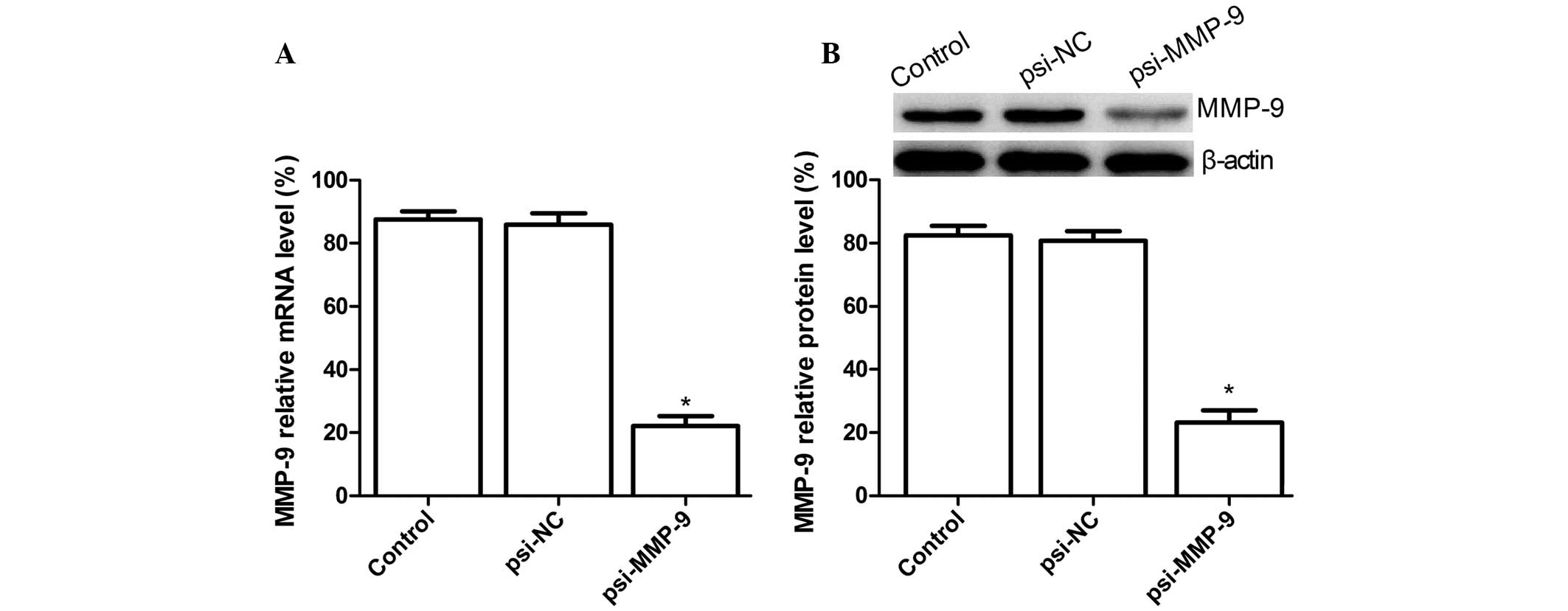
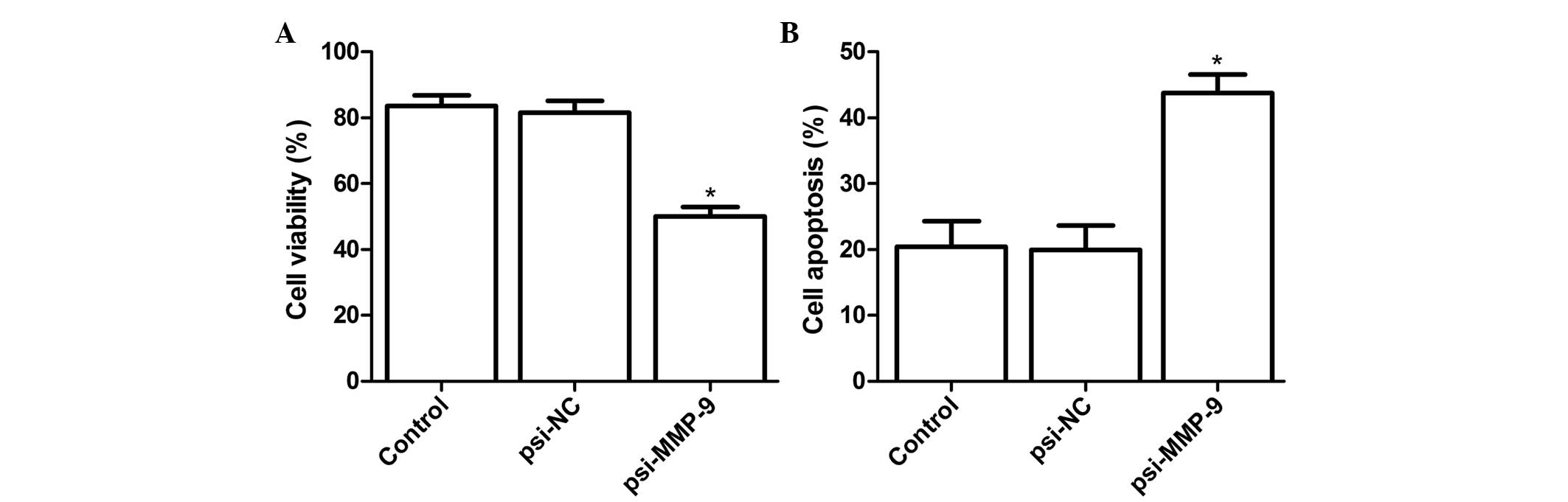
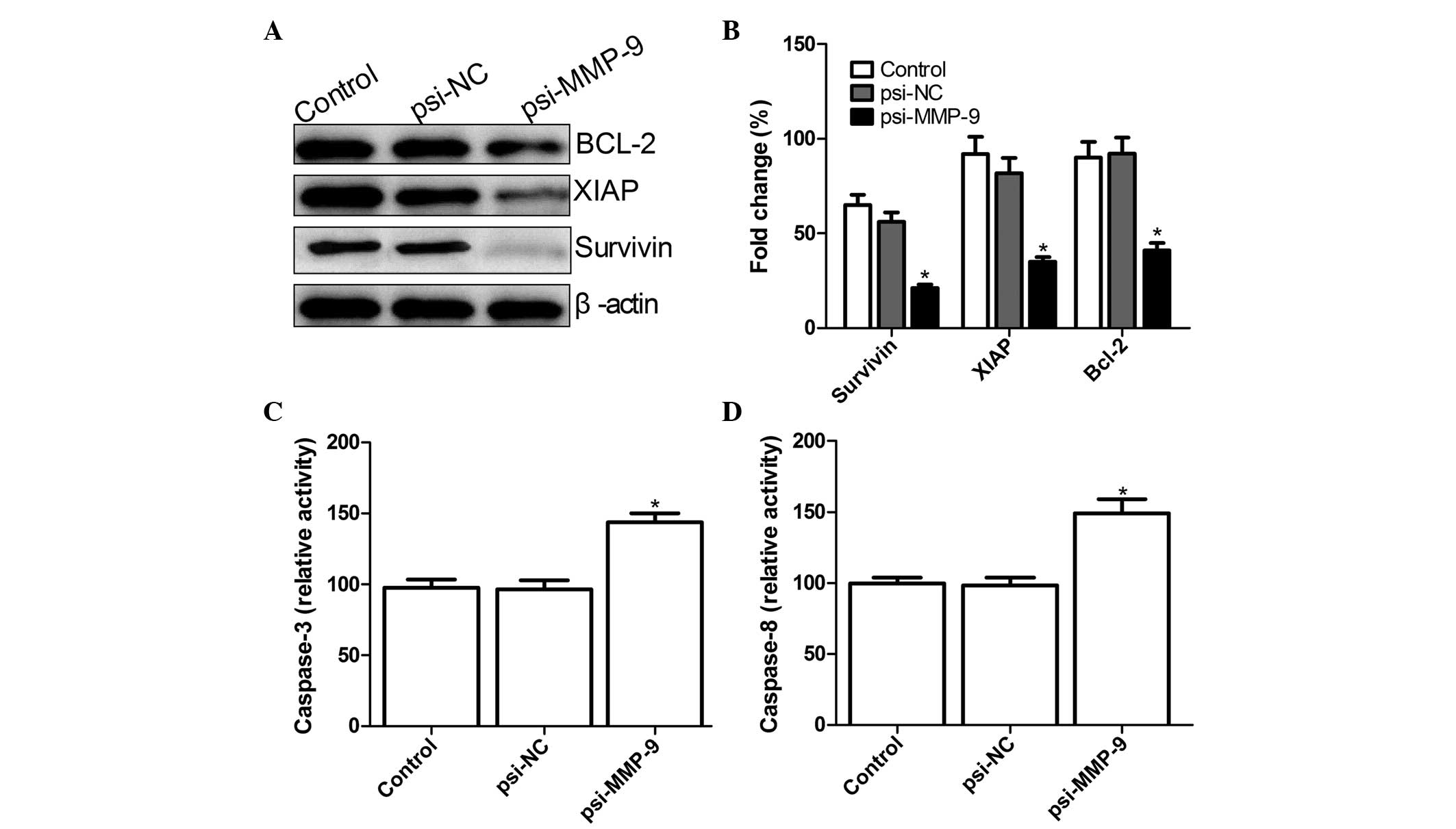
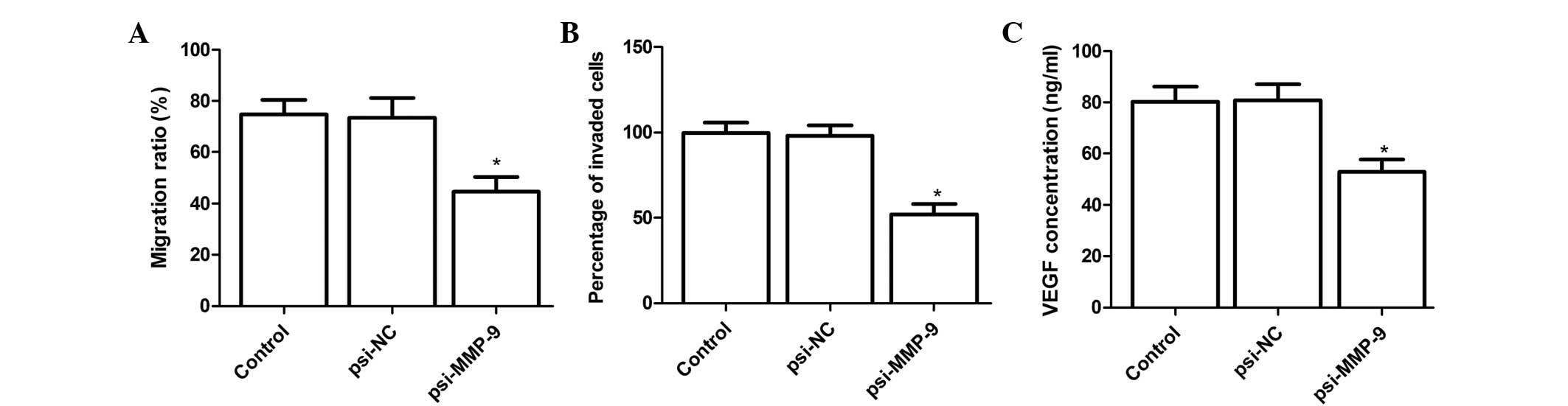
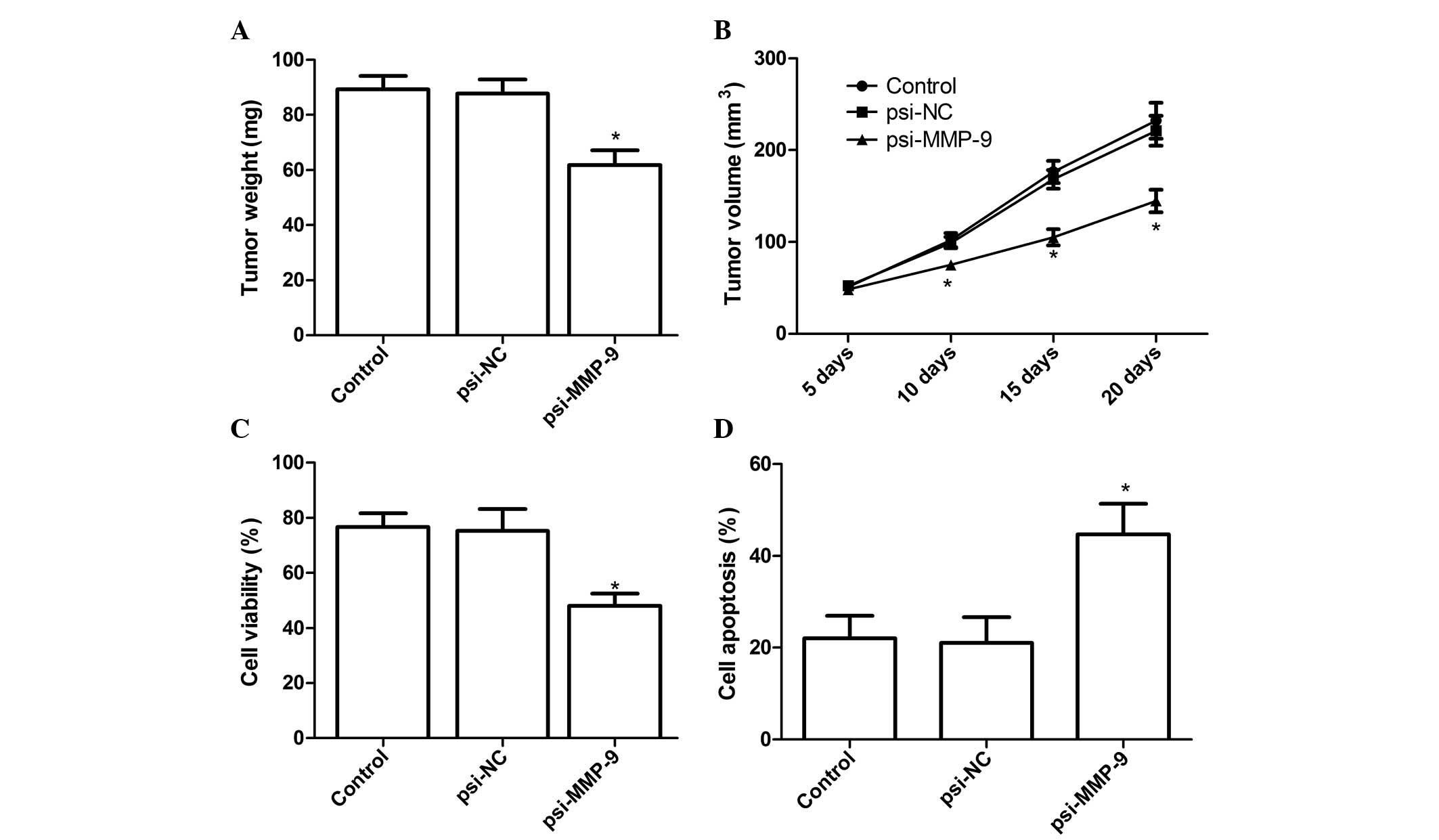
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 56:106–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cannistra SA: Cancer of the ovary. N Engl
J Med. 351:2519–2529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng C, Vangveravong S, McDunn JE, Hawkins
WG and Mach RH: Sigma-2 receptor ligand as a novel method for
delivering a SMAC mimetic drug for treating ovarian cancer. Br J
Cancer. 109:2368–2377. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Blasi F: Molecular mechanisms of
protease-mediated tumor invasiveness. J Surg Oncol Suppl. 3:21–23.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davidson B, Goldberg I, Berner A,
Kristensen GB and Reich R: EMMPRIN (extracellular matrix
metalloproteinase inducer) is a novel marker of poor outcome in
serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 20:161–169. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Folgueras AR1, Pendás AM, Sánchez LM and
López-Otín C: Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer: from new
functions to improved inhibition strategies. Int J Dev Biol.
