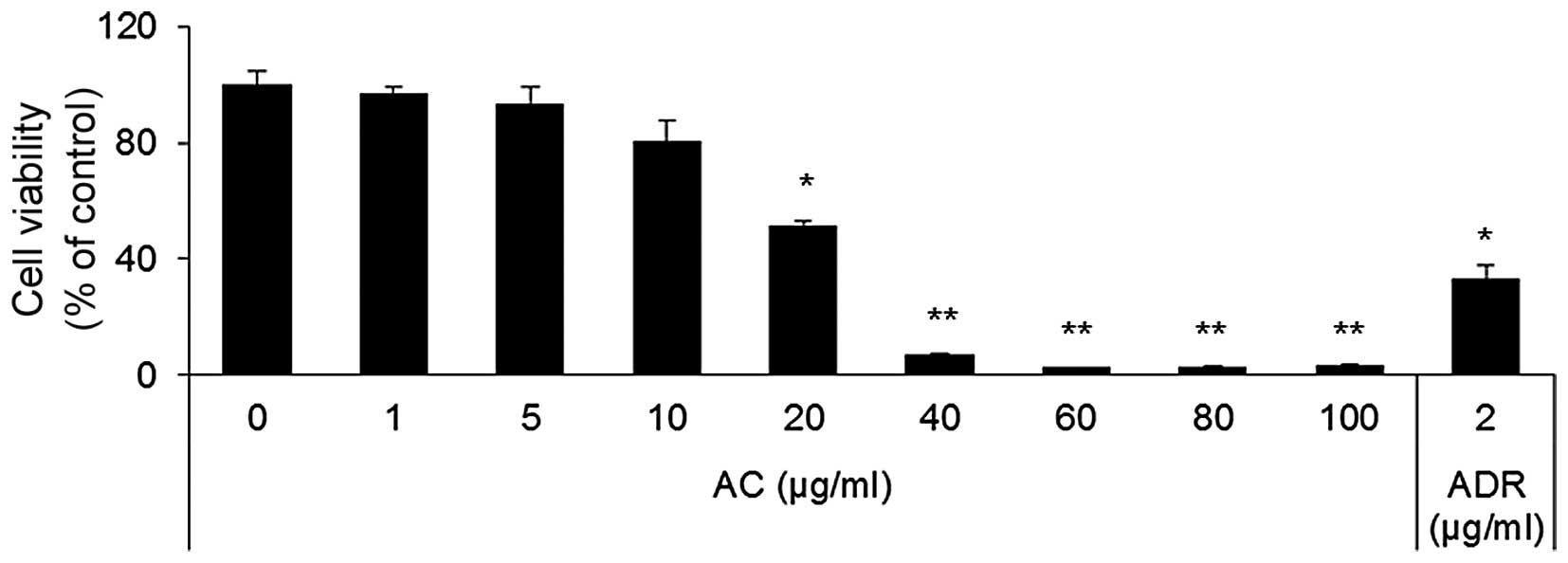
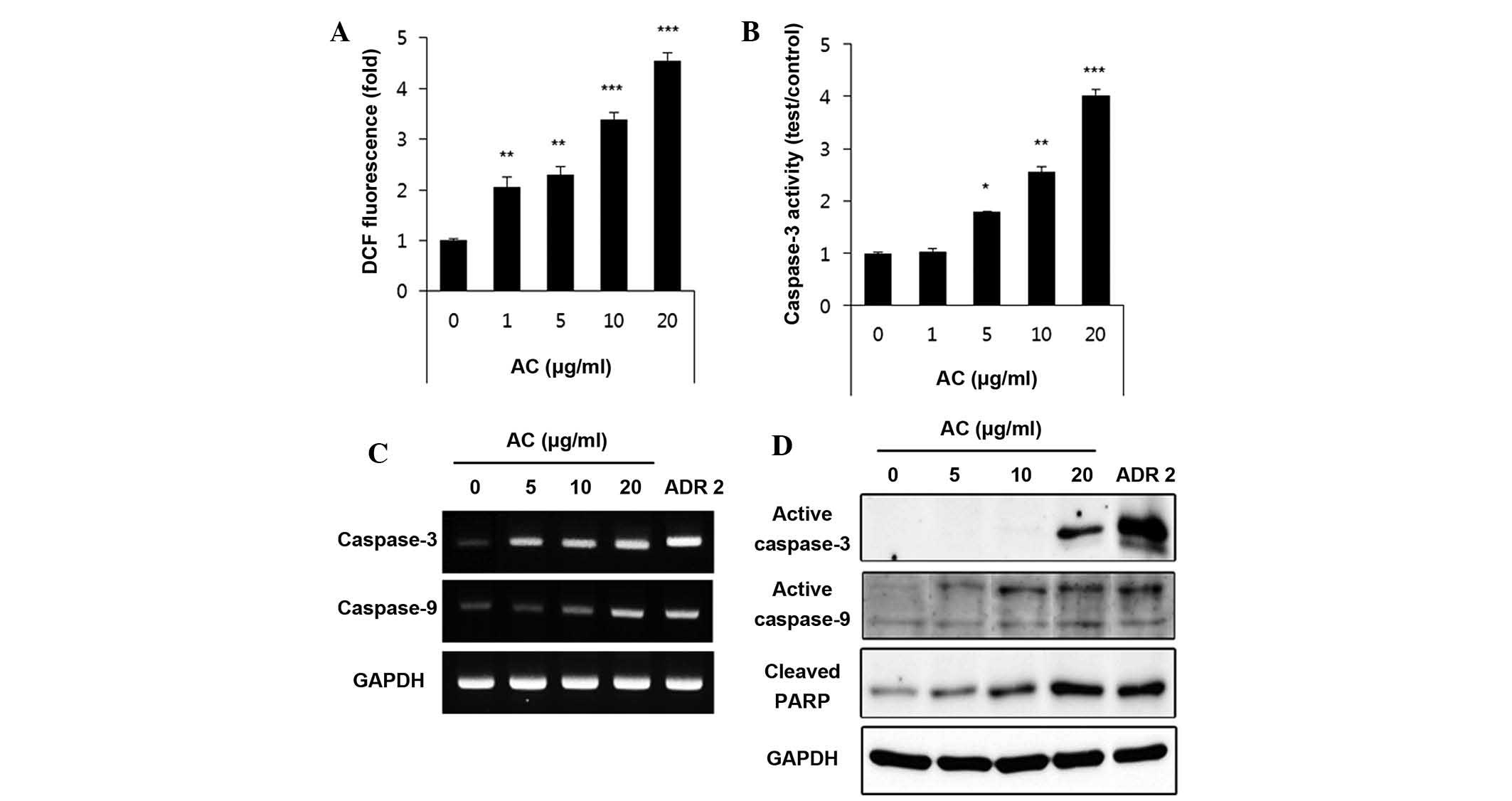
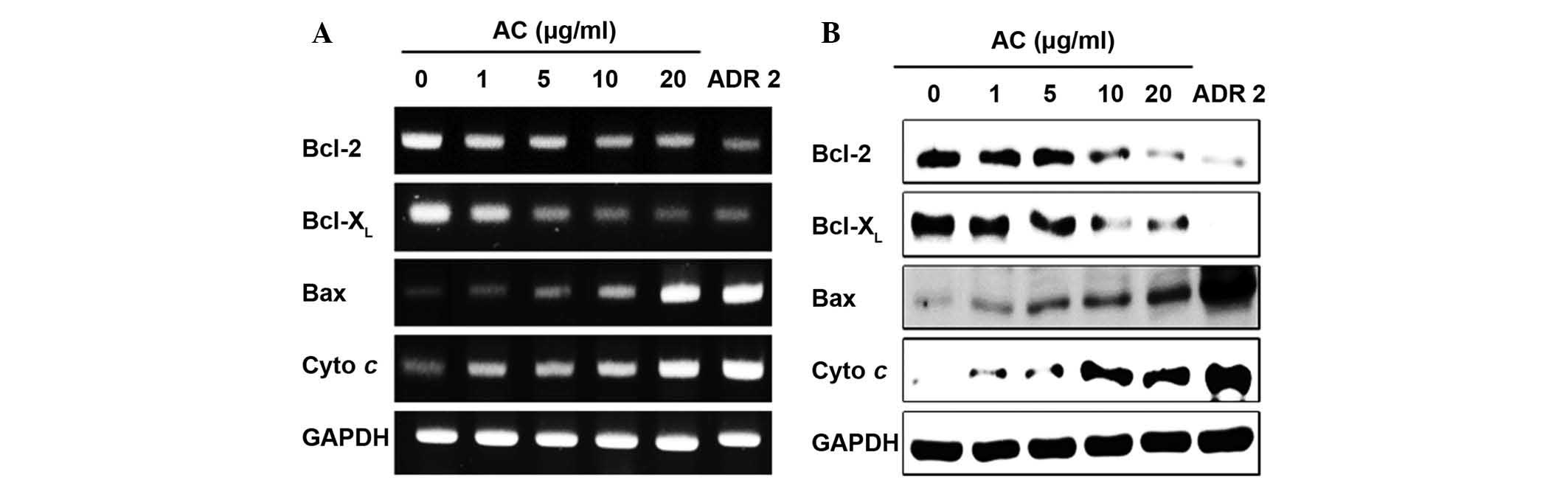
|
1
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF and Currie AR: Cell
death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 68:251–306.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Earnshaw WC: Nuclear changes in apoptosis.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 7:337–343. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nagata S: Apoptosis by death factor. Cell.
88:355–365. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC: Induction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 256:42–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kroemer G and Reed JC: Mitochondrial
control of cell death. Nat Med. 6:513–519. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S,
Poirier GG and Earnshaw WC: Cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose)
polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature.
