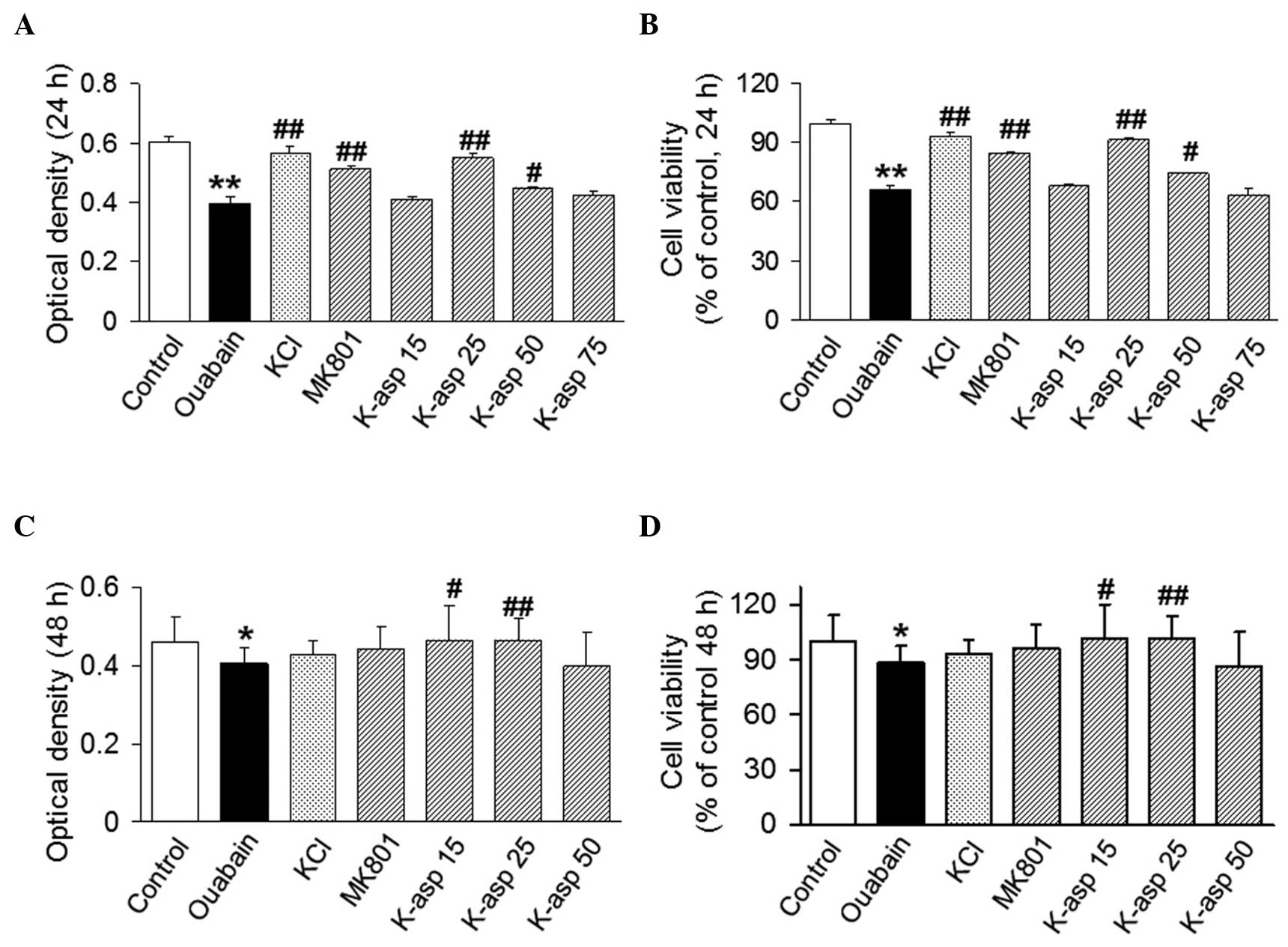
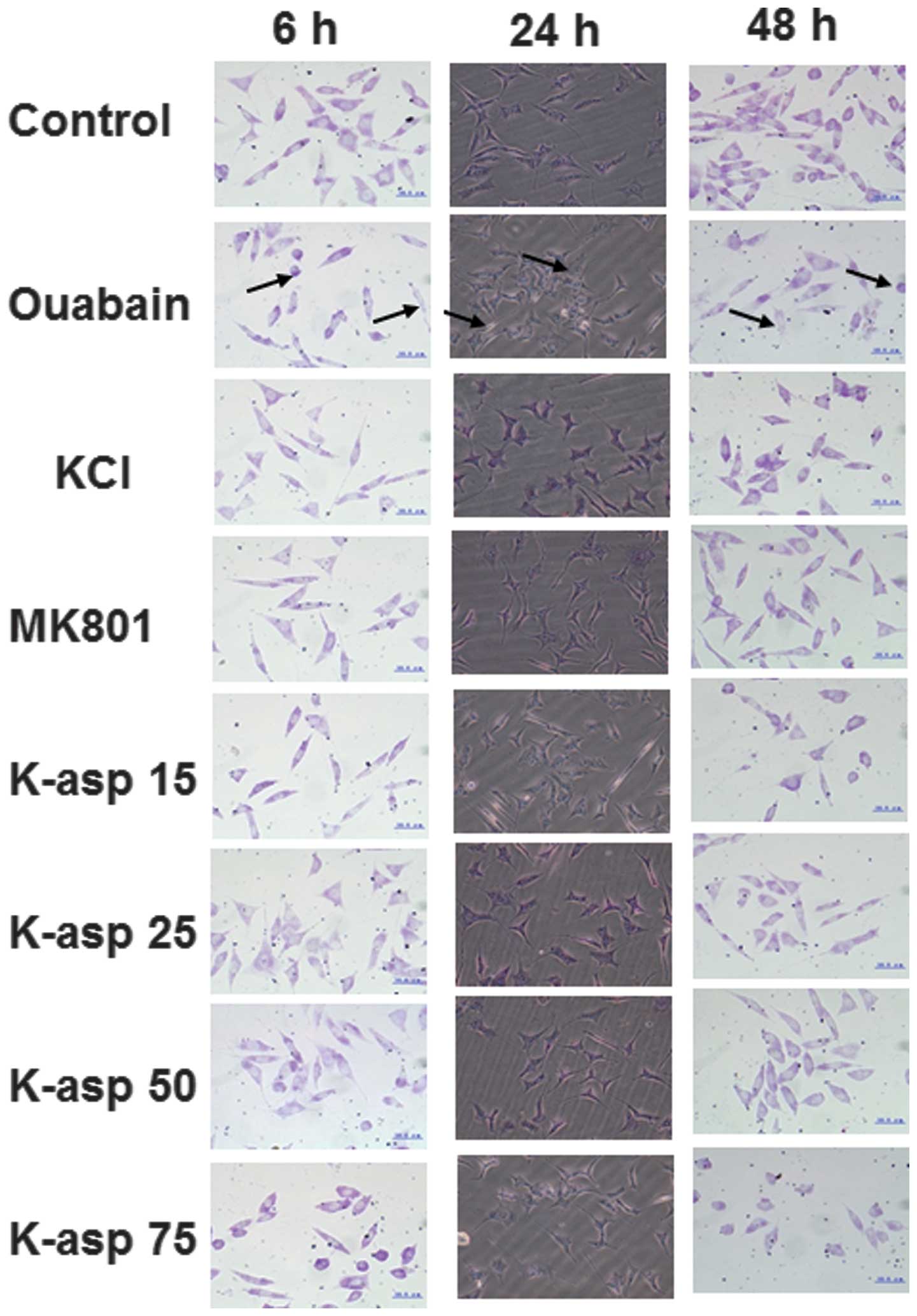
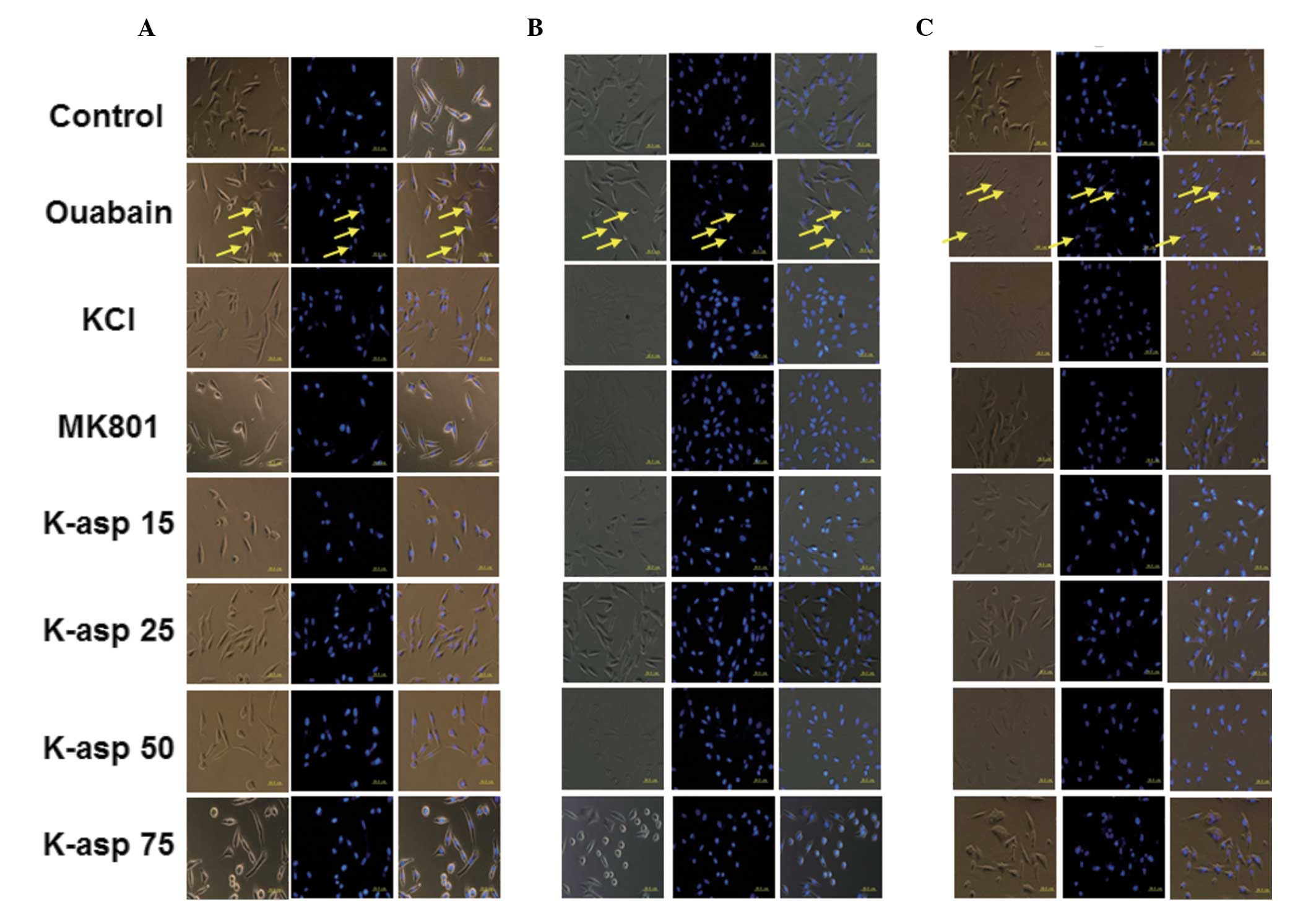
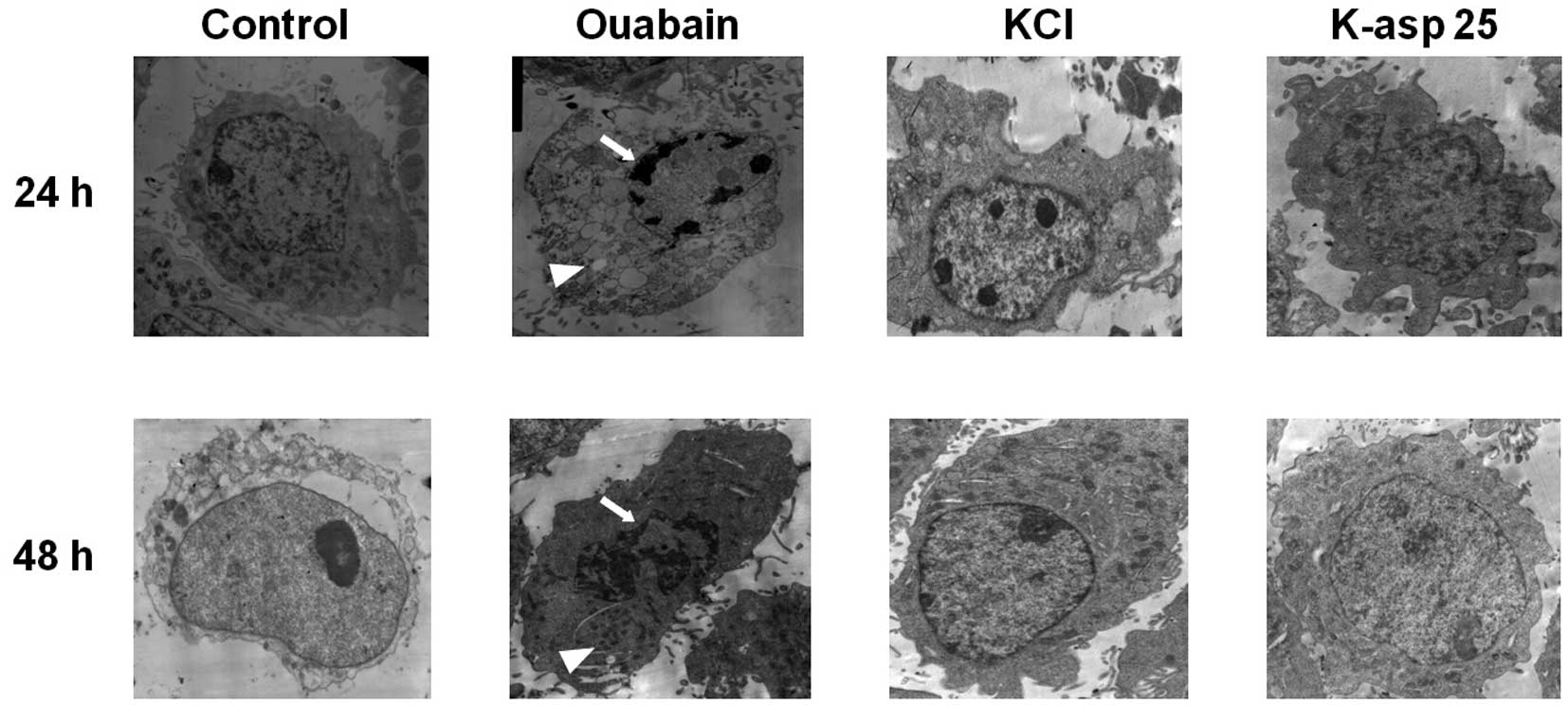
|
1
|
Abe K and Saito H: Involvement of
Na+-K+ pump in L-glutamate clearance by
cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Biol Pharm Bull. 23:1051–1054.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ueno Y, Ogino Y and Kinouchi T: Sodium,
potassium. Nihon Rinsho. 12:250–256. 2004.In Chinese.
|
|
3
|
Willard MD: Disorders of potassium
homeostasis. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 19:241–263. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shiino A, Nishida Y, Yasuda H, Suzuki M,
Matsuda M and Inubushi T: Magnetic resonance spectroscopic
determination of a neuronal and axonal marker in white matter
predicts reversibility of deficits in secondary normal pressure
hydrocephalus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 75:1141–1148. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suleiman MS, Dihmis WC, Caputo M, Angelini
GD and Bryan AJ: Changes in myocardial concentration of glutamate
and aspartate during coronary artery surgery. Am J Physiol.
