MM and Deza E: Encyclopedia of
Distances. Springer; Berlin Heidelberg: 2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Szekely GJ and Rizzo ML: Hierarchical
clustering via joint between-within distances: Extending Ward’s
minimum variance method. J Classif. 22:151–183. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huson DH, Richter DC, Rausch C, Dezulian
T, Franz M and Rupp R: Dendroscope: An interactive viewer for large
phylo-genetic trees. BMC Bioinformatics. 8:4602007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Hattori M, et al: From
genomics to chemical genomics: new developments in KEGG. Nucleic
Acids Res. 34:D354–D357. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Peden DB: The epidemiology and genetics of
asthma risk associated with air pollution. J Allergy Clin Immun.
115:213–219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
D’Amato G, Baena-Cagnani CE, Cecchi L, et
al: Climate change, air pollution and extreme events leading to
increasing prevalence of allergic respiratory diseases. Multidiscip
Respir Med. 8:122013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sugita M, Kuribayashi K, Nakagomi T,
Miyata S, Matsuyama T and Kitada O: Allergic bronchial asthma:
airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Intern Med.
42:636–643. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamaya M: Virus infection-induced
bronchial asthma exacerbation. Pulm Med. 2012:8348262012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Docherty SJ, Butcher LM, Schalkwyk LC and
Plomin R: Applicability of DNA pools on 500 K SNP microarrays for
cost-effective initial screens in genomewide association studies.
BMC Genomics. 8:2142007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yasuda H, Suzuki T, Zayasu K, et al:
Inflammatory and bronchospastic factors in asthma exacerbations
caused by upper respiratory tract infections. Tohoku J Exp Med.
207:109–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Husain M, Boermans HJ and Karrow NA:
Mesenteric lymph node transcriptome profiles in BALB/c mice
sensitized to three common food allergens. BMC Genomics. 12:122011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Di Valentin E, Crahay C, Garbacki N, et
al: New asthma biomarkers: lessons from murine models of acute and
chronic asthma. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 296:L185–L197.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Luzio JP, Rous BA, Bright NA, Pryor PR,
Mullock BM and Piper RC: Lysosome-endosome fusion and lysosome
biogenesis. J Cell Sci. 113:1515–1524. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zimmer A, Bouley J, Le Mignon M, et al: A
regulatory dendritic cell signature correlates with the clinical
efficacy of allergen-specific sublingual immunotherapy. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 129:1020–1030. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Y and Liu S: Protein-protein
interaction network analysis of children atopic asthma. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 16:867–872. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Caciotti A, Donati MA, Boneh A, et al:
Role of beta-galactosidase and elastin binding protein in lysosomal
and nonlysosomal complexes of patients with GM1-gangliosidosis. Hum
Mutat. 25:285–292. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hua H, Liang Z, Li W, et al: Phenotypic
and functional maturation of murine dendritic cells (DCs) induced
by purified Glycyrrhizin (GL). Int Immunopharmacol. 12:518–525.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eskelinen EL: Roles of LAMP-1 and LAMP-2
in lysosome biogenesis and autophagy. Mol Aspects Med. 27:495–502.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanaka Y, Guhde G, Suter A, et al:
Accumulation of autophagic vacuoles and cardiomyopathy in
LAMP-2-deficient mice. Nature. 406:902–906. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eskelinen EL, Tanaka Y and Saftig P: At
the acidic edge: emerging functions for lysosomal membrane
proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 13:137–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ausseil J, Loredo-Osti JC, Verner A, et
al: Localisation of a gene for mucopolysaccharidosis IIIC to the
pericentromeric region of chromosome 8. J Med Genet. 41:941–945.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fan X, Zhang H, Zhang S, et al:
Identification of the gene encoding the enzyme deficient in
mucopolysaccharidosis IIIC (Sanfilippo disease type C). Am J Hum
Genet. 79:738–744. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|