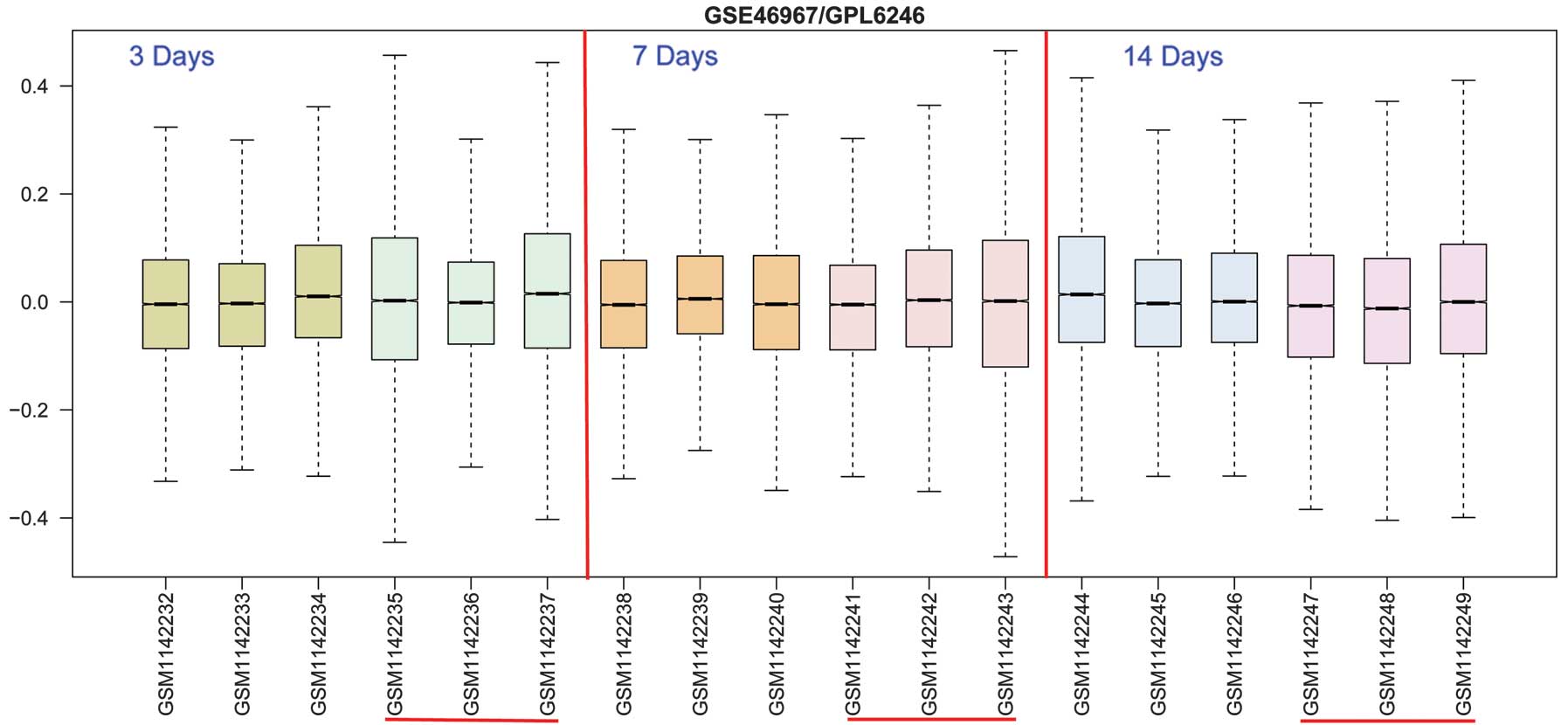
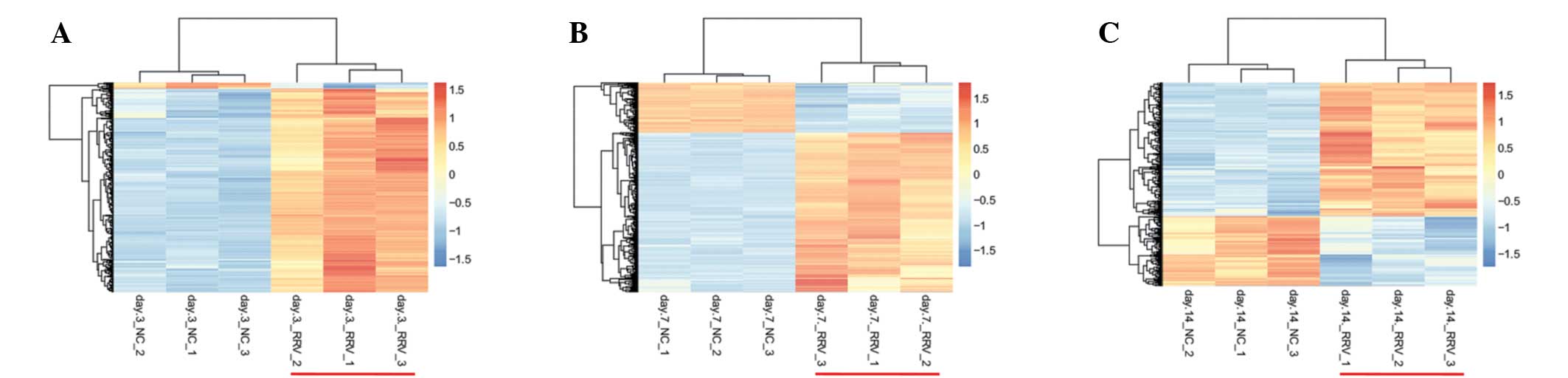
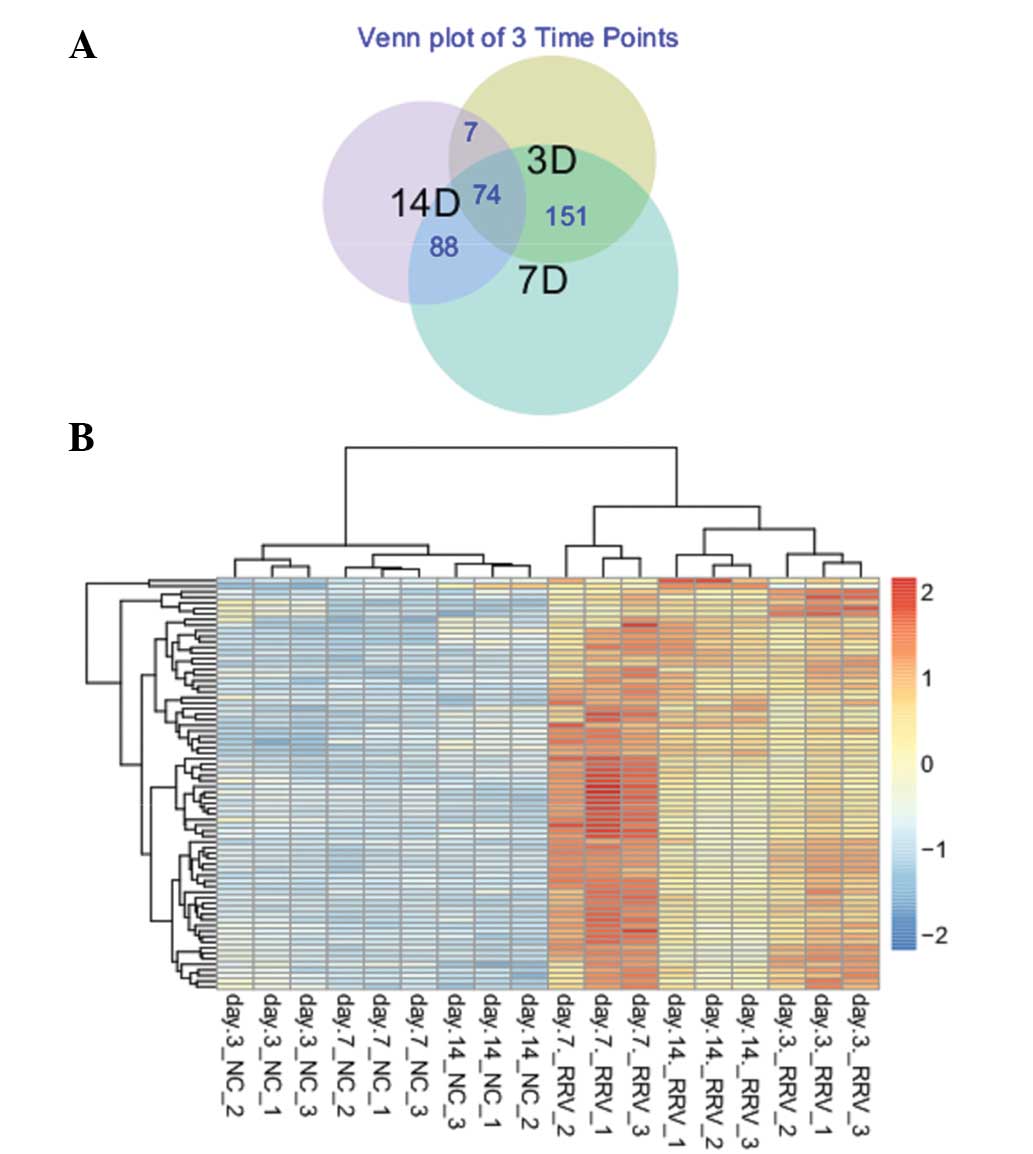
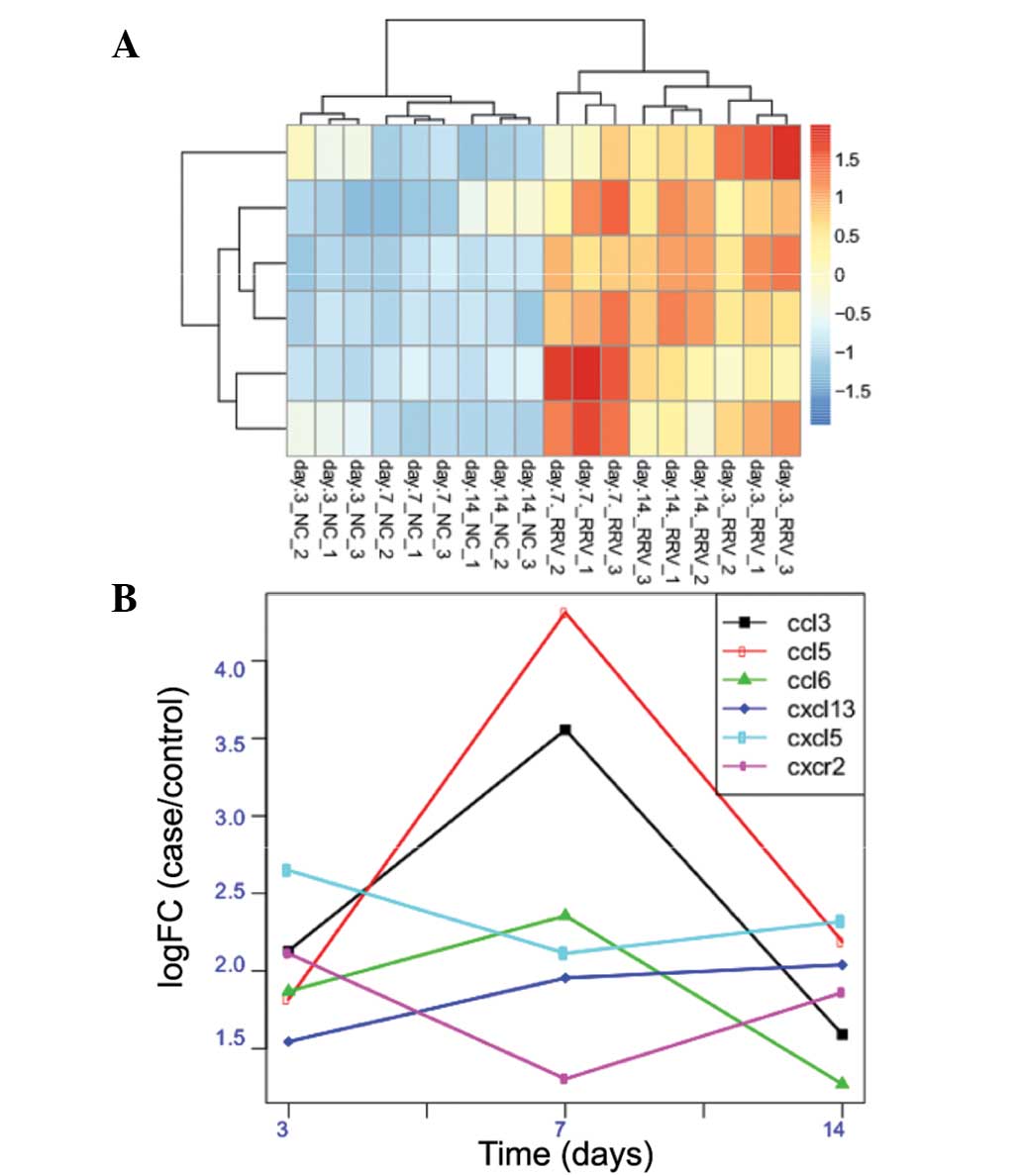
|
1
|
Mack CL, Feldman AG and Sokol RJ: Clues to
the etiology of bile duct injury in biliary atresia. Semin Liver
Dis. 32:307–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Petersen C: Pathogenesis and treatment
opportunities for biliary atresia. Clin Liver Dis. 10:73–88. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jimenez-Rivera C, Jolin-Dahel KS,
Fortinsky KJ, Gozdyra P and Benchimol EI: International incidence
and outcomes of biliary atresia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
56:344–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Davenport M, Ong E, Sharif K, et al:
Biliary atresia in England and Wales: results of centralization and
new benchmark. J Pediatr Surg. 46:1689–1694. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mendoza MM, Chiang JH, Lee SY, et al:
Reappraise the effect of redo-Kasai for recurrent jaundice
following Kasai operation for biliary atresia in the era of liver
transplantation. Pediatr Surg Int. 28:861–864. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bijl EJ, Bharwani KD, Houwen RH and de Man
RA: The long-term outcome of the Kasai operation in patients with
biliary atresia: a systematic review. Neth J Med. 71:170–173.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cronin DC, Squires J, Squires R,