48:411–424. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coussens LM, Tinkle CL, Hanahan D and Werb
Z: MMP-9 supplied by bone marrow-derived cells contributes to skin
carcinogenesis. Cell. 103:481–490. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuşku Cabuk F1, Yığıt S, Demır L,
Cakalağaoğlu F and Tarhan O: Correlation of survivin and MMP-9
expressions with prognosis and clinicopathological parameters in
surface epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Turk Patoloji Derg.
30:30–37. 2014.
|
|
10
|
Kamat AA, Fletcher M, Gruman LM, et al:
The clinical relevance of stromal matrix metalloproteinase
expression in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:1707–1714. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sillanpää S, Anttila M, Voutilainen K, et
al: Prognostic significance of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9)
in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 104:296–303. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cowden Dahl KD, Symowicz J, Ning Y, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 is a mediator of epidermal growth
factor-dependent e-cadherin loss in ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer
Res. 68:4606–4613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during
carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2:737–744. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hawinkels LJ, Zuidwijk K, Verspaget HW, et
al: VEGF release by MMP-9 mediated heparan sulphate cleavage
induces colorectal cancer angiogenesis. Eur J Cancer. 44:1904–1913.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang ZY, Liu Y, Liu LX, Ding XY, Zhang H
and Fang LQ: RNAi-mediated MMP-9 silencing inhibits mouse melanoma
cell invasion and migration in vitro and in vivo. Cell Biol Int.
37:849–854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yue PY, Leung EP, Mak NK and Wong RN: A
simplified method for quantifying cell migration/wound healing in
96-well plates. J Biomol Screen. 15:427–433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Li Z and Wang K: Combining
sorafenib with celecoxib synergistically inhibits tumor growth of
non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep.
31:1954–1960. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA,
Driver SE and Mello CC: Potent and specific genetic interference by
double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang YC, Taylor MM, Samson WK and
Phillips MI: Antisense inhibition: oligonucleotides, ribozymes, and
siRNAs. Methods Mol Med. 106:11–34. 2005.
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Ma C, Qian M, Wen Z, Jing H and Qian
D: Downregulation of NOB1 suppresses the proliferation and tumor
growth of non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. Oncol
Rep. 31:1271–1276. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin Y, Cui M, Teng H, Wang F, Yu W and Xu
T: Silencing the receptor of activated C-kinase 1 (RACK1)
suppresses tumorigenicity in epithelial ovarian cancer in vitro and
in vivo. Int J Oncol. 44:1252–1258. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sui G, Soohoo C, Affar B, et al: A DNA
vector-based RNAi technology to suppress gene expression in
mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:5515–5520. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miyagishi M, Sumimoto H, Miyoshi H,
Kawakami Y and Taira K: Optimization of an siRNA-expression system
with an improved hairpin and its significant suppressive effects in
mammalian cells. J Gene Med. 6:715–723. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin Y, Cui M, Xu T, Yu W and Zhang L:
Silencing of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibits the growth, invasion and
migration of ovarian cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:2499–2504.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gondi CS, Lakka SS, Dinh DH, Olivero WC,
Gujrati M and Rao JS: Downregulation of uPA, uPAR and MMP-9 using
small, interfering, hairpin RNA (siRNA) inhibits glioma cell
invasion, angiogenesis and tumor growth. Neuron Glia Biol.
1:165–176. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tummalapalli P, Spomar D, Gondi CS, et al:
RNAi-mediated abrogation of cathepsin B and MMP-9 gene expression
in a malignant meningioma cell line leads to decreased tumor
growth, invasion and angiogenesis. Int J Oncol. 31:1039–1050.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rao JS, Bhoopathi P, Chetty C, Gujrati M
and Lakka SS: MMP-9 short interfering RNA induced senescence
resulting in inhibition of medulloblastoma growth via p16(INK4a)
and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cancer Res.
67:4956–4964. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nagaraju GP, Nalla AK, Gupta R, et al:
siRNA-mediated downregulation of MMP-9 and uPAR in combination with
radiation induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest in Medulloblastoma. Mol
Cancer Res. 9:51–66. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kotipatruni RR, Nalla AK, Asuthkar S,
Gondi CS, Dinh DH and Rao JS: Apoptosis induced by knockdown of
uPAR and MMP-9 is mediated by inactivation of EGFR/STAT3 signaling
in medulloblastoma. PLoS One. 7:e447982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|