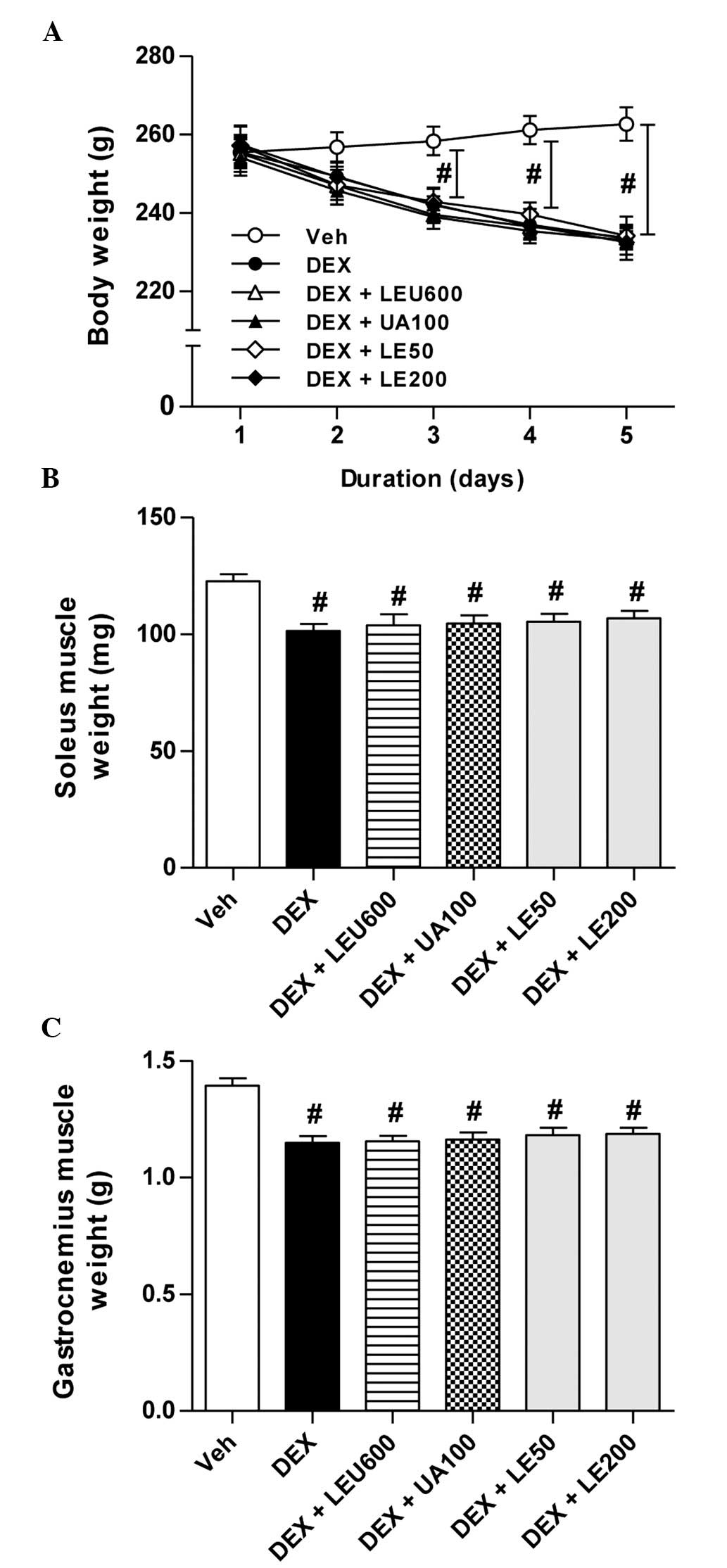
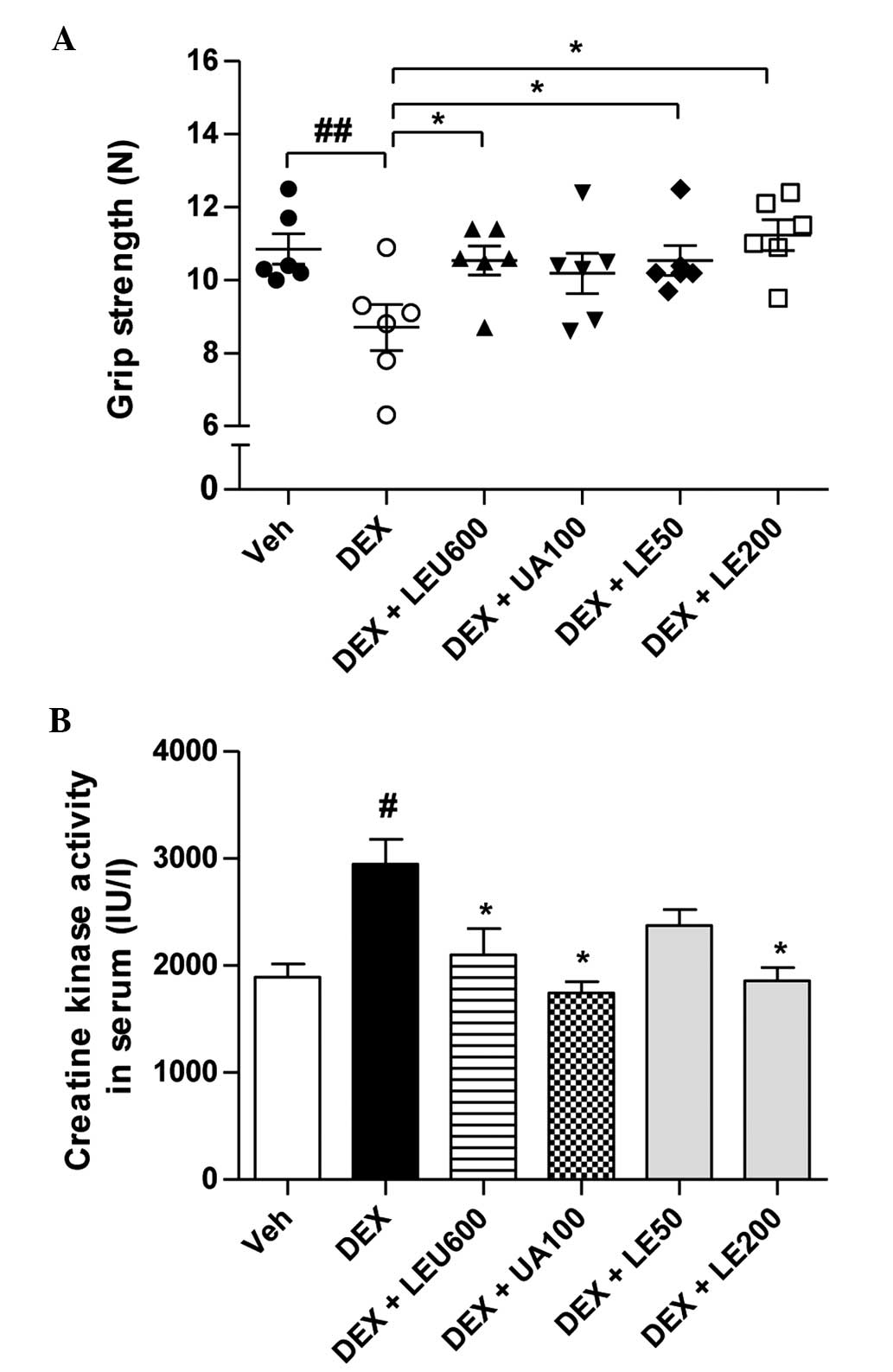
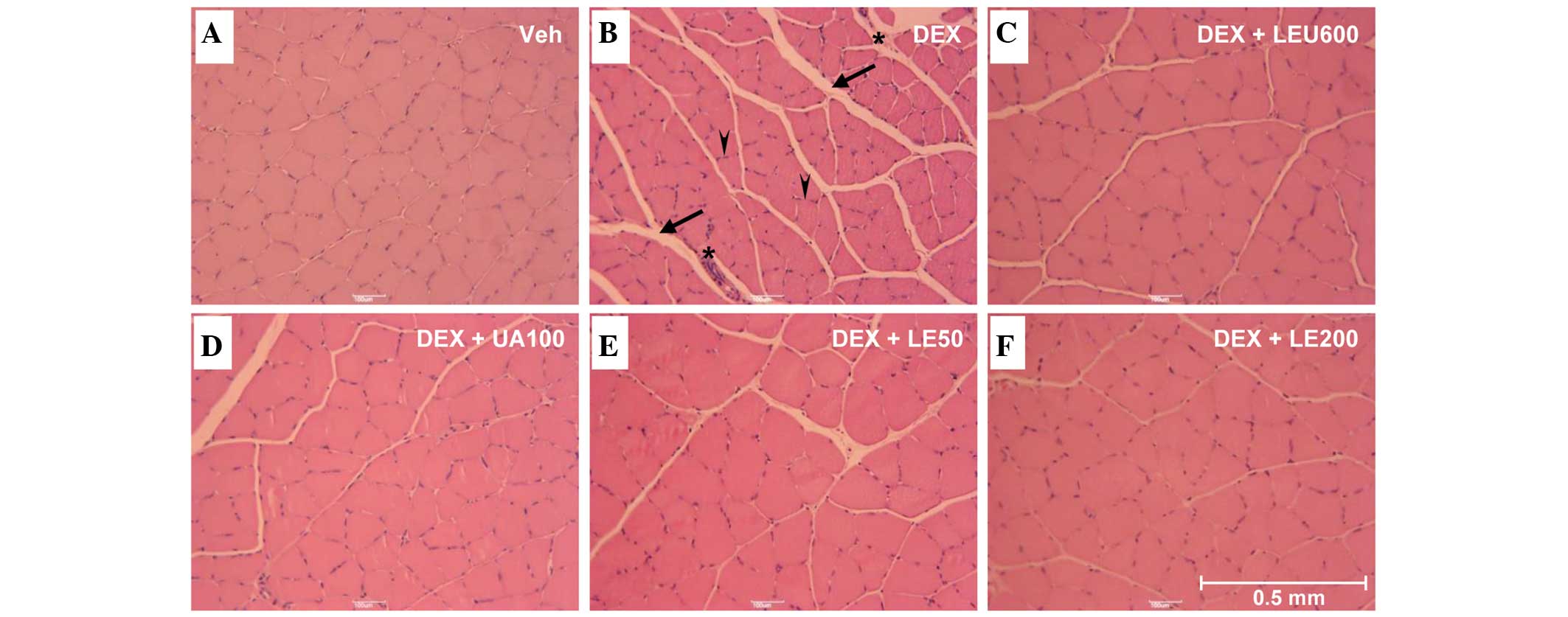
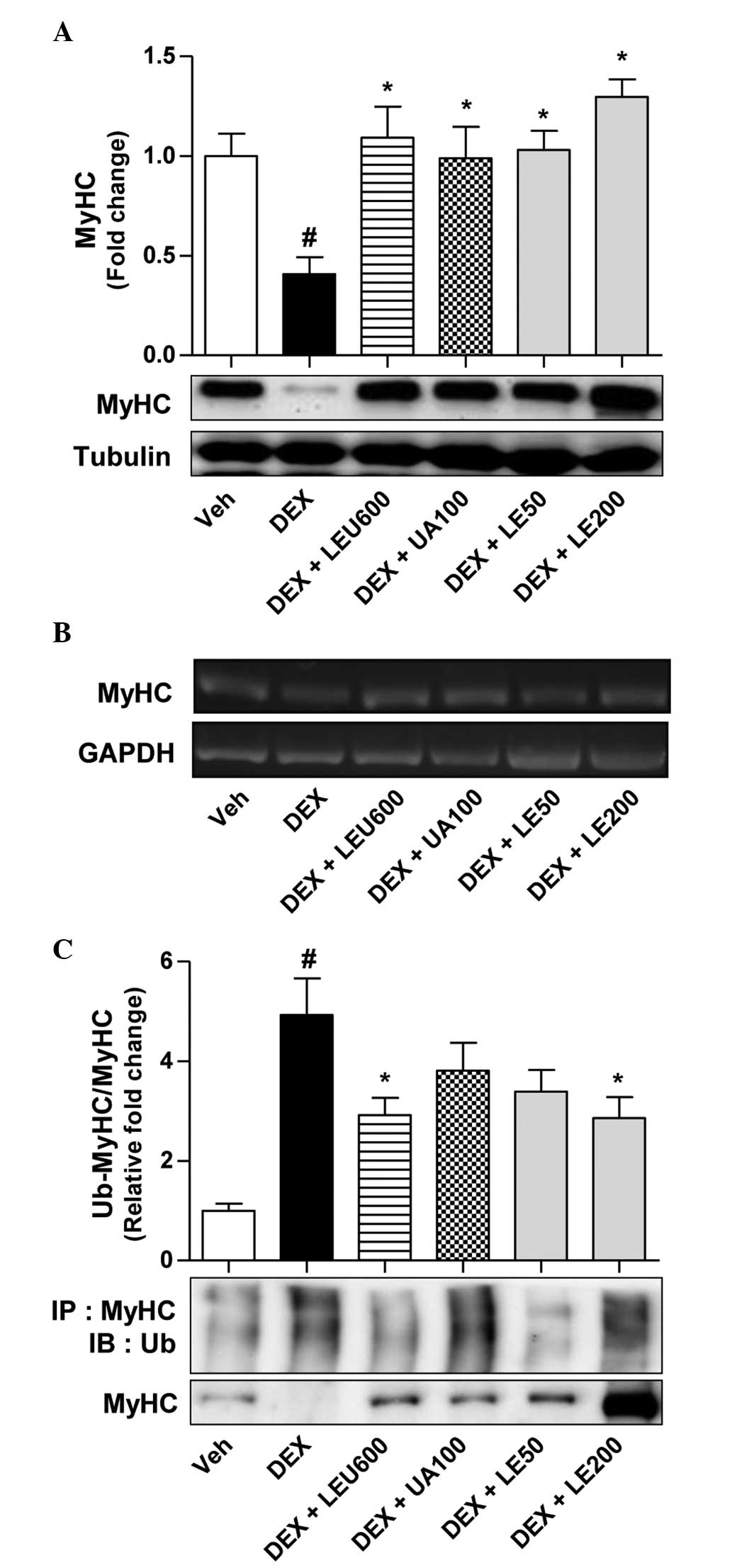
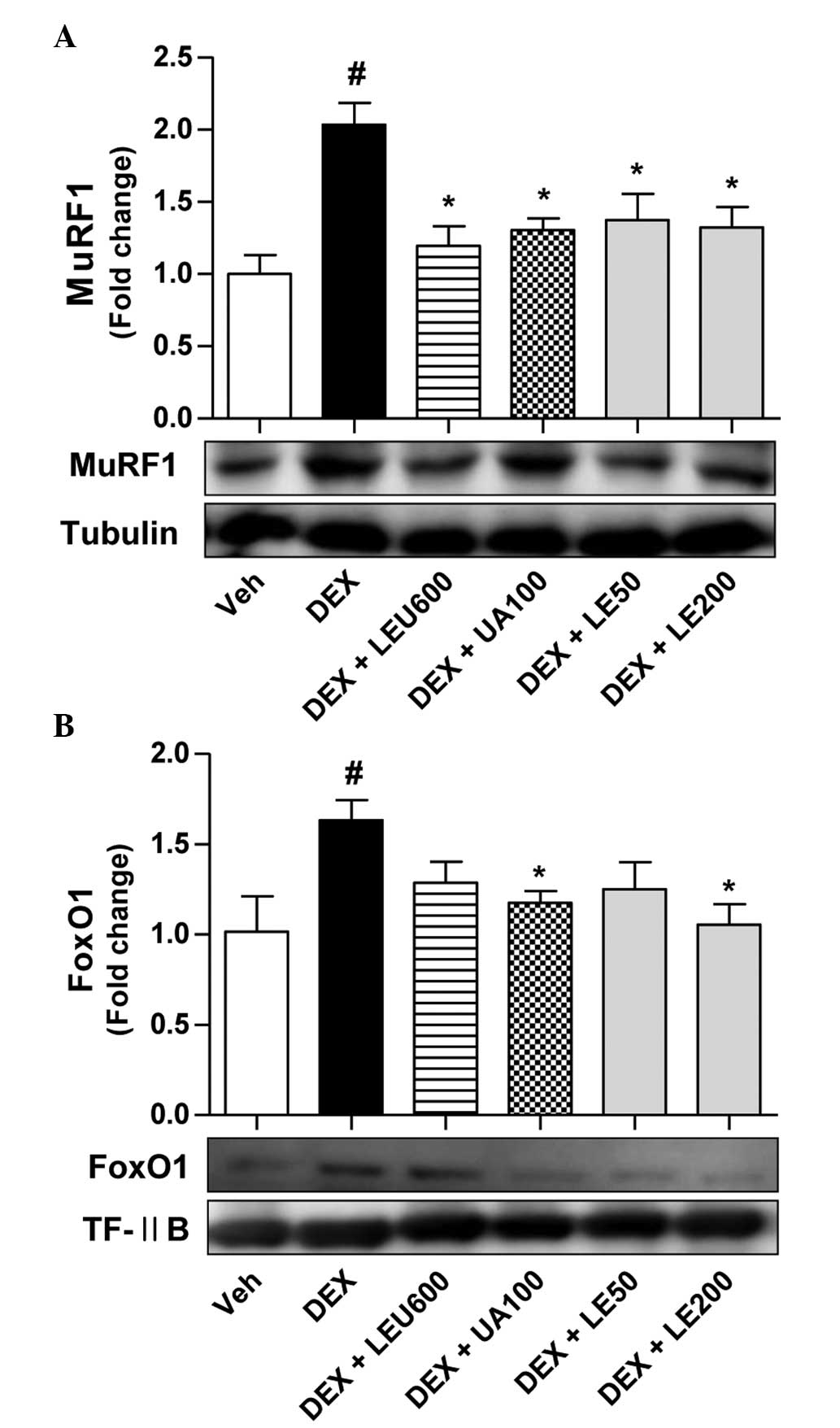
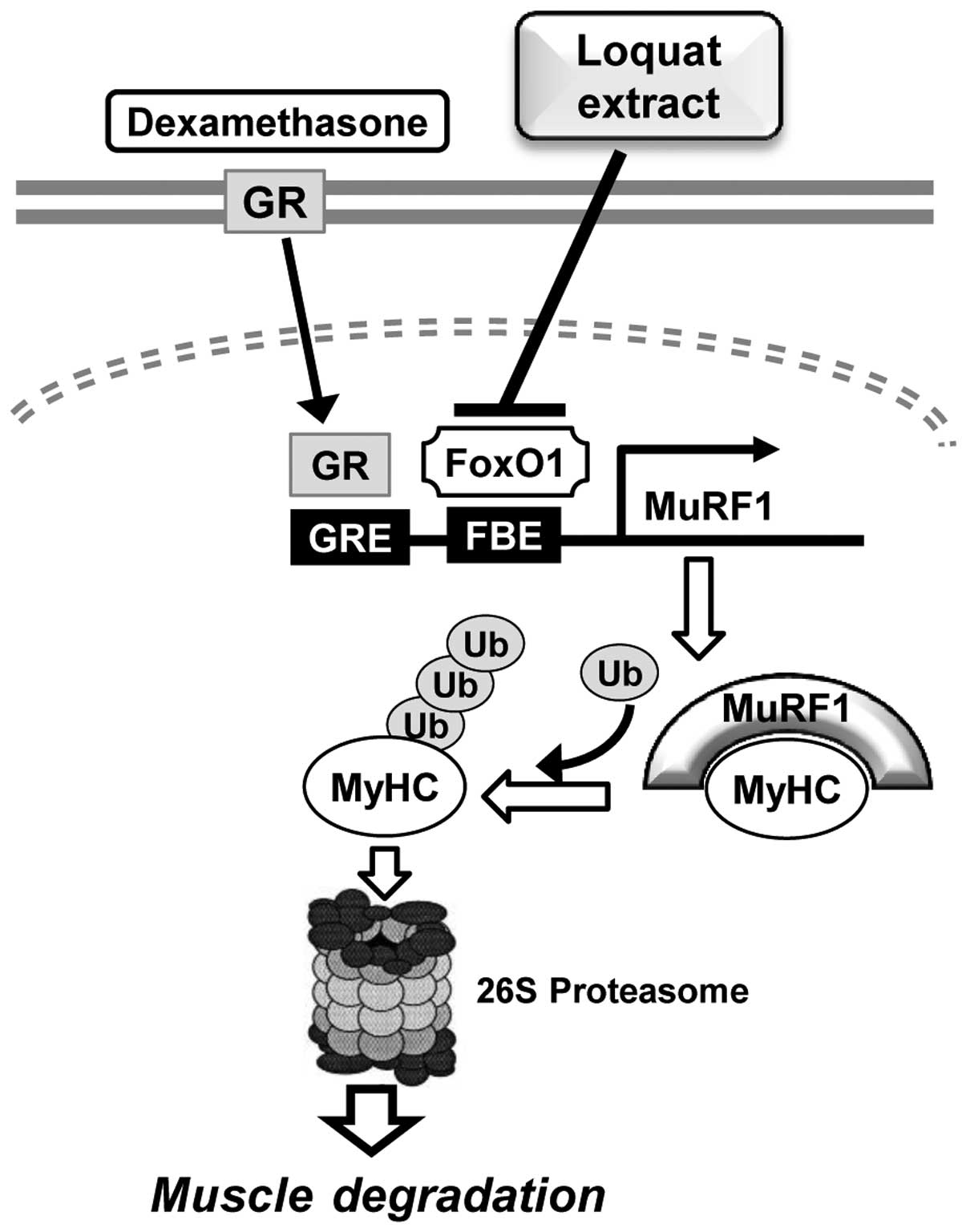
|
1
|
Banno N, Akihisa T, Tokuda H, et al:
Anti-inflammatory and antitumor-promoting effects of the triterpene
