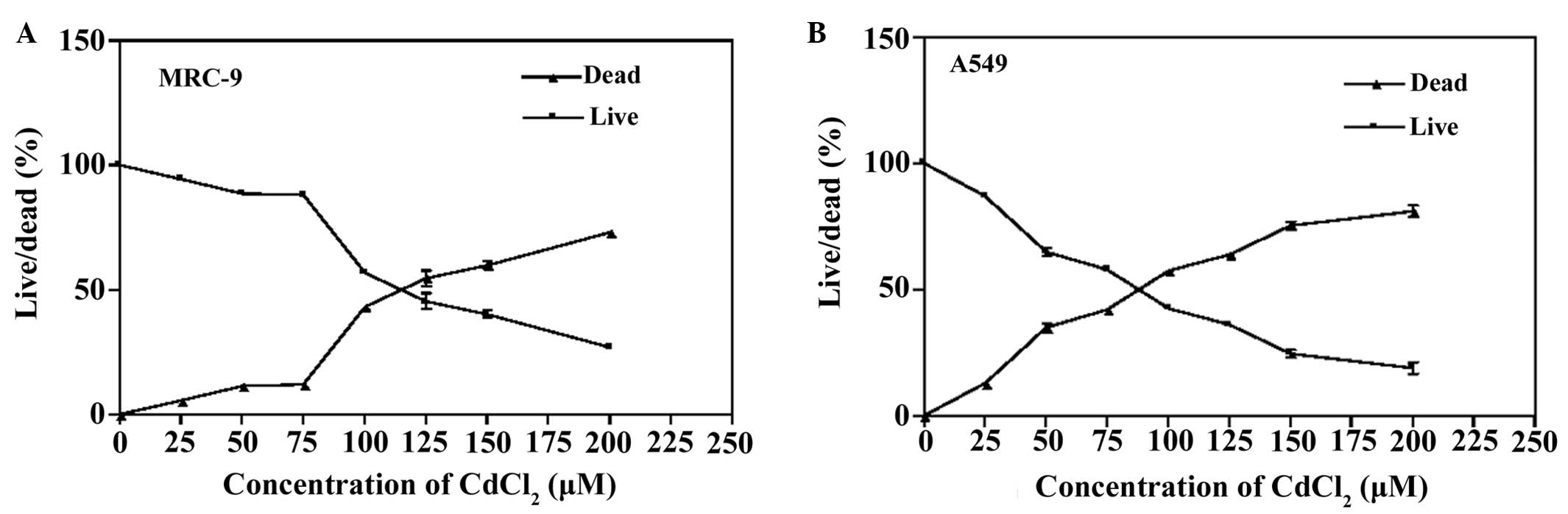
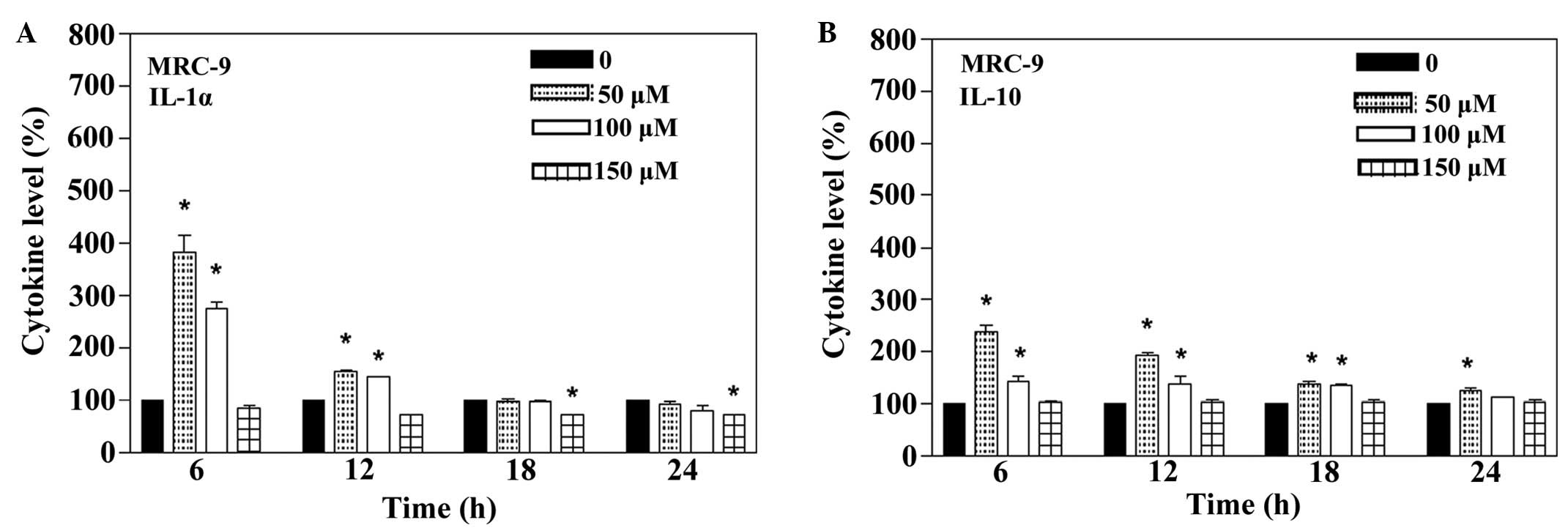
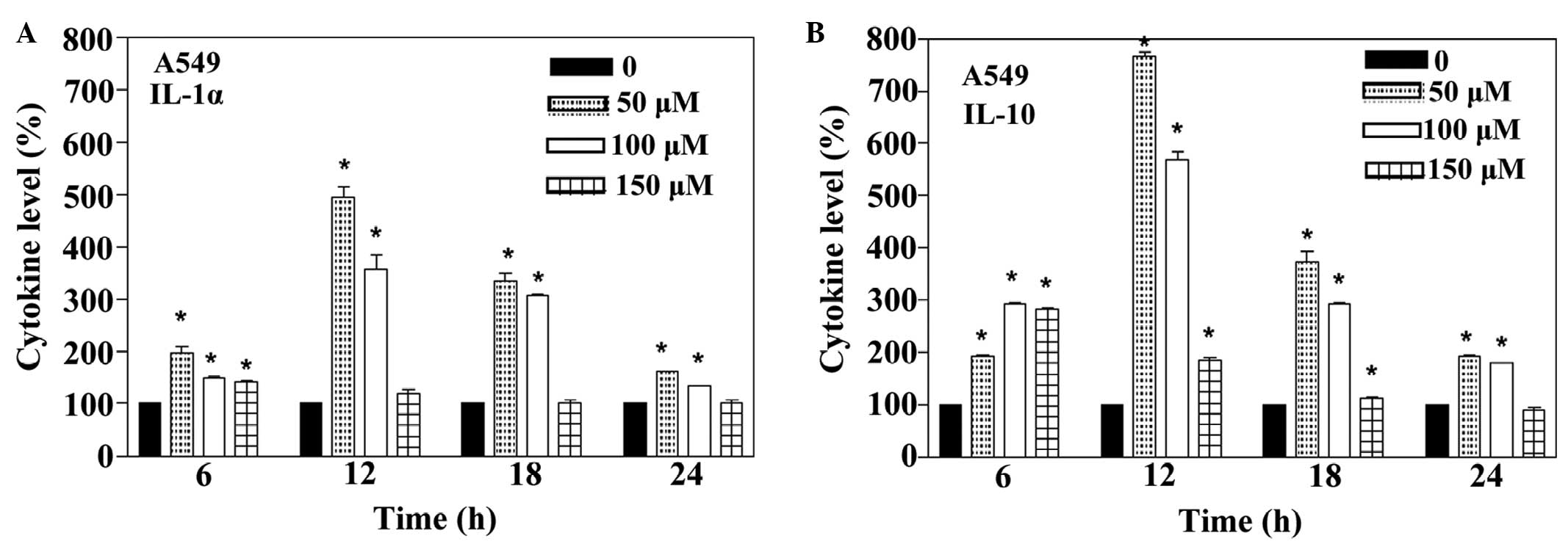
|
1
|
International agency for research on
cancer (IARC): Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic
Risks to Humans, Beryllium, Cadmium, Mercury and Exposures in the
Glass Manufacturing industry. IARC Scientific Publications; Lyon,
France: pp. 119–238. 1993
|
|
2
|
Goering PL, Waalkes MP and Klaassen CD:
Toxicology of cadmium. Toxicology of metals: Biochemical Aspects.
