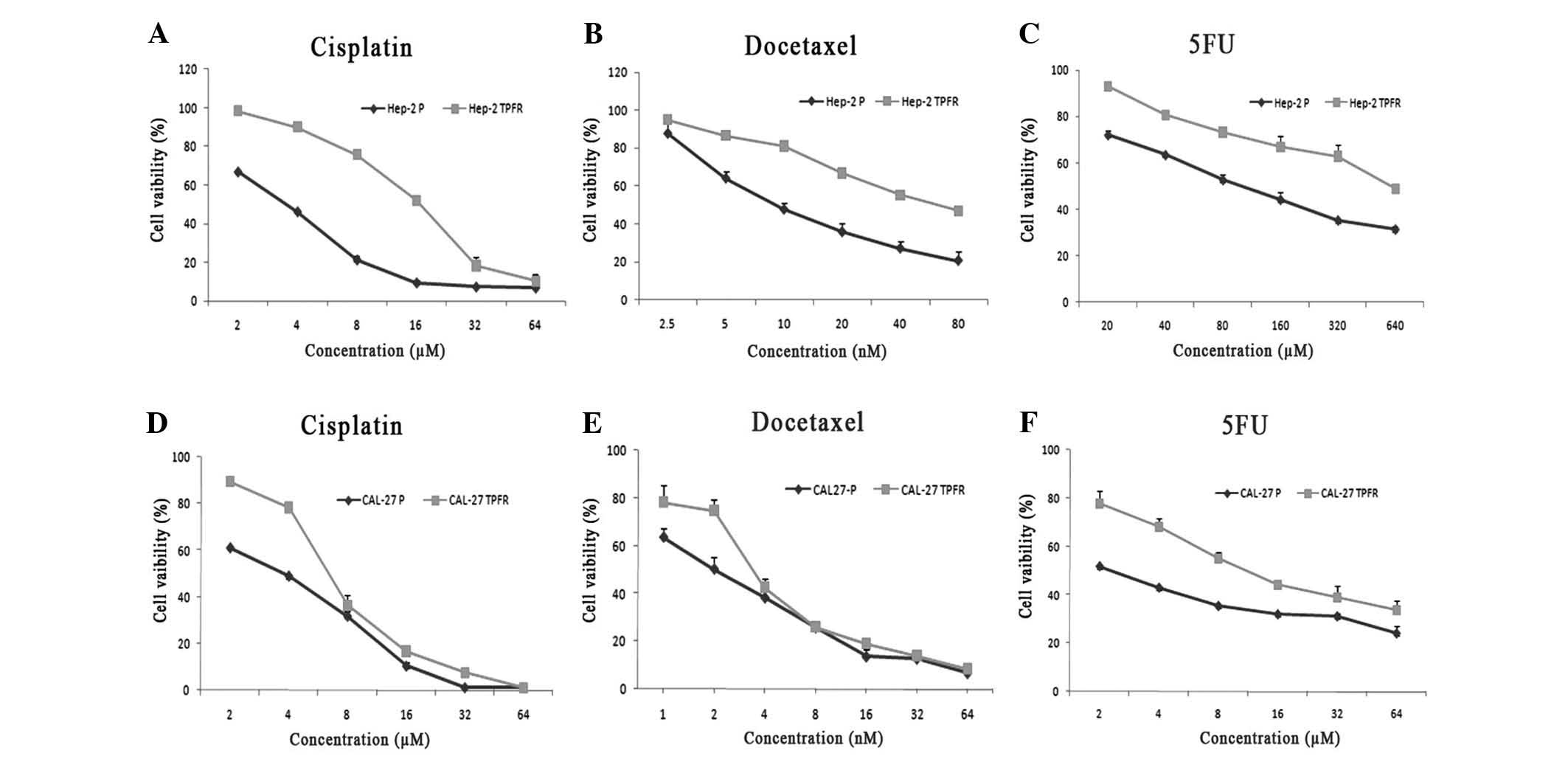
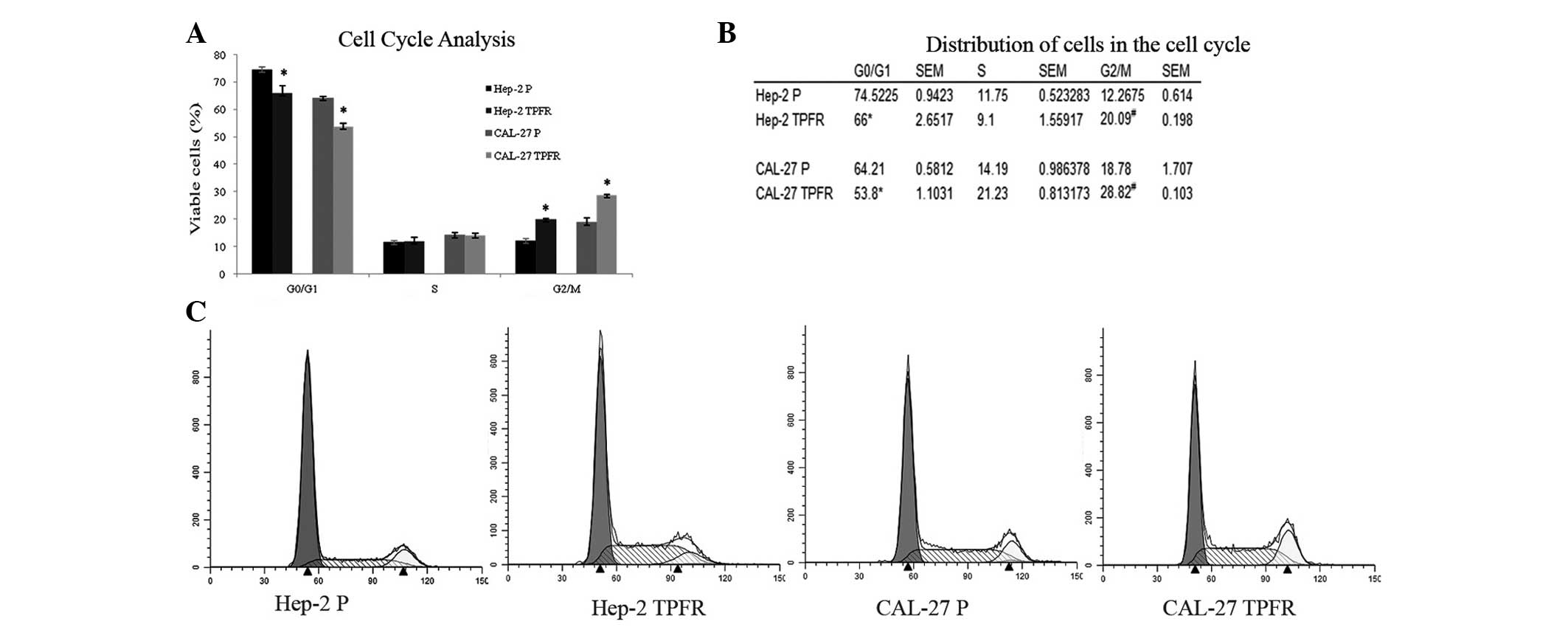
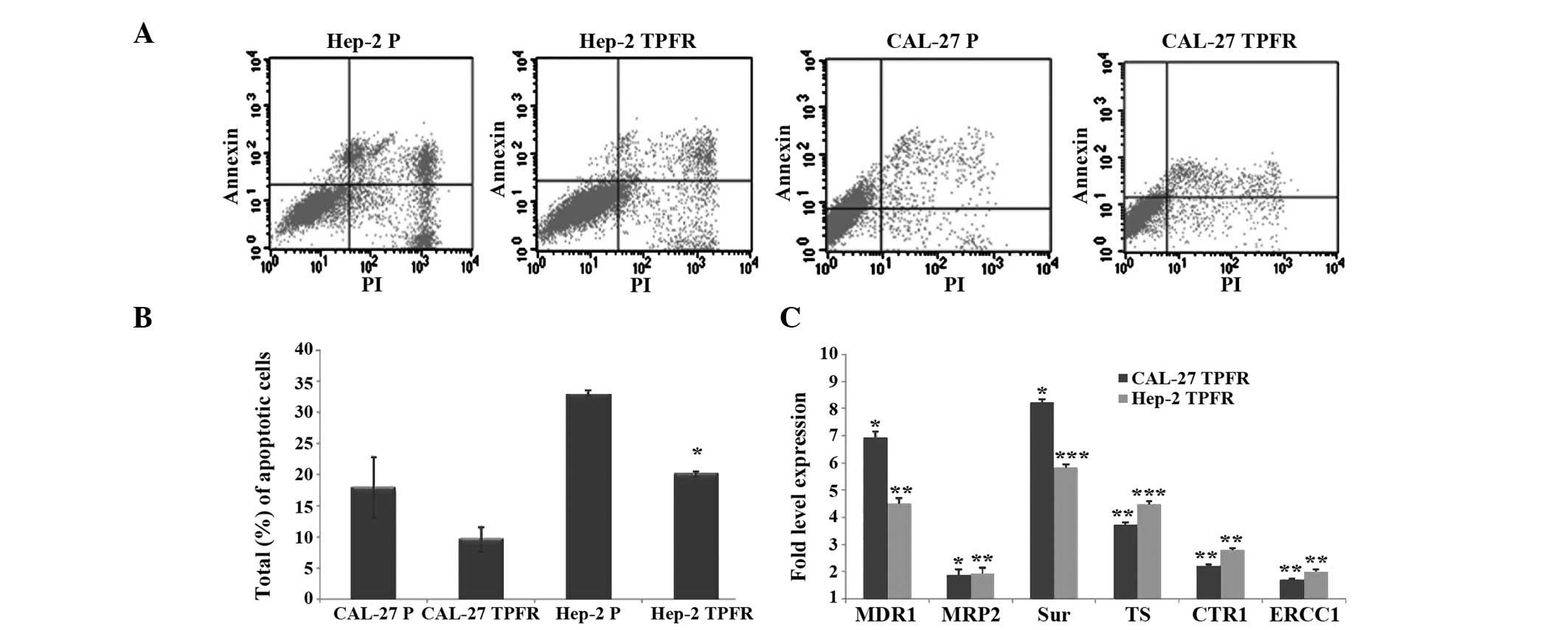
|
1
|
Kogashiwa Y, Sakurai H, Kimura T and Kohno
N: Docetaxel suppresses invasiveness of head and neck cancer cells
in vitro. Cancer Sci. 101:1382–1386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pignon JP, Syz N, Posner M, et al:
Adjusting for patient selection suggests the addition of docetaxel
to 5-fluorouracil-cisplatin induction therapy may offer survival
benefit in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Anticancer
Drugs. 15:331–340. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Salama JK, Seiwert TY and Vokes EE:
Chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 25:4118–4126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Posner MR, Hershock DM, Blajman CR, et al:
Cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or with docetaxel in head and neck
cancer. N Engl J Med. 357:1705–1715. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bourhis J, Le Maître A, Baujat B, Audry H
and Pignon JP: Individual patients’ data meta-analyses in head and
neck cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 19:188–194. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brockstein B, Haraf DJ, Rademaker AW, et
al: Patterns of failure, prognostic factors and survival in
