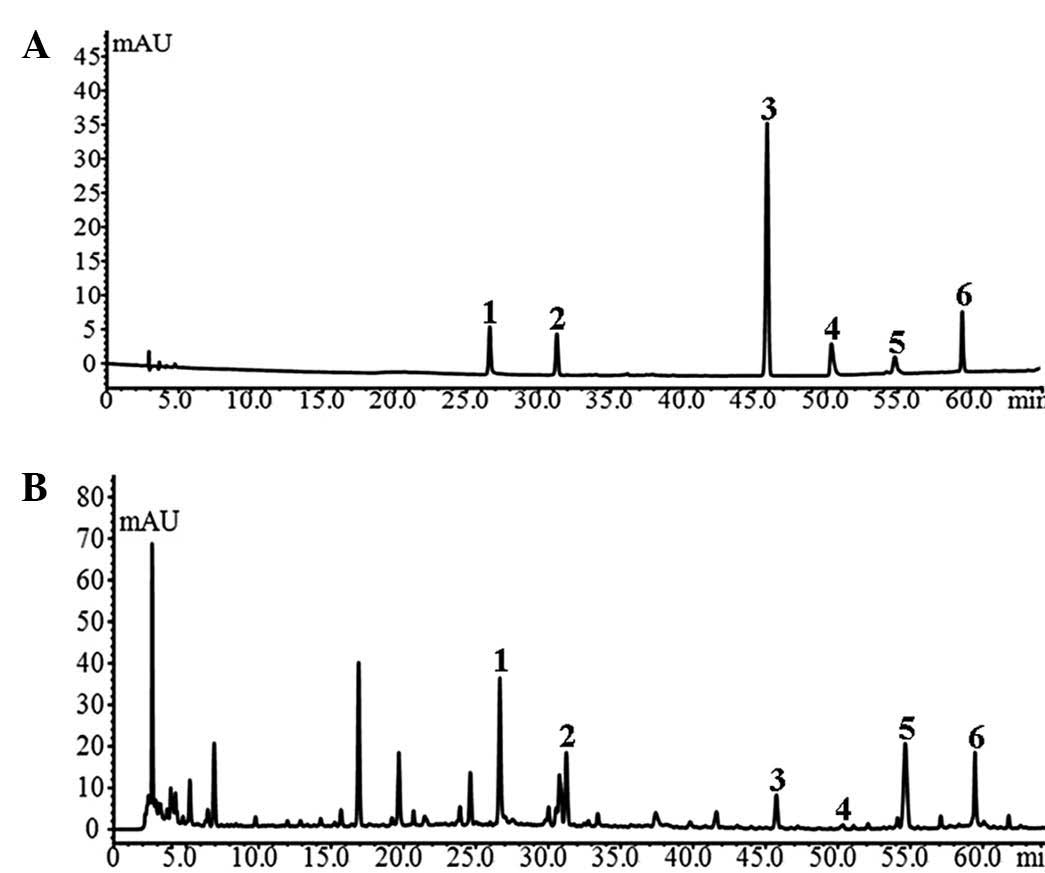
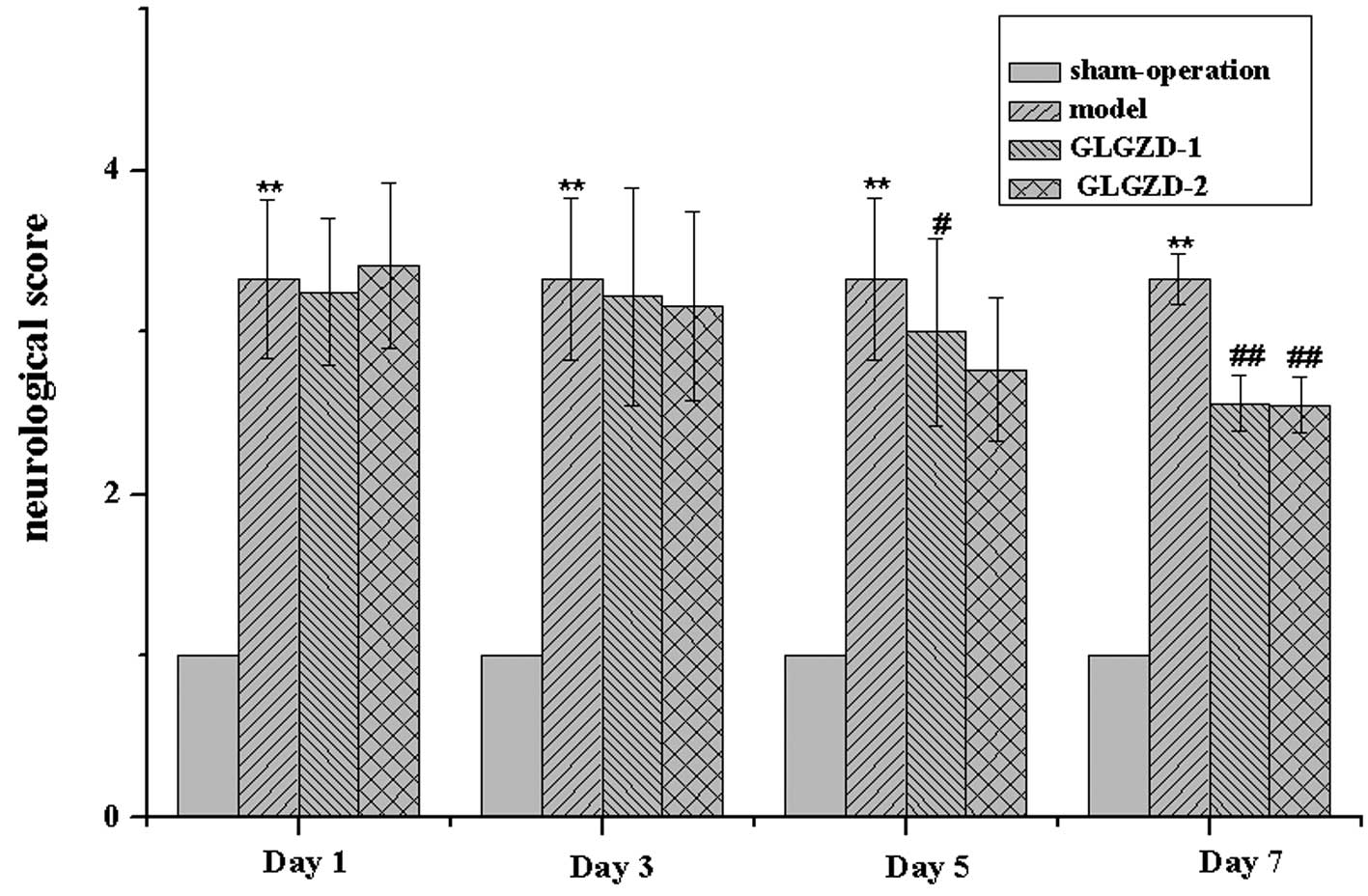
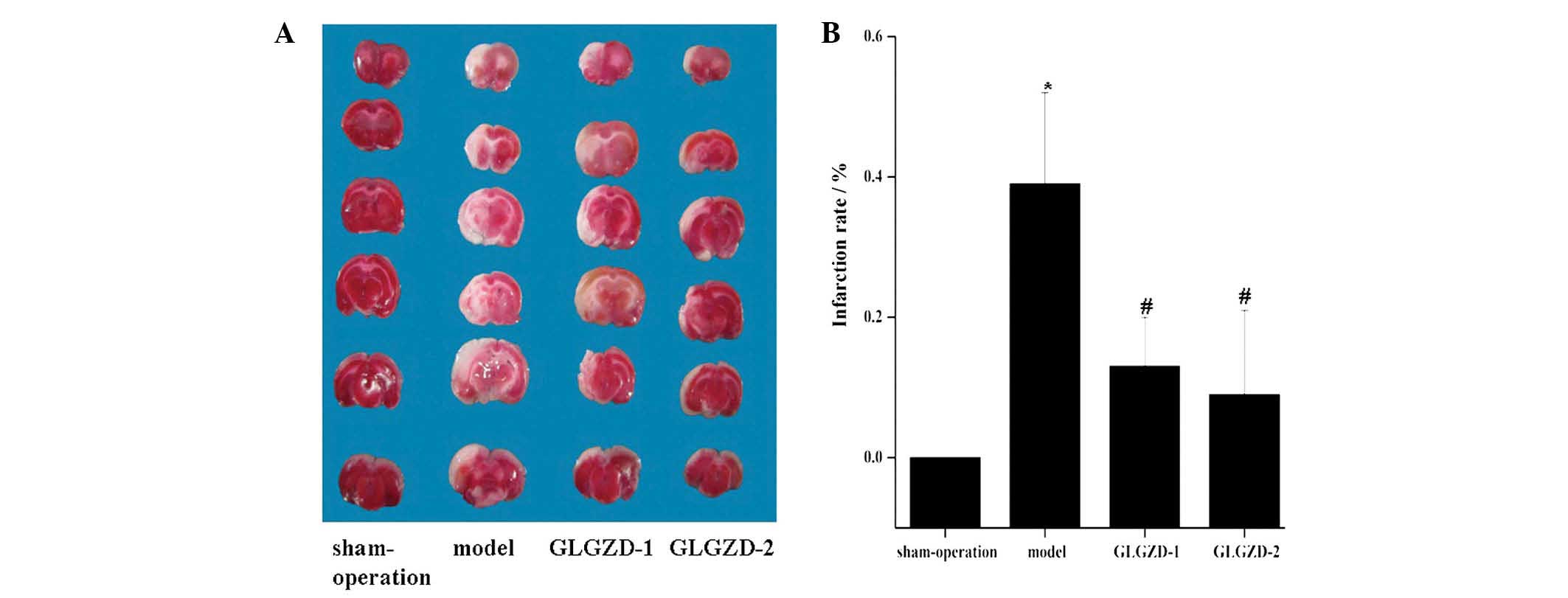
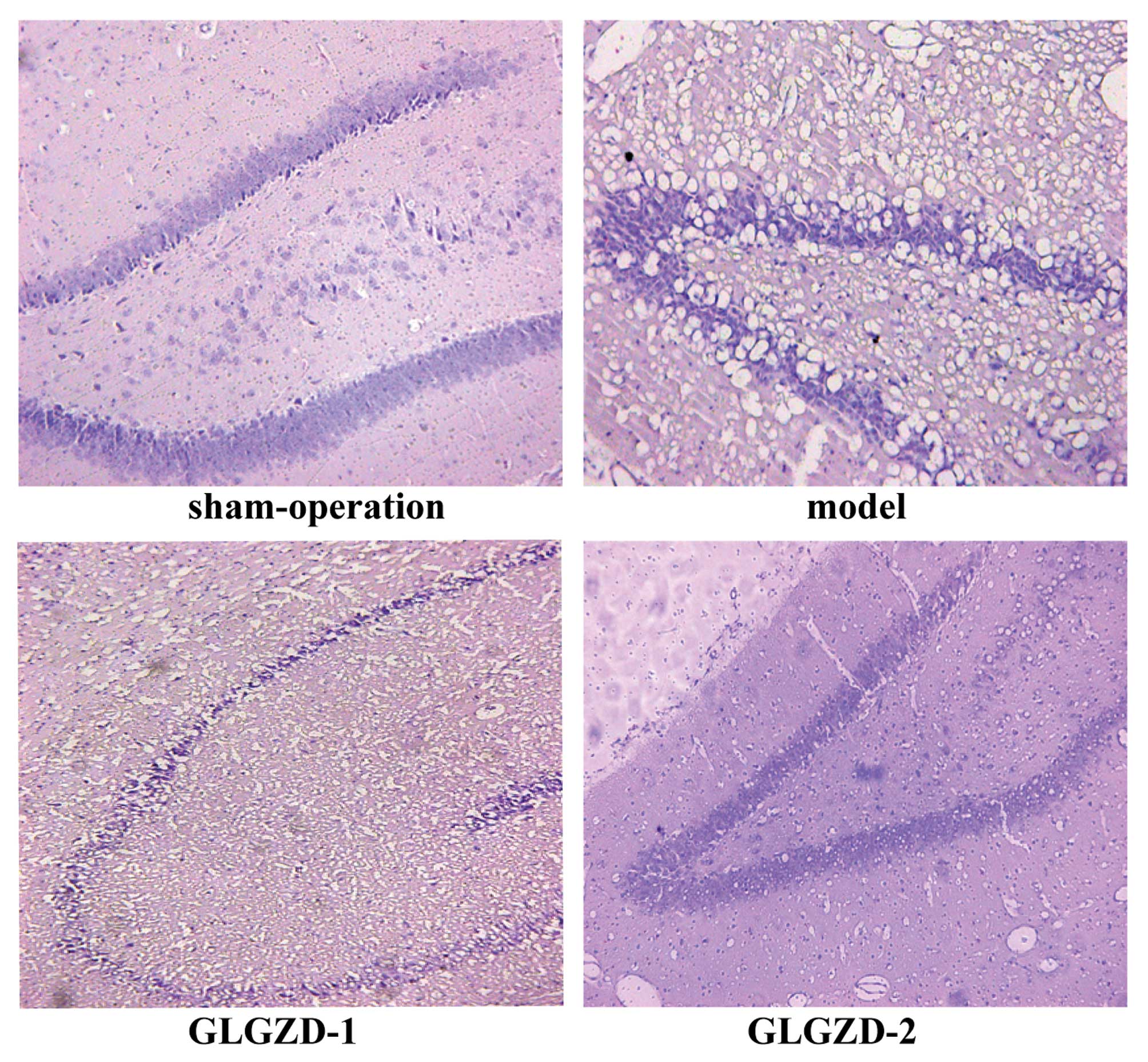
|
1
|
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M and Davis
SM: Stroke. Lancet. 371:1612–1623. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang J, Upadhyay UM and Tamargo RJ:
Inflammation in stroke and focal cerebral ischemia. Surg Neurol.
66:232–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klijn CJ and Hankey GJ: Management of
acute ischaemic stroke: new guidelines from the American stroke
association and European stroke initiative. Lancet Neurol.
2:698–701. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu ZS, Yao CH and Zhao D: China’s
