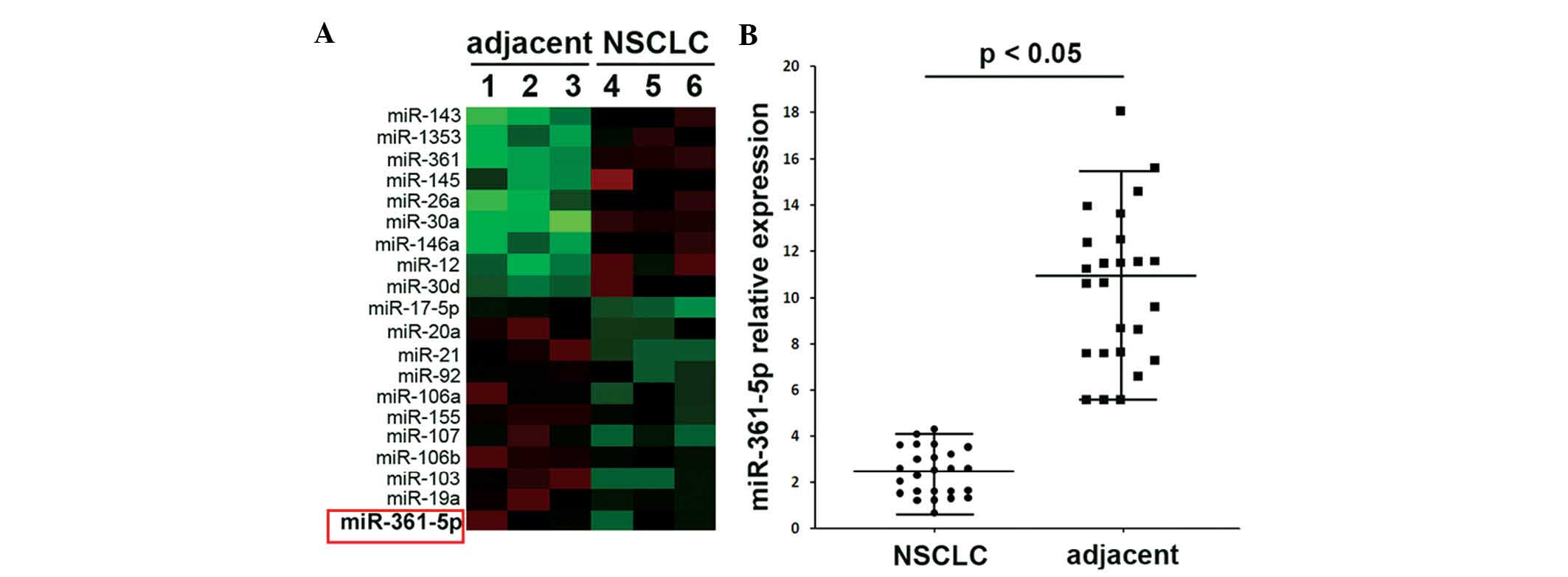
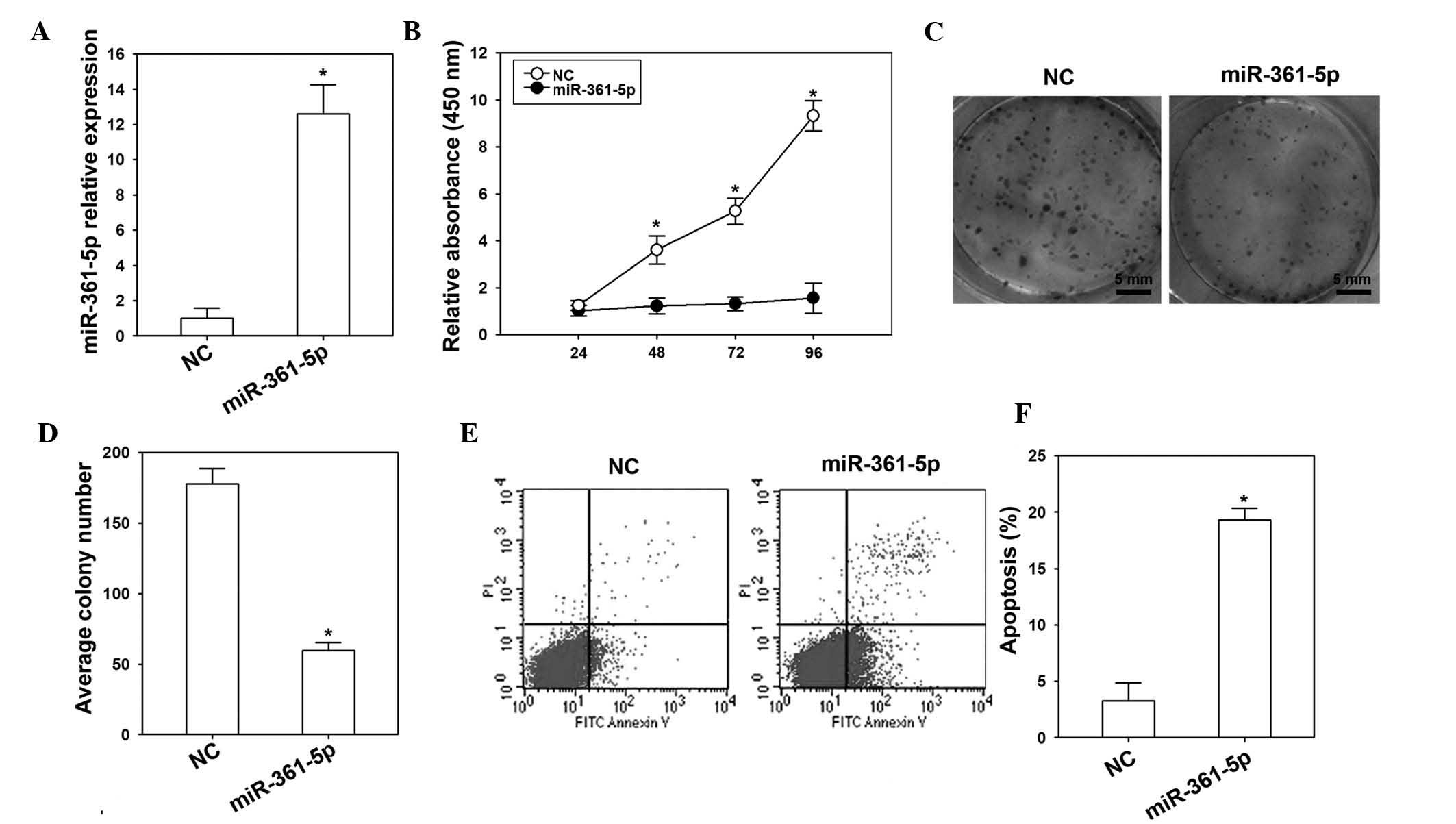
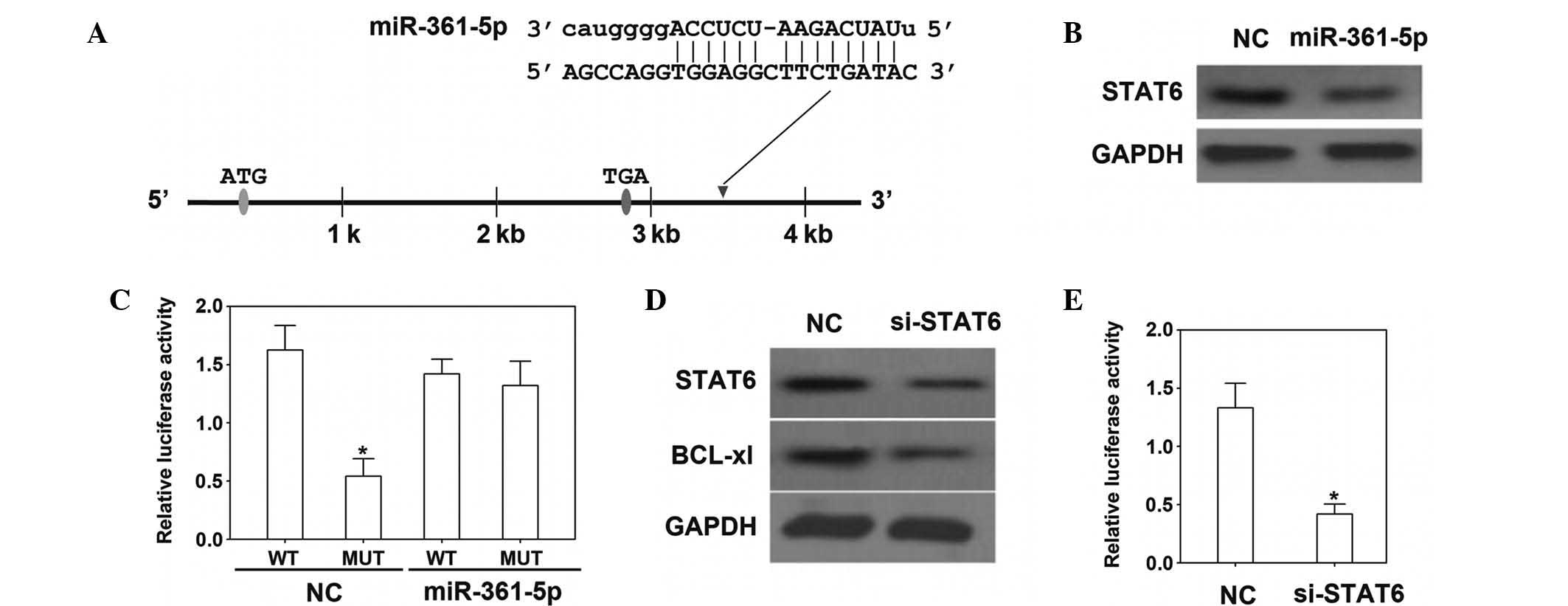
|
1
|
Xue C, Hu Z, Jiang W, Zhao Y, Xu F, Huang
Y, Zhao H, Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhao L, et al: National survey of the
medical treatment status for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in
China. Lung Cancer. 77:371–375. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye FJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Kuwano H,
Takahashi T and Mitsudomi T: Mutations of the epidermal growth
factor receptor gene in lung cancer: Biological and clinical
implications. Cancer Res. 64:8919–8923. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mitsudomi T, Viallet J, Mulshine JL,
Linnoila RI, Minna JD and Gazdar AF: Mutations of ras genes
distinguish a subset of non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines from
small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 6:1353–1362.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stephens P, Hunter C, Bignell G, Edkins S,
Davies H, Teague J, Stevens C, O'Meara S, Smith R, Parker A, et al:
