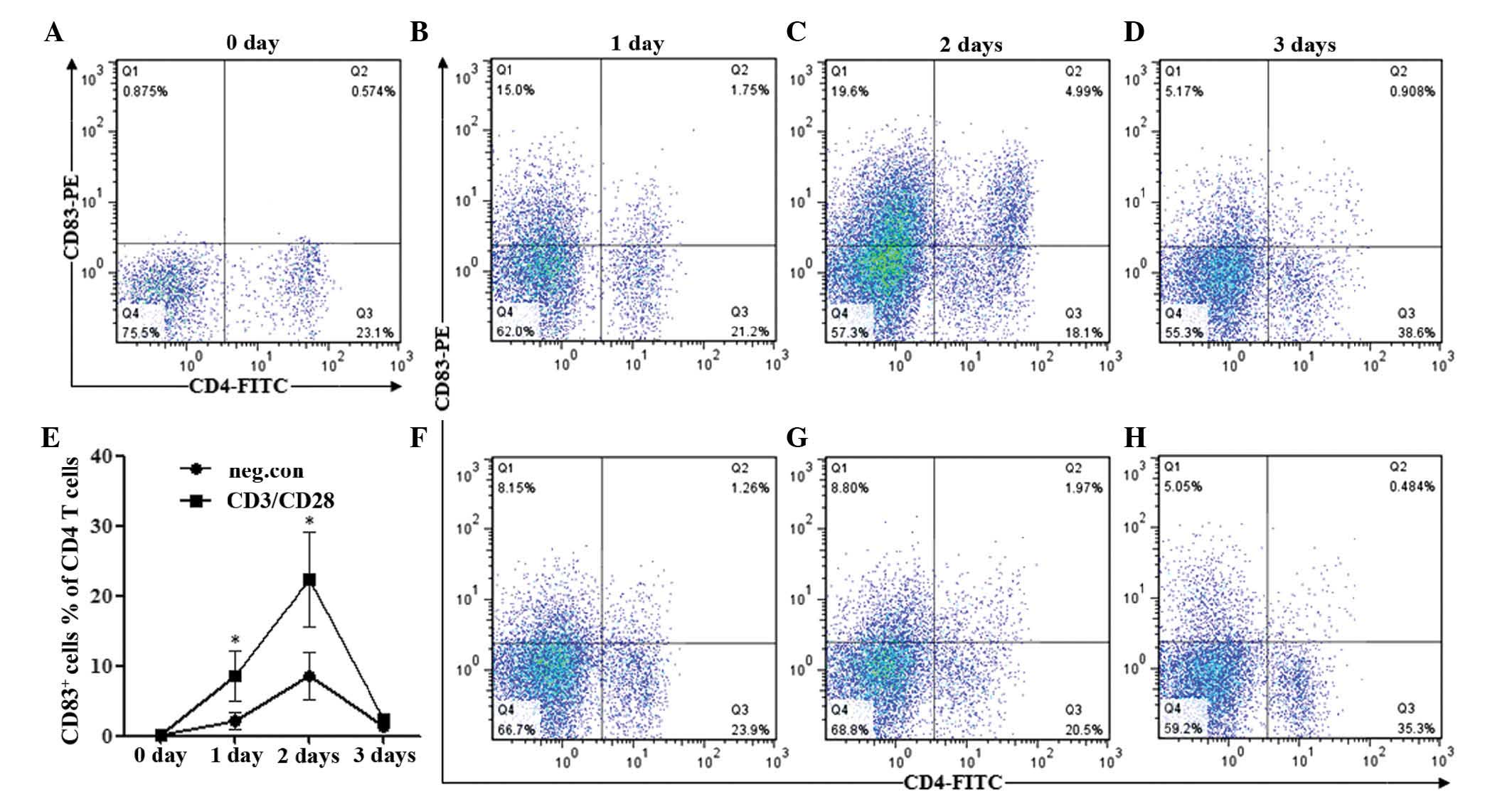
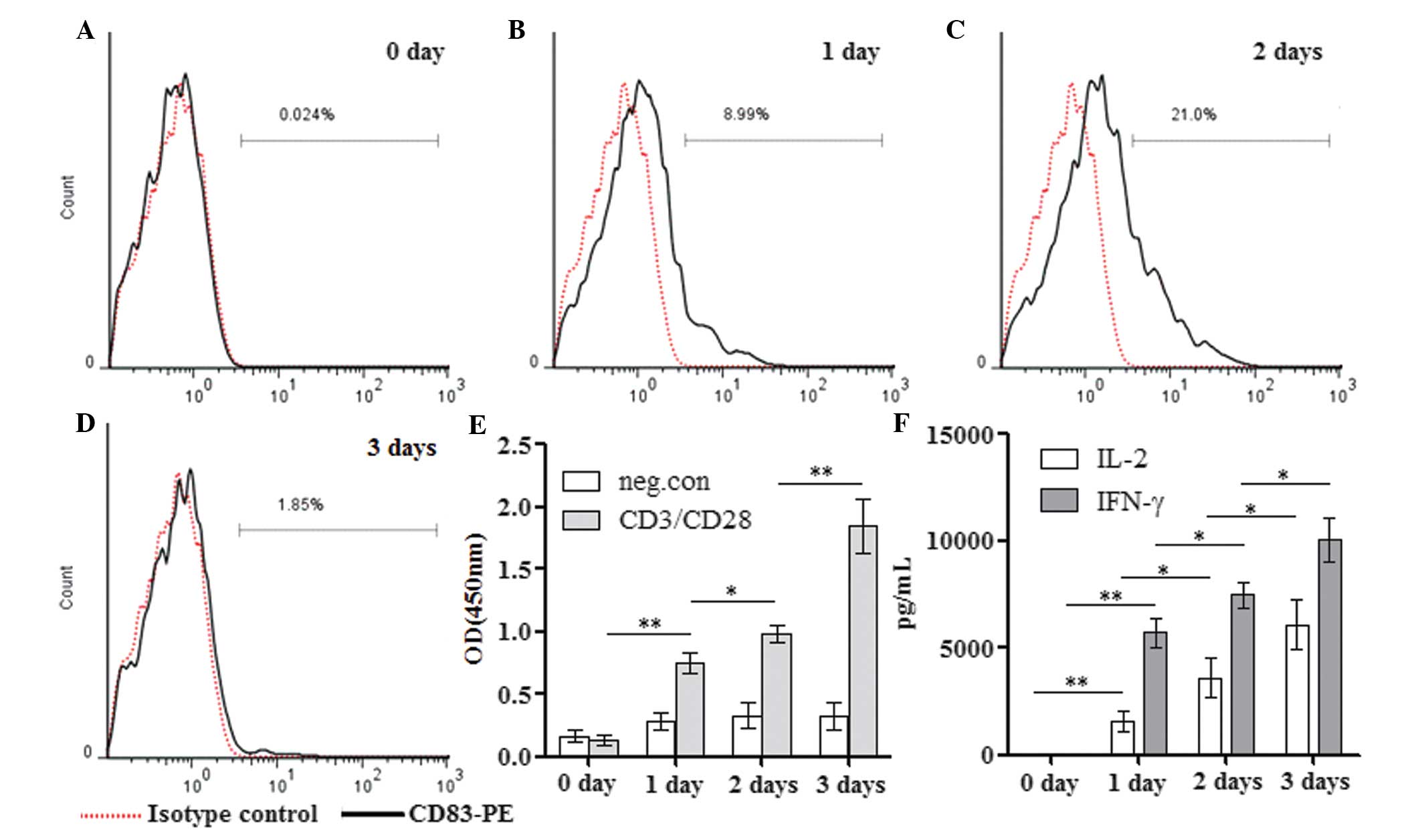
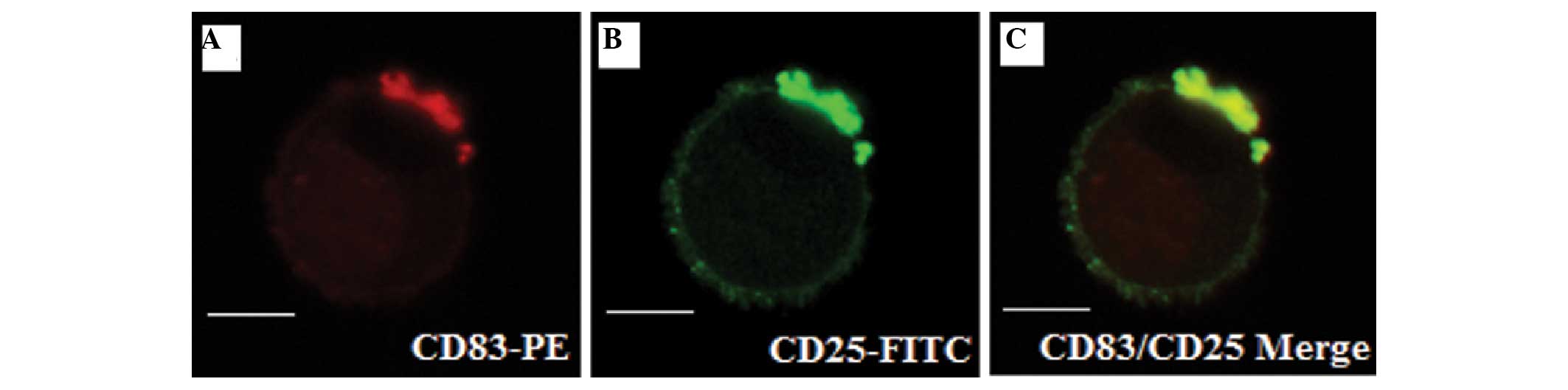
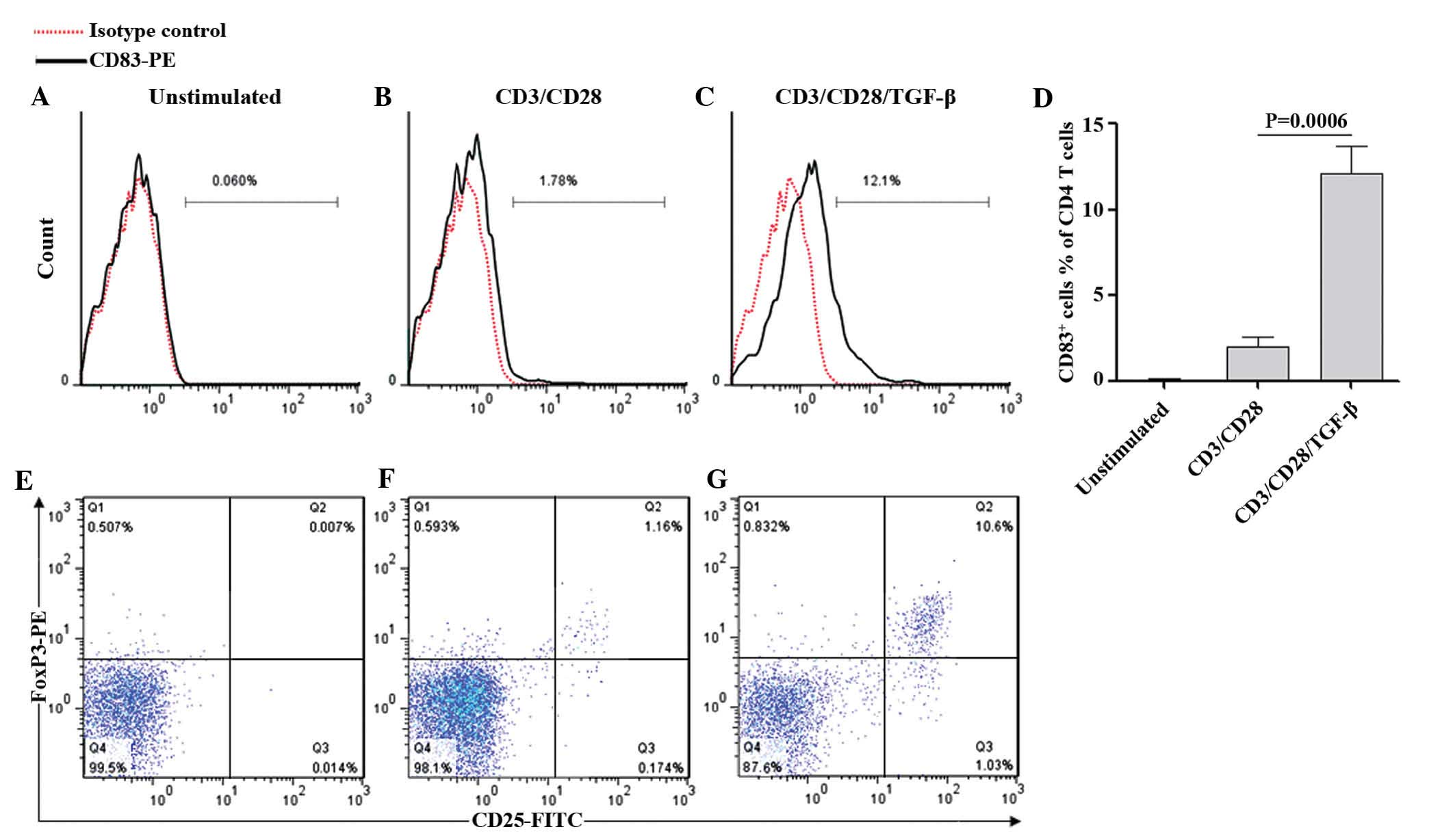
|
1
|
Zhou LJ, Schwarting R, Smith HM and Tedder
TF: A novel cell-surface molecule expressed by human
interdigitating reticulum cells, Langerhans cells and activated
lymphocytes is a new member of the Ig superfamily. J Immunol.
149:735–742. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou LJ and Tedder TF: CD14+
blood monocytes can differentiate into functionally mature
CD83+ dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:2588–2592. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Stein MF, Lang S, Winkler TH, et al:
Multiple interferon regulatory factor and NF-κB sites cooperate in
mediating cell-type- and maturation-specific activation of the
human CD83 promoter in dendritic cells. Mol Cell Biol.
