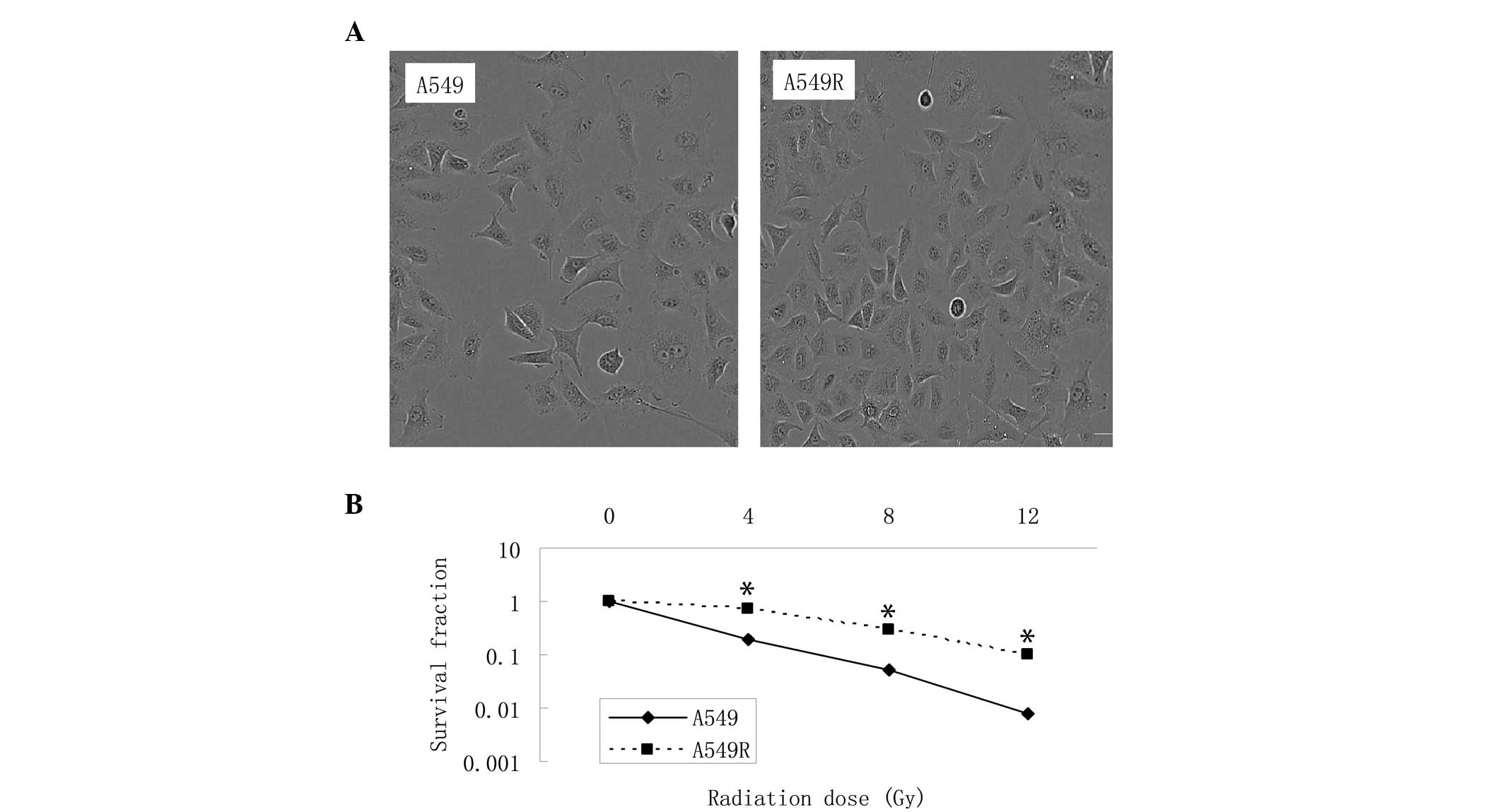
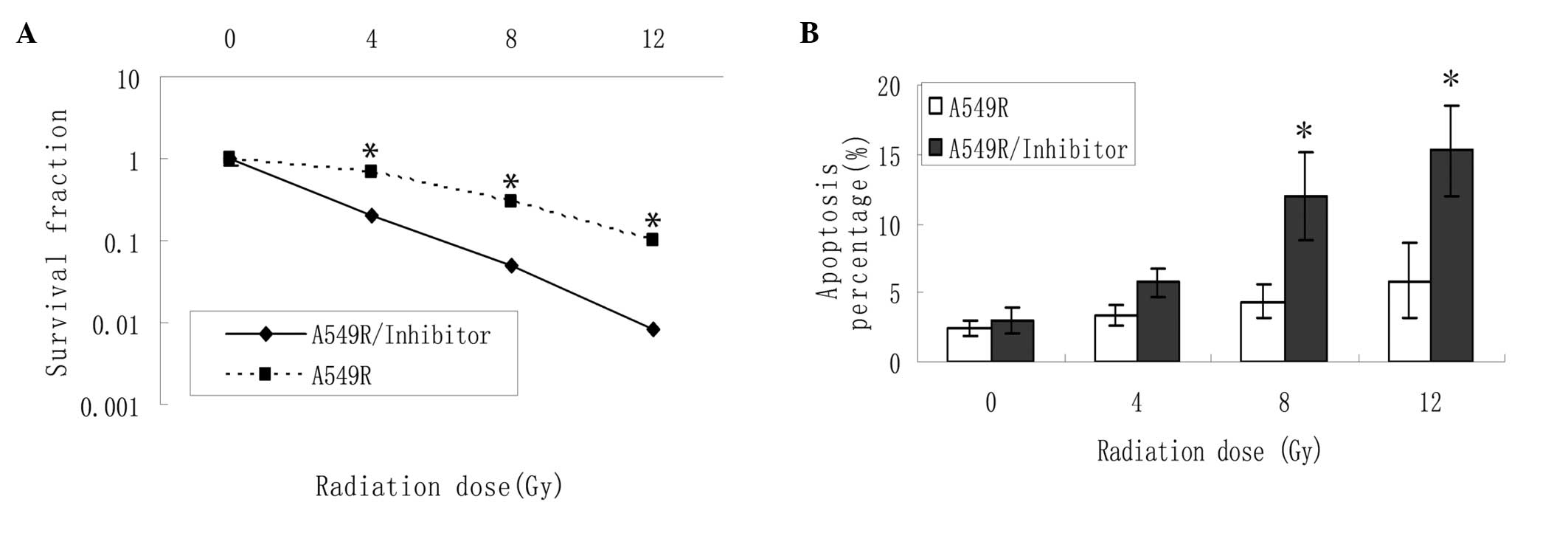
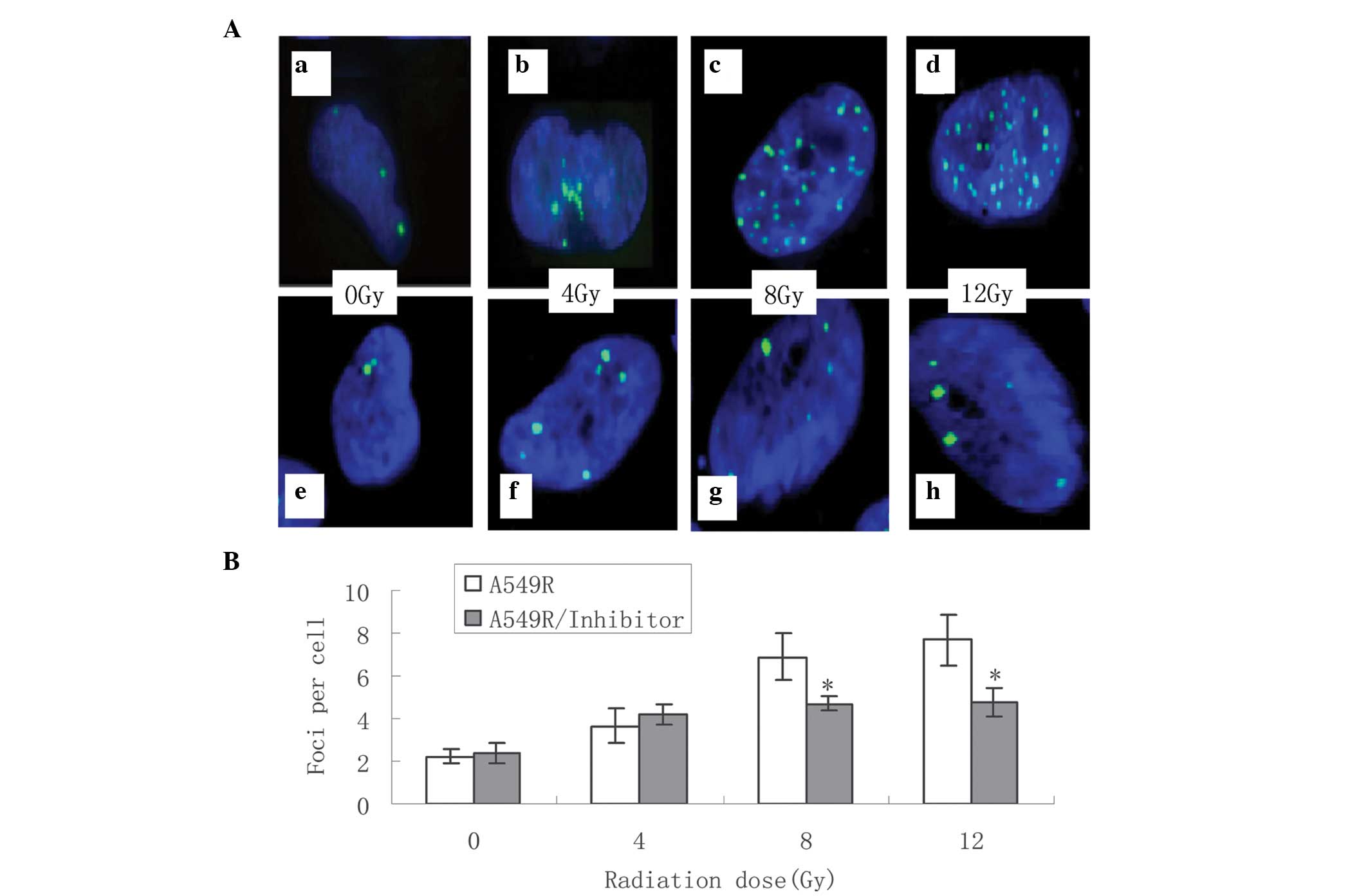
|
1
|
Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria JC and
Rabe KF: Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: Recent
developments. Lancet. 382:709–719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang HJ, Kim N, Seong KM, Youn H and Youn
B: Investigation of radiation-induced transcriptome profile of
radioresistant non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells using RNA-seq.
PloS One. 8:e593192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gupta S, Koru-Sengul T, Arnold SM, Devi
GR, Mohiuddin M and Ahmed MM: Low-dose fractionated radiation
potentiates the effects of cisplatin independent of the
hyper-radiation sensitivity in human lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 10:292–302. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li J, Yang CX, Mei ZJ, et al: Involvement
of cdc25c in cell cycle alteration of a radioresistant lung cancer
cell line established with fractionated ionizing radiation. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:5725–5730. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim YS, Kang MJ and Cho YM: Low production
of reactive oxygen species and high DNA repair: Mechanism of
