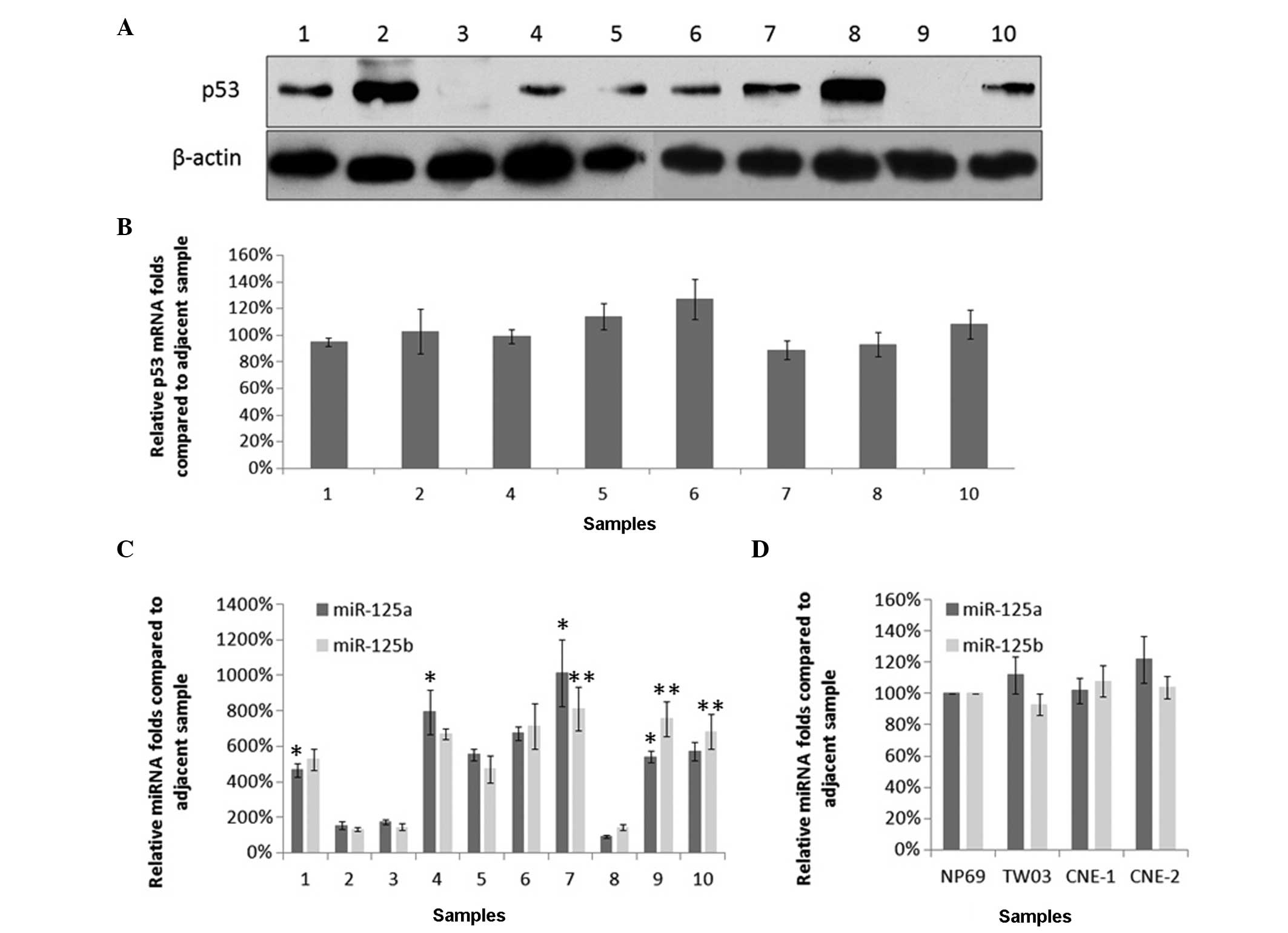
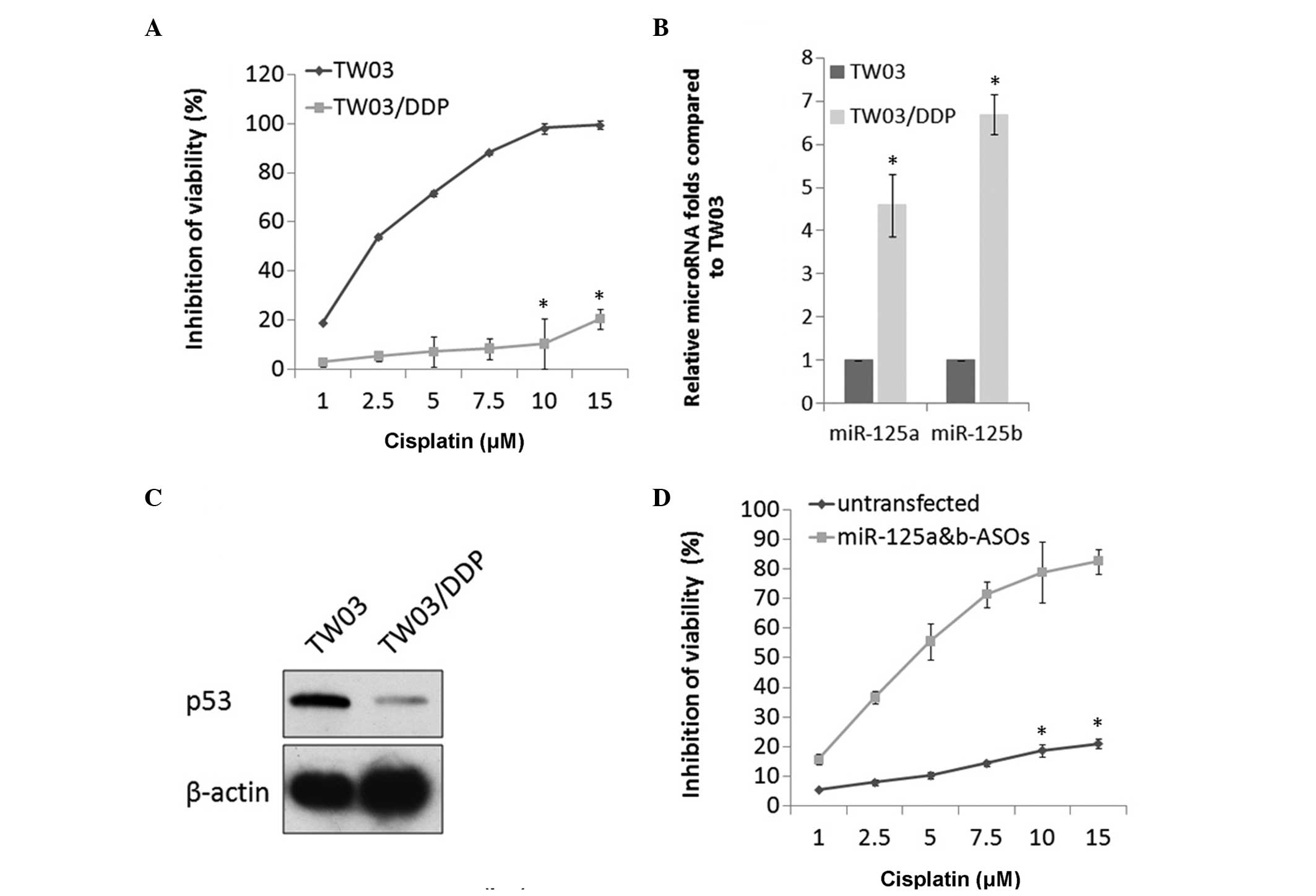
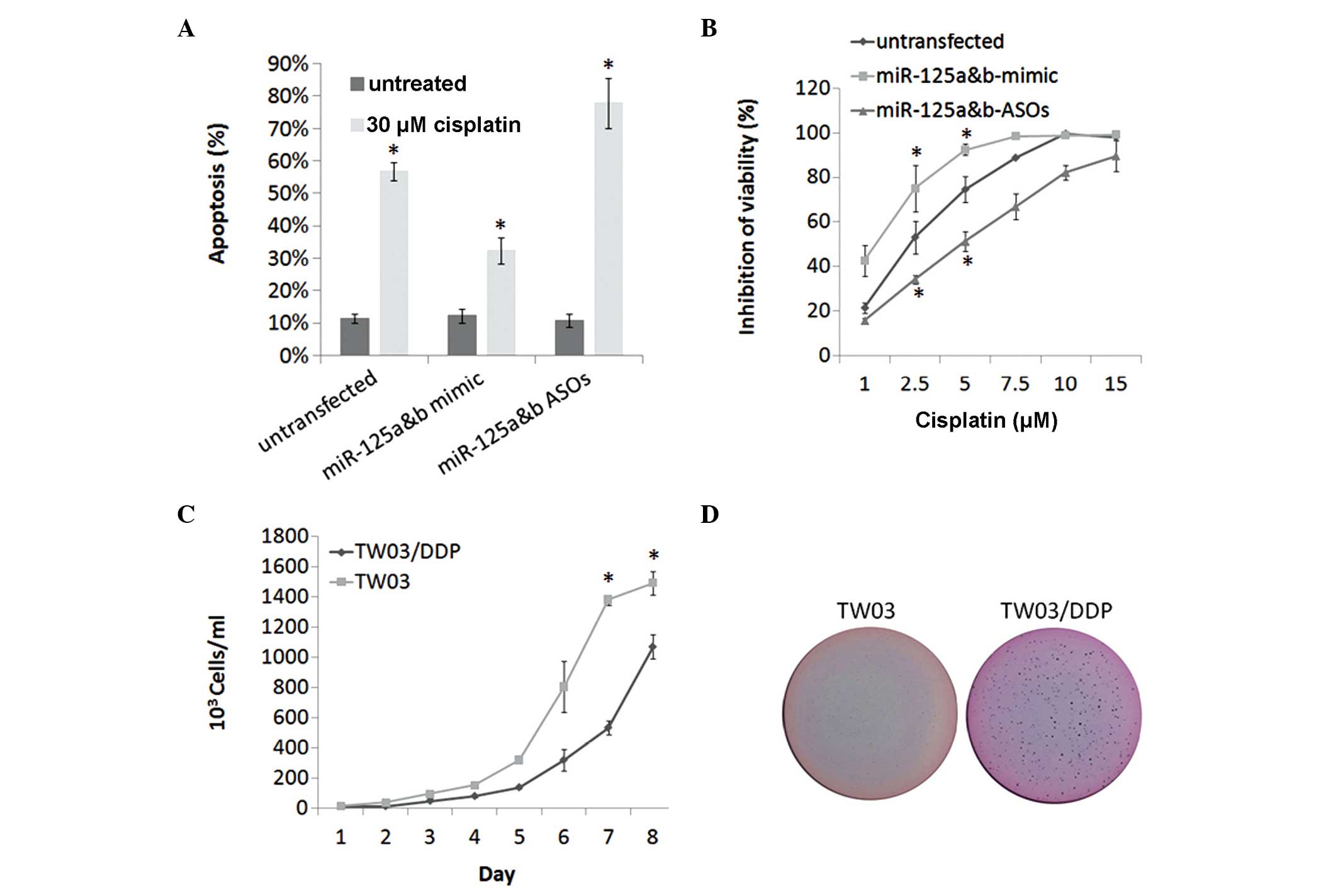
|
1
|
Wei WI and Sham JS: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 365:2041–2054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao SM, Simons MJ and Qian CN: The
prevalence and prevention of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China.
Chin J Cancer. 30:114–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Langendijk JA, Leemans CR, Buter J,
Berkhof J and Slotman BJ: The additional value of chemotherapy to
radiotherapy in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a
meta-analysis of the published literature. J Clin Oncol.