33:1331–1344. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fujimoto Y, Tu L, Miller AS, Bock C,
Fujimoto M, Doyle C, Steeber DA and Tedder TF: CD83 expression
influences CD4+ T cell development in the thymus. Cell.
108:755–767. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tze LE, Horikawa K, Domaschenz H, et al:
CD83 increases MHC II and CD86 on dendritic cells by opposing
IL-10-driven MARCH1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation. J Exp
Med. 208:149–165. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prechtel AT, Turza NM, Theodoridis AA and
Steinkasserer A: CD83 knockdown in monocyte-derived dendritic cells
by small interfering RNA leads to a diminished T cell stimulation.
J Immunol. 178:5454–5464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kretschmer B, Lüthje K, Ehrlich S,
Osterloh A, Piedavent M, Fleischer B and Breloer M: CD83 on murine
APC does not function as a costimulatory receptor for T cells.
Immunol Lett. 120:87–95. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pinho MP, Migliori IK, Flatow EA and
Barbuto JA: Dendritic cell membrane CD83 enhances immune responses
by boosting intracellular calcium release in T lymphocytes. J
Leukoc Biol. 95:755–762. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dudziak D, Nimmerjahn F, Bornkamm GW and
Laux G: Alternative splicing generates putative soluble CD83
proteins that inhibit T cell proliferation. J Immunol.
174:6672–6676. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bock F, Rössner S, Onderka J, et al:
Topical application of soluble CD83 induces IDO-mediated immune
modulation, increases Foxp3+ T cells and prolongs allogeneic
corneal graft survival. J Immunol. 191:1965–1975. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Starke C, Steinkasserer A, Voll RE and
Zinser E: Soluble human CD83 ameliorates lupus in NZB/W F1 mice.
Immunobiology. 218:1411–1415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuan Y, Wan L, Chen Y, et al: Production
and characterization of human soluble CD83 fused with the fragment
crystallizable region of human IgG1 in Pichia pastoris. Appl
Microbiol Biotechnol. 97:9409–9417. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eckhardt J, Kreiser S, Döbbeler M, et al:
Soluble CD83 ameliorates experimental colitis in mice. Mucosal
Immunol. 7:1006–1018. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo Y, Li R, Song X, et al: The Expression
and characterization of functionally active soluble CD83 by pichia
Pastoris using high-density fermentation. PLoS One. 9:e892642014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen L, Zhu Y, Zhang G, Gao C, Zhong W and
Zhang X: CD83-stimulated monocytes suppress T-cell immune responses
through production of prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:18778–18783. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reinwald S, Wiethe C, Westendorf AM,
Breloer M, Probst-Kepper M, Fleischer B, Steinkasserer A, Buer J
and Hansen W: CD83 expression in CD4+ T cells modulates
inflammation and autoimmunity. J Immunol. 180:5890–5897. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su LL, Iwai H, Lin JT and Fathman CG: The
transmembrane E3 ligase GRAIL ubiquitinates and degrades CD83 on
CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 183:438–444. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kumar S, Naqvi RA, Ali R, Rani R, Khanna N
and Rao DN: CD4+CD25+ T regs with acetylated
FoxP3 are associated with immune suppression in human leprosy. Mol
Immunol. 56:513–520. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen W, Jin W, Hardegen N, Lei KJ, Li L,
Marinos N, McGrady G and Wahl SM: Conversion of peripheral
CD4+CD25− naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta
induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med. 198:1875–1886.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kretschmer B, Kühl S, Fleischer B and
Breloer M: Activated T cells induce rapid CD83 expression on B
cells by engagement of CD40. Immunol Lett. 136:221–227. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lechmann M, Shuman N, Wakeham A and Mak
TW: The CD83 reporter mouse elucidates the activity of the CD83
promoter in B, T and dendritic cell populations in vivo. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:11887–11892. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yamane H and Paul WE: Early signaling
events that underlie fate decisions of naive CD4(+) T
cells toward distinct T-helper cell subsets. Immunol Rev.
252:12–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu A and Malek TR: Selective availability
of IL-2 is a major determinant controlling the production of
CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T regulatory
cells. J Immunol. 177:5115–5121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barron L, Dooms H, Hoyer KK, Kuswanto W,
Hofmann J, O'Gorman WE and Abbas AK: Cutting edge: mechanisms of
IL-2-dependent maintenance of functional regulatory T cells. J
Immunol. 185:6426–6430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rao PE, Petrone AL and Ponath PD:
Differentiation and expansion of T cells with regulatory function
from human peripheral lymphocytes by stimulation in the presence of
TGF-β. J Immunol. 174:1446–1455. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|