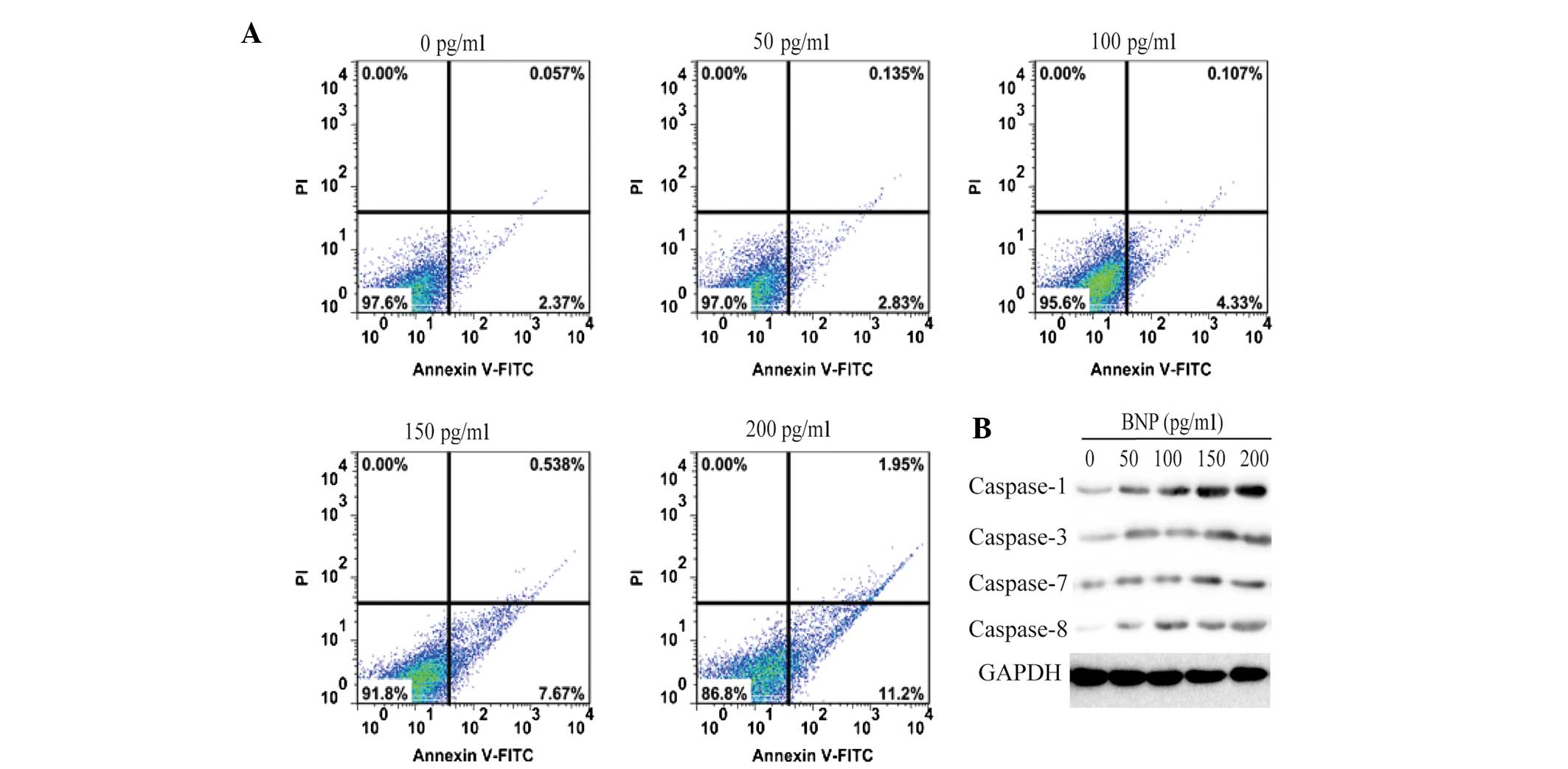
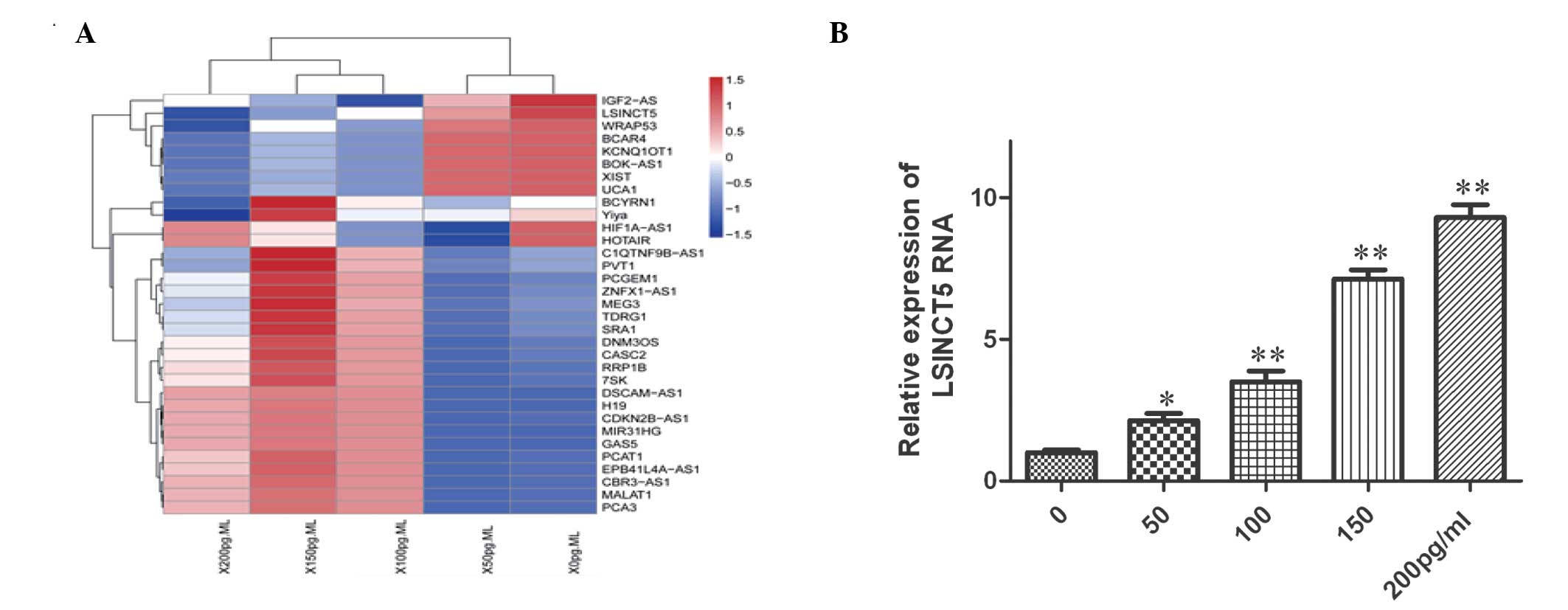
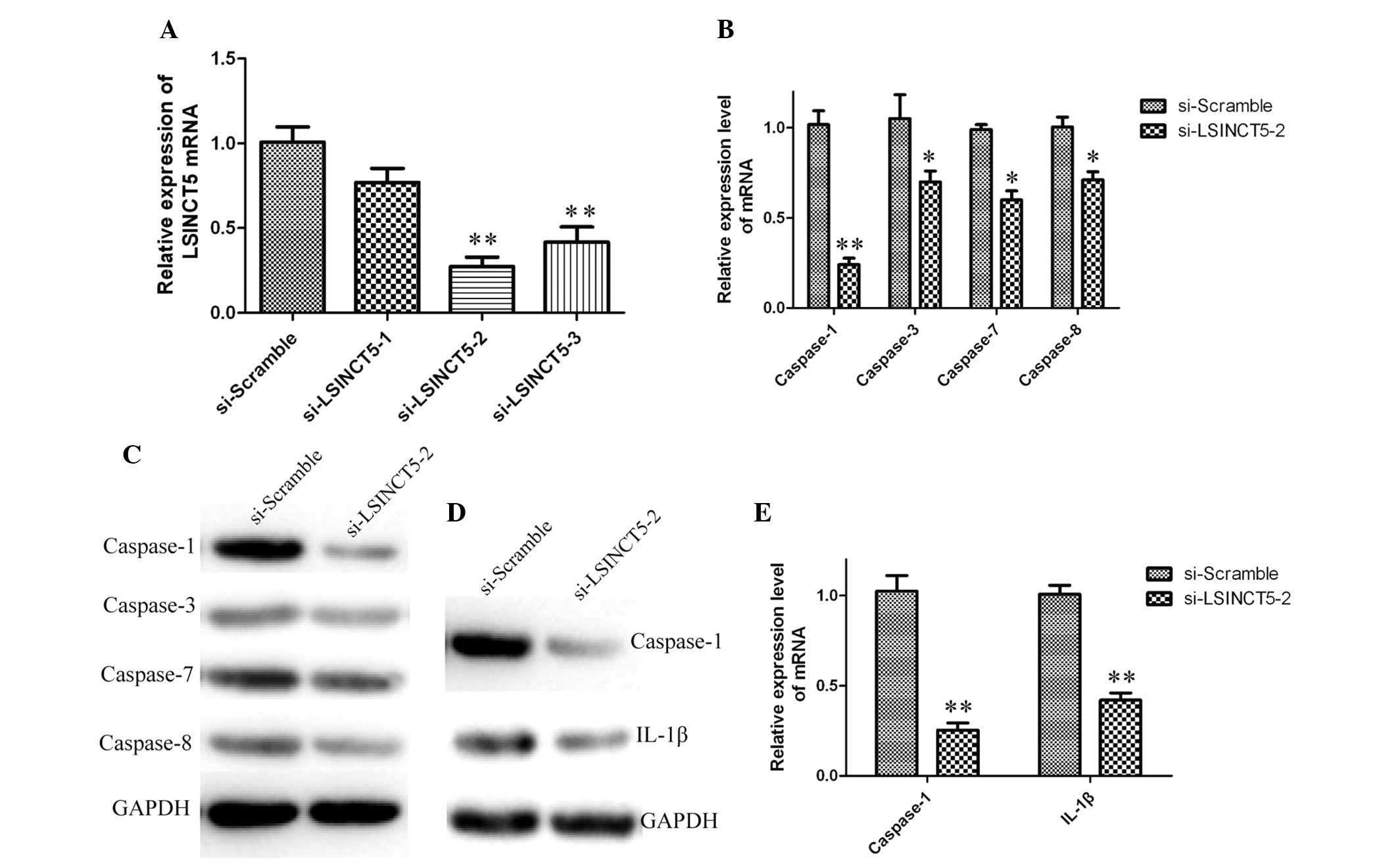
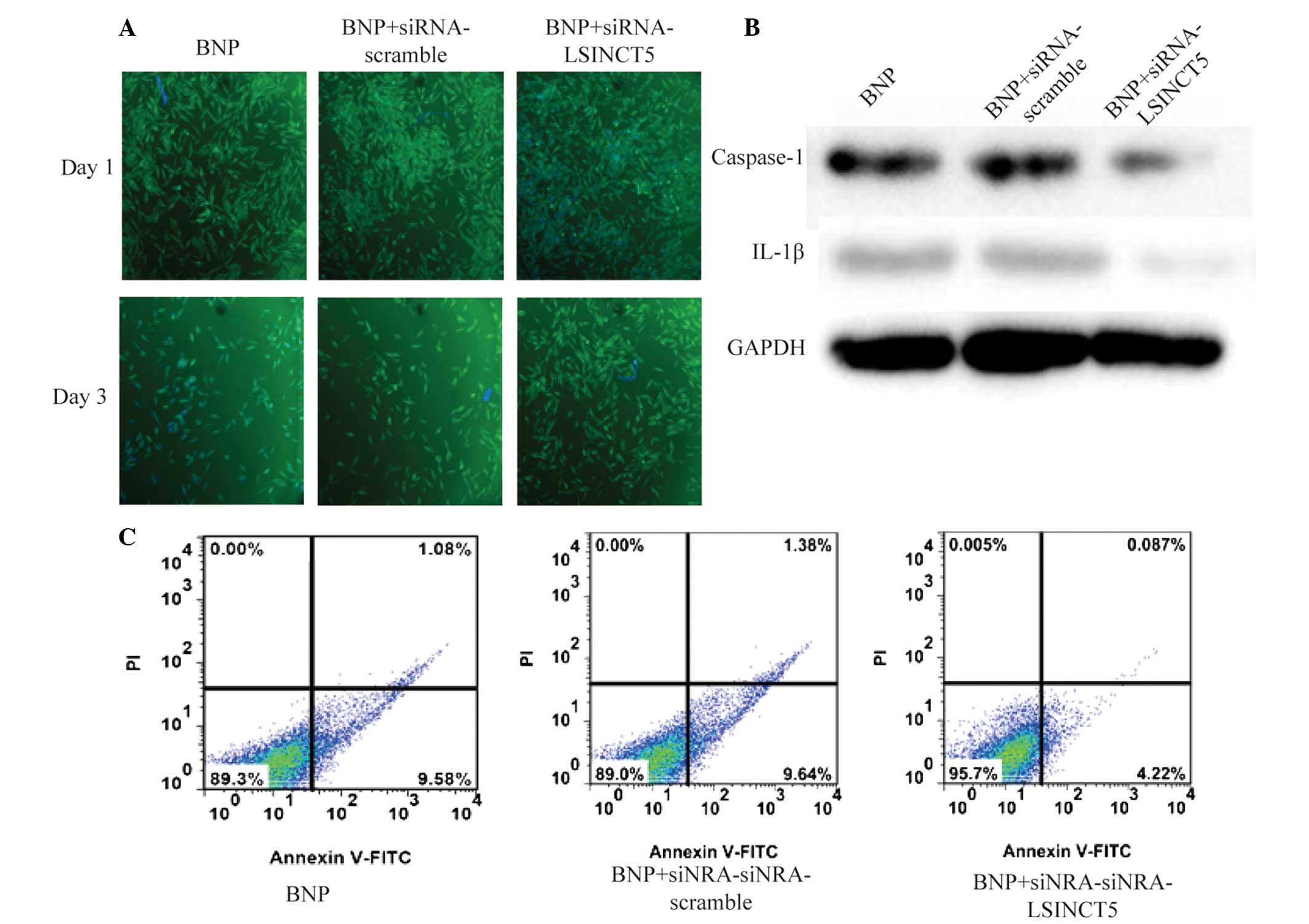
|
1
|
Granger CB, McMurray JJ, Yusuf S, Held P,
Michelson EL, Olofsson B, Ostergren J, Pfeffer MA and Swedberg K;
CHARM Investigators Committees: Effects of candesartan in patients
with chronic heart failure and reduced left-ventricular systolic
function intolerant to angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors:
The CHARM-Alternative trial. Lancet. 362:772–776. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gu D, Huang G and He J: Investigation of
prevalence and distributing feature of chronic heart failure in
Chinese adult population. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi.
31:3–6. 2002.In Chinese.
|
|
3
|
Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J,
Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi
JL, et al American College of Cardiology Foundation; American Heart
Association: Task Force on Practice Guidelines: 2013 ACCF/AHA
guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the
American college of cardiology foundation/american heart
association task force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol.
62:e147–e239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cowie MR: BNP-guided therapy for chronic
heart failure: Anything more than just an attractive concept? Eur
Heart J. 35:1507–1509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ishino M, Takeishi Y, Niizeki T, Watanabe
T, Nitobe J, Miyamoto T, Miyashita T, Kitahara T, Suzuki S, Sasaki
T, et al: Risk stratification of chronic heart failure patients by
multiple biomarkers: Implications of BNP, H-FABP and PTX3. Circ J.