Goyer RA and Cherias M: Handb Exp Pharmacol. 15:189–214. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Agency for Toxic Substances Disease
Registry (ATSDR): Toxicological Profile for Cadmium. Atlanta, GA:
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health
Service; pp. 1–512. 2012
|
|
4
|
Joseph P: Mechanisms of cadmium
carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 238:272–279. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chin TA and Templeton DM: Protective
elevations of glutathione and metallothionein in cadmium-exposed
mesangial cells. Toxicology. 77:145–156. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bridges CC and Zalups RK: Molecular and
ionic mimicry and the transport of toxic metals. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 204:274–308. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Habeebu SS, Liu J and Klaassen CD:
Cadmium-induced apoptosis in mouse liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
149:203–209. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rikans LE and Yamano T: Mechanisms of
cadmium-mediated acute hepatotoxicity. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
14:110–117. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin T, Lu J and Nordberg M: Toxicokinetics
and biochemistry of cadmium with special emphasis on the role of
metallothionein. Neurotoxicology. 19:529–535. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Waalkes MP, Anver M and Diwan BA:
Carcinogenic effects of cadmium in the noble (NBL/Cr) rat:
Induction of pituitary, testicular and injection site tumors and
intraepithelial proliferative lesions of the dorsolateral prostate.
Toxicol Sci. 52:154–161. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Boujelben M, Ghorbel F, Vincent C,
Makni-Ayadi F, Guermazi F, Croute F and El-Feki A: Lipid
peroxidation and HSP72/73 expression in rat following cadmium
chloride administration: Interactions of magnesium supplementation.
Exp Toxicol Pathol. 57:437–443. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ikediobi CO, Badisa VL, Ayuk-Takem LT,
Latinwo LM and West J: Response of antioxidant enzymes and redox
metabolites to cadmium-induced oxidative stress in CRL-1439 normal
rat liver cells. Int J Mol Med. 14:87–92. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Badisa VL, Latinwo LM, Odewumi CO,
Ikediobi CO, Badisa RB, Brooks-Walter A, Lambert AT and Nwoga J:
Cytotoxicity and stress gene microarray analysis in cadmium-exposed
CRL-1439 normal rat liver cells. Int J Mol Med. 22:213–219.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Odewumi CO, Badisa VL, Le UT, Latinwo LM,
Ikediobi CO, Badisa RB and Darling-Reed SF: Protective effects of
N-acetylcysteine against cadmium-induced damage in cultured rat
normal liver cells. Int J Mol Med. 27:243–248. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Odewumi CO, Buggs R, Badisa VL, Latinwo
LM, Badisa RB, Ikediobi CO, Darling-Reed SF and Owens MA:
Mitigative action of monoisoamy 1-2,3-dimercaptosuccinate (MiADMS)
against cadmium-induced damage in cultured rat normal liver cells.
Toxicol In Vitro. 25:1733–1739. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Navarro Silvera SA and Rohan TE: Trace
elements and cancer risk: A review of the epidemiologic evidence.
Cancer Causes Control. 18:7–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Straif K, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Baan R,
Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Guha N, Freeman C,
Galichet L, et al WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer
Monograph Working Group: A review of human Carcinogens part C:
Metals, arsenic, dusts and fibres. Lancet Oncol. 10:453–454. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kundu S, Sengupta S and Bhattacharyya A:
EGFR upregulates inflammatory and proliferative responses in human
lung adenocarcinoma cell line (A549), induced by lower dose of
cadmium chloride. Inhal Toxicol. 23:339–348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rogalska J, Pilat-Marcinkiewicz B and
Brzóska MM: Protective effect of zinc against cadmium
hepatotoxicity depends on this bioelement intake and level of
cadmium exposure: A study in a rat model. Chem Biol Interact.