Lung cancer: Intragenic ERBB2 kinase mutations in tumours. Nature.
431:525–526. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Temel JS, Greer JA, Muzikansky A,
Gallagher ER, Admane S, Jackson VA, Dahlin CM, Blinderman CD,
Jacobsen J, Pirl WF, et al: Early palliative care for patients with
metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:733–742.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schilsky RL: Personalized medicine in
oncology: The future is now. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 9:363–366. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gerber DE and Minna JD: ALK inhibition for
non-small cell lung cancer: From discovery to therapy in record
time. Cancer Cell. 18:548–551. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McManus MT and Sharp PA: Gene silencing in
mammals by small interfering RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 3:737–747. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu SL, Chen HY, Chang GC, Chen CY, Chen
HW, Singh S, Cheng CL, Yu CJ, Lee YC, Chen HS, et al: MicroRNA
signature predicts survival and relapse in lung cancer. Cancer
Cell. 13:48–57. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M,
Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et
al: Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang ZX, Bian HB, Wang JR, Cheng ZX, Wang
KM and De W: Prognostic significance of serum miRNA-21 expression
in human non-small cell lung cancer. J Surg Oncol. 104:847–851.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Larzabal L, de Aberasturi AL, Redrado M,
Rueda P, Rodriguez MJ, Bodegas ME, Montuenga LM and Calvo A:
TMPRSS4 regulates levels of integrin α5 in NSCLC through miR-205
activity to promote metastasis. Br J Cancer. 110:764–774. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Foss KM, Sima C, Ugolini D, Neri M, Allen
KE and Weiss GJ: MiR-1254 and miR-574-5p: Serum-based microRNA
biomarkers for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Oncol. 6:482–488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chin LJ, Ratner E, Leng S, Zhai R, Nallur
S, Babar I, Muller RU, Straka E, Su L, Burki EA, et al: A SNP in a
let-7 microRNA complementary site in the KRAS 3′ untranslated
region increases non-small cell lung cancer risk. Cancer Res.