72:1800–1805. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G,
McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, Strömberg A, van
Veldhuisen DJ, Atar D, Hoes AW, et al ESC Committee for Practice
Guidelines (CPG): ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of
acute and chronic heart failure 2008. The Task Force for the
diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008 of
the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with
the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the
European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). Eur J Heart
Fail. 10:933–989. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O'Shea P, Daly R, Kasim S and Tormey WP:
B-Type natriuretic peptide in the cardiology department. Ir Med J.
105:341–343. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Porapakkham P, Zimmet H, Billah B and Krum
H: B-type natriuretic peptide-guided heart failure therapy: A
meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 170:507–514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Szondy Z: Methylprednisolone and
2-chloroadenosine induce DNA fragmentation at different stages of
human T-lymphocyte development. Immunol Lett. 58:59–65. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Klein G: Cancer, apoptosis, and nonimmune
surveillance. Cell Death Differ. 11:13–17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Shimohama S: Apoptosis in Alzheimer's
disease - an update. Apoptosis. 5:9–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li M, Wu Z, Niu W, Wan Y, Zhang L, Shi G
and Xi X: The protective effect of curcumin against the 19-kDa
Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein-induced inflammation and
apoptosis in human macrophages. Mol Med Rep. 10:3261–3267.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Olivetti G, Abbi R, Quaini F, Kajstura J,
Cheng W, Nitahara JA, Quaini E, Di Loreto C, Beltrami CA, Krajewski
S, et al: Apoptosis in the failing human heart. N Engl J Med.
336:1131–1141. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Narula J, Haider N, Virmani R, DiSalvo TG,
Kolodgie FD, Hajjar RJ, Schmidt U, Semigran MJ, Dec GW and Khaw BA:
Apoptosis in myocytes in end-stage heart failure. N Engl J Med.
335:1182–1189. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ishino S, Kuge Y, Takai N, Tamaki N,
Strauss HW, Blackenberg FG, Shiomi M and Saji H: 99mTc-Annexin A5
for noninvasive characterization of atherosclerotic lesions:
Imaging and histological studies in myocardial infarction-prone
Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. Eur J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 34:889–899. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li D, Williams V, Liu L, Chen H, Sawamura
T, Romeo F and Mehta JL: Expression of lectin-like oxidized
low-density lipoprotein receptors during ischemia-reperfusion and
its role in determination of apoptosis and left ventricular
dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 41:1048–1055. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fliss H and Gattinger D: Apoptosis in
ischemic and reperfused rat myocardium. Circ Res. 79:949–956. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leung KP, Qu YH, Qiao DF, Xie WB, Li DR,
Xu JT, Wang HJ and Yue X: Critical role of insulin-like growth
factor binding protein-5 in methamphetamine-induced apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes. Mol Med Rep. 10:2306–2312. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng YJ, Tan N, Zeng HK, Fu YH and Dong
XL: Effects of BNP preconditioning on myocardial cell apoptosis and
expressions of bcl-2 and Bax during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury in rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 90:3431–3434. 2010.In
Chinese.
|
|
20
|
Mattick JS and Makunin IV: Non-coding RNA.
Hum Mol Genet. 15:R17–R29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang Y, Li H, Hou S, Hu B, Liu J and Wang
J: The noncoding RNA expression profile and the effect of lncRNA
AK126698 on cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer
cell. PLoS One. 8:e653092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang K, Long B, Zhou LY, Liu F, Zhou QY,
Liu CY, Fan YY and Li PF: CARL lncRNA inhibits anoxia-induced
mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by impairing
miR-539-dependent PHB2 downregulation. Nat Commun.
5:35962014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Henriksen JH, Gøtze J, Fuglsang S,
Christensen E, Bendtsen F and Møller S: Increased circulating
pro-brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP) and brain natriuretic
peptide (BNP) in patients with cirrhosis: Relation to
cardiovascular dysfunction and severity of disease. Gut.
52:1511–1517. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Smit B, Spoelstra-de Man AM, Girbes AR and
de Waard MC: NT-proBNP in cardiopulmonary resuscitated patients
treated with mild therapeutic hypothermia is not independently
associated with mortality: a retrospective observational study. BMC
anesthesiology. 15:482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beer S, Golay S, Bardy D, Feihl F,
Gaillard RC, Bachmann C, Waeber B and Ruiz J: Increased plasma
levels of N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) in type
2 diabetic patients with vascular complications. Diabetes Metab.
