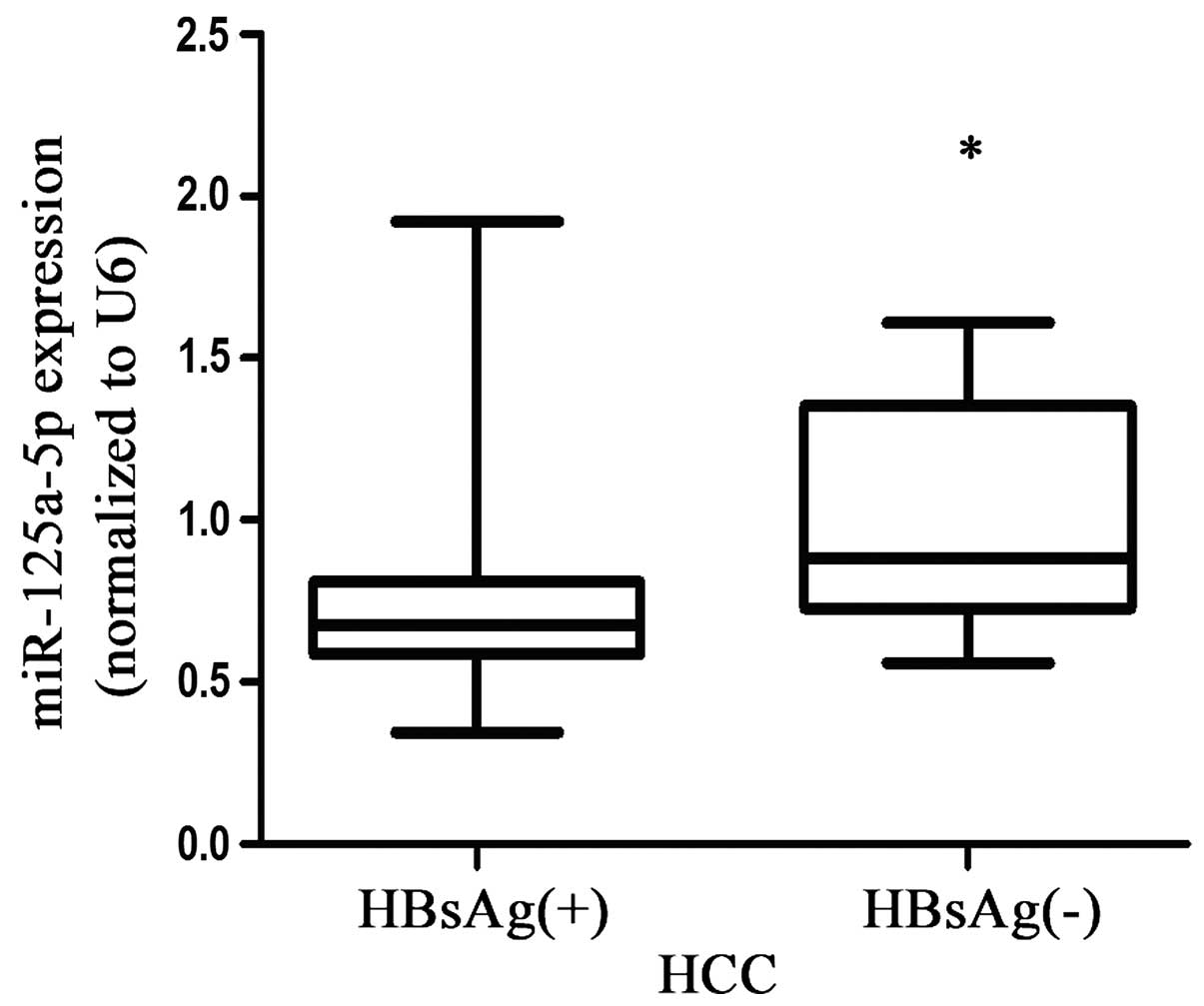
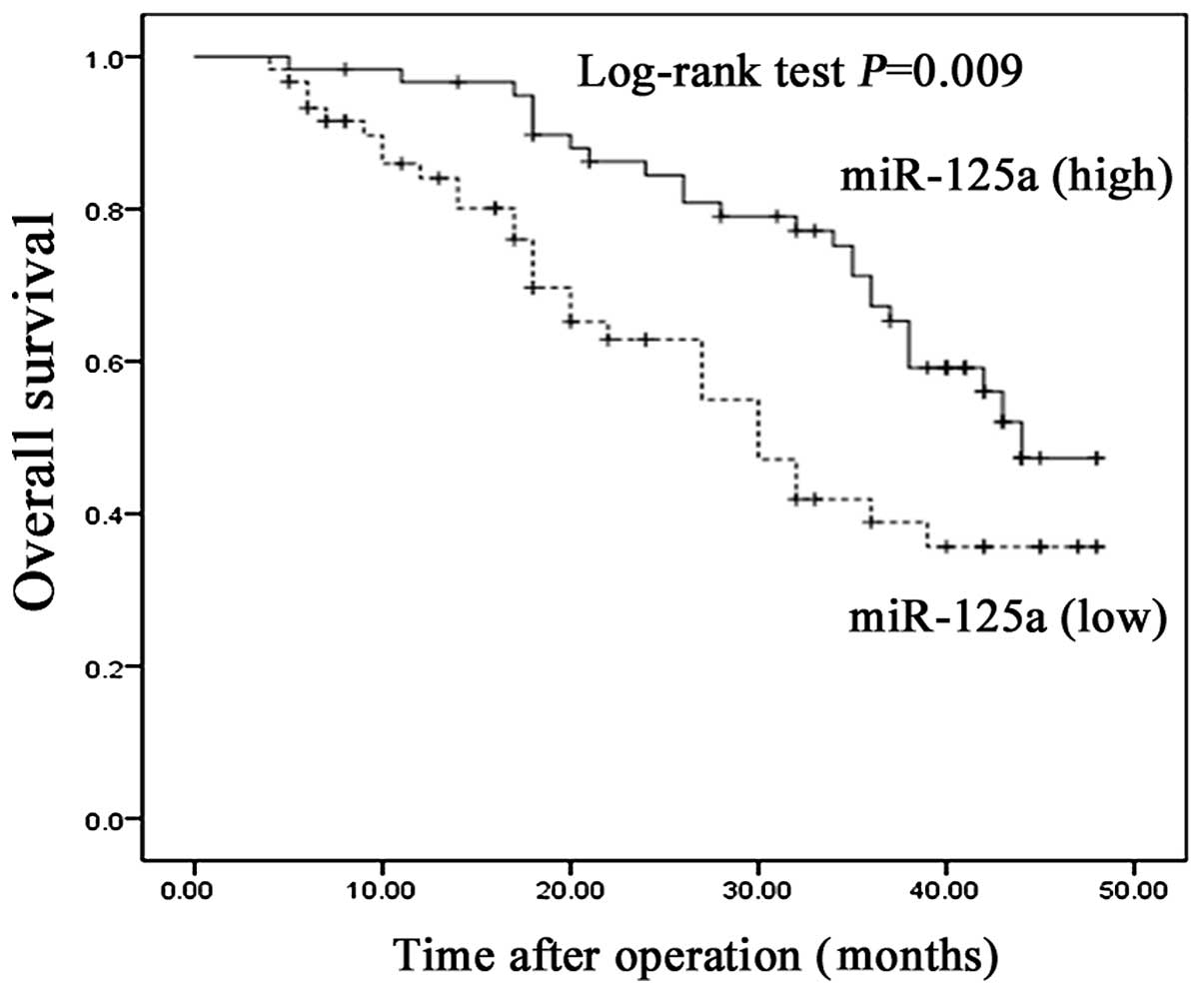
|
1
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li L, Guo Z, Wang J, Mao Y and Gao Q:
Serum miR-18a: a potential marker for hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma screening. Dig Dis Sci. 57:2910–2916.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ding J, Huang S, Wu S, et al: Gain of
miR-151 on chromosome 8q24.3 facilitates tumour cell migration and
spreading through downregulating RhoGDIA. Nat Cell Biol.
