Spandidos Publications style
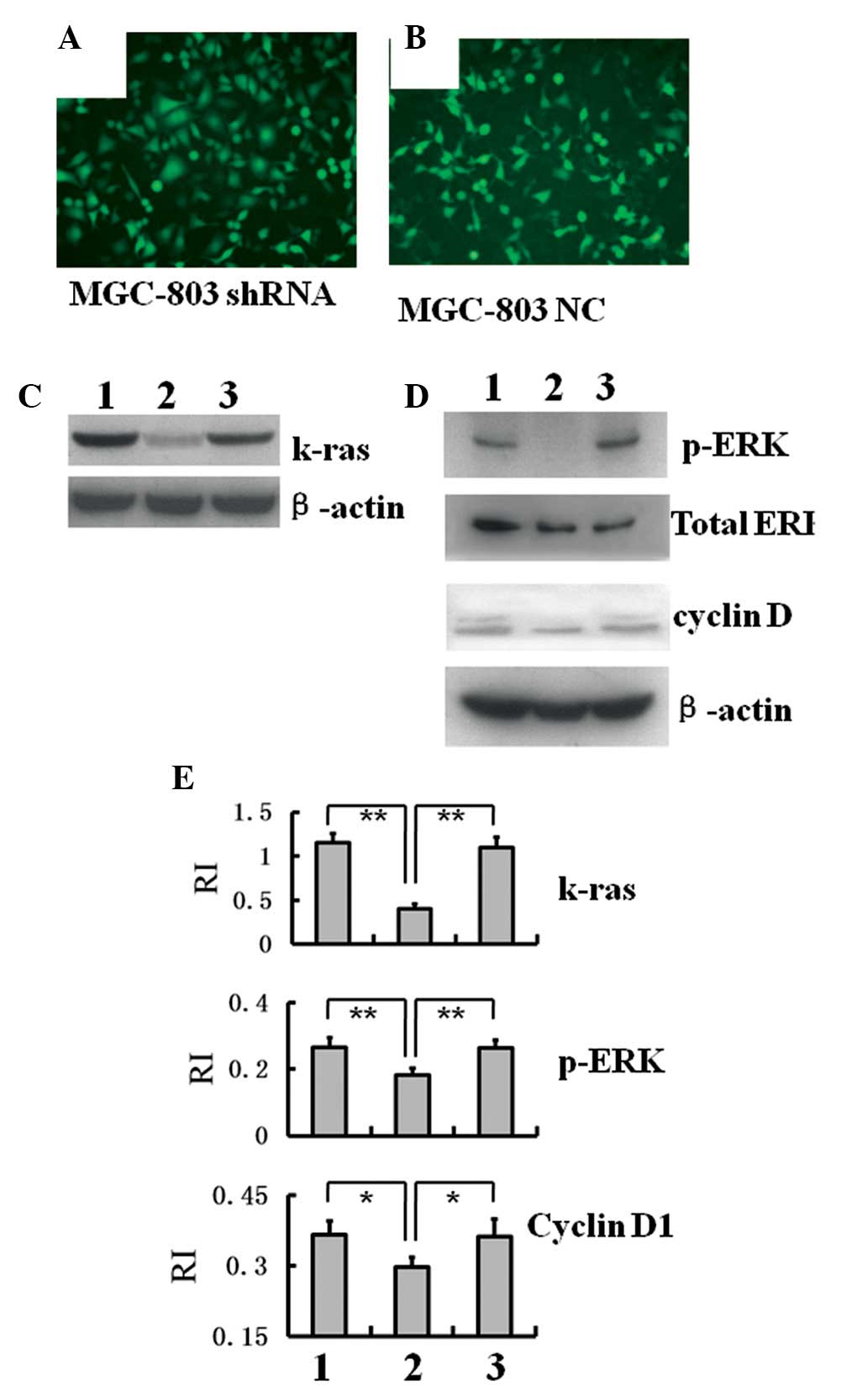
Hu J, Cheng T, Zhang L, Sun B, Deng L and Xu H: Anti-tumor peptide AP25 decreases cyclin D1 expression and inhibits MGC-803 proliferation via phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase-, Src-, c-Jun N-terminal kinase- and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-associated pathways. Mol Med Rep 12: 4396-4402, 2015.
APA
Hu, J., Cheng, T., Zhang, L., Sun, B., Deng, L., & Xu, H. (2015). Anti-tumor peptide AP25 decreases cyclin D1 expression and inhibits MGC-803 proliferation via phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase-, Src-, c-Jun N-terminal kinase- and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-associated pathways. Molecular Medicine Reports, 12, 4396-4402. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3912
MLA
Hu, J., Cheng, T., Zhang, L., Sun, B., Deng, L., Xu, H."Anti-tumor peptide AP25 decreases cyclin D1 expression and inhibits MGC-803 proliferation via phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase-, Src-, c-Jun N-terminal kinase- and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-associated pathways". Molecular Medicine Reports 12.3 (2015): 4396-4402.
Chicago
Hu, J., Cheng, T., Zhang, L., Sun, B., Deng, L., Xu, H."Anti-tumor peptide AP25 decreases cyclin D1 expression and inhibits MGC-803 proliferation via phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase-, Src-, c-Jun N-terminal kinase- and phosphoinositide 3-kinase-associated pathways". Molecular Medicine Reports 12, no. 3 (2015): 4396-4402. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3912