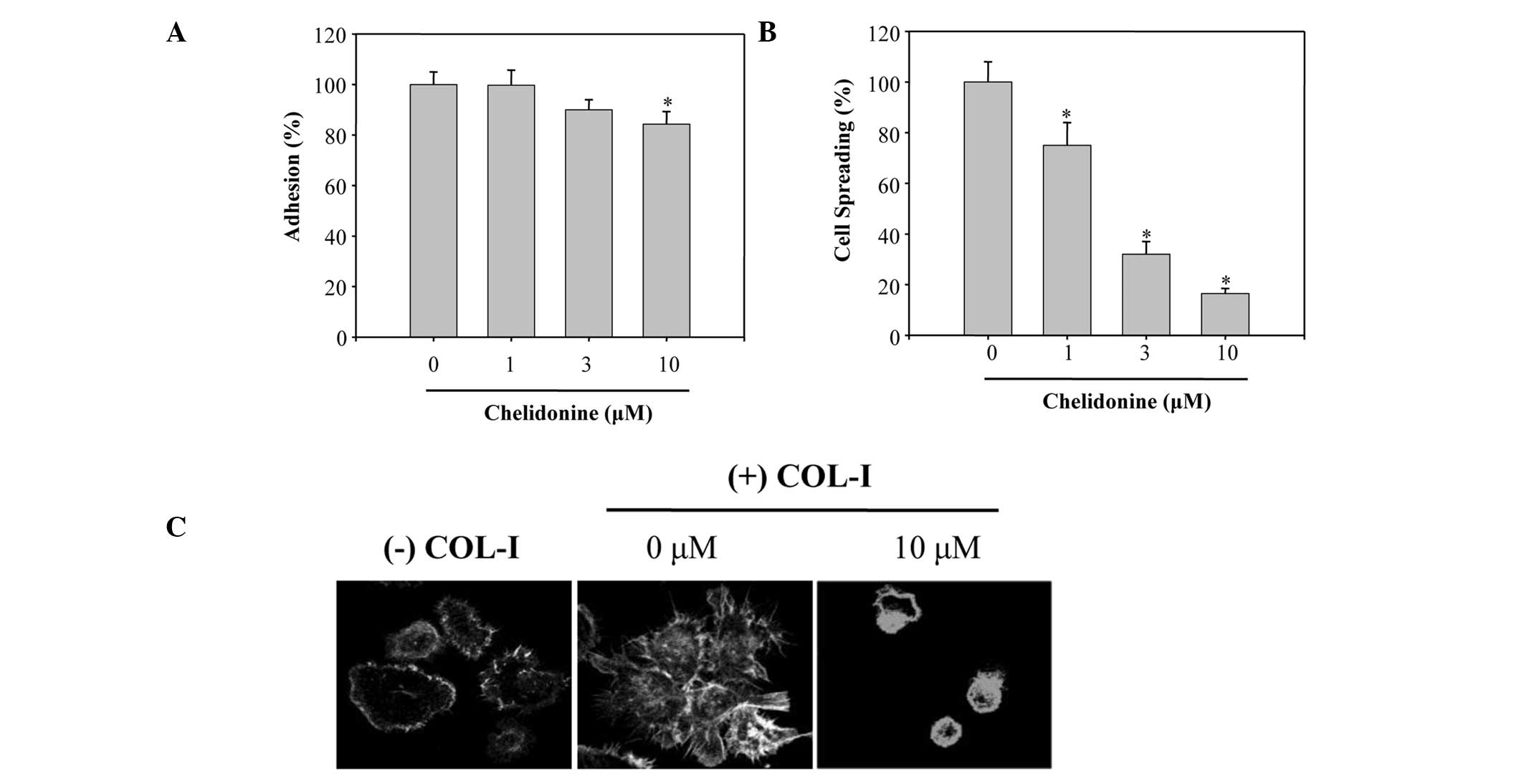
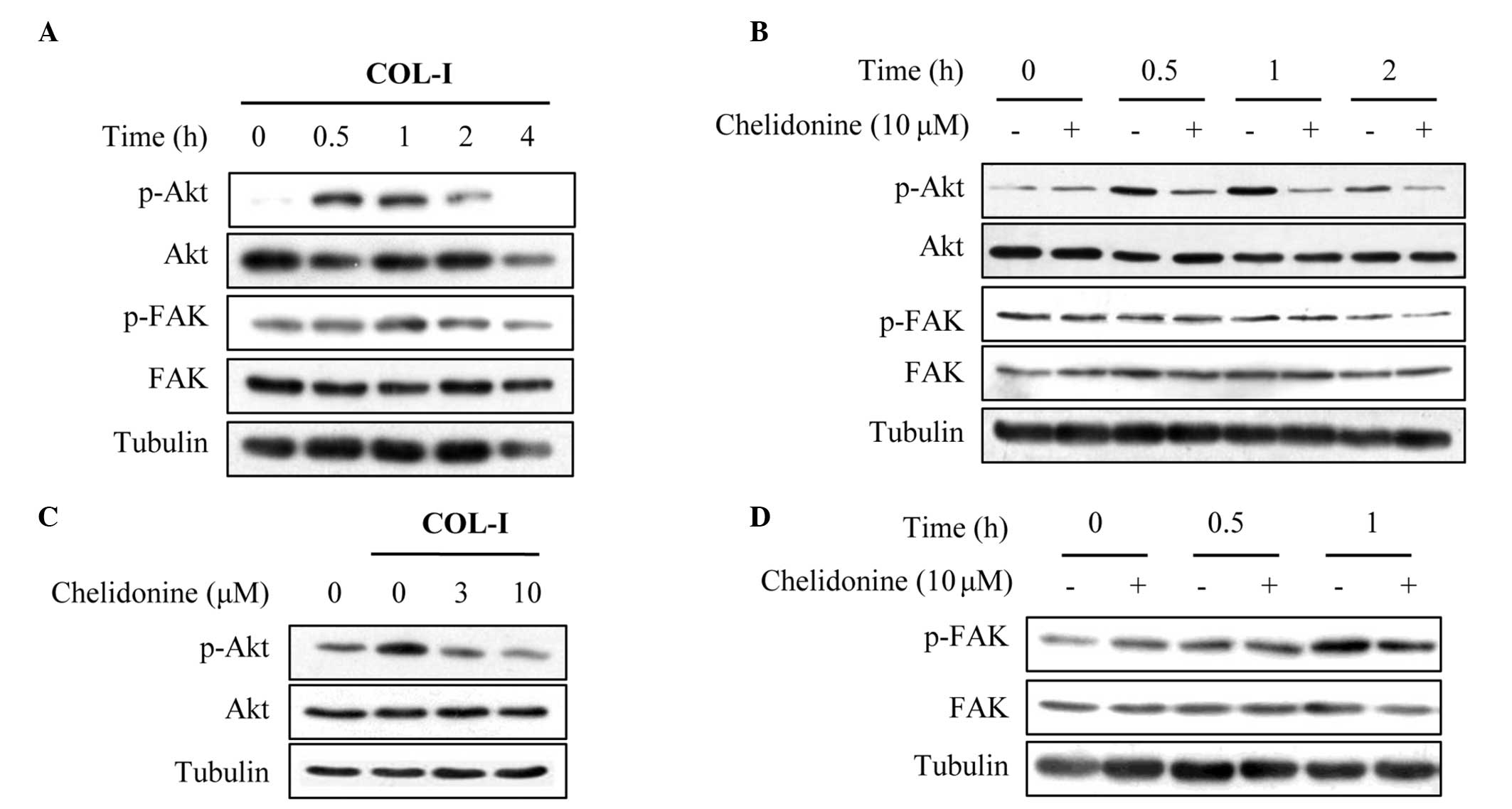
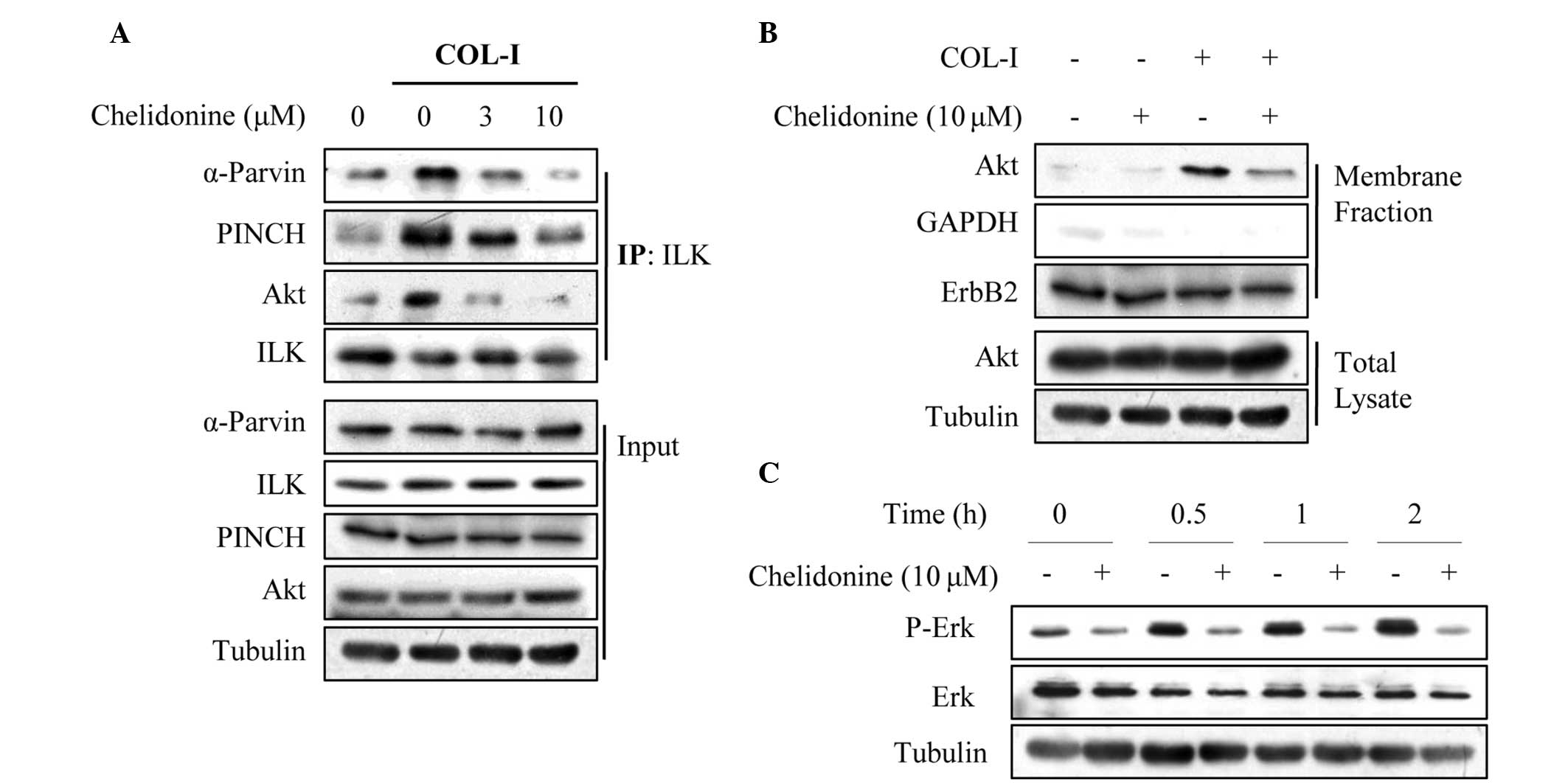
|
1
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo W and Giancotti FG: Integrin
signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:816–826. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Watt FM: Role of integrins in regulating
epidermal adhesion, growth and differentiation. EMBO J.
21:3919–3926. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hynes RO: Integrins: bidirectional,
allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 110:673–687. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C,
Fitz-Gibbon L, Coppolino MG, Radeva G, Filmus J, Bell JC and Dedhar
S: Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a
new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature. 379:91–96. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Legate KR, Montañez E, Kudlacek O and
Fässler R: ILK, PINCH and parvin: the tIPP of integrin signalling.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:20–31. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schaller MD and Parsons JT: Focal adhesion
kinase and associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 6:705–710.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McDonald PC, Fielding AB and Dedhar S:
Integrin-linked kinase - essential roles in physiology and cancer
biology. J Cell Sci. 121:3121–3132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fukuda K, Gupta S, Chen K, Wu C and Qin J:
The pseudoactive site of ILK is essential for its binding to
alpha-Parvin and localization to focal adhesions. Mol Cell.
