|
1
|
Peng P, Zhu L, Lang J, Wang WY and Shi HH:
Unilateral sacrospinous ligament fixation for treatment of genital
prolapse. Chin Med J (Engl). 123:19952010.
|
|
2
|
Jelovsek JE, Maher C and Barber MD: Pelvic
organ prolapse. Lancet. 369:1027–1038. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wondrak GT, Roberts MJ, Jacobson MK and
Jacobson EL: 3-hydroxypyridine chromophores are endogenous
sensitizers of photooxidative stress in human skin cells. J Biol
Chem. 279:30009–30020. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mizutari K, Ono T, Ikeda K, Kayashima K
and Horiuchi S: Photo-enhanced modification of human skin elastin
in actinic elastosis by N(epsilon)-(carboxymethyl) lysine, one of
the glycoxidation products of the maillard reaction. J Invest
Dermatol. 108:797–802. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu D and Kassab GS: Role of shear stress
and stretch in vascular mechanobiology. J Roy Soc Interface.
8:1379–1385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tan JL: Cell proliferation,
differentiation, apoptosis under a serial stretches and the
underlying mechanisms. PhD dissertation. The Fourth Military
Medical University; Xi'an: 2010
|
|
7
|
Choy KW, Liu YM, Chu CY, Wang CC, Lui WT,
Lee LL, Pang MW, Rogers MS and Yip SK: High isoprostane level in
