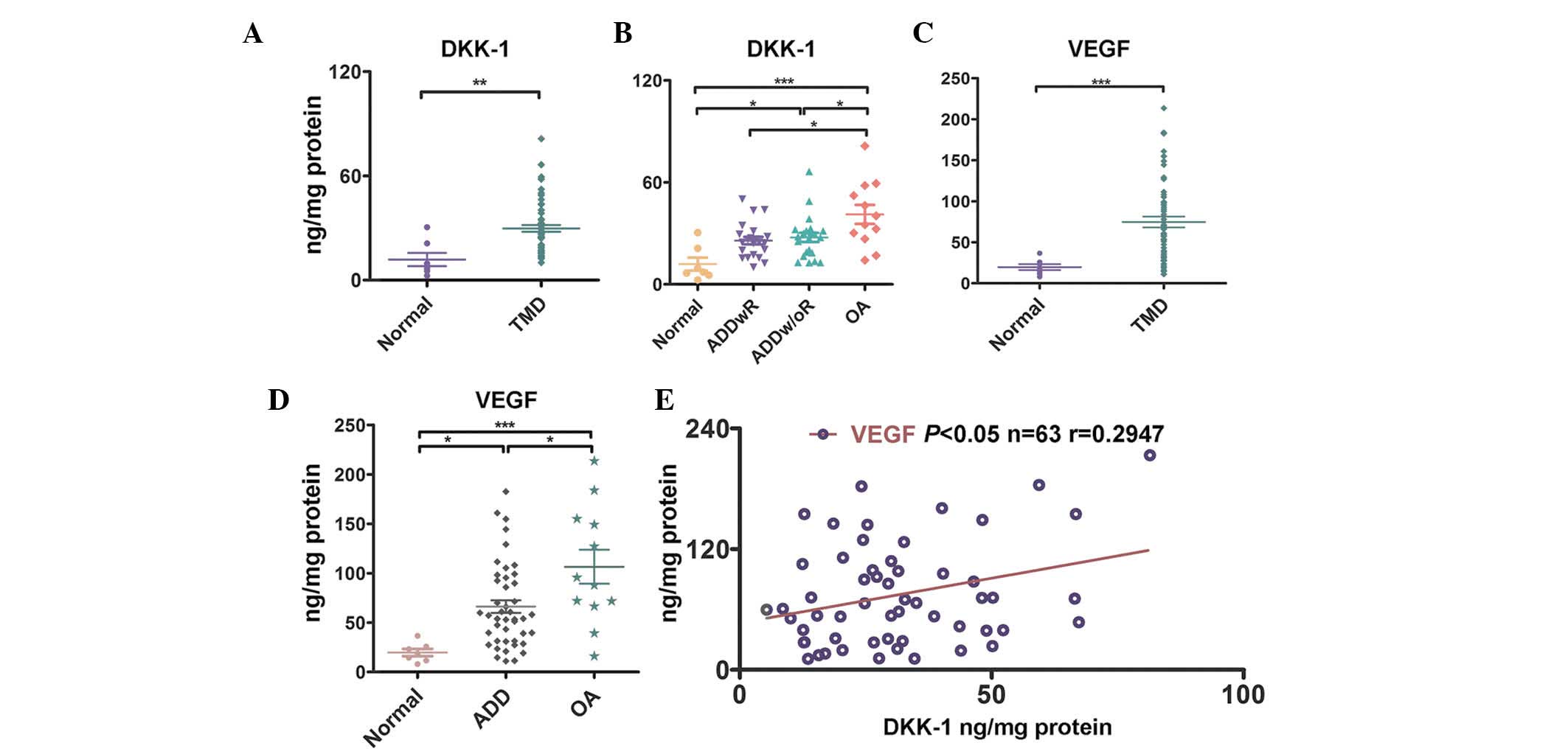
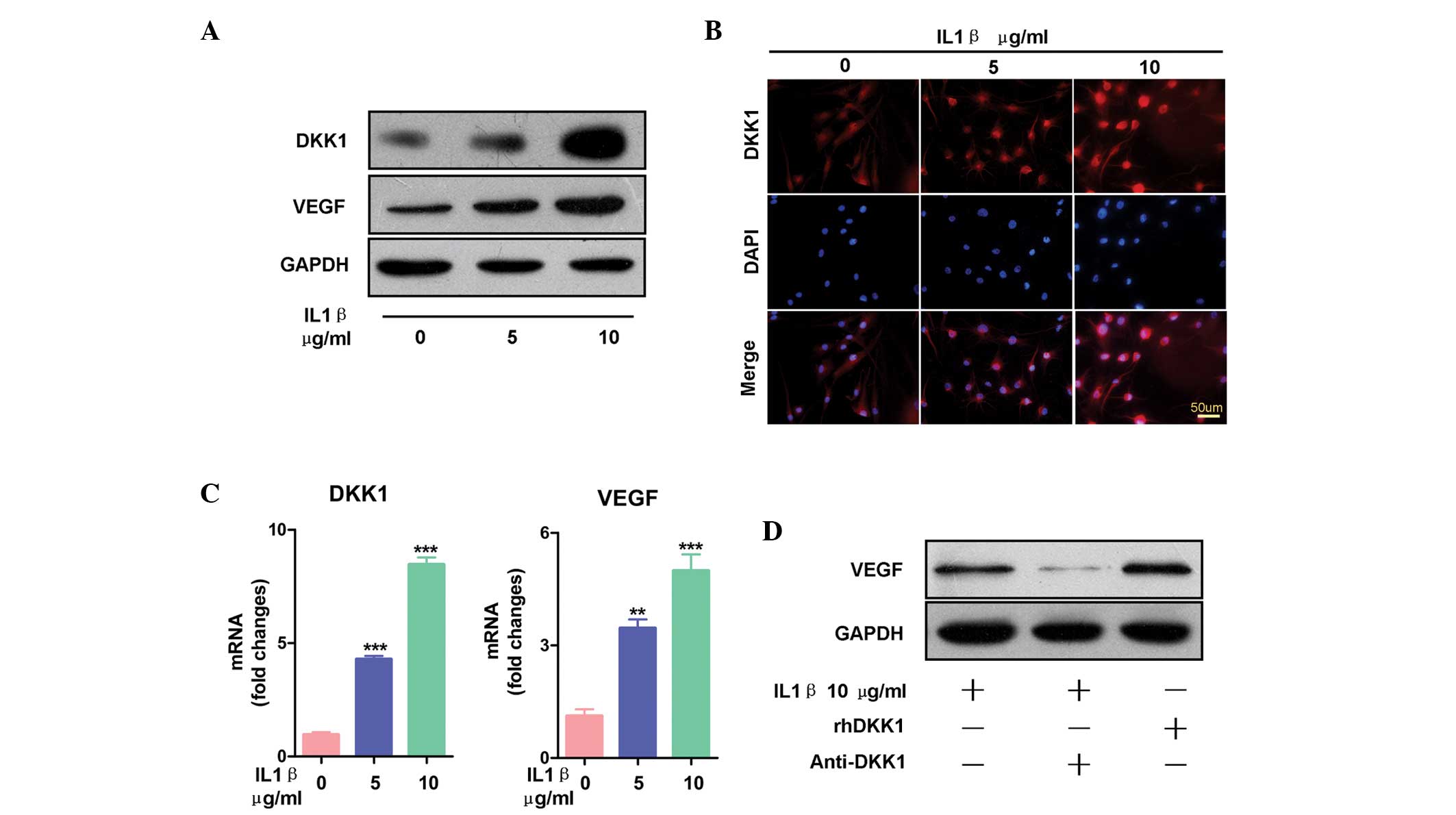
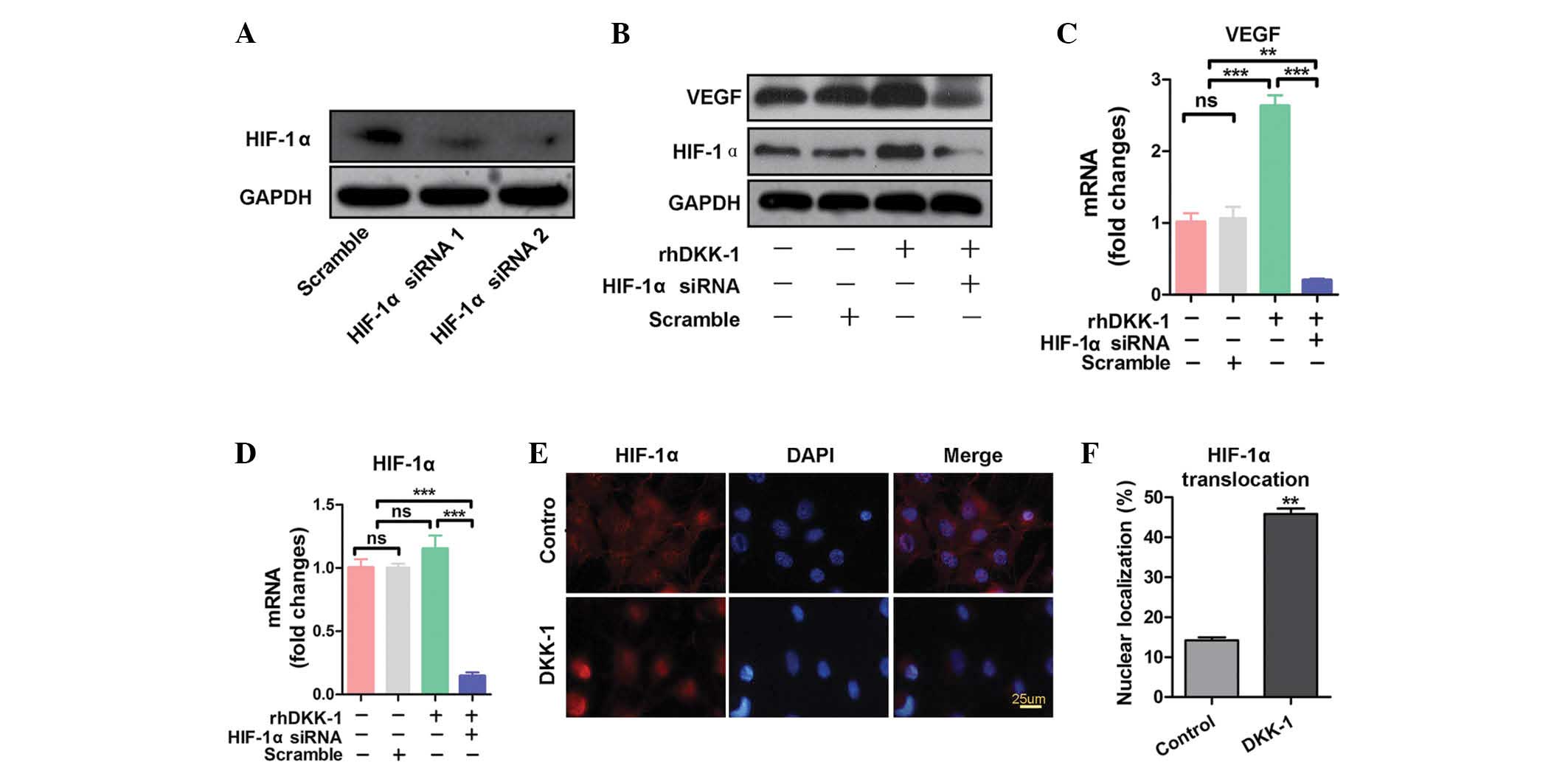
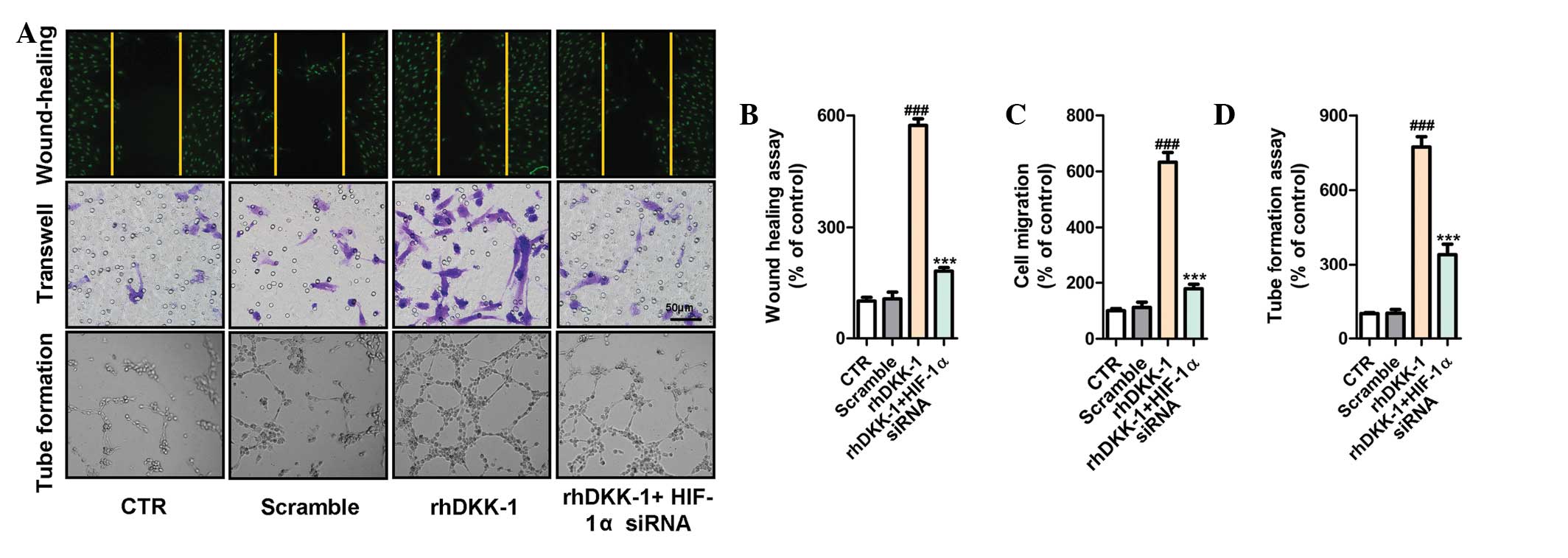
|
1
|
Aliko A, Ciancaglini R, Alushi A, Tafaj A
and Ruci D: Temporomandibular joint involvement in rheumatoid
arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis. Int
J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 40:704–709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Boer EW, Dijkstra PU, Stegenga B, de
Bont LG and Spijkervet FK: Value of cone-beam computed tomography
in the process of diagnosis and management of disorders of the
temporomandibular joint. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 52:241–246.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Satoh K, Ogura N, Akutsu M, Kuboyama N,
Kuyama K, Yamamoto H and Kondoh T: Expression of cyclooxygenase-1
and -2 in IL-1beta-induced synovitis of the temporomandibular
joint. J Oral Pathol Med. 38:584–590. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Varol A, Basa S, Topsakal A and Akpinar I:
Assessment of synovial vascularization by power Doppler
ultrasonography in TMJ internal derangements treated
arthroscopically. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 46:625–630. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Camejo Fde A, Almeida LE, Doetzer AD,
Caporal KS, Ambros V, Azevedo M, Alanis LR, Olandoski M, Noronha L
and Trevilatto PC: FasL expression in articular discs of human
temporomandibular joint and association with osteoarthrosis. J Oral
Pathol Med. 43:69–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sato J, Segami N, Nishimura M, Yoshimura
H, Demura N, Yoshitake Y and Nishikawa K: Correlation between the
arthroscopic diagnosis of synovitis and microvessel density in