272:H1063–H1069. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saunders EC, Ng WW, Chambers JM, et al:
Isotopomer profiling of Leishmania mexicana promastigotes reveals
important roles for succinate fermentation and aspartate uptake in
tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) anaplerosis, glutamate synthesis and
growth. J Biol Chem. 286:27706–27717. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Olanow CW and Tatton WG: Etiology and
pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 22:123–144.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bellavite P: The superoxide-forming
enzymatic system of phagocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 4:225–261.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Halliwell B and Gutteridge JM: Lipid
peroxidation in brain homogenates: the role of iron and hydroxyl
radicals. J Neurochem. 69:1330–1331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gardner AM, Xu FH, Fady C, Jacoby FJ,
Duffey DC, Tu Y and Lichtenstein A: Apoptotic vs. nonapoptotic
cytotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic Biol Med.
22:73–83. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xiao AY, Wei L, Xia S, Rothman S and Yu
SP: Ionic mechanism of ouabain induced concurrent apoptosis and
necrosis in individual cultured cortical neurons. Neuroscience.
22:1350–1362. 2002.
|
|
12
|
Huang X, Moir RD, Tanzi RE, Bush AI and
Rogers JT: Redox-active metals, oxidative stress and Alzheimer’s
disease pathology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1012:153–163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kulikov A, Eva A, Kirch U, Boldyrev A and
Scheiner-Bobis G: Ouabain activates signaling pathways associated
with cell death in human neuroblastoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1768:1691–1702. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu SP, Yeh C, Strasser U, Tian M and Choi
DW: NMDA receptor mediated K+ efflux and neuronal apoptosis.
Science. 284:336–339. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang XQ, Xiao AY, Sheline C, et al:
Apoptotic insults impair Na+-K+-ATPase
activity as a mechanism of neuronal death mediated by concurrent
ATP deficiency and oxidant stress. J Cell Sci. 116:2099–2110. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiao AY, Wang XQ, Yang A and Yu SP: Slight
impairment of Na+-K+-ATPase synergistically aggravates ceramide-
and beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis in cortical neurons. Brain Res.
955:253–259. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yurinskaya VE, Rubashkin AA and Vereninov
AA: Balance of unidirectional monovalent ion fluxes in cells
undergoing apoptosis: why does Na+-K+ pump suppression not cause
cell swelling? J Physiol. 589:2197–2211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brevet M, Ahidouch A, Sevestre H, Merviel
P, El Hiani Y, Robbe M and Ouadid-Ahidouch H: Expression of K+
channels in normal and cancerous human breast. Histol Histopathol.
23:965–972. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hernández-Enríquez B, Arellano RO and
Morán J: Role for ionic fluxes on cell death and apoptotic volume
decrease in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Neuroscience.
167:298–311. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang XP, Tan H, Chen BY and Deng CQ:
Astragalus extract alleviates nerve injury after cerebral ischemia
by improving energy metabolism and inhibiting apoptosis. Biol Pharm
Bull. 35:449–454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang M, Qiu J, Mi W, Wang F and Qu J: In
vitro effect of altering potassium concentration in artificial
endolymph on apoptosis and ultrastructure features of olfactory
bulb neural precursor cells. Neurosci Lett. 487:383–388. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jorgensen PL and Pedersen PA:
Structure-function relationships of Na+, K+, ATP, or Mg2+ binding
and energy transduction in Na, K-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1505:57–74. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gugliotta T, De Luca G, Romano P, Rigano
C, Scuteri A and Romano L: Effects of lead chloride on human
erythrocyte membranes and on kinetic anion sulphate and glutathione
concentrations. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 17:586–597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Noguchi T, Kamiyama N and Kashiwayanagi M:
Modulation of voltage-gated ion channels on SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma
by non-ionic surfactant, Cremophor EL. Biol Pharm Bull.
33:2013–2017. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|