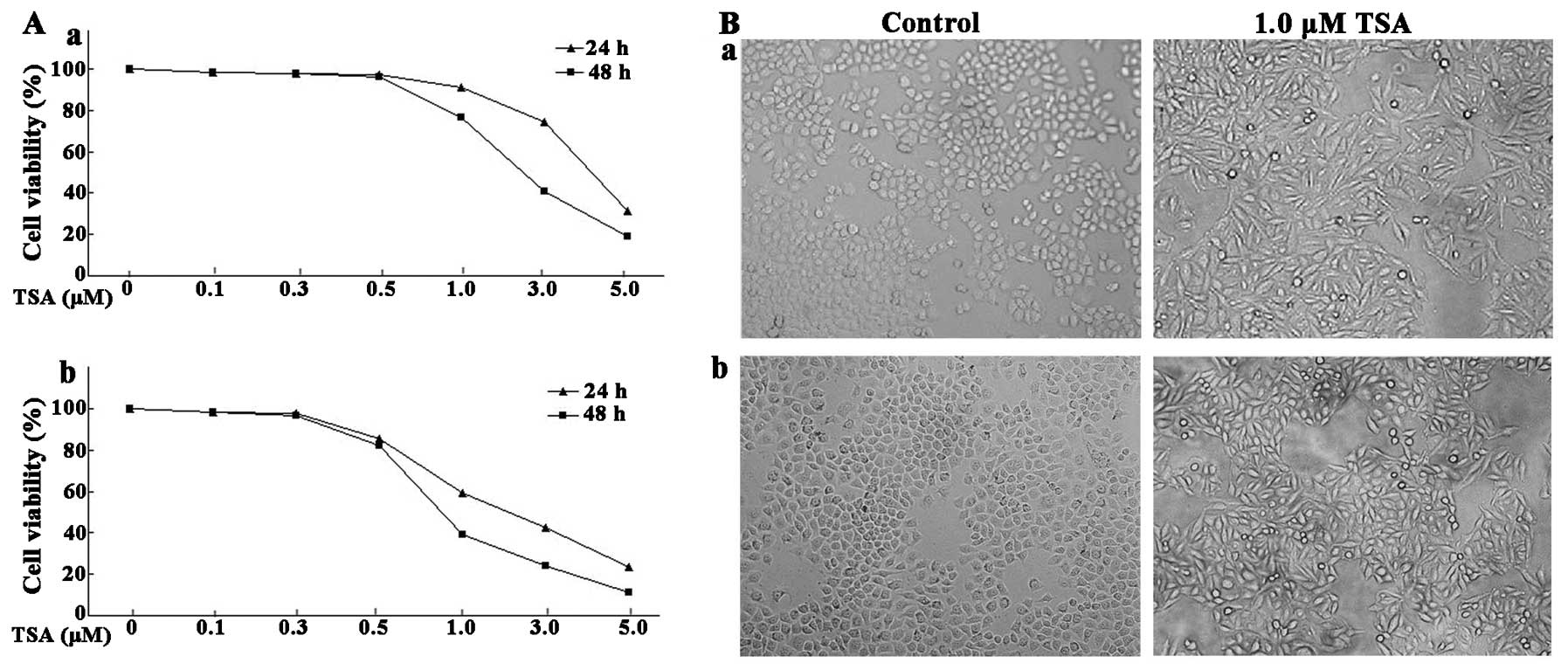
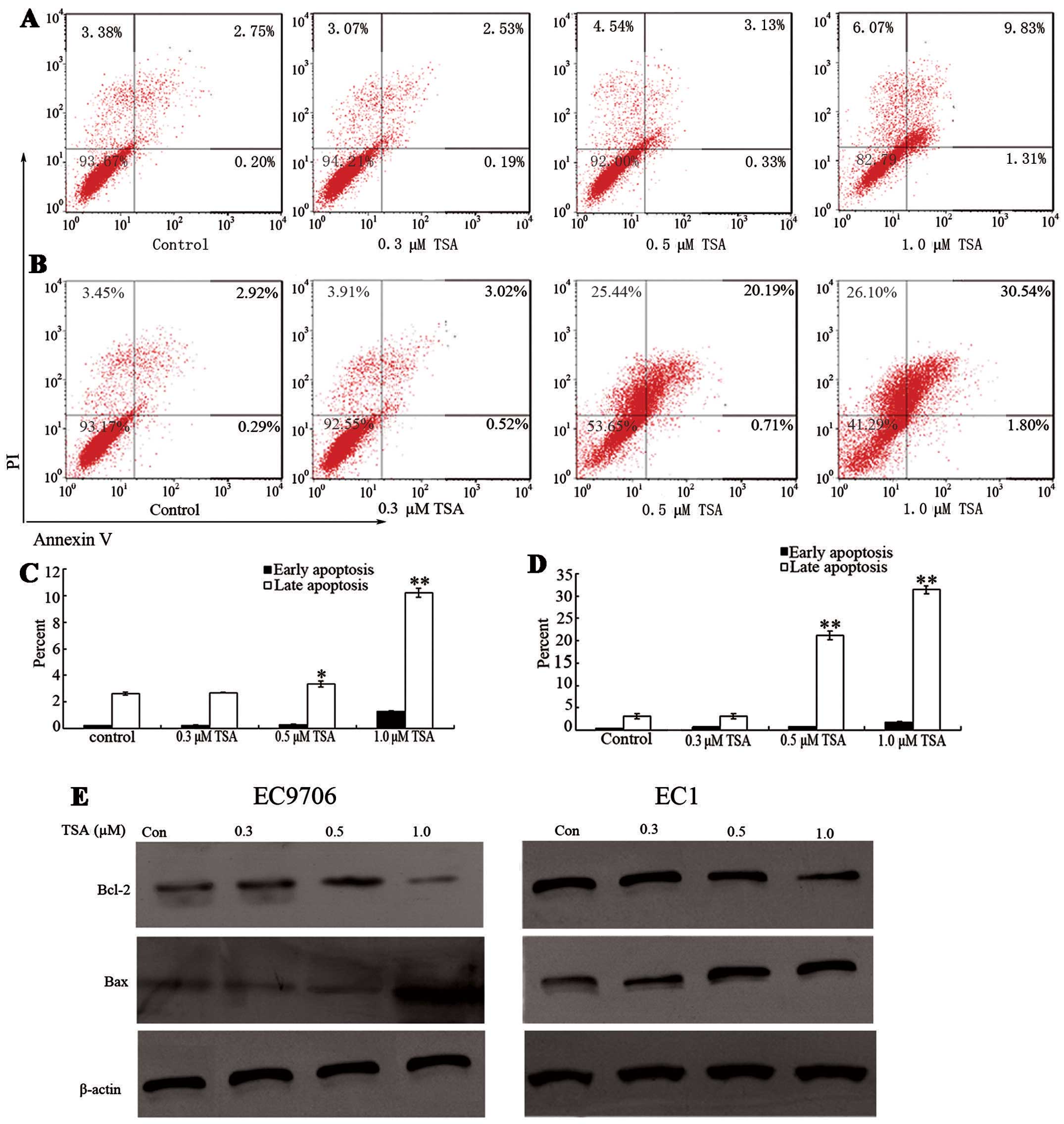
|
1
|
Zhu H, Huo X, Chen L, Wang H and Yu H:
Clinical experience with radio-, chemo- and hyperthermotherapy
combined trimodality on locally advanced esophageal cancer. Mol
Clin Oncol. 1:1009–1012. 2013.
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Minsky BD, Pajak TF, Ginsberg RJ, et al:
INT 0123 (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 94–05) phase III trial
of combined-modality therapy for esophageal cancer: high-dose
versus standard-dose radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 20:1167–1174.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Minucci S and Pelicci PG: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more)
treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:38–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reichert N, Choukrallah MA and Matthias P:
Multiple roles of class I HDACs in proliferation, differentiation
and development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:2173–2187. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ellis L, Atadja PW and Johnstone RW:
Epigenetics in cancer: targeting chromatin modifications. Mol
Cancer Ther. 8:1409–1420. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ellis L and Pili R: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors: advancing therapeutic strategies in hematological and
solid malignancies. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 3:2411–2469. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Abbas A and Gupta S: The role of histone
deacetylases in prostate cancer. Epigenetics. 3:300–309. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bonfils C, Walkinshaw DR, Besterman JM,
Yang XJ and Li Z: Pharmacological inhibition of histone
deacetylases for the treatment of cancer, neurodegenerative
disorders and inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin Drug Discov.
3:1041–1065. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ropero S and Esteller M: The role of
histone deacetylases (HDACs) in human cancer. Mol Oncol. 1:19–25.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cress WD and Seto E: Histone deacetylases,
transcriptional control and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 184:1–16. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meng F, Sun G, Zhong M, Yu Y and Brewer
MA: Inhibition of DNA methyltransferases, histone deacetylases and
lysine-specific demethylase-1 suppresses the tumorigenicity of the
ovarian cancer ascites cell line SKOV3. Int J Oncol. 43:495–502.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ueki N, Lee S, Sampson NS and Hayman MJ:
Selective cancer targeting with prodrugs activated by histone
deacetylases and a tumour-associated protease. Nat Commun.