synovial tissues in patients with internal derangement of the
temporomandibular joint. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 31:101–106. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dejana E and Lampugnani MG: Differential
adhesion drives angiogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 16:305–306. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ke J, Liu Y, Long X, Li J, Fang W, Meng Q
and Zhang Y: Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in
synovial fibroblasts from human temporomandibular joint by hypoxia.
J Oral Pathol Med. 36:290–296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song J, Cao L and Li Y: RNA
interference-mediated inhibition of survivin and VEGF in pancreatic
cancer cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 7:1651–1655. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao W, Sweeney C, Connolly M, Kennedy A,
Ng CT, McCormick J, Veale DJ and Fearon U: Notch-1 mediates
hypoxia-induced angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis
Rheum. 64:2104–2113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao HY, Wang GP, Huang SH, Li Y, Cai SW,
Zhang J, Chen HG and Wu WB: HIF-1α silencing suppresses growth of
lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells through induction of apoptosis. Mol
Med Rep. 9:911–915. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
She Q, Xia S, Deng SB, Du JL, Li YQ, He L,
Xiao J and Xiang YL: Angiogenesis in a rat model following
myocardial infarction induced by hypoxic regulation of
VEGF165 gene-transfected EPCs. Mol Med Rep. 6:1281–1287.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Park H, Jung HY, Choi HJ, Kim DY, Yoo JY,
Yun CO, Min JK, Kim YM and Kwon YG: Distinct roles of DKK1 and DKK2