36:819–830. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wickström SA, Lange A, Montanez E and
Fässler R: The ILK/PINCH/parvin complex: the kinase is dead, long
live the pseudokinase! EMBO J. 29:281–291. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C,
Fitz-Gibbon L, Coppolino MG, Radeva G, Filmus J, Bell JC and Dedhar
S: Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a
new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature. 379:91–96. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chiswell BP, Zhang R, Murphy JW, Boggon TJ
and Calderwood DA: The structural basis of integrin-linked
kinase-PINCH interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:20677–20682.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hannigan G, Troussard AA and Dedhar S:
Integrin-linked kinase: a cancer therapeutic target unique among
its ILK. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:51–63. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Colombo ML and Bosisio E: Pharmacological
activities of Chelidonium majus L. (Papaveraceae). Pharmacol Res.
33:127–134. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hohenwarter O, Strutzenberger K, Katinger
H, Liepins A and Nowicky JW: Selective inhibition of in vitro cell
growth by the anti-tumour drug Ukrain. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 18:1–4.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kemény-Beke A, Aradi J, Damjanovich J,
Beck Z, Facskó A, Berta A and Bodnár A: Apoptotic response of uveal
melanoma cells upon treatment with chelidonine, sanguinarine and
chel-erythrine. Cancer Lett. 237:67–75. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Panzer A, Joubert AM, Bianchi PC, Hamel E
and Seegers JC: The effects of chelidonine on tubulin
polymerisation, cell cycle progression and selected signal
transmission pathways. Eur J Cell Biol. 80:111–118. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Noureini SK and Wink M: Transcriptional
down regulation of hTERT and senescence induction in HepG2 cells by
chelidonine. World J Gastroenterol. 15:3603–3610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park JE, Cuong TD, Hung TM, Lee I, Na M,
Kim JC, Ryoo S, Lee JH, Choi JS, Woo MH and Min BS: Alkaloids from
Chelidonium majus and their inhibitory effects on LPS-induced NO
production in RAW264.7 cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 21:6960–6963.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hwangbo C, Park J and Lee JH:
mda-9/Syntenin protein positively regulates the activation of Akt
protein by facilitating integrin-linked kinase adaptor function
during adhesion to type I collagen. J Biol Chem. 286:33601–33612.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hwangbo C, Kim J, Lee JJ and Lee JH:
Activation of the integrin effector kinase focal adhesion kinase in
cancer cells is regulated by crosstalk between protein kinase
Calpha and the PDZ adapter protein mda-9/Syntenin. Cancer Res.
70:1645–1655. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel
RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, Parsons JT and Horwitz AR: Cell
migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science.
302:1704–1709. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hehlgans S, Haase M and Cordes N:
Signalling via integrins: implications for cell survival and
anticancer strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1775:163–180.
2007.
|
|
24
|
van Nimwegen MJ and van de Water B: Focal
adhesion kinase: a potential target in cancer therapy. Biochem
Pharmacol. 73:597–609. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Restuccia DF and Hemmings BA: Cell
signaling. Blocking Akt-ivity. Science. 325:1083–1084. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Filippa N, Sable CL, Hemmings BA and Van
Obberghen E: Effect of phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 on
protein kinase B translocation and its subsequent activation. Mol
Cell Biol. 20:5712–5721. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Niu CQ and He LY: Determination of
isoquinoline alkaloids in Chelidonium majus L. by ion-pair
high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 542:193–199.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Biswas SJ, Bhattacharjee N and
Khuda-Bukhsh AR: Efficacy of a plant extract (Chelidonium majus L.)
in combating induced hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Food Chem
Toxicol. 46:1474–1487. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ernst E and Schmidt K: Ukrain-a new cancer
cure? A systematic review of randomised clinical trials. BMC
Cancer. 5:692005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hynes RO: Integrins: bidirectional,
allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 110:673–687. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|