cardinal ligament-derived fibroblasts and urine sample of women
with uterine prolapse. BJOG. 115:1179–1183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Visco AG and Yuan L: Differential gene
expression in pubococ-cygeus muscle from patients with pelvic organ
prolapse. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 189:102–112. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Makpol S, Azura Jam F, Anum Mohd Yusof Y
and Zurinah Wan Ngah W: Modulation of collagen synthesis and its
gene expression in human skin fibroblasts by tocotrienol-rich
fraction. Arch Med Sci. 7:889–895. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim E J, Chung N, Park SH, Lee KH, Kim SW,
Kim JY, Bai SW and Jeon MJ: Involvement of oxidative stress and
mitochondrial apoptosis in the pathogenesis of pelvic organ
prolapse. J Urol. 189:588–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wen Y, Ho JY, Polan ML and Chen B:
Expression of apoptotic factors in vaginal tissues from women with
urogenital prolapse. Neurourol and Urodynam. 30:1627–1632. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
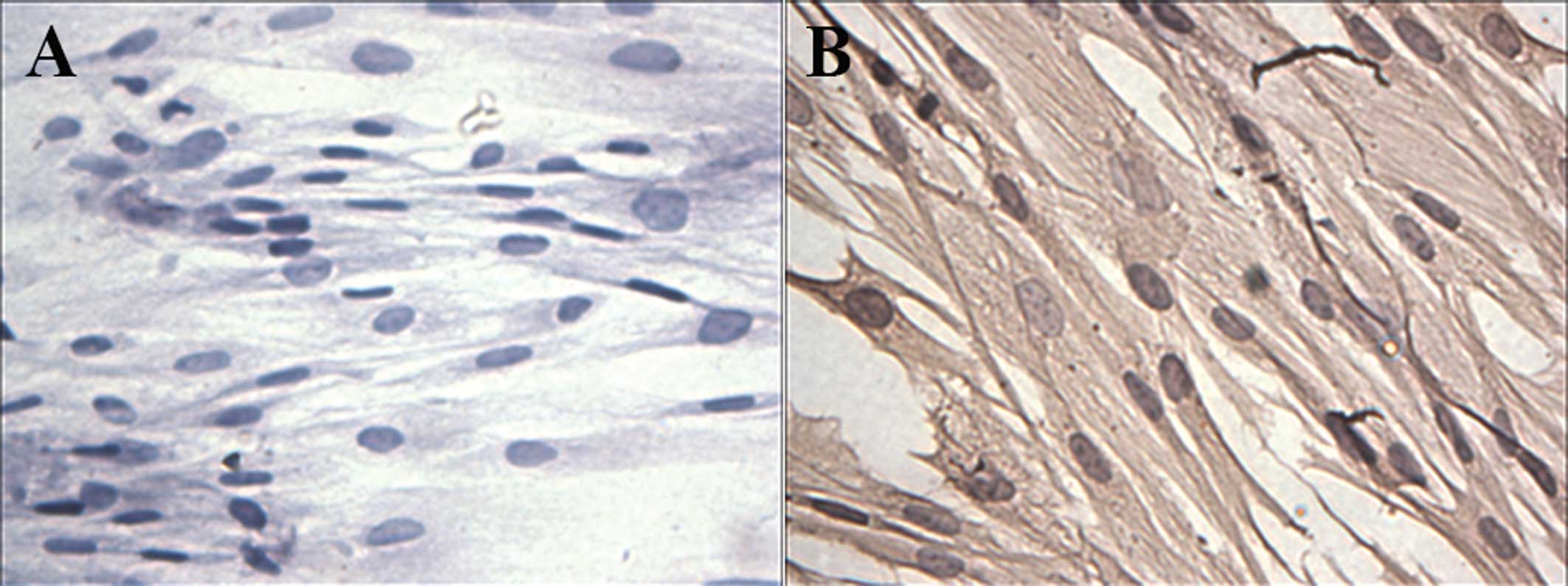
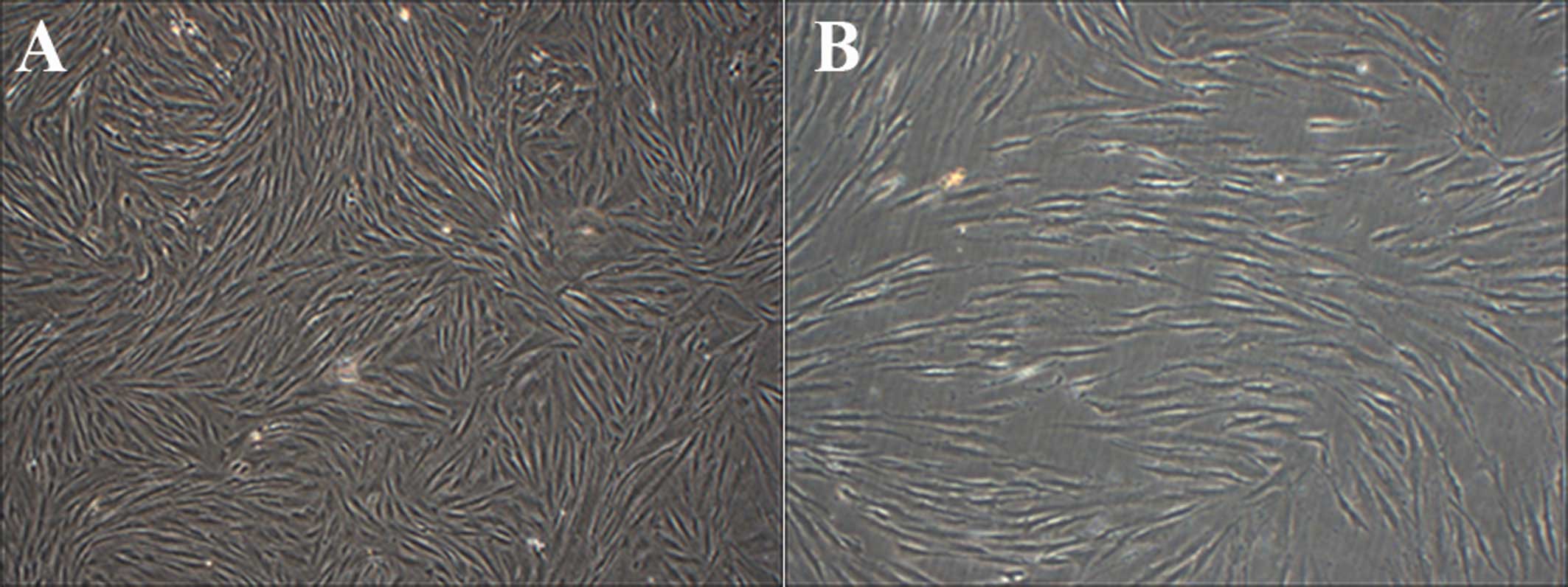
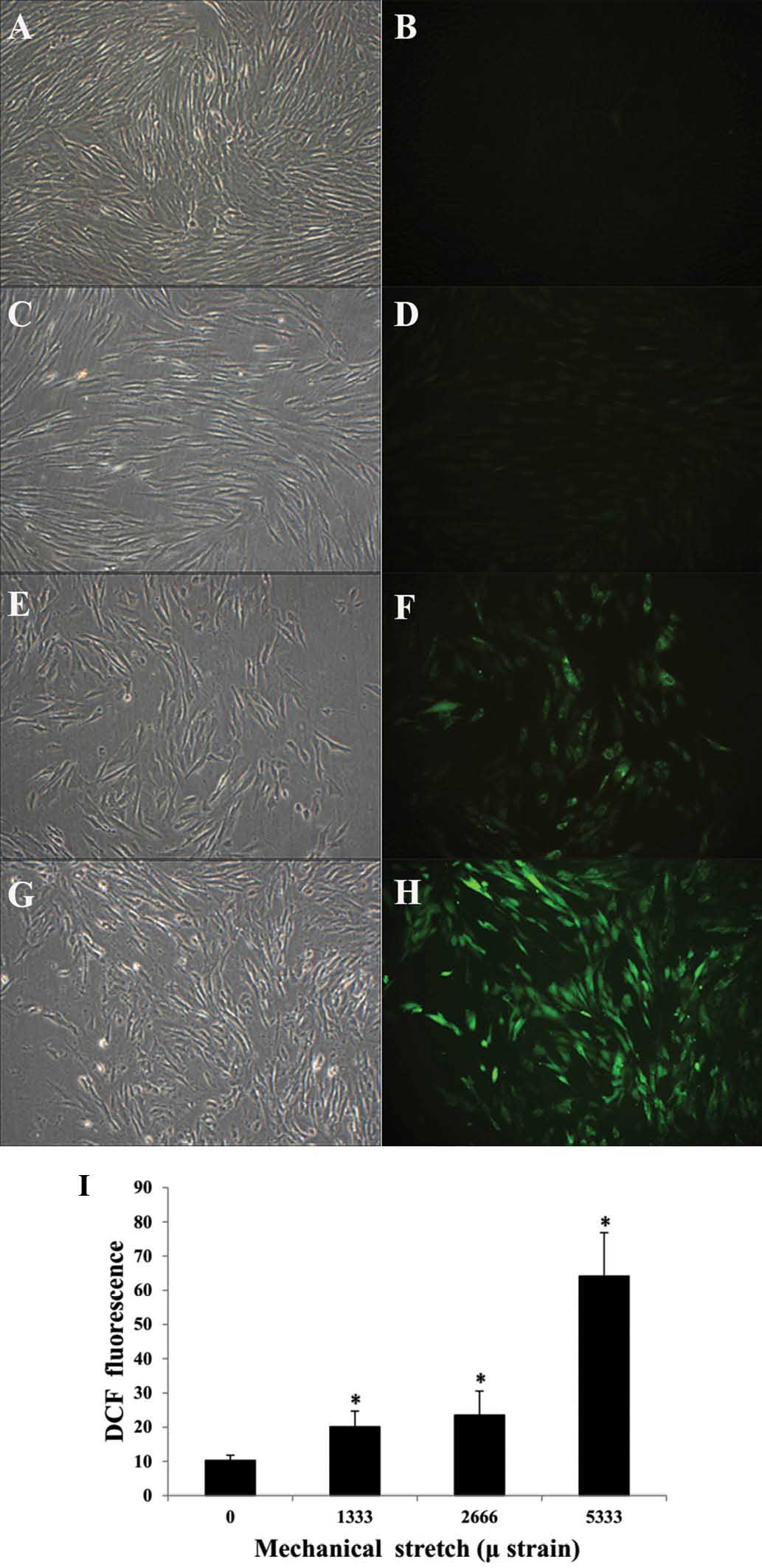
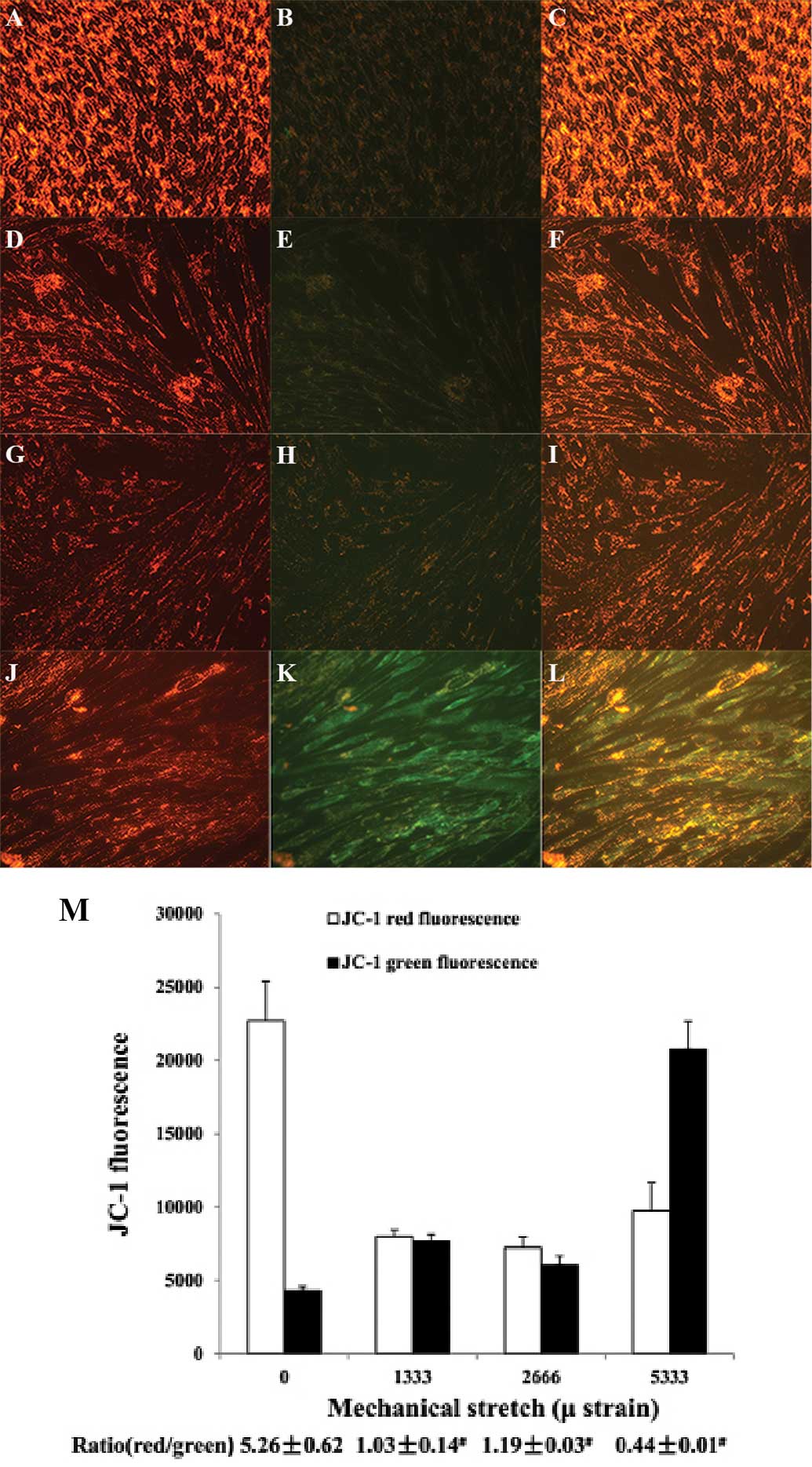
Bao R, Liu X and Zhou J: Primary culture
and identification of human fibroblasts. J XinX Med Coll.