in tumor angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 17:221–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Weng LH, Ko JY, Wang CJ, Sun YC and Wang
FS: Dkk-1 promotes angiogenic responses and cartilage matrix
proteinase secretion in synovial fibroblasts from osteoarthritic
joints. Arthritis Rheum. 64:3267–3277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang H, Yu C, Dai J, Keller JM, Hua A,
Sottnik JL, Shelley G, Hall CL, Park SI, Yao Z, et al: Parathyroid
hormone-related protein inhibits DKK-1 expression through
c-Jun-mediated inhibition of β-catenin activation of the DKK-1
promoter in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 33:2464–2477. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Smadja DM, d'Audigier C, Weiswald LB,
Badoual C, Dangles-Marie V, Mauge L, Evrard S, Laurendeau I,
Lallemand F, Germain S, et al: The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1
increases endothelial progenitor cell angiogenic potential.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:2544–2552. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dworkin SF and LeResche L: Research
diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders: Review,
criteria, examinations and specifications, critique. J Craniomandib
Disord. 6:301–355. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kostrzewa-Janicka J, Jurkowski P,
Nedzi-Gora M and Mierzwinska-Nastalska E: Inflammatory markers in
temporoman-dibular joint disorders. Cent Eur J Immunol. 37:290–293.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cai HX, Luo JM, Long X, Li XD and Cheng Y:
Free-radical oxidation and superoxide dismutase activity in
synovial fluid of patients with temporomandibular disorders. J
Orofac Pain. 20:53–58. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Long X, Ke J, Meng QG, Lee WC,