loco-regionally advanced head and neck cancer treated with
concomitant chemoradiotherapy: a 9-year, 337-patient,
multi-institutional experience. Ann Oncol. 15:1179–1186. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stordal B, Hamon M, McEneaney V, et al:
Resistance to paclitaxel in a cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer
cell line is mediated by P-glycoprotein. PLoS One. 7:e407172012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Duan Z, Ames RY, Ryan M, Hornicek FJ,
Mankin H and Seiden MV: CDDO-Me, a synthetic triterpenoid, inhibits
expression of IL-6 and Stat3 phosphorylation in multi-drug
resistant ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
63:681–689. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wahl H, Tan L, Griffith K, Choi M and Liu
JR: Curcumin enhances Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 105:104–112.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Duan Z, Duan Y, Lamendola DE, et al:
Overexpression of MAGE/GAGE genes in
paclitaxel/doxorubicin-resistant human cancer cell lines. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:2778–2785. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Husain A, He G, Venkatraman ES and Spriggs
DR: BRCA1 up-regulation is associated with repair-mediated
resistance to cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Cancer Res.
58:1120–1123. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hill BT, Whelan RD, Shellard SA, McClean S
and Hosking LK: Differential cytotoxic effects of docetaxel in a
range of mammalian tumor cell lines and certain drug resistant
sublines in vitro. Invest New Drugs. 12:169–182. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Plumb JA, Luo W and Kerr DJ: Effect of
polyunsaturated fatty acids on the drug sensitivity of human tumour
cell lines resistant to either cisplatin or doxorubicin. Br J
Cancer. 67:728–733. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamano Y, Uzawa K, Saito K, et al:
Identification of cisplatin-resistance related genes in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:437–449. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Aoki K, Ogawa T, Ito Y and Nakashima S:
Cisplatin activates survival signals in UM-SCC-23 squamous cell
carcinoma and these signal pathways are amplified in
cisplatin-resistant squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 11:375–379.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gosepath EM, Eckstein N, Hamacher A, et
al: Acquired cisplatin resistance in the head-neck cancer cell line
Cal27 is associated with decreased DKK1 expression and can
partially be reversed by overexpression of DKK1. Int J Cancer.