12:390–399. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bi Q, Tang S, Xia L, et al: Ectopic
expression of MiR-125a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting MMP11 and VEGF. PloS One.
7:e401692012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Coppola N, Potenza N, Pisaturo M, et al:
Liver microRNA has-miR-125a-5p in HBV chronic infection:
correlation with HBV replication and disease progression. PLoS One.
8:e653362013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al:
Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers
for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 18:997–1006.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fang C, Zhu DX, Dong HJ, et al: Serum
microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for diffuse large B cell
lymphoma. Annals Hematol. 91:553–559. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, et al: Serum
microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS One. 3:e31482008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al:
Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer
detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10513–10518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim KH, Kim ND and Seong BL: Discovery and
development of anti-HBV agents and their resistance. Molecules.
15:5878–5908. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu X, Wan X, Li Z, Lin C, Zhan Y and Lu
X: Golgi protein 73 (GP73), a useful serum marker in liver
diseases. Clin Chem Lab Med. 49:1311–1316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, et al: Risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum
hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA. 295:65–73. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
2004 guidelines for surgical treatment of
primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Chinese Journal of Hepatology.
13:329–330. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, et al:
Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol.
22:696–699. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yao J, Liang L, Huang S, et al:
MicroRNA-30d promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting
Galphai2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 51:846–856.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lau DT and Bleibel W: Current status of
antiviral therapy for hepatitis B. Therap Adv Gastroenterol.
1:61–75. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bayram A, Erkilic S, Ozkur A, Bayram M and
Sari I: Quantification of intrahepatic total hepatitis B virus DNA
in chronic hepatitis B patients and its relationship with liver
histology. J Clin Pathol. 61:338–342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yuen MF, Ng IO, Fan ST, et al:
Significance of HBV DNA levels in liver histology of HBeAg and
Anti-HBe positive patients with chronic hepatitis B. Am J
Gastroenterol. 99:2032–2037. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
European Association For The Study Of The
Liver: EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of chronic
hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 50:227–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Russo A and Potenza N: Antiviral effects
of human microRNAs and conservation of their target sites. FEBS
Lett. 585:2551–2555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Potenza N, Papa U, Mosca N, Zerbini F,
Nobile V and Russo A: Human microRNA hsa-miR-125a-5p interferes
with expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nucleic Acids
Res. 39:5157–5163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park SO, Kumar M and Gupta S: TGF-beta and
iron differently alter HBV replication in human hepatocytes through
TGF-beta/BMP signaling and cellular microRNA expression. PloS One.
7:e392762012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sekiya Y, Ogawa T, Yoshizato K, Ikeda K
and Kawada N: Suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation by
microRNA-29b. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 412:74–79. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vizzutti F, Arena U, Rega L and Pinzani M:
Non invasive diagnosis of portal hypertension in cirrhotic
patients. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 32:80–87. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie SB, Yao JL, Zheng RQ, Peng XM and Gao
ZL: Serum hyaluronic acid, procollagen type III and IV in
histological diagnosis of liver fibrosis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Dis Int. 2:69–72. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parsian H, Rahimipour A, Nouri M, et al:
Serum hyaluronic acid and laminin as biomarkers in liver fibrosis.
J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 19:169–174. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lydatakis H, Hager IP, Kostadelou E,
Mpousmpoulas S, Pappas S and Diamantis I: Non-invasive markers to
predict the liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Liver Int. 26:864–871. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ahmed F, Perz JF, Kwong S, Jamison PM,
Friedman C and Bell BP: National trends and disparities in the
incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma, 1998–2003. Prev Chronic Dis.
5:A742008.
|
|
29
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qi P, Cheng SQ, Wang H, Li N, Chen YF and
Gao CF: Serum microRNAs as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma
in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS
One. 6:e284862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|