22:4604–4012. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fajac A, Da Silva J, Ahomadegbe JC, Rateau
JG, Bernaudin JF, Riou G and Bénard J: Cisplatin-induced apoptosis
and p53 gene status in a cisplatin-resistant human ovarian
carcinoma cell line. Int J Cancer. 68:67–74. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jin Y, Cai XY, Shi YX, Xia XY, Cai YC, Cao
Y, Zhang WD, Hu WH and Jiang WQ: Comparison of five cisplatin-based
regimens frequently used as the first-line protocols in metastatic
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1717–1725.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fraser M, Bai T and Tsang BK: Akt promotes
cisplatin resistance in human ovarian cancer cells through
inhibition of p53 phosphorylation and nuclear function. Int J
Cancer. 122:534–546. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Leung EL, Fraser M, Fiscus RR and Tsang
BK: Cisplatin alters nitric oxide synthase levels in human ovarian
cancer cells: involvement in p53 regulation and cisplatin
resistance. Br J Cancer. 98:1803–1809. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Michels J, Brenner
C, Szabadkai G, Harel-Bellan A, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Systems
biology of cisplatin resistance: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 5:1257–1274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zamble DB, Jacks T and Lippard SJ:
p53-Dependent and-independent responses to cisplatin in mouse
testicular teratocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:6163–6168. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bragado P, Armesilla A, Silva A and Porras
A: Apoptosis by cisplatin requires p53 mediated p38alpha MAPK
activation through ROS generation. Apoptosis. 12:1733–1742. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moreno CS, Matyunina L, Dickerson EB,
Schubert N, Bowen NJ, Logani S, Benigno BB and McDonald JF:
Evidence that p53-mediated cell-cycle-arrest inhibits
chemotherapeutic treatment of ovarian carcinomas. PLoS One.
2:e4412007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Petit T, Bearss DJ, Troyer DA, Munoz RM
and Windle JJ: p53-independent response to cisplatin and
oxaliplatin in MMTV-ras mouse salivary tumors. Mol Cancer Ther.
2:165–171. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Michelle MR and Zahid HS: Resistance and
gain-of-resistance phenotypes in cancers harboring wild-type p53.
Biochem Pharmacol. 83:1049–1062. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nishida N, Mimori K, Fabbri M, Yokobori T,
Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Ishii H, Doki Y and Mori M:
MicroRNA-125a-5p is an independent prognostic factor in gastric
cancer and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells
in combination with trastuzumab. Clin Cancer Res. 17:2725–2733.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao YM, Zhou JM, Wang LR, He HW, Wang XL,
Tao ZH, Sun HC, Wu WZ, Fan J, Tang ZY and Wang L: HIWI is
associated with prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
after curative resection. Cancer. 118:2708–2717. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Le MT, Teh C, Shyh-Chang N, Xie H, Zhou B,
Korzh V, Lodish HF and Lim B: MicroRNA-125b is a novel negative
regulator of p53. Genes Dev. 23:862–876. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rao X, Huang X, Zhou Z and Lin X: An
improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat
Bioinforma Biomath. 3:71–85. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feudis PD, Debernardis D, Beccaglia P,
Valenti M, Siré EG, Arzani D, Stanzione S, Parodi S, D'lncalci M,
Russo P and Broggini M: DDP-induced cytotoxicity is not influenced
by p53 in nine human ovarian cancer cell lines with different p53
status. Br J Cancer. 76:474–479. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kovalchuk O, Filkowski J, Meservy J,
Ilnytskyy Y, Tryndyak VP, Chekhun VF and Pogribny IP: Involvement
of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells to
chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2152–2159.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang Z, Wu H, Xia J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Huang
K, Wagar N, Yoon Y, Cho HT, Scala S and Shim H: Involvement of
miR-326 in chemotherapy resistance of breast cancer through
modulating expression of multidrugresistance-associated protein 1.
Biochem Pharmacol. 79:817–824. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Pogribny IP, Filkowski JN, Tryndyak VP,
Golubov A, Shpyleva SI and Kovalchuk O: Alterations of microRNAs
and their targets are associated with acquired resistance of MCF-7
breast cancer cells to cisplatin. Int J Cancer. 127:1785–1794.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao JJ, Lin J, Yang H, Kong W, He L, Ma
X, Coppola D and Cheng JQ: MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates
estrogen receptor alpha and is associated with tamoxifen resistance
in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 283:31079–31086. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z and Kong D: Novel
targets for prostate cancer chemoprevention. Endocr Relat Cancer.
17:195–212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu N, Brodin P, Wei T, Meisqen F, Eidsmo
L, Nagy N, Kemeny L, Ståhle M, Sonkoly E and Pivarcsi A: mir-125b,
a microRNA downregulated in psoriasis, modulates keratinocyte
proliferation by targeting FGFR2. J Invest Dermatol. 131:1521–1529.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|