31:567–573. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weber M, Bazzino O, Navarro Estrada JL,
Fuselli JJ, Botto F, Perez de Arenaza D, Möllmann H, Nef HN,
Elsässer A and Hamm CW: N-terminal B-type natriuretic peptide
assessment provides incremental prognostic information in patients
with acute coronary syndromes and normal troponin T values upon
admission. J Am Coll Cardiol. 51:1188–1195. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li Y, Song P, Zhu Q, Yin QY, Ji JW, Li W
and Bian HM: Liguzinediol improved the heart function and inhibited
myocardial cell apoptosis in rats with heart failure. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 35:1257–1264. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suo C, Sun L and Yang S: Alpinetin
activates the δ receptor instead of the κ and µreceptor pathways to
protect against rat myocardial cell apoptosis. Exp Ther Med.
7:109–116. 2014.
|
|
30
|
Hirota H, Chen J, Betz UA, Rajewsky K, Gu
Y, Ross J Jr, Müller W and Chien KR: Loss of a gp130 cardiac muscle
cell survival pathway is a critical event in the onset of heart
failure during biomechanical stress. Cell. 97:189–198. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Song XJ, Yang CY, Liu B, Wei Q, Korkor MT,
Liu JY and Yang P: Atorvastatin inhibits myocardial cell apoptosis
in a rat model with post-myocardial infarction heart failure by
downregulating ER stress response. Int J Med Sci. 8:564–572. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kang PM and Izumo S: Apoptosis in heart:
basic mechanisms and implications in cardiovascular diseases.
Trends Mol Med. 9:177–182. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mital S, Barbone A, Addonizio LJ,
Quaegebeur JM, Mosca RJ, Oz MC and Hintze TH: Endogenous
endothelium-derived nitric oxide inhibits myocardial caspase
activity: Implications for treatment of end-stage heart failure. J
Heart Lung Transplant. 21:576–585. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Narula J, Pandey P, Arbustini E, Haider N,
Narula N, Kolodgie FD, Dal Bello B, Semigran MJ, Bielsa-Masdeu A,
Dec GW, et al: Apoptosis in heart failure: Release of cytochrome c
from mitochondria and activation of caspase-3 in human
cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:8144–8149. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Wang J, Qi SY, Ru LS, Ding C, Wang
HJ, Zhao JS, Li JJ, Li AY and Wang DM: Reduced endoplasmic
reticulum stress might alter the course of heart failure via
caspase-12 and JNK pathways. Can J Cardiol. 30:368–375. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Prescimone T, D'Amico A, Caselli C,
Cabiati M, Viglione F, Caruso R, Verde A, Del Ry S, Trivella MG and
Giannessi D: Caspase-1 transcripts in failing human heart after
mechanical unloading. Cardiovasc Pathol. 24:11–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Syed FM, Hahn HS, Odley A, Guo Y, Vallejo
JG, Lynch RA, Mann DL, Bolli R and Dorn GW II: Proapoptotic effects
of caspase-1/interleukin-converting enzyme dominate in myocardial
ischemia. Circ Res. 96:1103–1109. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Merkle S, Frantz S, Schön MP, Bauersachs
J, Buitrago M, Frost RJ, Schmitteckert EM, Lohse MJ and Engelhardt
S: A role for caspase-1 in heart failure. Circ Res. 100:645–653.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
DeOcesano-Pereira C, Amaral MS, Par reira
KS, Ayupe AC, Jacysyn JF, Amarante-Mendes GP, Reis EM and
Verjovski-Almeida S: Long non-coding RNA INXS is a critical
mediator of BCL-XS induced apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:8343–8355. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu WH, Zhang JB, Dang Z, Li X, Zhou T, Liu
J, Wang DS, Song WJ and Dou KF: Long non-coding RNA URHC regulates
cell proliferation and apoptosis via ZAK through the ERK/MAPK
signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci.
10:664–676. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|