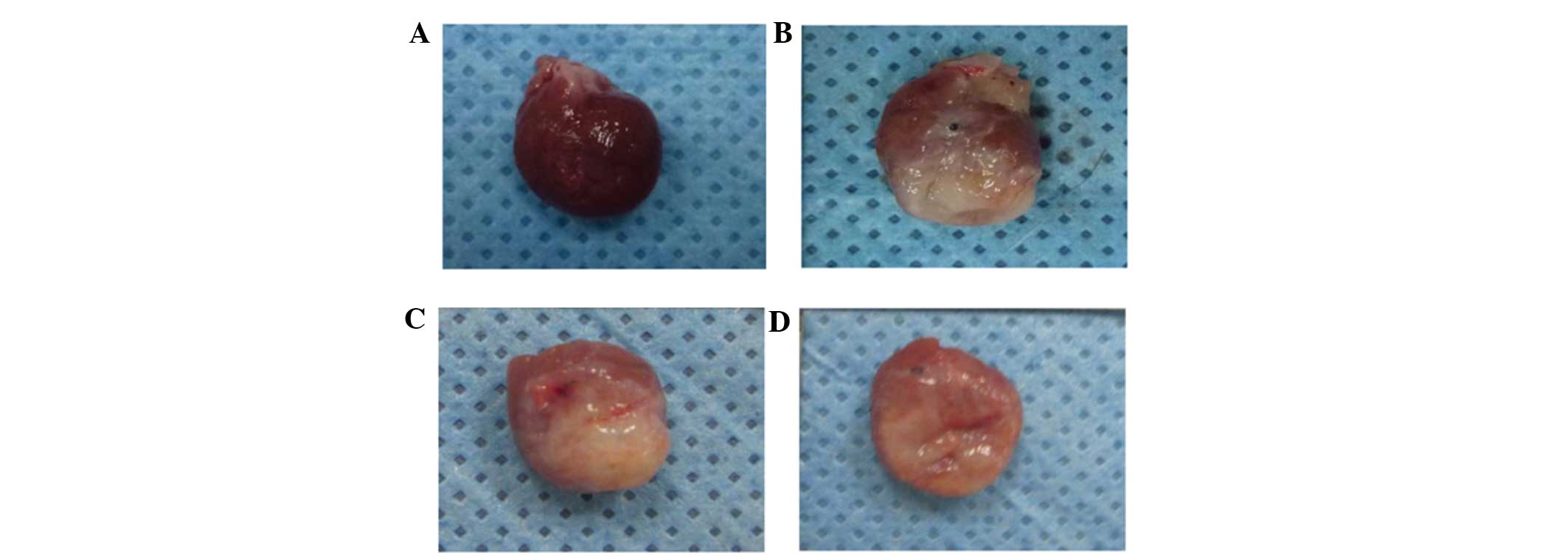
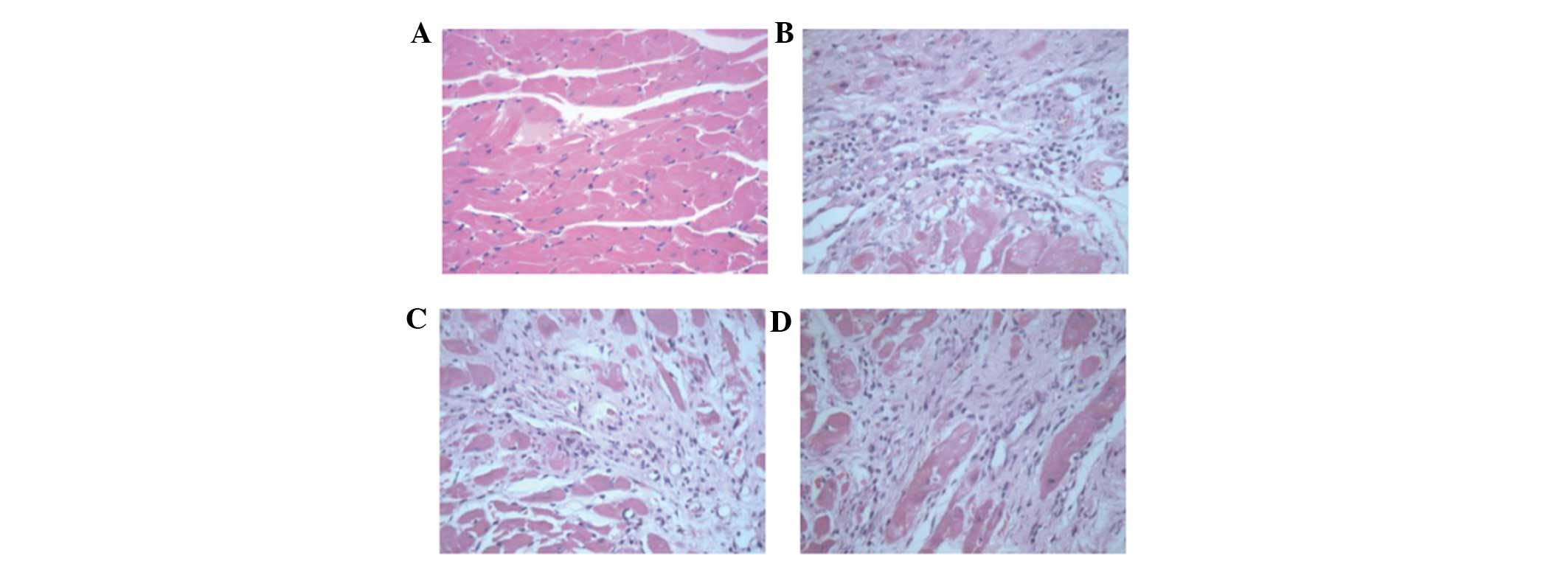
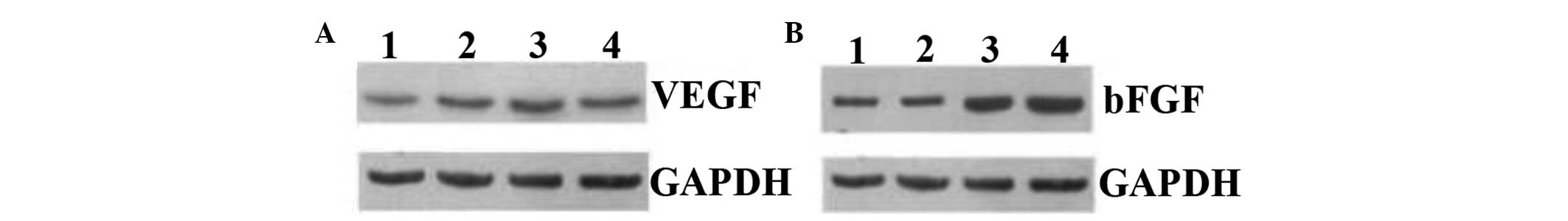
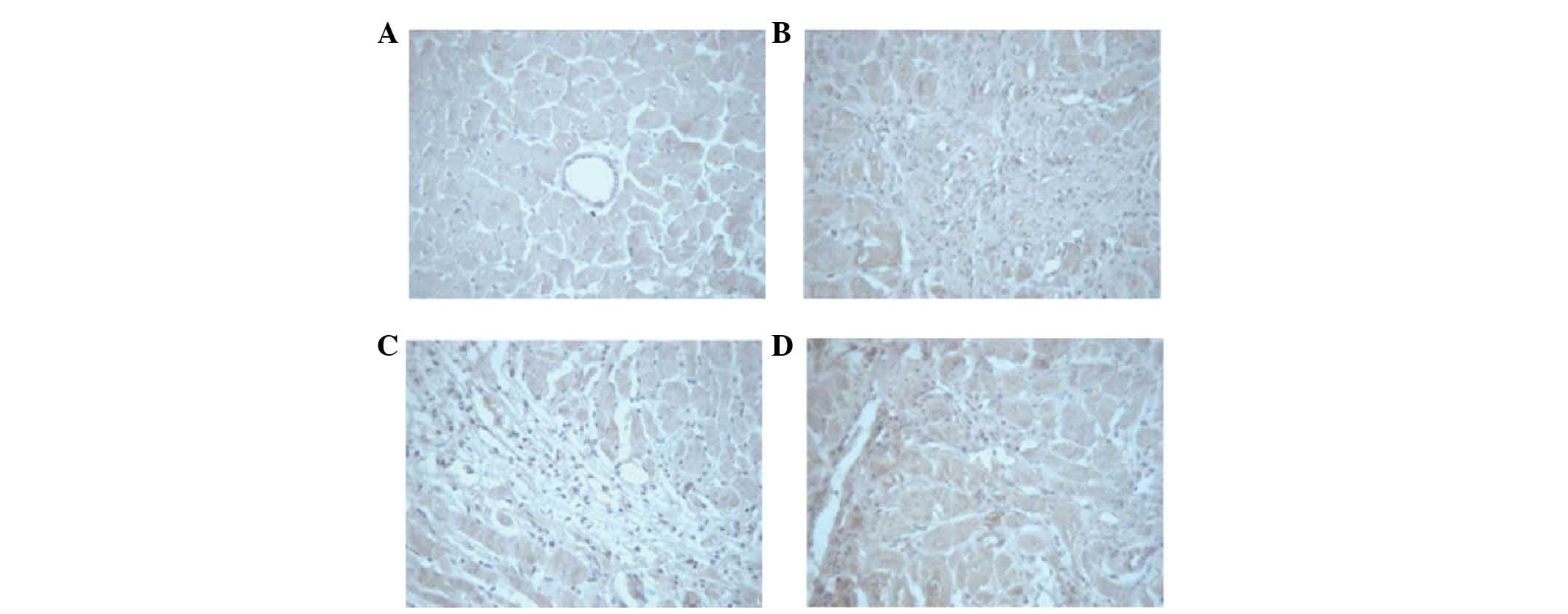
|
1
|
Orphanou K, Stassopoulou A and Keravnou E:
Risk assessment for primary coronary heart disease event using
dynamic Bayesian networks. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.
