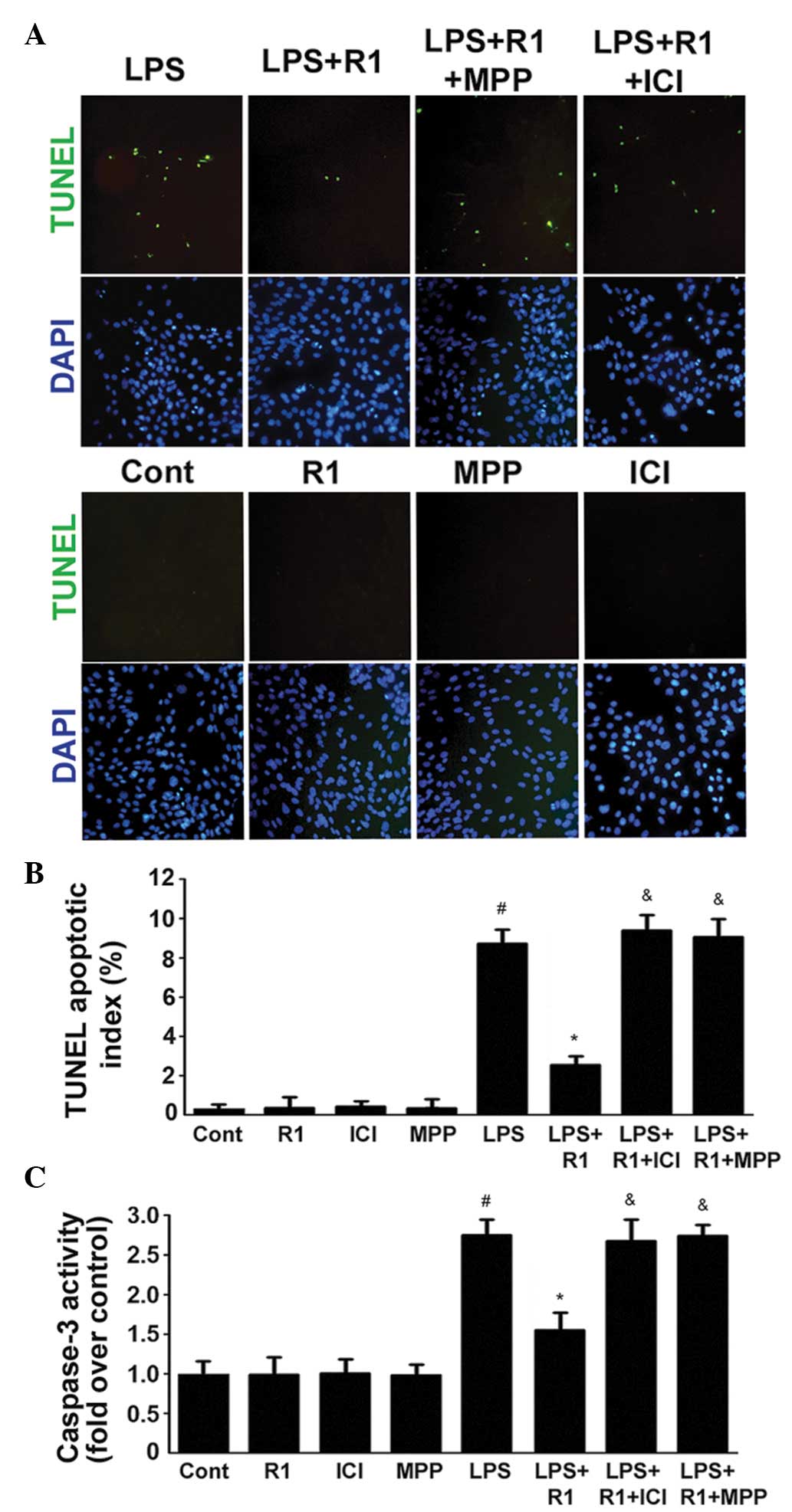
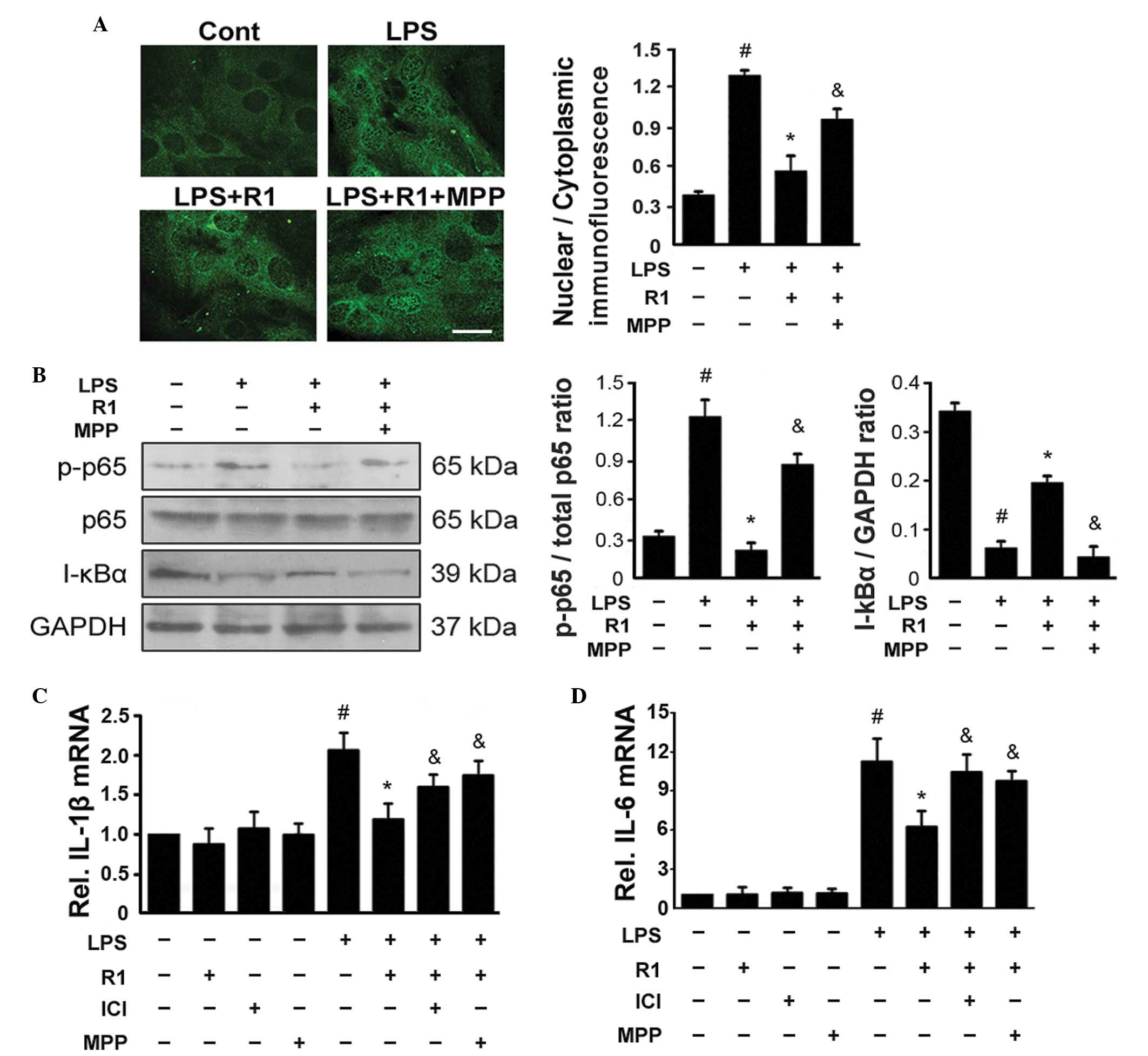
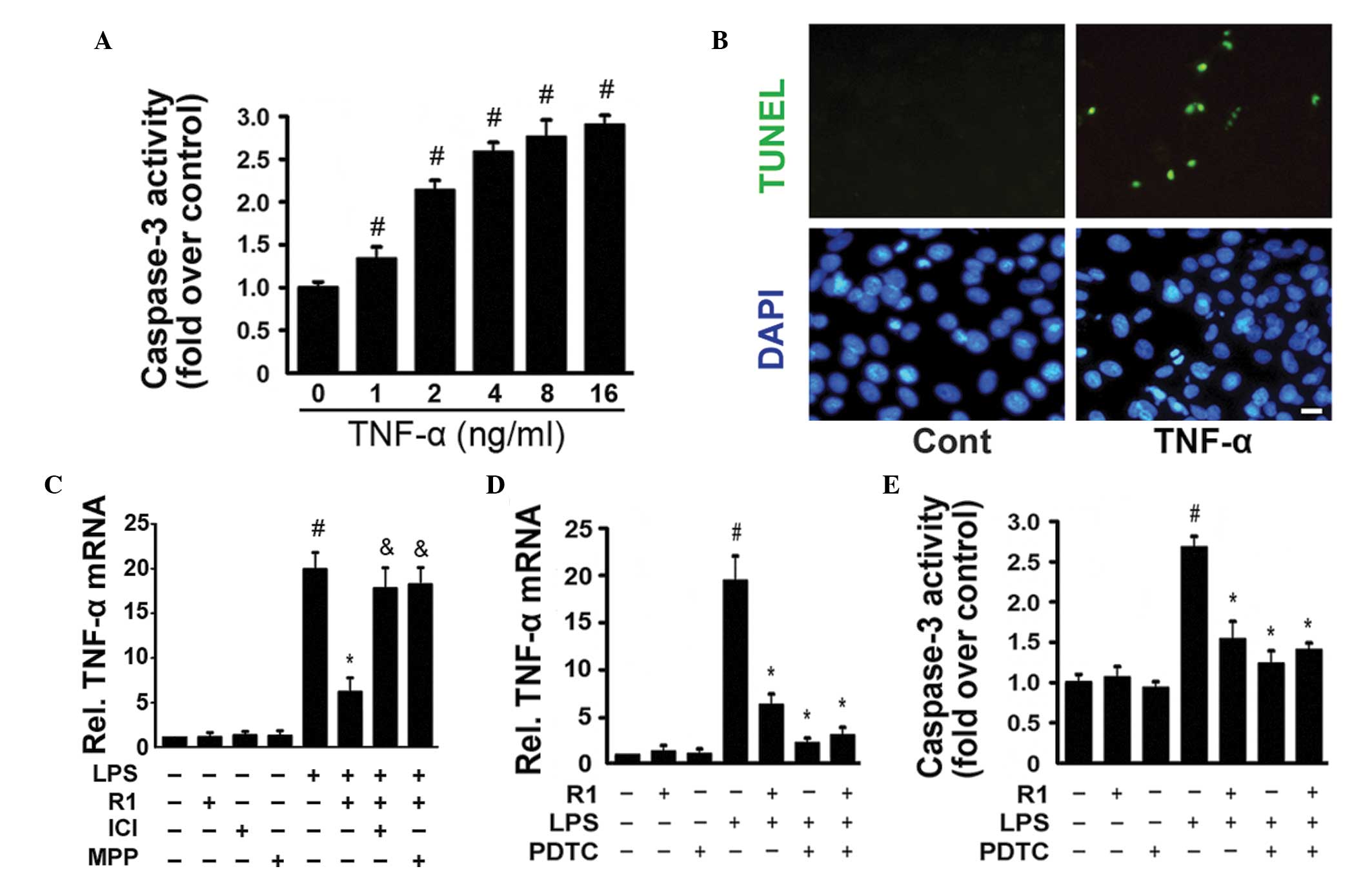
|
1
|
Merx MW and Weber C: Sepsis and the heart.
Circulation. 116:793–802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crouser E, Exline M, Knoell D and Wewers
MD: Sepsis: links between pathogen sensing and organ damage. Curr
Pharm Des. 14:1840–1852. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S and Moss M:
The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through
2000. N Engl J Med. 348:1546–1554. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rudiger A and Singer M: Mechanisms of
sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med. 35:1599–1608.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baumgarten G, Knuefermann P, Schuhmacher
G, et al: Toll-like receptor 4, nitric oxide, and myocardial
depression in endotoxemia. Shock. 25:43–49. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hickson-Bick DL, Jones C and Buja LM:
Stimulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy by
lipopolysaccharide in the neonatal rat cardiomyocyte protects
against programmed cell death. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 44:411–418.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zanotti-Cavazzoni SL and Hollenberg SM:
Cardiac dysfunction in severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr Opin
Crit Care. 15:392–397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Davani EY, Boyd JH, Dorscheid DR, et al:
Cardiac ICAM-1 mediates leukocyte-dependent decreased ventricular
contractility in endotoxemic mice. Cardiovasc Res. 72:134–142.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu H, Shan L, Schiller PW, Mai A and Peng
T: Histone deacetylase-3 activation promotes tumor necrosis
factor-alpha (TNF-α) expression in cardiomyocytes during
lipopolysaccharide stimulation. J Biol Chem. 285:9429–9436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Adamopoulos S, Parissis JT and Kremastinos
DT: A glossary of circulating cytokines in chronic heart failure.