68:8535–8540. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roth C, Stückrath I, Pantel K, Izbicki JR,
Tachezy M and Schwarzenbach H: Low levels of cell-free circulating
miR-361-3p and miR-625* as blood-based markers for
discriminating malignant from benign lung tumors. PLoS One.
7:e382482012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Watahiki A and Wang Y, Morris J, Dennis K,
O'Dwyer HM, Gleave M, Gout PW and Wang Y: MicroRNAs associated with
metastatic prostate cancer. PLoS One. 6:e249502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khella HW, White NM, Faragalla H, Gabril
M, Boazak M, Dorian D, Khalil B, Antonios H, Bao TT, Pasic MD, et
al: Exploring the role of miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma
progression and metastasis through bioinformatic and experimental
analyses. Tumor Biol. 33:131–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kanitz A, Imig J, Dziunycz PJ, Primorac A,
Galgano A, Hofbauer GF, Gerber AP and Detmar M: The expression
levels of microRNA-361-5p and its target VEGFA are inversely
correlated in human cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
7:e495682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu D, Tao T, Xu B, Chen S, Liu C, Zhang
L, Lu K, Huang Y, Jiang L, Zhang X, et al: MiR-361-5p acts as a
tumor suppressor in prostate cancer by targeting signal transducer
and activator of transcription-6 (STAT6). Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 445:151–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Humphrey PA: Gleason grading and
prognostic factors in carcinoma of the prostate. Mod Pathol.
17:292–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U
and Segal E: The role of site accessibility in microRNA target
recognition. Nature Genetics. 39:1278–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rabinowits G, Gerçel-Taylor C, Day JM,
Taylor DD and Kloecker GH: Exosomal microRNA: A diagnostic marker
for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 10:42–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang JG, Wang JJ, Zhao F, Liu Q, Jiang K
and Yang GH: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) represses tumor suppressor PTEN
and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC). Clin Chim Acta. 411:846–852. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Romano G, Acunzo M, Garofalo M, Di Leva G,
Cascione L, Zanca C, Bolon B, Condorelli G and Croce CM: MiR-494 is
regulated by ERK1/2 and modulates TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
non-small-cell lung cancer through BIM down-regulation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 109:16570–16575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guan P, Yin Z, Li X, Wu W and Zhou B:
Meta-analysis of human lung cancer microRNA expression profiling
studies comparing cancer tissues with normal tissues. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 31:542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Q, Wang S, Wang H, Li P and Ma Z:
MicroRNAs: Novel biomarkers for lung cancer diagnosis, prediction
and treatment. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 237:227–235. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu X, Xi X, Yan Q, Zhang Z, Cai B, Lu W
and Wan X: MicroRNA-361-5p facilitates cervical cancer progression
through mediation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Med
Oncol. 30:7512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wurster AL, Tanaka T and Grusby MJ: The
biology of Stat4 and Stat6. Oncogene. 19:2577–2584. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Das S, Shetty P, Valapala M, Dasgupta S,
Gryczynski Z and Vishwanatha JK: Signal transducer and activator of
transcription 6 (STAT6) is a novel interactor of annexin A2 in
prostate cancer cells. Biochemistry. 49:2216–2226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li BH, Yang XZ, Li PD, Yuan Q, Liu XH,
Yuan J and Zhang WJ: IL-4/Stat6 activities correlate with apoptosis
and metastasis in colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
369:554–560. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cui X, Zhang L, Luo J, Rajasekaran A,
Hazra S, Cacalano N and Dubinett SM: Unphosphorylated STAT6
contributes to constitutive cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 26:4253–4260. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hida T, Yatabe Y, Achiwa H, Muramatsu H,
Kozaki K, Nakamura S, Ogawa M, Mitsudomi T, Sugiura T and Takahashi
T: Increased expression of cyclooxygenase 2 occurs frequently in
human lung cancers, specifically in adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res.
58:3761–3764. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Grusby MJ and
Clements VK: Cutting edge: STAT6-deficient mice have enhanced tumor
immunity to primary and metastatic mammary carcinoma. J Immunol.
165:6015–6019. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|