population of stroke morbidity, mortality, epidemiological studies.
Chin J Epidemiology. 24:236–239. 2003.
|
|
5
|
Brouns R and De Deyn PP: The complexity of
neurobiological processes in acute ischemic stroke. Clin Neurol
Neurosurg. 111:483–495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amantea D, Nappi G, Bernardi G, Bagetta G
and Corasaniti MT: Post-ischemic brain damage: pathophysiology and
role of inflammatory mediators. FEBS J. 276:13–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, di Sciacca
R, Pinto A and Licata G: Inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic
stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 14:3574–3589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Terao S, Yilmaz G, Stokes KY, Ishikawa M,
Kawase T and Granger DN: Inflammatory and injury responses to
ischemic stroke in obese mice. Stroke. 39:943–950. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C and Moskowitz MA:
Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends
Neurosci. 22:391–397. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Son HY, Han HS, Jung HW and Park YK: Panax
notoginseng attenuates the infarct volume in rat ischemic brain and
the inflammatory response of microglia. J Pharmacol Sci.
109:368–379. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han HS and Yenari MA: Cellular targets of
brain inflammation in stroke. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 4:522–529.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Allan SM and Rothwell NJ: Cytokines and
acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2:734–744. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qing Wang, Xian Nan Tang and Yenari Midori
A: The inflammatory response in stroke. J Neuroimmuno. 1184:53–68.
2007.
|
|
14
|
Yang GY, Gong C, Qin Z, Ye W, Mao Y and
Bertz AL: Inhibition of TNFalpha attenuates infarct volume and
ICAM-1 expression in ischemic mouse brain. Neuro Report.
9:2131–2134. 1998.
|
|
15
|
Guo RB, Wang GF, Zhao AP, Gu J, Sun XL and
Hu G: Paeoniflorin protects against ischemia-induced brain damages
in rats via inhibiting MAPKs/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses.
