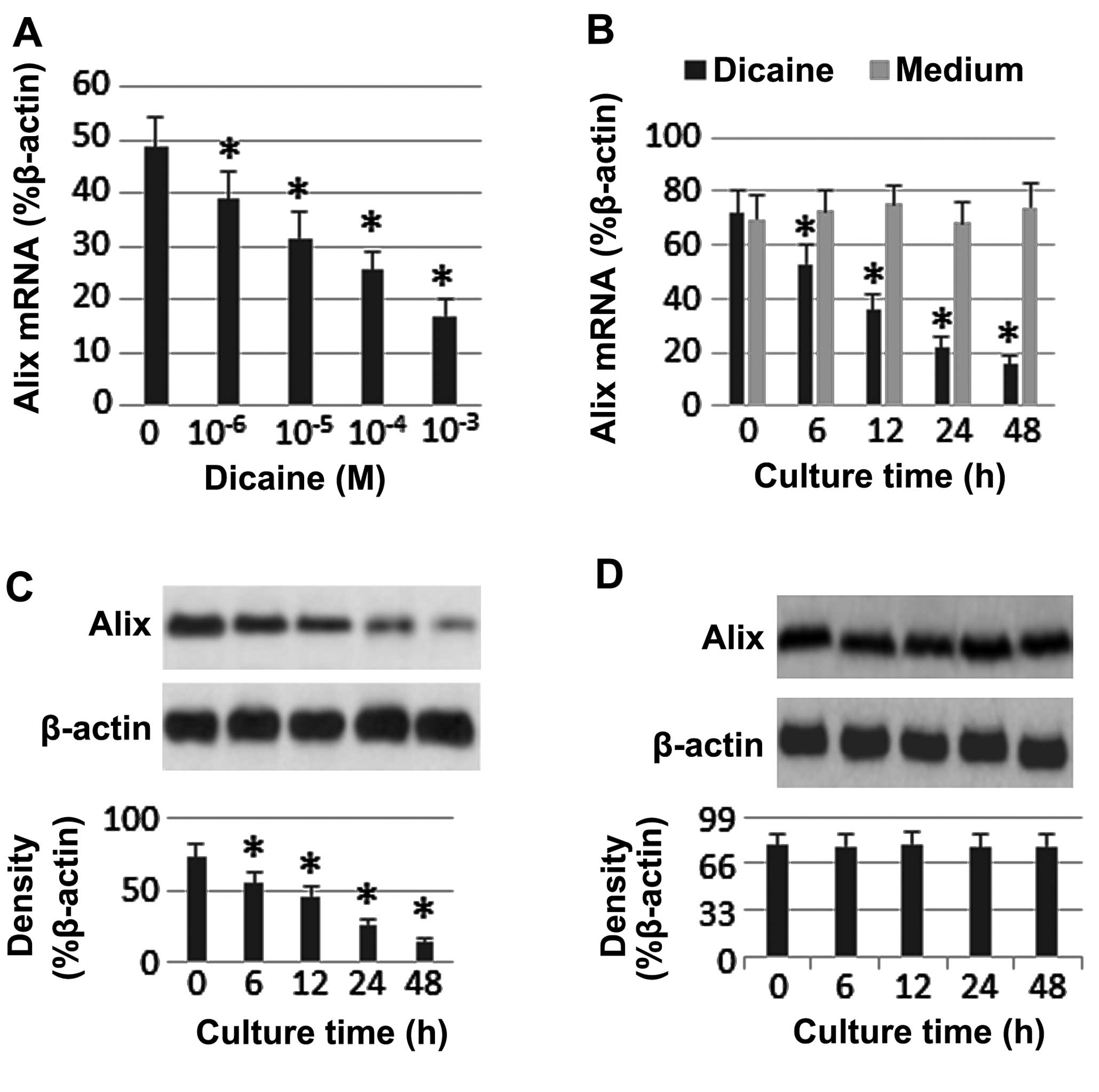
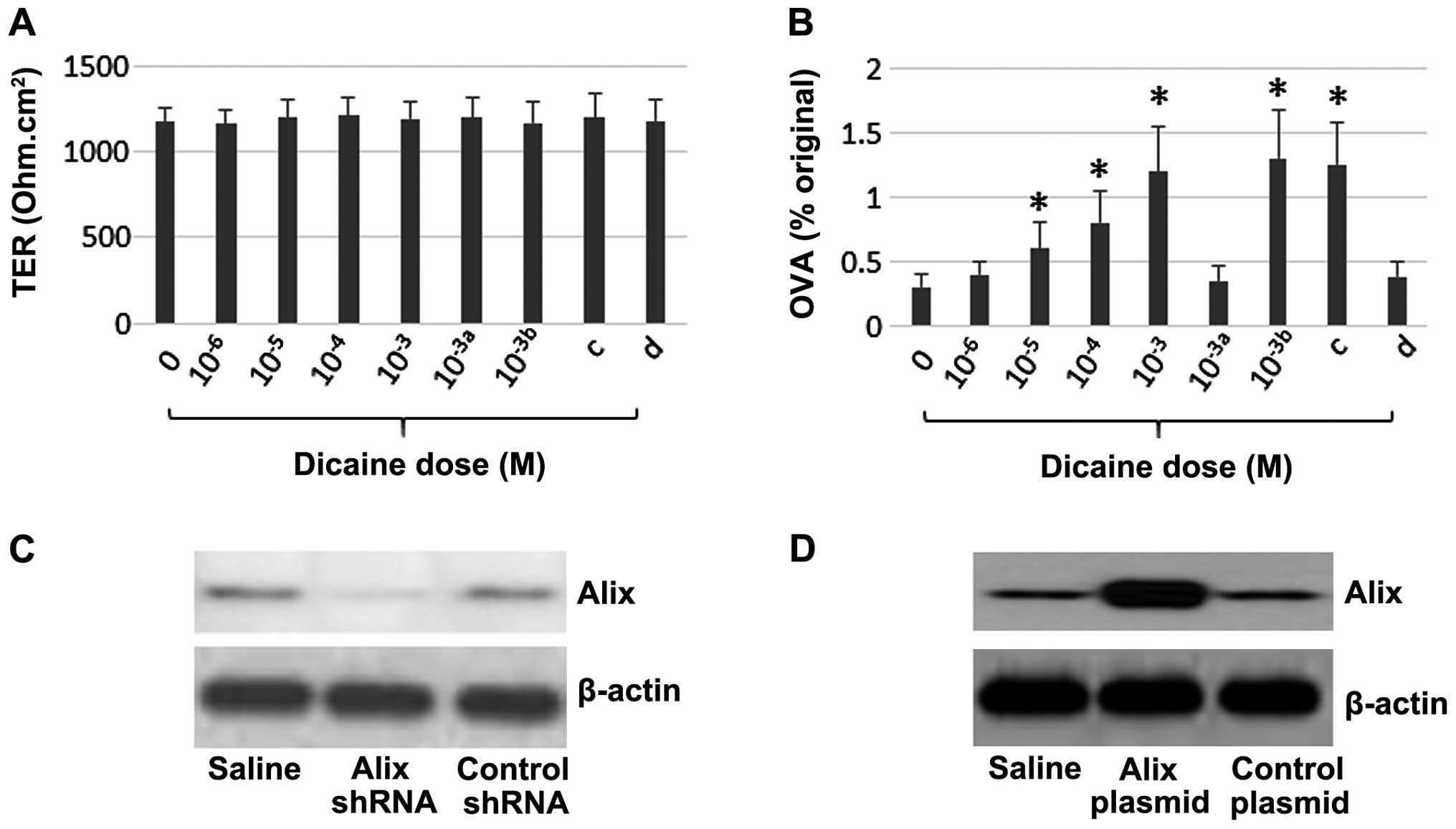
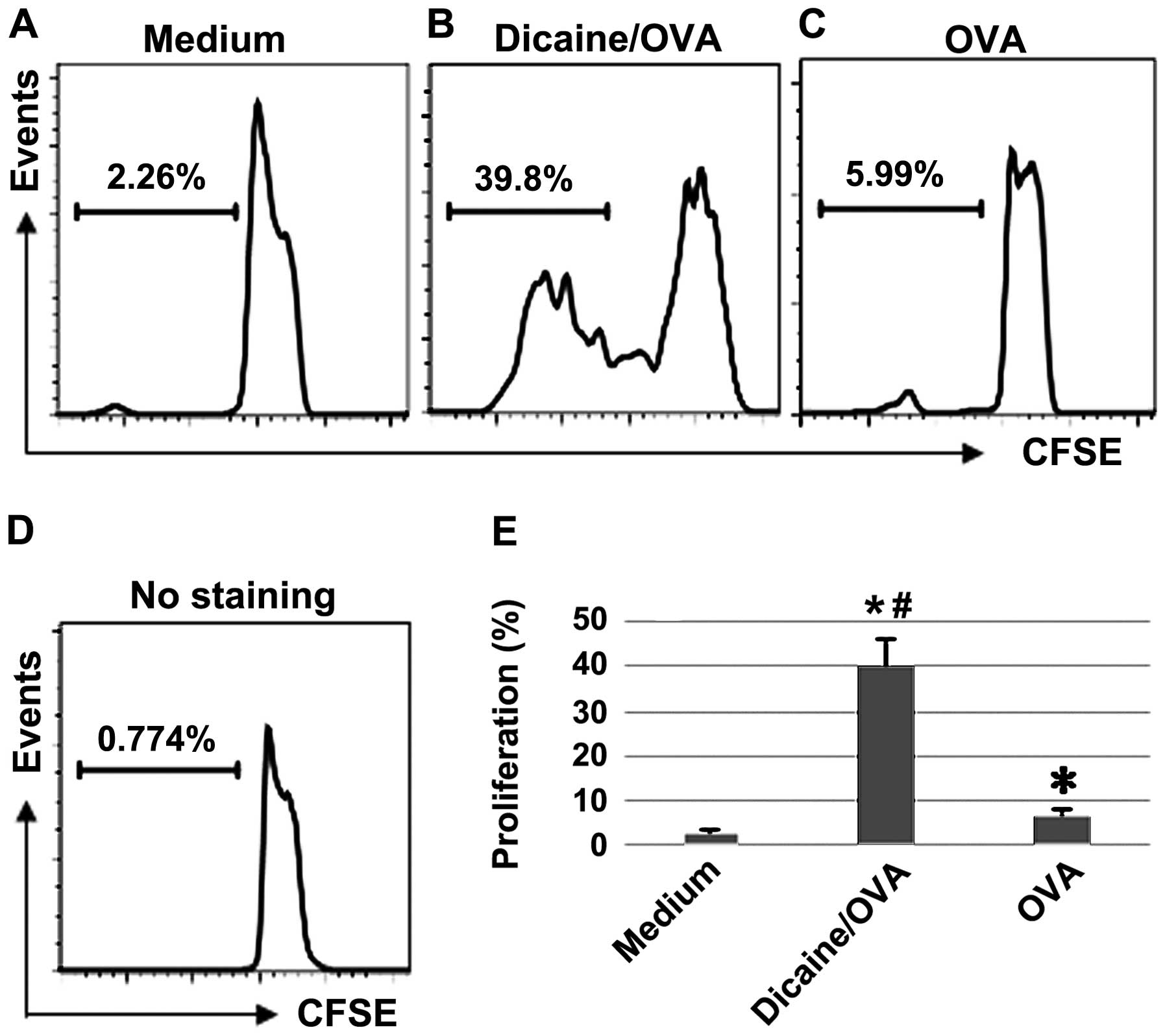
|
1
|
Leino MS, Loxham M, Blume C, et al:
Barrier disrupting effects of alternaria alternata extract on
bronchial epithelium from asthmatic donors. PLoS One. 8:e712782013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suzuki T: Regulation of intestinal
epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci.