123:2013–2019. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gu F, Ma Y, Zhang Z, et al: Expression of
Stat3 and Notch1 is associated with cisplatin resistance in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 23:671–676.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li L, Jiang AC, Dong P, Wan Y and Yu ZW:
The characteristics of Hep-2 cell with multiple drug resistance
induced by Taxol. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 137:659–664. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mizumachi T, Suzuki S, Naito A, et al:
Increased mitochondrial DNA induces acquired docetaxel resistance
in head and neck cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:831–838. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Yasumatsu R, Nakashima T, Uryu H, et al:
The role of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression in
resistance to 5-fluorouracil in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Oral Oncol. 45:141–147. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Beck A, Etienne MC, Chéradame S, et al: A
role for dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase and thymidylate synthase
in tumour sensitivity to fluorouracil. Eur J Cancer. 30A:1517–1522.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoo GH, Lin HS, Iskander AJ, et al:
Docetaxel associated pathways in cisplatin resistant head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma: a pilot study. Laryngoscope.
115:1938–1946. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Coley HM: Development of drug-resistant
models. Methods Mol Med. 88:267–273. 2004.
|
|
24
|
Murakami H, Ito S, Tanaka H, Kondo E,
Kodera Y and Nakanishi H: Establishment of new intraperitoneal
paclitaxel-resistant gastric cancer cell lines and comprehensive
gene expression analysis. Anticancer Res. 33:4299–4307.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rao GH, Liu HM, Li BW, et al:
Establishment of a human colorectal cancer cell line P6C with stem
cell properties and resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 34:793–804. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Loh YN, Hedditch EL, Baker LA, Jary E,
Ward RL and Ford CE: The Wnt signalling pathway is upregulated in
an in vitro model of acquired tamoxifen resistant breast cancer.
BMC Cancer. 13:1742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takahashi K, Tanaka M, Inagaki A, et al:
Establishment of a 5-fluorouracil-resistant triple-negative breast
cancer cell line. Int J Oncol. 43:1985–1991. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maseki S, Ijichi K, Tanaka H, et al:
Acquisition of EMT phenotype in the gefitinib-resistant cells of a
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line through
Akt/GSK-3β/snail signalling pathway. Br J Cancer. 106:1196–1204.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Negoro K, Yamano Y, Fushimi K, et al:
Establishment and characterization of a cisplatin-resistant cell
line, KB-R, derived from oral carcinoma cell line, KB. Int J Oncol.
30:1325–1332. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nakamura M, Nakatani K, Uzawa K, et al:
Establishment and characterization of a cisplatin-resistant oral
squamous cell carcinoma cell line, H-1R. Oncol Rep. 14:1281–1286.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pinto AL and Lippard SJ: Binding of the
antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) (cisplatin) to DNA.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 780:167–180. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Owellen RJ, Hartke CA, Dickerson RM and
Hains FO: Inhibition of tubulin-microtubule polymerization by drugs
of the Vinca alkaloid class. Cancer Res. 36:1499–1502.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Loehrer PJ Sr, Einhorn LH, Williams SD,
Hui SL, Estes NC and Pennington K: Cisplatin plus 5-FU for the
treatment of adenocarcinoma of the colon. Cancer Treat Rep.
69:1359–1363. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qin H, Luo J, Zhu YP, Xie HL, Yang WQ and
Lei WB: Combination of taxanes, cisplatin and fluorouracil as
induction chemotherapy for locally advanced head and neck cancer: a
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e515262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hitt R, Paz-Ares L, Brandariz A, et al:
Induction chemotherapy with paclitaxel, cisplatin and
5-fluorouracil for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck:
long-term results of a phase II trial. Ann Oncol. 13:1665–1673.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hussain M, Salwen W, Kucuk O and Ensley J:
Paclitaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil in patients with advanced
or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a
preliminary report. Semin Oncol. 24:S19–43. S19–45. 1997.
|
|
38
|
Choi YJ, Chung J, Shin HJ, et al:
Induction chemotherapy of docetaxel and Cisplatin for the elderly
patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer
Res Treat. 39:1–5. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Adamo V, Ferraro G, Pergolizzi S, et al:
Paclitaxel and cisplatin in patients with recurrent and metastatic
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 40:525–531.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu YL, Zhang GQ, Yang Y, Zhang CY, Fu RX
and Yang YM: Genistein induces G2/M arrest in gastric cancer cells
by increasing the tumor suppressor PTEN expression. Nutr Cancer.