radio-resistance of prostate cancer stem cells. Anticancer Res.
33:4469–4474. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vignard J, Mirey G and Salles B:
Ionizing-radiation induced DNA double-strand breaks: a direct and
indirect lighting up. Radiother Oncol. 108:362–369. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Beskow C, Skikuniene J, Holgersson A, et
al: Radioresistant cervical cancer shows upregulation of the NHEJ
proteins DNA-PKcs, Ku70 and Ku86. Br J Cancer. 101:816–821. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Daido S, Yamamoto A, Fujiwara K, Sawaya R,
Kondo S and Kondo Y: Inhibition of the DNA-dependent protein kinase
catalytic subunit radiosensitizes malignant glioma cells by
inducing autophagy. Cancer Res. 65:4368–4375. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Negroni A, Stronati L, Grollino MG,
Barattini P, Gumiero D and Danesi DT: Radioresistance in a tumour
cell line correlates with radiation inducible Ku 70/80 end-binding
activity. Int J Radiat Biol. 84:265–276. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vandersickel V, Mancini M, Slabbert J, et
al: The radiosensitizing effect of Ku70/80 knockdown in MCF10A
cells irradiated with X-rays and p(66)+Be(40) neutrons. Radiat
Oncol. 5:302010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang C and Lees-Miller SP: Detection and
repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double strand breaks: New
developments in nonhomologous end joining. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 86:440–449. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khanna KK, Lavin MF, Jackson SP and
Mulhern TD: ATM a central controller of cellular responses to DNA
damage. Cell Death Differ. 8:1052–1065. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bakkenist CJ and Kastan MB: DNA damage
activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer
dissociation. Nature. 421:499–506. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tichy A, Durisova K, Salovska B, et al:
Radio-sensitization of human leukaemic MOLT-4 cells by
DNA-dependent protein kinase inhibitor, NU7441. Radiat Environ
Biophys. 53:83–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Keogh MC, Kim JA, Downey M, et al: A
phosphatase complex that dephosphorylates gammaH2AX regulates DNA
damage checkpoint recovery. Nature. 439:497–501. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Leu JD, Chiu YW, Lo CC, et al: Enhanced
cellular radio-sensitivity induced by cofilin-1 over-expression is
associated with reduced DNA repair capacity. Int J Radiat Biol.