Mazariegos G and Lantos JD: Parental refusal of a liver transplant
for a child with biliary atresia. Pediatrics. 131:141–146. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shimadera S, Iwai N, Deguchi E, Kimura O,
Fumino S and Yokoyama T: The inv mouse as an experimental model of
biliary atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 42:1555–1560. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mack CL, Falta MT, Sullivan AK, et al:
Oligoclonal expansions of CD4+ and CD8+
T-cells in the target organ of patients with biliary atresia.
Gastroenterology. 133:278–287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
de Carvalho E, Ivantes CA and Bezerra JA:
Extrahepatic biliary atresia: current concepts and future
directions. J Pediatr (Rio J). 83:105–120. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Soomro GB, Abbas Z, Hassan M, Luck N,
Memon Y and Khan AW: Is there any association of extra hepatic
biliary atresia with cytomegalovirus or other infections. J Pak Med
Assoc. 61:281–283. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mahjoub F, Shahsiah R, Ardalan FA, et al:
Detection of Epstein Barr virus by chromogenic in situ
hybridization in cases of extra-hepatic biliary atresia. Diagn
Pathol. 3:192008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schaffer K, Hassan J, Staines A, et al:
Surveillance of Epstein-Barr virus loads in adult liver
transplantation: associations with age, sex, posttransplant times,
and transplant indications. Liver Transpl. 17:1420–1426. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Whitington PF, Malladi P, Melin-Aldana H,
Azzam R, Mack CL and Sahai A: Expression of osteopontin correlates
with portal biliary proliferation and fibrosis in biliary atresia.
Pediatr Res. 57:837–844. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mack CL: The pathogenesis of biliary
atresia: evidence for a virus-induced autoimmune disease. Semin
Liver Dis. 27:233–242. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leonhardt J, Stanulla M, Von Wasielewski
R, et al: Gene expression profile of the infective murine model for
biliary atresia. Pediatr Surg Int. 22:84–89. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Schreiber RA and Kleinman RE: Biliary
atresia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 35(Suppl 1): S11–S16. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mack CL, Tucker RM, Sokol RJ, et al:
Biliary atresia is associated with CD4+ Th1
cell-mediated portal tract inflammation. Pediatr Res. 56:79–87.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lages CS, Simmons J, Chougnet CA and
Miethke AG: Regulatory T cells control the CD8 adaptive immune
response at the time of ductal obstruction in experimental biliary
atresia. Hepatology. 56:219–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bezerra JA, Tiao G, Ryckman FC, et al:
Genetic induction of proinflammatory immunity in children with
biliary atresia. Lancet. 360:1653–1659. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakamura K and Tanoue A: Etiology of
biliary atresia as a developmental anomaly: recent advances. J
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 20:459–464. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hirschfield GM, Liu X, Xu C, et al:
Primary biliary cirrhosis associated with HLA, IL12A, and IL12RB2
variants. N Engl J Med. 360:2544–2555. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barrett T, Troup DB, Wilhite SE, et al:
NCBI GEO: mining tens of millions of expression profiles - database
and tools update. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:D760–D765. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fujita A, Sato JR, Rodrigues Lde O,
Ferreira CE and Sogayar MC: Evaluating different methods of
microarray data normalization. BMC bioinformatics. 7:4692006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Anders S, McCarthy DJ, Chen Y, et al:
Count-based differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data
using R and Bioconductor. Nat Protoc. 8:1765–1786. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol. 57:289–300.