4:27352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wilson PM, Labonte MJ, Martin SC, et al:
Sustained inhibition of deacetylases is required for the antitumor
activity of the histone deactylase inhibitors panobinostat and
vorinostat in models of colorectal cancer. Invest New Drugs.
31:845–857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Xiao W, Chen W, Luo L, Ye S and
Liu Y: The epigenetic modifier trichostatin A, a histone
deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lens epithelial cells. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e8842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stein C, Riedl S, Rüthnick D, Nötzold RR
and Bauer UM: The arginine methyltransferase PRMT6 regulates cell
proliferation and senescence through transcriptional repression of
tumor suppressor genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:9522–9533. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai Y, Cui W, Chen W, et al: The effects
of a histone deacetylase inhibitor on biological behavior of
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell lines and insights into the
underlying mechanisms. Cancer Cell Int. 13:572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Spiegel S, Milstien S and Grant S:
Endogenous modulators and pharmacological inhibitors of histone
deacetylases in cancer therapy. Oncogene. 31:537–551. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Mutze K, Langer R, Becker K, et al:
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 1 and 2 expression and chemotherapy in
gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:3336–3343. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jurkin J, Zupkovitz G, Lagger S, et al:
Distinct and redundant functions of histone deacetylases HDAC1 and
HDAC2 in proliferation and tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle. 10:406–412.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hoshino I and Matsubara H: Recent advances
in histone deacetylase targeted cancer therapy. Surg Today.
40:809–815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Noureen N, Rashid H and Kalsoom S:
Identification of type-specific anticancer histone deacetylase
inhibitors: road to success. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
66:625–633. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marson CM: Histone deacetylase inhibitors:
design, structure-activity relationships and therapeutic
implications for cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 9:661–692.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rezaei PF, Fouladdel S, Hassani S, et al:
Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by pericarp
polyphenol-rich extract of Baneh in human colon carcinoma HT29
cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1054–1059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ward CS, Eriksson P, Izquierdo-Garcia JL,
Brandes AH and Ronen SM: HDAC inhibition induces increased choline
uptake and elevated phosphocholine levels in MCF7 breast cancer
cells. PLoS One. 8:e626102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Watson JA, McKenna DJ, Maxwell P, et al:
Hyperacetylation in prostate cancer induces cell cycle aberrations,
chromatin reorganization and altered gene expression profiles. J
Cell Mol Med. 14:1668–1682. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gerard C and Goldbeter A: From quiescence
to proliferation: Cdk oscillations drive the mammalian cell cycle.
Front Physiol. 3:4132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yagi Y, Fushida S, Harada S, et al:
Effects of valproic acid on the cell cycle and apoptosis through
acetylation of histone and tubulin in a scirrhous gastric cancer
cell line. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1492010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang C, Fu M, Mani S, Wadler S,
Senderowicz AM and Pestell RG: Histone acetylation and the
cell-cycle in cancer. Front Biosci. 6:D610–D629. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aguero MF, Facchinetti MM, Sheleg Z and
Senderowicz AM: Phenoxodiol, a novel isoflavone, induces G1 arrest
by specific loss in cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activity by
p53-independent induction of p21WAF1/CIP1. Cancer Res.
65:3364–3373. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Queiroz AB, Focchi G, Dobo C, Gomes TS,
Ribeiro DA and Oshima CT: Expression of p27, p21 (WAF/Cip1) and p16
(INK4a) in normal oral epithelium, oral squamous papilloma and oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 30:2799–2803.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tula-Sanchez AA, Havas AP, Alonge PJ, et
al: A model of sensitivity and resistance to histone deacetylase
inhibitors in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: Role of
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:949–961.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
You BR and Park WH: Trichostatin A induces
apoptotic cell death of HeLa cells in a Bcl-2 and oxidative
stress-dependent manner. Int J Oncol. 42:359–366. 2013.
|
|
34
|
Hacker S, Karl S, Mader I, et al: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors prime medulloblastoma cells for
chemotherapy-induced apoptosis by enhancing p53-dependent Bax
activation. Oncogene. 30:2275–2281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang J, Roberts TM and Shivdasani RA:
Targeting PI3K signaling as a therapeutic approach for colorectal
cancer. Gastroenterology. 141:50–61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen CS, Weng SC, Tseng PH, Lin HP and
Chen CS: Histone acetylation-independent effect of histone
deacetylase inhibitors on Akt through the reshuffling of protein
phosphatase 1 complexes. J Biol Chem. 280:38879–38887. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu B and Kuang A: Genetic alterations in
MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways and the generation,
progression, diagnosis and therapy of thyroid cancer. Sheng Wu Yi
Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 29:1221–1225. 2012.In Chinese.
|