65:1034–1041. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ismail IA, Kang KS, Lee HA, Kim JW and
Sohn YK: Genistein-induced neuronal apoptosis and G2/M cell cycle
arrest is associated with MDC1 up-regulation and PLK1
down-regulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 575:12–20. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nawab A, Thakur VS, Yunus M, Ali Mahdi A
and Gupta S: Selective cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis
in human prostate cancer cells by a polyphenol-rich extract of
Solanum nigrum. Int J Mol Med. 29:277–284. 2012.
|
|
43
|
Wang WZ, Cheng J, Luo J and Zhuang SM:
Abrogation of G2/M arrest sensitizes curcumin-resistant hepatoma
cells to apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 582:2689–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang Q, Fan S, Eastman A, Worland PJ,
Sausville EA and O’Connor PM: UCN-01: a potent abrogator of G2
checkpoint function in cancer cells with disrupted p53. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 88:956–965. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sun XC, Cheng HY, Deng YX, Shao RG and Ma
J: Tetrandrine: a potent abrogator of G2 checkpoint function in
tumor cells and its mechanism. Biomed Environ Sci. 20:495–501.
2007.
|
|
46
|
Chappell J and Dalton S: Altered cell
cycle regulation helps stem-like carcinoma cells resist apoptosis.
BMC Biol. 8:632010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pratt MA, Niu MY and Renart LI: Regulation
of survivin by retinoic acid and its role in paclitaxel-mediated
cytotoxicity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Apoptosis. 11:589–605.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nestal de Moraes G, Silva KL, Vasconcelos
FC and Maia RC: Survivin overexpression correlates with an
apoptosis-resistant phenotype in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.
Oncol Rep. 25:1613–1619. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ohishi Y, Oda Y, Uchiumi T, et al:
ATP-binding cassette super-family transporter gene expression in
human primary ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 8:3767–3775.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee J, Jiffar T and Kupferman ME: A novel
role for BDNF-TrkB in the regulation of chemotherapy resistance in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e302462012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Köberle B, Ditz C, Kausch I, Wollenberg B,
Ferris RL and Albers AE: Metastases of squamous cell carcinoma of
the head and neck show increased levels of nucleotide excision
repair protein XPF in vivo that correlate with increased
chemoresistance ex vivo. Int J Oncol. 36:1277–1284. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hayes M, Lan C, Yan J, et al: ERCC1
expression and outcomes in head and neck cancer treated with
concurrent cisplatin and radiation. Anticancer Res. 31:4135–4139.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Song IS, Savaraj N, Siddik ZH, et al: Role
of human copper transporter Ctr1 in the transport of platinum-based
antitumor agents in cisplatin-sensitive and cisplatin-resistant
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:1543–1549. 2004.
|
|
54
|
Holzer AK, Samimi G, Katano K, et al: The
copper influx transporter human copper transport protein 1
regulates the uptake of cisplatin in human ovarian carcinoma cells.
Mol Pharmacol. 66:817–823. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Peters GJ, Backus HH, Freemantle S, et al:
Induction of thymidylate synthase as a 5-fluorouracil resistance
mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1587:194–205. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wong NA, Brett L, Stewart M, et al:
Nuclear thymidylate synthase expression, p53 expression and 5-FU
response in colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 85:1937–1943. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Saiki Y, Ogawa T, Shiga K, Sunamura M,
Kobayashi T and Horii A: A Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell
Carcinoma Cell Line with Acquired
cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum-Resistance Shows Remarkable
Upregulation of BRCA1 and Hypersensitivity to Taxane. Int J
Otolaryngol. 2011:5218522011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tamatani T, Ferdous T, Takamaru N, et al:
Antitumor efficacy of sequential treatment with docetaxel and
5-fluorouracil against human oral cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
41:1148–1156. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|