371:346–347. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ and Yuan J: Cleavage of
BID by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas
pathway of apoptosis. Cell. 94:491–501. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kyosseva SV: Mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling. Int Rev Neurobiol. 59:201–220. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Keshet Y and Seger R: The MAP kinase
signaling cascades: a system of hundreds of components regulates a
diverse array of physiological functions. Methods Mol Biol.
661:3–38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sumbayev VV and Yasinska IM: Regulation of
MAP kinase-dependent apoptotic pathway: implication of reactive
oxygen and nitrogen species. Arch Biochem Biophys. 436:406–412.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Loyola LA, Bórquez J, Morales G,
San-Martín A, Darias J, Flores N and Giménez A: Mulinane-type
diterpenoids from Azorella compacta display antiplasmodial
activity. Phytochemistry. 65:1931–1935. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wachter GA, Franzblau SG, Montenegro G,
Suarez E, Fortunato RH, Saavedra E and Timmermann BN: A new
antitu-bercular mulinane diterpenoid from Azorella madreporica
Clos. J Nat Prod. 61:965–968. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Areche C, Rojas-Alvarez F, Campos-Briones
C, Lima C, Pérez EG and Sepúlveda B: Further mulinane diterpenoids
from Azorella compacta. J Pharm Pharmacol. 65:1231–1238. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wachter GA, Matooq G, Hoffmann JJ, Maiese
WM, Singh MP, Montenegro G and Timmermann BN: Antibacterial
diterpenoid acids from Azorella compacta. J Nat Prod. 62:1319–1321.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fuentes NL, Sagua H, Morales G, Borquez J,
San Martin A, Soto J and Loyola LA: Experimental antihyperglycemic
effect of diterpenoids of llareta Azorella compacta (Umbelliferae)
Phil in rats. Phytother Res. 19:713–716. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee K, Kwon OK, Xia Y and Ahn KS: Effect
of AC-264, a novel indole derivative, on apoptosis in HL-60 cells.
Bull Korean Chem Soc. 31:3777–3781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pink JJ, Wuerzberger-Davies S, Tagliarino
C, Planchon SM, Yang X, Froelich CJ and Boothman DA: Activation of
a cysteine protease in MCF-7 and T47D breast cancer cells during
beta-lapachone-mediated apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 255:144–155. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ren G, Zhao YP, Yang L and Fu CX:
Anti-proliferative effect of clitocine from the mushroom
Leucopaxillus giganteus on human cervical cancer HeLa cells by
inducing apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 262:190–200. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu SJ, Ng LT, Chen CH, Lin DL, Wang SS and
Lin CC: Antihepatoma activity of Physalis angulata and P. peruviana
extracts and their effects on apoptosis in human Hep G2 cells. Life
Sci. 74:2061–2073. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Andersson B, Janson V, Behnam-Motlagh P,
Henriksson R and Grankvist K: Induction of apoptosis by
intracellular potassium ion depletion: Using the fluorescent dye
PBFI in a 96-well plate method in cultured lung cancer cells.
Toxicol In vitro. 20:986–994. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hall PA: Assessing apoptosis: A critical
survey. Endocr Relat Cancer. 6:3–8. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Galluzzi L, Larochette N, Zamzami N and
Kroemer G: Mitochondria as therapeutic targets for cancer
chemotherapy. Oncogene. 25:4812–4830. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Belloc F, Dumain P, Boisseau MR,
Jalloustre C, et al: A flow cytometric method using Hoechst 33342
and propidium iodide for simultaneous cell cycle analysis and
apoptosis determination in unfixed cells. Cytometry. 17:59–65.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang L, Wu S, Zhang Q, Liu F and Wu P:
23,24-Dihydrocucurbitacin B induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest and
mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
(Bcap37). Cancer Lett. 256:267–278. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang R, Li C, Song D, Zhao G, Zhao L and
Jing Y: Ethacrynic acid butyl-ester induces apoptosis in leukemia
cells through a hydrogen peroxide mediated pathway independent of
glutathione S-transferase P1-1 inhibition. Cancer Res.
67:7856–7864. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cullen SP and Martin SJ: Caspase
activation pathways: Some recent progress. Cell Death Differ.
16:935–938. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zheng TS, Hunot S, Kuida K, Momoi T,
Srinivasan A, Nicholson DW, Lazebnik Y and Flavell RA: Deficiency
in caspase-9 or caspase-3 induces compensatory caspase activation.
Nat Med. 6:1241–1247. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moon DO, Kim MO, Choi YH, Kim ND, Chang JH
and Kim GY: Bcl-2 overexpression attenuates SP600125-induced
apoptosis in human leukemia U937 cells. Cancer Lett. 264:316–325.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV,
Deacon E, Salmon M and Lord JM: Serine/threonine protein kinases
and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 256:34–41. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|