89:433–444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
An J, Huang YC, Xu QZ, et al: DNA-PKcs
plays a dominant role in the regulation of H2AX phosphorylation in
response to DNA damage and cell cycle progression. BMC Mol Biol.
11:182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Du L, Zhou LJ, Pan XJ, et al:
Radiosensitization and growth inhibition of cancer cells mediated
by an scFv antibody gene against DNA-PKcs in vitro and in vivo.
Radiat Oncol. 5:702010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xiong H, Lee RJ, Haura EB, Edwards JG,
Dynan WS and Li S: Intranuclear delivery of a novel
antibody-derived radiosensitizer targeting the DNA-dependent
protein kinase catalytic subunit. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
83:1023–1030. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhou X, Zhang X, Xie Y, Tanaka K, Wang B
and Zhang H: DNA-PKcs inhibition sensitizes cancer cells to
carbon-ion irradiation via telomere capping disruption. PLoS One.
8:e726412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Veuger SJ, Curtin NJ, Richardson CJ, Smith
GC and Durkacz BW: Radiosensitization and DNA repair inhibition by
the combined use of novel inhibitors of DNA -dependent protein
kinase and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Cancer Res. 63:6008–6015.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Veuger SJ, Curtin NJ, Smith GC and Durkacz
BW: Effects of novel inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1
and the DNA-dependent protein kinase on enzyme activities and DNA
repair. Oncogene. 23:7322–7329. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Uphoff CC and Drexler HG: Detecting
mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by polymerase chain
reaction. Methods Mol Biol. 731:93–103. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bristow RG, Jang A, Peacock J, Chung S,
Benchimol S and Hill RP: Mutant p53 increases radioresistance in
rat embryo fibroblasts simultaneously transfected with HPV16-E7
and/or activated H-ras. Oncogene. 9:1527–1536. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maroschik B, Gürtler A, Krämer A, et al:
Radiation-induced alterations of histone post-translational
modification levels in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Radiat Oncol.
9:152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Djuzenova CS, Elsner I, Katzer A, et al:
Radiosensitivity in breast cancer assessed by the histone γ-H2AX
and 53BP1 foci. Radiat Oncol. 8:982013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fernández MI, Gong Y, Ye Y, et al: γ-H2AX
level in peripheral blood lymphocytes as a risk predictor for
bladder cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:2543–2547. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lee SH and Kim CH: DNA-dependent protein
kinase complex: A multifunctional protein in DNA repair and damage
checkpoint. Mol Cells. 13:159–166. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hefferin ML and Tomkinson AE: Mechanism of
DNA double-strand break repair by non-homologous end joining. DNA
Repair (Amst). 4:639–648. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gil del Alcazar CR, Hardebeck MC, et al:
Inhibition of DNA double-strand break repair by the dual PI3K/mTOR
inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 as a strategy for radiosensitization of
glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1235–1248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tonotsuka N, Hosoi Y, Miyazaki S, et al:
Heterogeneous expression of DNA-dependent protein kinase in
esophageal cancer and normal epithelium. Int J Mol Med. 18:441–447.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ryu JS, Um JH, Kang CD, et al:
Fractionated irradiation leads to restoration of drug sensitivity
in MDR cells that correlates with down-regulation of P-gp and
DNA-dependent protein kinase activity. Radiat Res. 162:527–535.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ciszewski WM, Tavecchio M, Dastych J and
Curtin NJ: DNA-PK inhibition by NU7441 sensitizes breast cancer
cells to ionizing radiation and doxorubicin. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 143:47–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Qu YY, Hu SL, Xu XY, et al: Nimotuzumab
enhances the radiosensitivity of cancer cells in vitro by
inhibiting radiation-induce d DNA damage repair. Plos one.
8:e707272013. View Article : Google Scholar
|