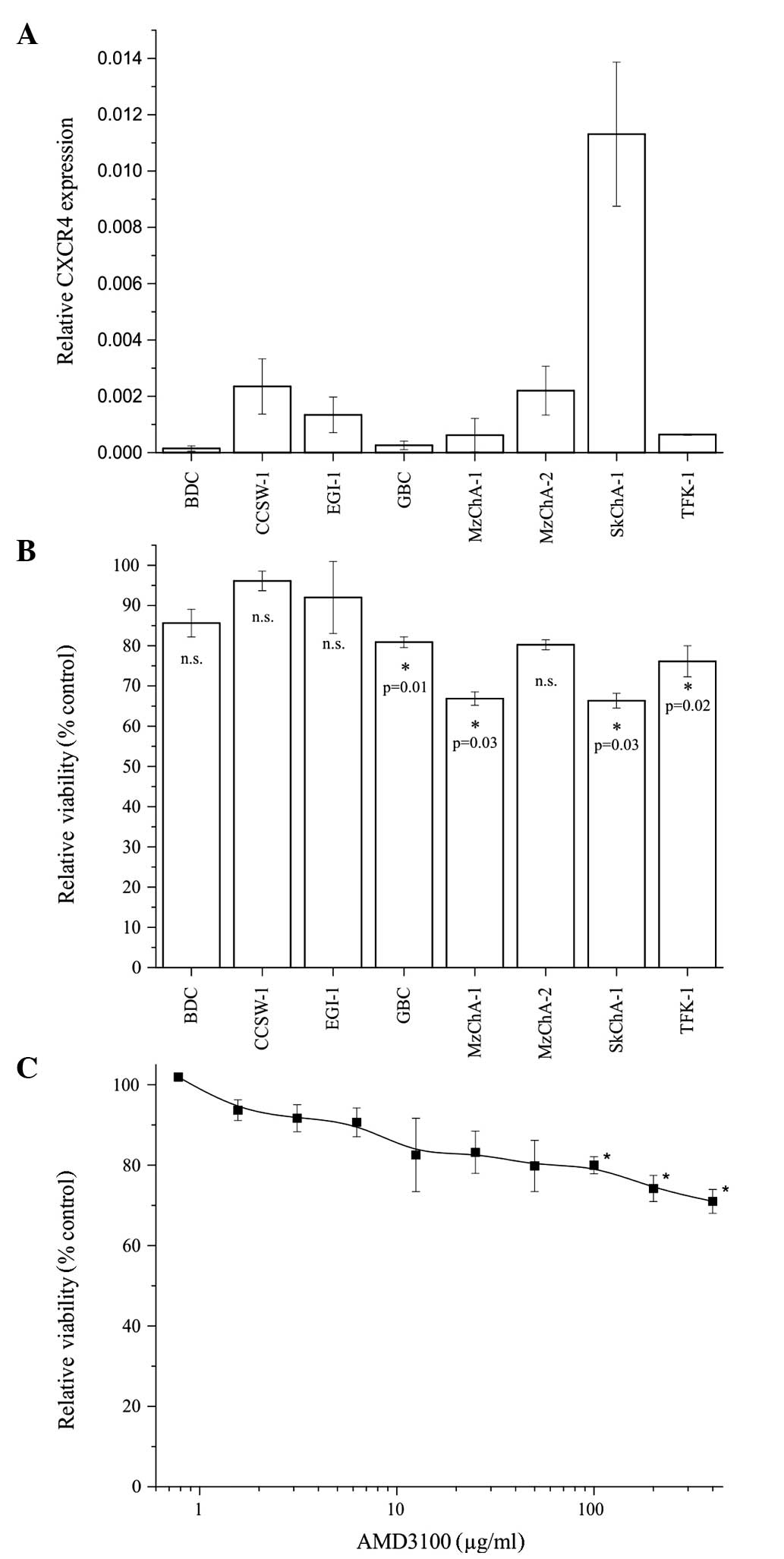
|
1
|
de Groen PC, Gores GJ, LaRusso NF,
Gunderson LL and Nagorney DM: Biliary tract cancers. N Engl J Med.
341:1368–1378. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Braconi C and Patel T: Cholangiocarcinoma:
new insights into disease pathogenesis and biology. Infect Dis Clin
North Am. 24:871–884. vii2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malhi H and Gores GJ: Cholangiocarcinoma:
modern advances in understanding a deadly old disease. J Hepatol.