Holmes J, Bellazzi R, Sacchi L and Peek N: 9105. Springer
International Publishing; pp. 161–165. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu Y and Liu RX: The research progress of
Traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of coronary
atherosclerosis heart disease. Hebei J of Trad Chin Med.
35:1476–1478. 2013.In Chinese.
|
|
3
|
Tao HM, Qin S and Zhang DY: Research
progress of coronary heart disease in women. Adv Cardiovasc Dis.
35:250–253. 2014.In Chinese.
|
|
4
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, et al:
Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2013 update:
A report from the American heart association. Circulation.
127:143–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li XY and Fu ZQ: Pharmacotherapy of
coronary heart disease in the elderly. J Med Res. 40:3–5. 2011.In
Chinese.
|
|
6
|
de bakker JM, van capelle FJ, Janse MJ,
Wilde AA, Coronel R, Becker AE, Dingemans KP, van Hemel NM and
Hauer RN: Reentry as a cause of ventricular tachycardia in patients
with chronic ischemic heart disease: Electrophysiologic and
anatomic correlation. Circulation. 77:589–606. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang LM, Zhang SD and Ann YC: Treatment of
ventricular arrhythmia after myocardial infarction. Chinese Journal
of Cardiovascular Review. 6:144–146. 2008.In Chinese.
|
|
8
|
Meng QC: Treatment and prevention of
reperfusion arrhythmia after thrombolytic therapy for acute
myocardial infarction. Journal of Medical Forum. 27:55–57. 2006.In
Chinese.
|
|
9
|
Bates ER and Topol EJ: Limitations of
thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction complicated by
congestive heart failure and cardiogenic shock. J Am Coll Cardiol.
18:1077–1084. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kones R: Primary prevention of coronary
heart disease: Integration of new data, evolving views, revised
goals and role of rosuvastatin in management. A comprehensive
survey. Drug Des Devel Ther. 5:325–380. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ware JA and Simons M: Angiogenesis in
ischemicheart disease. Nat Med. 3:158–164. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rissanen TT, Korpisalo P, Markkanen JE,
Liimatainen T, Ordén MR, Kholová I, de Goede A, Heikura T, Gröhn OH
and Ylä-Herttuala S: Blood flow remodels growing vasculature during
vascular endothelial growth factor gene therapy and determines
between capillary arterialization and sprouting angiogenesis.
Circulation. 112:3937–3946. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dragneva G, Korpisalo P and Ylä-Herttuala
S: Promoting blood vessel growth in ischemic diseases: Challenges
in translating preclinical potential into clinical success. Dis
Model Mech. 6:312–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Q, Li J, Wang J, Li J, Janicki JS and
Fan D: Effects and mechanisms of Chinese herbal medicine in
ameliorating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:9256252013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu YF, Liu SW and Liu ZX: Effects of
Ginsenosiee Rb1 on blood vessel regeneration after ischemia and
reperfusion in rats. Chin J Histochem Cytochem. 17:39–44. 2008.In
Chinese.
|
|
16
|
Han D, Zhang Y, Liu M, et al: The
hemodynamic and antioxidant effects of Astragaloside on ventricular
remodeling rats. Chin J Lab Diag. 17:1956–1959. 2013.In
Chinese.