Eur J Heart Fail. 3:517–526. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Collins T, Read MA, Neish AS, Whitley MZ,
Thanos D and Maniatis T: Transcriptional regulation of endothelial
cell adhesion molecules: NF-κB and cytokine-inducible enhancers.
FASEB J. 9:899–909. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fischer E, Van Zee KJ, Marano MA, et al:
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist circulates in experimental
inflammation and in human disease. Blood. 79:2196–2200.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ceylan-Isik AF, Zhao P, Zhang B, Xiao X,
Su G and Ren J: Cardiac overexpression of metallothionein rescues
cardiac contractile dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress
but not autophagy in sepsis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:367–378. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Peng T, Lu X, Lei M, Moe GW and Feng Q:
Inhibition of p38 MAPK decreases myocardial TNF-α expression and
improves myocardial function and survival in endotoxemia.
Cardiovasc Res. 59:893–900. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van Empel VP, Bertrand AT, Hofstra L,
Crijns HJ, Doevendans PA and De Windt LJ: Myocyte apoptosis in
heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 67:21–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hale SL, Birnbaum Y and Kloner RA:
Estradiol, administered acutely, protects ischemic myocardium in
both female and male rabbits. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2:47–52.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baker L, Meldrum KK, Wang M, et al: The
role of estrogen in cardiovascular disease. J Surg Res.
115:325–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ylikorkala O: HRT as secondary prevention
of cardiovascular disease. Maturitas. 47:315–318. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schröder J, Kahlke V, Staubach KH, Zabel P
and Stuber F: Gender differences in human sepsis. Arch Surg.
133:1200–1205. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Usui T: Pharmaceutical prospects of
phytoestrogens. Endocr J. 53:7–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang HS and Wang SQ: Notoginsenoside R1
inhibits TNF-α-induced fibronectin production in smooth muscle
cells via the ROS/ERK pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 40:1664–1674.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun K, Wang CS, Guo J, et al: Protective
effects of ginsenoside Rb1, ginsenoside Rg1, and notoginsenoside R1
on lipopolysaccharide-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat
mesentery. Life Sci. 81:509–518. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang WJ, Wojta J and Binder BR:
Notoginsenoside R1 counteracts endotoxin-induced activation of
endothelial cells in vitro and endotoxin-induced lethality in mice
in vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 17:465–474. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baeuerle PA and Henkel T: Function and
activation of nf-κb in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol.
12:141–179. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lennikov A, Kitaichi N, Noda K, et al:
Amelioration of endotoxin-induced uveitis treated with an iκb
kinase β inhibitor in rats. Mol Vis. 18:2586–2597. 2012.
|
|
26
|
Zandi E, Chen Y and Karin M: Direct
phosphorylation of IkappaB by IKKα and IKKβ: discrimination between
free and NF-κB-bound substrate. Science. 281:1360–1363. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carlson DL, Willis MS, White DJ, Horton JW
and Giroir BP: Tumor necrosis factor-α-induced caspase activation
mediates endotoxin-related cardiac dysfunction. Crit Care Med.
33:1021–1028. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tatsumi T, Akashi K, Keira N, et al:
Cytokine-induced nitric oxide inhibits mitochondrial energy
production and induces myocardial dysfunction in endotoxin-treated
rat hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 37:775–784. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Brinckmann M, Kaschina E, Altarche-Xifró
W, et al: Estrogen receptor α supports cardiomyocytes indirectly
through post-infarct cardiac c-kit+ cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
47:66–75. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu CH, Liu JY, Wu JP, et al: et al
17β-estradiol reduces cardiac hypertrophy mediated through the
up-regulation of PI3K/Akt and the suppression of calcineurin/NF-AT3
signaling pathways in rats. Life Sci. 78:347–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Murphy E: Estrogen signaling and
cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 109:687–696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xi YD, Yu HL, Ding J, et al: Flavonoids
protect cerebrovascular endothelial cells through Nrf2 and PI3K
from β-amyloid peptide-induced oxidative damage. Curr Neurovasc
Res. 9:32–41. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun B, Xiao J, Sun XB and Wu Y:
Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates cardiac dysfunction in endotoxemic
mice: an insight into oestrogen receptor activation and PI3K/Akt
signalling. Br J Pharmacol. 168:1758–1770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Xiao J, Wang NL, Sun B and Cai GP:
Estrogen receptor mediates the effects of pseudoprotodiocsin on
adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
299:C128–C138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|