acids from the leaves of Eriobotrya japonica. Biol Pharm Bull.
28:1995–1999. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Uto T, Suangkaew N, Morinaga O, Kariyazono
H, Oiso S and Shoyama Y: Eriobotryae folium extract suppresses
LPS-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression by inhibition of NF-kappaB
and MAPK activation in murine macrophages. Am J Chin Med.
38:985–994. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Tommasi N, De Simone F, Pizza C, et al:
Constituents of Eriobotrya japonica. A study of their antiviral
properties. J Nat Prod. 55:1067–1073. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shimizu M, Uemitsu N, Shirota M, Matsumoto
K and Tezuka Y: A new triterpene ester from Eriobotrya japonica.
Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 44:2181–2182. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen Q, Zhang Y, Zhang W and Chen Z:
Identification and quantification of oleanolic acid and ursolic
acid in Chinese herbs by liquid chromatography-ion trap mass
spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr. 25:1381–1388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hsu YL, Kuo PL and Lin CC: Proliferative
inhibition, cell-cycle dysregulation, and induction of apoptosis by
ursolic acid in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Life
Sci. 75:2303–2316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Zhang F, Yang L, et al: Ursolic
acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of cancer cells
in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:4193432011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kunkel SD, Suneja M, Ebert SM, et al: mRNA
expression signatures of human skeletal muscle atrophy identify a
natural compound that increases muscle mass. Cell Metab.