|
|
17
|
Wang YP, Li XY, Song CQ and Hu ZB: Effect
of astragaloside IV on T, B lymphocyte proliferation and peritoneal
macrophage function in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 23:263–266.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yin Y, Li WP, Gong HL, Zhu FF, Li WZ and
Wu GC: Protective effect of astragaloside on focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Am J Chin Med. 38:517–527.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang JS, Yu JM, Ju L, et al: Effects of
Astragalosides on angiogenesis in myocardium infarction rats. Chin
J Prim Med Pharm. 19:215–217. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Zhang L, Liu Q, Lu L, Zhao X, Gao X and
Wang Y: Astragaloside IV stimulates angiogenesis and increases
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α accumulation via phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 338:485–491. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Luca A, Carotenuto A, Rachiglio A,
Gallo M, Maiello MR, Aldinucci D, Pinto A and Normanno N: The role
of the EGFR signaling in tumor microenvironment. J Cell Physiol.
214:559–567. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Böttcher RT and Niehrs C: Fibroblast
growth factor signaling during early vertebrate development. Endocr
Rev. 26:63–77. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Andersson H and Brittebo E: Proangiogenic
effects of environmentally relevant levels of bisphenol A in human
primary endothelial cells. Arch Toxicol. 86:465–474. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Clark JD, Gebhart GF, Gonder JC, Keeling
ME and Kohn DF: Special Report: The 1996 Guide for the Care and Use
of Laboratory Animals. ILAR J. 38:41–48. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reddy BY, Greco SJ, Patel PS, Trzaska KA
and Rameshwar P: RE-1-silencing transcription factor shows
tumor-suppressor functions and negatively regulates the oncogenic
TAC1 in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
106:4408–4413. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weidner N: Intratumor microvessel density
as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol. 147:9–19.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aurgemma GP and Gaasch WH: Quantitative
evaluation of left ventricular structure, wall stress, and systolic
function. The Practice of Clinical Echocardiography. Otto CM: 2nd
edition. Elsevier Saunders; Philadelphia, PA: pp. 65–87. 2002
|
|
28
|
Meiners S, Dreger H, Fechner M, Bieler S,
Rother W, Günther C, Baumann G, Stangl V and Stangl K: Suppression
of cardio-myocyte hypertrophy by inhibition of the
ubiquitin-proteasome system. Hypertension. 51:302–308. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cochain C, Channon KM and Silvestre JS:
Angiogenesis in the infarcted myocardium. Antioxid Redox Signal.
18:1100–1113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Role of the
vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 23:1011–1027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pohl-Schickinger A, Koehne P, Schmitz T,
Schmitt KR, Hübler M, Redlin M, Berger F and Stiller B: Vascular
endothelial growth factor and its soluble receptor in infants with
congenital cardiac disease. Cardiol Young. 20:505–508. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shibuya M: VEGF-VEGFR signals in health
and disease. Biomol Ther. 22:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wafai R, Tudor EM, Angus JA and Wright CE:
Vascular effects of FGF-2and VEGF-B in rabbits with bilateral hind
limb ischemia. J Vasc Res. 46:45–54. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Schirmer SH, van Nooijen FC, Piek JJ and
van Royen N: Stimulation of collateral artery growth: Travelling
further down the road to clinical application. Heart. 95:191–197.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Hu G, Li S, Li ZH, Lam CO, Hong
SJ, Kwan YW, Chan SW, Leung GP and Lee SM: Pro-angiogenic activity
of astragaloside IV in HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish in vivo. Mol
Med Rep. 5:805–811. 2012.
|
|
36
|
Karanu FN, Murdoch B, Gallacher L, Wu DM,
Koremoto M, Sakano S and Bhatia M: The notch ligand jagged-1
represents a novel growth factor of human hematopoietic stem cells.
J Exp Med. 192:1365–1372. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Benedito R, Roca C, Sörensen I, Adams S,
Gossler A, Fruttiger M and Adams RH: The notch ligands Dll4 and
Jagged1 have opposing effects on angiogenesis. Cell. 137:1124–1135.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hernandez SL, Banerjee D, Garcia A,
Kangsamaksin T, Cheng WY, Anastassiou D, Funahashi Y,
Kadenhe-Chiweshe A, Shawber CJ, Kitajewski JK, et al: Notch and
VEGF pathways play distinct but complementary roles in tumor
angiogenesis. Vasc Cell. 5:172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|