45:856–867. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Valle J, Wasan H, Palmer DH, et al:
Cisplatin plus gemcitabine versus gemcitabine for biliary tract
cancer. N Engl J Med. 362:1273–1281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Valle JW, Furuse J, Jitlal M, et al:
Cisplatin and gemcitabine for advanced biliary tract cancer: a
meta-analysis of two randomised trials. Ann Oncol. 25:391–398.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Furusato B, Mohamed A, Uhlén M and Rhim
JS: CXCR4 and cancer. Pathol Int. 60:497–505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kucia M, Reca R, Miekus K, et al:
Trafficking of normal stem cells and metastasis of cancer stem
cells involve similar mechanisms: pivotal role of the SDF-1-CXCR4
axis. Stem Cells. 23:879–894. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zlotnik A: Chemokines and cancer. Int J
Cancer. 119:2026–2029. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Allinen M, Beroukhim R, Cai L, et al:
Molecular characterization of the tumor microenvironment in breast
cancer. Cancer Cell. 6:17–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fernandis AZ, Prasad A, Band H, Klösel R
and Ganju RK: Regulation of CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis and
chemoinvasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 23:157–167. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lapteva N, Yang AG, Sanders DE, Strube RW
and Chen SY: CXCR4 knockdown by small interfering RNA abrogates
breast tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Gene Ther. 12:84–89. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liang Z, Yoon Y, Votaw J, Goodman MM,
Williams L and Shim H: Silencing of CXCR4 blocks breast cancer
metastasis. Cancer Res. 65:967–971. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, et al:
Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis.
Nature. 410:50–56. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Burger M, Glodek A, Hartmann T, et al:
Functional expression of CXCR4 (CD184) on small-cell lung cancer
cells mediates migration, integrin activation, and adhesion to
stromal cells. Oncogene. 22:8093–8101. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Samara GJ, Lawrence DM, Chiarelli CJ, et
al: CXCR4-mediated adhesion and MMP-9 secretion in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 214:231–241. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geminder H, Sagi-Assif O, Goldberg L, et
al: A possible role for CXCR4 and its ligand, the CXC chemokine
stromal cell-derived factor-1, in the development of bone marrow
metastases in neuroblastoma. J Immunol. 167:4747–4757. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schimanski CC, Bahre R, Gockel I, et al:
Dissemination of hepatocellular carcinoma is mediated via chemokine
receptor CXCR4. Br J Cancer. 95:210–217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ottaiano A, di Palma A, Napolitano M, et
al: Inhibitory effects of anti-CXCR4 antibodies on human colon
cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 54:781–791. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Leelawat K, Keeratichamroen S, Leelawat S
and Tohtong R: CD24 induces the invasion of cholangiocarcinoma
cells by upregulating CXCR4 and increasing the phosphorylation of
ERK1/2. Oncol Lett. 6:1439–1446. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leelawat K, Leelawat S, Narong S and
Hongeng S: Roles of the MEK1/2 and AKT pathways in CXCL12/CXCR4
induced cholangiocarcinoma cell invasion. World J Gastroenterol.
13:1561–1568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee HJ, Lee K, Lee DG, et al: Chemokine
(C-X-C motif) ligand 12 is associated with gallbladder carcinoma
progression and is a novel independent poor prognostic factor. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:3270–3280. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gentilini A, Rombouts K, Galastri S, et
al: Role of the stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)-CXCR4 axis in the
interaction between hepatic stellate cells and cholangiocarcinoma.
J Hepatol. 57:813–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Okamoto K, Tajima H, Nakanuma S, et al:
Angiotensin II enhances epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
through the interaction between activated hepatic stellate cells
and the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCR4 axis in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Oncol. 41:573–582. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Girbl T, Lunzer V, Greil R, Namberger K
and Hartmann TN: The CXCR4 and adhesion molecule expression of
CD34+ hematopoietic cells mobilized by ‘on-demand’ addition of
plerixafor to granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor. Transfusion.
54:2325–2335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fruehauf S: Current Clinical Indications
for Plerixafor. Transfusion medicine and hemotherapy: offizielles
Organ der Deutschen Gesellschaft fur Transfusionsmedizin und
Immunhamatologie. 40:246–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Kiesslich T, Alinger B, Wolkersdörfer GW,
Ocker M, Neureiter D and Berr F: Active Wnt signalling is
associated with low differentiation and high proliferation in human
biliary tract cancer in vitro and in vivo and is sensitive to
pharmacological inhibition. Int J Oncol. 36:49–58. 2010.
|
|
27
|
Wachter J, Neureiter D, Alinger B, et al:
Influence of five potential anticancer drugs on wnt pathway and
cell survival in human biliary tract cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci.
8:15–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kiesslich T, Neureiter D, Alinger B, et
al: Uptake and photo-toxicity of meso-tetrahydroxyphenyl chlorine
are highly variable in human biliary tract cancer cell lines and
correlate with markers of differentiation and proliferation.
Photochem Photobiol Sci. 9:734–743. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chou TC: Theoretical basis, experimental
design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in
drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev. 58:621–681. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C and
Birnbaum D: Breast cancer stem cells: tools and models to rely on.
BMC Cancer. 9:2022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang M, Xiao J, Shen M, et al: Isolation
and characterization of tumorigenic extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
cells with stem cell-like properties. Int J Cancer. 128:72–81.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Singh S, Srivastava SK, Bhardwaj A, Owen
LB and Singh AP: CXCL12-CXCR4 signalling axis confers gemcitabine
resistance to pancreatic cancer cells: a novel target for therapy.
Br J Cancer. 103:1671–1679. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|