PLoS One. 7:e497012012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tarkowski E, Rosengren L, Blomstrand C,
Wikkelso C, Jensen C, Ekholm S and Tarkowski A: Early intrathecal
production of interleukin-6 predicts the size of brain lesion in
stroke. Stroke. 26:1393–1398. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Camarata PJ, Heros RC and Latchaw RE:
‘Brain attack’: the rationale for treating stroke as a medical
emergency. Neurosurgery. 34:144–157. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ringleb PA, Schellinger PD, Schranz C and
Hacke W: Thrombolytic therapy within 3 to 6 hours after onset of
ischemic stroke : useful or harmful? Stroke. 33:1437–1441. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tao BH, Yang H, Xu ZX and Liu SY: Effect
and safety of combined therapy of defibringen, anticoagulation and
anti-plateletget for progressivity stroke. Chinese General
Practice. 11:2134–2136. 2008.
|
|
20
|
Camerlingo M, Salvi P, Belloni G, Cesana
BM and Mamoli A: Intravenous heparin started within the first 3
hours after onset of symptoms as a treatment for acute nonlacunar
hemispheric cerebral infarctions. Stroke. 36:2415–2420. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang W, Ying WB, Bo JL, Wu T and Ding XS:
Edaravone clinical safety evaluation. Chinese J Neurology.
42:486–489. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Shuaib A, Lees KR, Lyden P, et al: Emeribe
U., SAINT II Trial Investigators: NXY-059 for the treatment of
acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 357:1562–1571. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cho HJ and Kim YJ: Efficacy and safety of
oral citicoline in acute ischemic stroke: drug surveillance study
in 4,191 cases. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 31:171–176. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun X: Research on formula treating
paralysis and spasticity from ‘treatise on febrile and
miscellaneous diseases’. Chinese Journal of Basic Medicine In
Traditional Chinese Medicine. 8:644–645. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
25
|
Zhang L and Ai H: Effects of Gua Lou Gui
Zhi decoction on c-fos and c-jun in epileptic rats. Journal of
Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 23:21–22. 2005.In
Chinese.
|
|
26
|
Yang C, Chen L and Tao J: New usage of a
classical formula-Gua Lou Gui Zhi decoction. Liaoning Journal of
Traditional Chinese Medicine. 8:166–167. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
27
|
Hu H, Li Z, Zhu X, et al: Gua Lou Gui Zhi
decoction suppresses LPS-induced activation of the TLR4/NF-κB
pathway in BV-2 murine microglial cells. Int J Mol Me.
31:1327–1332. 2013.
|
|
28
|
Huang J, Tao J, Xue XH, et al: Gua Lou Gui
Zhi decoction exerts neuroprotective effects on post-stroke
spasticity via the modulation of glutamate levels and AMPA receptor
expression. Inter J Mol Med. 31:841–848. 2013.
|
|
29
|
Muir KW, Tyrrell P, Sattar N and Warburton
E: Inflammation and ischaemic stroke. Curr Opin Neurol. 20:334–342.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han HS and Yenari MA: Cellular targets of
brain inflammation in stroke. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 4:522–529.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang ZQ, Wu DC, Huang FP and Yang GY:
Inhibition of MEK/ERK 1 and 2 pathway reduces pro-inflammatory
cytokine interleukin-1 expression in focal cerebral ischemia. Brain
Res. 996:55–66. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu T, Clark RK, McDonnell PC, Young PR,
White RF, Barone FC and Feuerstein GZ: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke. 25:1481–1488. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gee JM, Kalil A, Shea C and Becker KJ:
Lymphocytes: potential mediators of postischemic injuryand
neuroprotection. Stroke. 38:783–788. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang XQ, Peng YP, Lu JH, Cao BB and Qiu
YH: Neuroprotection of interleukin-6 against NMDA attack and its
signal transduction by JAK and MAPK. Neurosci Lett. 450:122–126.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Baeuerle PA and Henkel T: Function and
activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol.
12:141–179. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Berti R, Williams AJ, Moffett JR, et al:
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory gene
expression associated with ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 22:1068–1079. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|