70:631–659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
McCole DF: Regulation of epithelial
barrier function by the inflammatory bowel disease candidate gene,
PTPN2. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1257:108–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sevilla LM, Latorre V, Sanchis A and Pérez
P: Epidermal inactivation of the glucocorticoid receptor triggers
skin barrier defects and cutaneous inflammation. J Invest Dermatol.
133:361–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yu Y, Liu ZQ, Liu XY, et al:
Stress-derived corticotropin releasing factor breaches epithelial
endotoxin tolerance. PLoS One. 8:e657602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng PY, Feng BS, Oluwole C, et al:
Psychological stress induces eosinophils to produce corticotrophin
releasing hormone in the intestine. Gut. 58:1473–1479. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu T, Wang BQ, Wang CS and Yang PC:
Concurrent exposure to thermal stress and oral Ag induces
intestinal sensitization in the mouse by a mechanism of regulation
of IL-12 expression. Immunol Cell Biol. 84:430–439. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang PC, Jury J, Söderholm JD, et al:
Chronic psychological stress in rats induces intestinal
sensitization to luminal antigens. Am J Pathol. 168:104–114. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kobayashi K, Ohno S, Uchida S, Amano O,
Sakagami H and Nagasaka H: Cytotoxicity and type of cell death
induced by local anesthetics in human oral normal and tumor cells.
Anticancer Res. 32:2925–2933. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Strappazzon F, Torch S, Chatellard-Causse
C, et al: Alix is involved in caspase 9 activation during
calcium-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 397:64–69.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fisher RD, Chung HY, Zhai Q, et al:
Structural and biochemical studies of ALIX/AIP1 and its role in
retrovirus budding. Cell. 128:841–852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhai Q, Fisher RD, Chung HY, et al:
Structural and functional studies of ALIX interactions with YPXnL
late domains of HIV-1 and EIAV. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 15:43–49.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hoffmann M, Kim SC, Sartor RB and Haller
D: Enterococcus faecalis strains differentially regulate Alix/AIP1
protein expression and ERK 1/2 activation in intestinal epithelial
cells in the context of chronic experimental colitis. J Proteome
Res. 8:1183–1192. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yan H, Yi H, Xia L, et al: Staphylococcal
enterotoxin B suppresses Alix and compromises intestinal epithelial
barrier functions. J Biomed Sci. 21:292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang PC, Berin MC, Yu LC, et al: Enhanced
intestinal transepithelial antigen transport in allergic rats is
mediated by IgE and CD23 (FcepsilonRII). J Clin Invest.
106:879–886. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu LC, Yang PC, Berin MC, et al: Enhanced
transepithelial antigen transport in intestine of allergic mice is
mediated by IgE/CD23 and regulated by interleukin-4.
Gastroenterology. 121:370–381. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu LC, Montagnac G, Yang PC, et al:
Intestinal epithelial CD23 mediates enhanced antigen transport in
allergy: evidence for novel splice forms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 285:G223–G234. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang PC, Jury J, Söderholm JD, Sherman PM,
McKay DM and Perdue MH: Chronic psychological stress in rats
induces intestinal sensitization to luminal antigens. Am J Pathol.
168:104–114. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saatian B, Rezaee F, Desando S, Emo J,
Chapman T, Knowlden S and Georas SN: Interleukin-4 and
interleukin-13 cause barrier dysfunction in human airway epithelial
cells. Tissue Barriers. 1:e243332013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mahul-Mellier AL, Strappazzon F,
Chatellard-Causse C, Blot B, Béal D, Torch S, Hemming F, Petiot A,
Verna JM, Fraboulet S and Sadoul R: Alix and ALG-2 make a link
between endosomes and neuronal death. Biochem Soc Trans.
37:200–203. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Trioulier Y, Torch S, Blot B, Cristina N,
Chatellard-Causse C, Verna JM and Sadoul R: Alix, a protein
regulating endosomal trafficking, is involved in neuronal death. J
Biol Chem. 279:2046–2052. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|