Doocey JM and Zhu F: Regulation of HAS expression in human synovial
lining cells of TMJ by IL-1beta. Arch Oral Biol. 53:60–65. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Sun ZJ, Bian Y and Kulkarni AB:
MicroRNA-135b acts as a tumor promoter by targeting the
hypoxia-inducible factor pathway in genetically defined mouse model
of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 331:230–238.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu Y, Zhu L, Liu L, Zhang J and Peng B:
Interleukin-17A stimulates migration of periodontal ligament
fibroblasts via p38 MAPK/NF-κB-dependent MMP-1 expression. J Cell
Physiol. 229:292–299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Akutsu M, Ogura N, Ito K, Kawashima M,
Kishida T and Kondoh T: Effects of interleukin-1β and tumor
necrosis factor-α on macrophage inflammatory protein-3α production
in synovial fibroblast-like cells from human temporomandibular
joints. J Oral Pathol Med. 42:491–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Choi HJ, Park H, Lee HW and Kwon YG: The
Wnt pathway and the roles for its antagonists, DKKS, in
angiogenesis. IUBMB Life. 64:724–731. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Min JK, Park H, Choi HJ, Kim Y, Pyun BJ,
Agrawal V, Song BW, Jeon J, Maeng YS, Rho SS, et al: The WNT
antagonist Dickkopf2 promotes angiogenesis in rodent and human
endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 121:1882–1893. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jung IL, Kang HJ, Kim KC and Kim IG:
Knockdown of the Dickkopf 3 gene induces apoptosis in a lung
adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 26:33–38. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
D'Amelio P, Roato I, Oderda M, Soria F,
Zitella A, Ferracini R, Mengozzi G, Gontero P and Isaia GC: DKK-1