13:627–638. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Palma L, Marinelli M, Pavan M and Orazi
A: Ubiquitin ligases MuRF1 and MAFbx in human skeletal muscle
atrophy. Joint Bone Spine. 75:53–57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Foletta VC, White LJ, Larsen AE, Leger B
and Russell AP: The role and regulation of MAFbx/atrogin-1 and
MuRF1 in skeletal muscle atrophy. Pflugers Arch. 461:325–335. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Witt SH, Granzier H, Witt CC and Labeit S:
MURF-1 and MURF-2 target a specific subset of myofibrillar proteins
redundantly: towards understanding MURF-dependent muscle
ubiquitination. J Mol Biol. 350:713–722. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Clarke BA, Drujan D, Willis MS, et al: The
E3 Ligase MuRF1 degrades myosin heavy chain protein in
dexamethasone-treated skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 6:376–385. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tintignac LA, Lagirand J, Batonnet S,
Sirri V, Leibovitch MP and Leibovitch SA: Degradation of MyoD
mediated by the SCF (MAFbx) ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem.
280:2847–2856. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sandri M, Sandri C, Gilbert A, et al: Foxo
transcription factors induce the atrophy-related ubiquitin ligase
atrogin-1 and cause skeletal muscle atrophy. Cell. 117:399–412.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Waddell DS, Baehr LM, van den Brandt J, et
al: The glucocorticoid receptor and FOXO1 synergistically activate
the skeletal muscle atrophy-associated MuRF1 gene. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 295:E785–E797. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kamei Y, Miura S, Suzuki M, et al:
Skeletal muscle FOXO1 (FKHR) transgenic mice have less skeletal
muscle mass, down-regulated Type I (slow twitch/red muscle) fiber
genes, and impaired glycemic control. J Biol Chem. 279:41114–41123.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jung HA, Park JC, Chung HY, Kim J and Choi
JS: Antioxidant flavonoids and chlorogenic acid from the leaves of
Eriobotrya japonica. Arch Pharm Res. 22:213–218. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Noh KK, Chung KW, Choi YJ, et al:
beta-Hydroxy beta-meth-ylbutyrate improves dexamethasone-induced
muscle atrophy by modulating the muscle degradation pathway in SD
Rat. PLoS One. 9:e1029472014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Magal M, Dumke CL, Urbiztondo ZG, et al:
Relationship between serum creatine kinase activity following
exercise-induced muscle damage and muscle fibre composition. J
Sports Sci. 28:257–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Holecek M: Muscle wasting in animal models
of severe illness. Int J Exp Pathol. 93:157–171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morley JE: Sarcopenia in the elderly. Fam
Pract. 29(Suppl 1): i44–i48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stitt TN, Drujan D, Clarke BA, et al: The
IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway prevents expression of muscle
atrophy-induced ubiquitin ligases by inhibiting FOXO transcription
factors. Mol Cell. 14:395–403. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Romanick M, Thompson LV and Brown-Borg HM:
Murine models of atrophy, cachexia, and sarcopenia in skeletal
muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1832:1410–1420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schakman O, Gilson H and Thissen JP:
Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced myopathy. J Endocrinol.
197:1–10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamamoto D, Maki T, Herningtyas EH, et al:
Branched-chain amino acids protect against dexamethasone-induced
soleus muscle atrophy in rats. Muscle Nerve. 41:819–827. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gehrig SM, van der Poel C, Sayer TA, et
al: Hsp72 preserves muscle function and slows progression of severe
muscular dystrophy. Nature. 484:394–398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Toumi H, Hegge J, Subbotin V, et al: Rapid
intravascular injection into limb skeletal muscle: a damage
assessment study. Mol Ther. 13:229–236. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, et al: Akt
promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead
transcription factor. Cell. 96:857–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kops GJ, de Ruiter ND, De Vries-Smits AM,
Powell DR, Bos JL and Burgering BM: Direct control of the Forkhead
transcription factor AFX by protein kinase B. Nature. 398:630–634.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|