193:191–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shimabukuro DW, Sawa T and Gropper MA:
Injury and repair in lung and airways. Crit. Care Med. 31(8 Suppl):
S524–S531. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Grivennikov SI, Kuprash DV, Liu ZG and
Nedospasov SA: Intracellular signals and events activated by
cytokines of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily: From simple
paradigms to complex mechanisms. Int Rev Cytol. 252:129–161. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barksby HE, Lea SR, Preshaw PM and Taylor
JJ: The expanding family of interleukin-1 cytokines and their role
in destructive inflammatory disorders. Clin Exp Immunol.
149:217–225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trandem K, Jin Q, Weiss KA, James BR, Zhao
J and Perlman S: Virally expressed interleukin-10 ameliorates acute
encephalomyelitis and chronic demyelination in coronavirus-infected
mice. J Virol. 85:6822–6831. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Odewumi CO, Fils-Aime S, Badisa VL,
Latinwo LM, Ruden ML, Ikediobi C and Badisa RB: Chemoprotective
effect of monoisoamyl 2, 3-dimercaptosuccinate (MiADMS) on
cytokines expression in cadmium chloride treated human lung cells.
Environ Toxicol. 30:704–711. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Badisa RB, Tzakou O, Couladis M and
Pilarinou E: Cytotoxic activities of some Greek Labiatae herbs.
Phytother Res. 17:472–476. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ipsen J and Feigl P: Bancroft's
Introduction to Biostatistics. Second Edition. Harper and Row; New
York: pp. 1641970
|
|
27
|
Krocova Z, Macela A, Kroca M and
Hernychova L: The immu-nomodulatory effect(s) of lead and cadmium
on the cells of immune system in vitro. Toxicol In Vitro. 14:33–40.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Janssen AM, van Duijn W, Kubben FJ,
Griffioen G, Lamers CB, van Krieken JH, van de Velde CJ and
Verspaget HW: Prognostic significance of metallothionein in human
gastrointestinal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1889–1896.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Balharry D, Sexton K and BéruBé KA: An in
vitro approach to assess the toxicity of inhaled tobacco smoke
components: Nicotine, cadmium, formaldehyde and urethane.
Toxicology. 244:66–76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bergman M, Djaldetti M, Salman H and
Bessler H: Inflammation and colorectal cancer: Does aspirin affect
the interaction between cancer and immune cells? Inflammation.
34:22–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Romoser AA, Chen PL, Berg JM, Seabury C,
Ivanov I, Criscitiello MF and Sayes CM: Quantum dots trigger
immunomodulation of the NFκB pathway in human skin cells. Mol
Immunol. 48:1349–1359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kayama F, Yoshida T, Elwell MR and Luster
MI: Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cadmium-induced
hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 131:224–234. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kawano Y, Furukawa Y, Kawano Y, Abe W,
Hirakawa T and Narahara H: Cadmium chloride induces the expression
of metallothionein mRNA by endometrial stromal cells and
amnion-derived (WISH) cells. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 71:240–244.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Katsumata N, Eguchi K, Fukuda M, Yamamoto
N, Ohe Y, Oshita F, Tamura T, Shinkai T and Saijo N: Serum levels
of cytokines in patients with untreated primary lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 2:553–559. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bermúdez-Morales VH, Peralta-Zaragoza O,
Alcocer-González JM, Moreno J and Madrid-Marina V: IL-10 expression
is regulated by HPV E2 protein in cervical cancer cells. Mol Med
Report. 4:369–375. 2011.
|
|
36
|
Thévenod F and Lee WK: Cadmium and
cellular signaling cascades: Interactions between cell death and
survival pathways. Arch Toxicol. 87:1743–1786. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|