in prostate cancer diagnosis and follow up. BMC Clin Pathol.
14:112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kumagai K, Hamada Y, Holmlund AB, Gotoh A,
Nakaoka K, Arai G, Yamane S and Suzuki R: The levels of vascular
endothelial growth factor in the synovial fluid correlated with the
severity of arthroscopically observed synovitis and clinical
outcome after temporomandibular joint irrigation in patients with
chronic closed lock. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol
Endod. 109:185–190. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Trisciuoglio D, Gabellini C, Desideri M,
Ragazzoni Y, De Luca T, Ziparo E and Del Bufalo D: Involvement of
BH4 domain of bcl-2 in the regulation of HIF-1-mediated VEGF
expression in hypoxic tumor cells. Cell Death Differ. 18:1024–1035.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vadlapatla RK, Vadlapudi AD, Pal D,
Mukherji M and Mitra AK: Ritonavir inhibits HIF-1α-mediated VEGF
expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Eye
(Lond). 28:93–101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang L, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Ren J, Zhang R,
Zeng H, Li Q and Wu G: Inhibitory action of Celastrol on
hypoxia-mediated angiogenesis and metastasis via the HIF-1α
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 27:407–415. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aicher A, Kollet O, Heeschen C, Liebner S,
Urbich C, Ihling C, Orlandi A, Lapidot T, Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S:
The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 mobilizes vasculogenic progenitor
cells via activation of the bone marrow endosteal stem cell niche.
Circ Res. 103:796–803. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|