5:0152011.In Chinese.
|
|
13
|
Chow D and Rodríguez LV: Epidemiology and
prevalence of pelvic organ prolapse. Curr Opin Urol. 23:293–298.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jean-Charles C, Rubod C, Brieu M,
Boukerrou M, Fasel J and Cosson M: Biomechanical properties of
prolapsed or non-prolapsed vaginal tissue: impact on genital
prolapse surgery. Int Urogynecol J. 21:1535–1538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lang JH and Zhang XD: Obstetrics and
Gynecology Clinical Anatomy. 2010 edition. Shandong Science and
Technology Press; Jinan: pp. 692010
|
|
16
|
Ewies AA, Elshafie M, Li J, Stanley A,
Thompson J, Styles J, White I and Al-Azzawi F: Changes in
transcription profile and cytoskeleton morphology in pelvic
ligament fibroblasts in response to stretch: The effects of
estradiol and levormeloxifene. Mol Human Reprod. 14:127–135. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li XN: Study on the methods and platform
of image processing for cellular biomechanical experiments. PhD
dissertation. Sichuan University; Chengdu: 2003
|
|
18
|
Fransen M, Nordgren M, Wang B and
Apanasets O: Role of peroxisomes in ROS/RNS-metabolism:
Implications for human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1822:1363–1373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Grote K, Flach I, Luchtefeld M, Akin E,
Holland SM, Drexler H and Schieffer B: Mechanical stretch enhances
mRNA expression and proenzyme release of matrix metalloproteinase-2
(MMP-2) via NAD (P) H oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Circ
Res. 92:e80–e86. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB and Sil PC:
Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and
mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol.
87:1157–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Teshima Y, Takahashi N, Thuc LC, Nishio S,
Nagano-Torigoe Y, Miyazaki H, Ezaki K, Yufu K, Hara M, Nakagawa M
and Saikawa T: High-glucose condition reduces cardioprotective
effects of insulin against mechanical stress-induced cell injury.
Life Sci. 87:154–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choudhary R, Baker KM and Pan J: All-trans
retinoic acid prevents angiotensin II- and mechanical
stretch-induced reactive oxygen species generation and
cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 215:172–181. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Meyer T, Meyer U, Stratmann U, Wiesmann HP
and Joos U: Identification of apoptotic cell death in distraction
osteogenesis. Cell Biol Int. 23:439–446. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ning QM and Qang XR: Early apoptosis
induced by mechanical stretch in human alveolar typeIIepithelial
cells. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Medical Science
Edition). 27:961–964. 2007.
|
|
25
|
Li H, Zhang XY, Wu TJ, Cheng W, Liu X,
Jiang TT, Wen J, Li J, Ma QL and Hua ZC: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress regulates rat mandibular cartilage thinning under
compressive mechanical stress. J Biol Chem. 288:18172–18183. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ding F, Shao ZW, Yang SH, Wu Q, Gao F and
Xiong LM: Role of mitochondrial pathway in compression-induced
apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. Apoptosis. 17:579–590. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miao YL, Hu CH, Wang JL, et al: The
preliminary study on biomechanical properties of posterior vaginal
wall tissue of the patient with rectocele. Chinese J Clin Obstet
Gynecol. 9:180–183. 2008.In Chinese.
|