1995.
|
|
27
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: Fast R
functions for robust correlations and hierarchical clustering. J
Stat Softw. 46:112012.
|
|
28
|
Mukherjee S, Chen Z and Gangopadhyay A: A
privacy-preserving technique for Euclidean distance-based mining
algorithms using Fourier-related transforms. VLDB J. 15:293–315.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pirooznia M, Nagarajan V and Deng Y:
GeneVenn - A web application for comparing gene lists using Venn
diagrams. Bioinformation. 1:420–422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hulsegge I, Kommadath A and Smits MA:
Globaltest and GOEAST: two different approaches for Gene Ontology
analysis. BMC Proc. 3(Suppl 4): S102009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mack CL, Tucker RM, Sokol RJ and Kotzin
BL: Armed CD4+ Th1 effector cells and activated
macrophages participate in bile duct injury in murine biliary
atresia. Clin Immunol. 115:200–209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in health and
disease. Nat Med. 9:653–660. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ramos CDL, Canetti C, Souto JT, et al:
MIP-alpha[CCL3] acting on the CCR1 receptor mediates neutrophil
migration in immune inflammation via sequential release of
TNF-alpha and LTB4. J Leukoc Biol. 78:167–177. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ekman AK, Fransson M, Rydberg C, Adner M
and Cardell LO: Nasal challenge with LPS stimulates the release of
macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha. Int Arch Allergy Immunol.
149:154–160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Gwak GY, et al: CCR1
and CCR5 promote hepatic fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest.
119:1858–1870. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zerfaoui M, Naura AS, Errami Y, et al:
Effects of PARP-1 deficiency on airway inflammatory cell
recruitment in response to LPS or TNF: differential effects on
CXCR2 ligands and Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines. J Leukoc
Biol. 86:1385–1392. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hirano Y, Hirano F, Fujii H and Makino I:
Fibrates suppress chenodeoxycholic acid-induced RANTES expression
through inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. Eur J Pharmacol.
448:19–26. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yamamoto S, Shimizu S, Kiyonaka S, et al:
TRPM2-mediated Ca2+ influx induces chemokine production
in monocytes that aggravates inflammatory neutrophil infiltration.
Nat Med. 14:738–747. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schlecker E, Stojanovic A, Eisen C, et al:
Tumor-infiltrating monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells
mediate CCR5-dependent recruitment of regulatory T cells favoring
tumor growth. J Immunol. 189:5602–5611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Robertson MJ: Role of chemokines in the
biology of natural killer cells. J Leukoc Biol. 71:173–183.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Murphy PM and Tiffany HL: Cloning of
complementary DNA encoding a functional human interleukin-8
receptor. Science. 253:1280–1283. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Stillie R, Farooq SM, Gordon JR and
Stadnyk AW: The functional significance behind expressing two IL-8
receptor types on PMN. J Leukoc Biol. 86:529–543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Okabe H, Beppu T, Ueda M, et al:
Identification of CXCL5/ENA-78 as a factor involved in the
interaction between cholangiocarcinoma cells and cancer-associated
fibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 131:2234–2241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li A, King J, Moro A, et al:
Overexpression of CXCL5 is associated with poor survival in
patients with pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol. 178:1340–1349. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
van de Pavert SA, Olivier BJ, Goverse G,
et al: Chemokine CXCL13 is essential for lymph node initiation and
is induced by retinoic acid and neuronal stimulation. Nat Immunol.
10:1193–1199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shivakumar P, Campbell KM, Sabla GE, et
al: Obstruction of extrahepatic bile ducts by lymphocytes is
regulated by IFN-γ in experimental biliary atresia. J Clin Invest.
114:322–329. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ansel KM, Harris RB and Cyster JG: CXCL13
is required for B1 cell homing, natural antibody production, and
body cavity immunity. Immunity. 16:67–76. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hjelmström P, Fjell J, Nakagawa T, Sacca
R, Cuff CA and Ruddle NH: Lymphoid tissue homing chemokines are
expressed in chronic inflammation. Am J Pathol. 156:1133–1138.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|