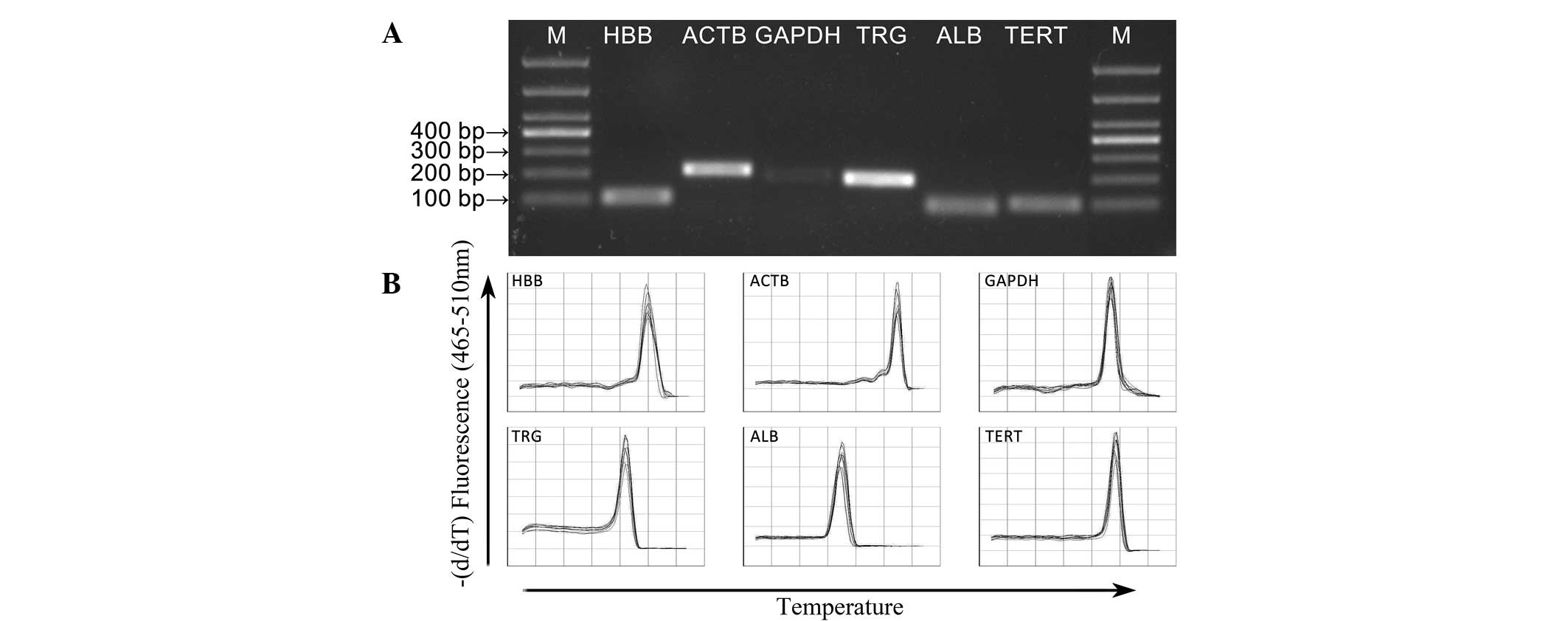
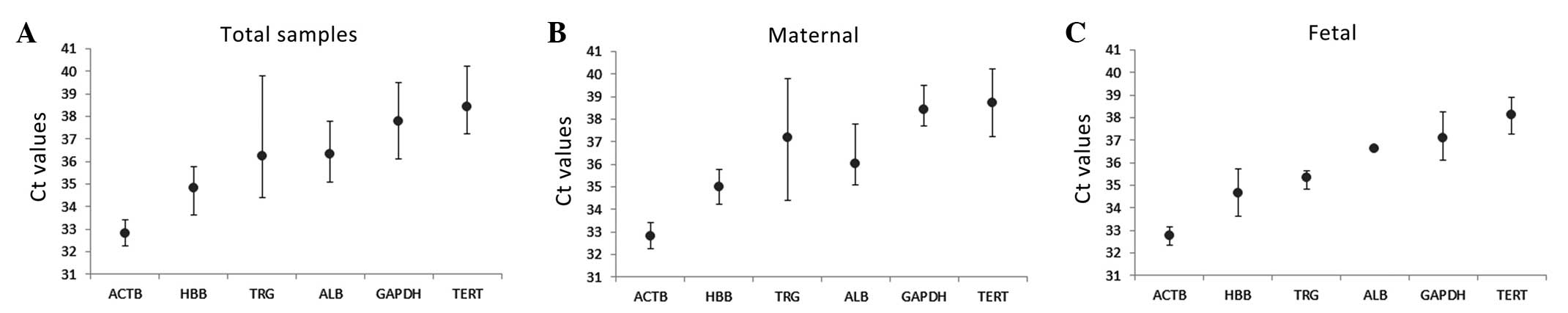
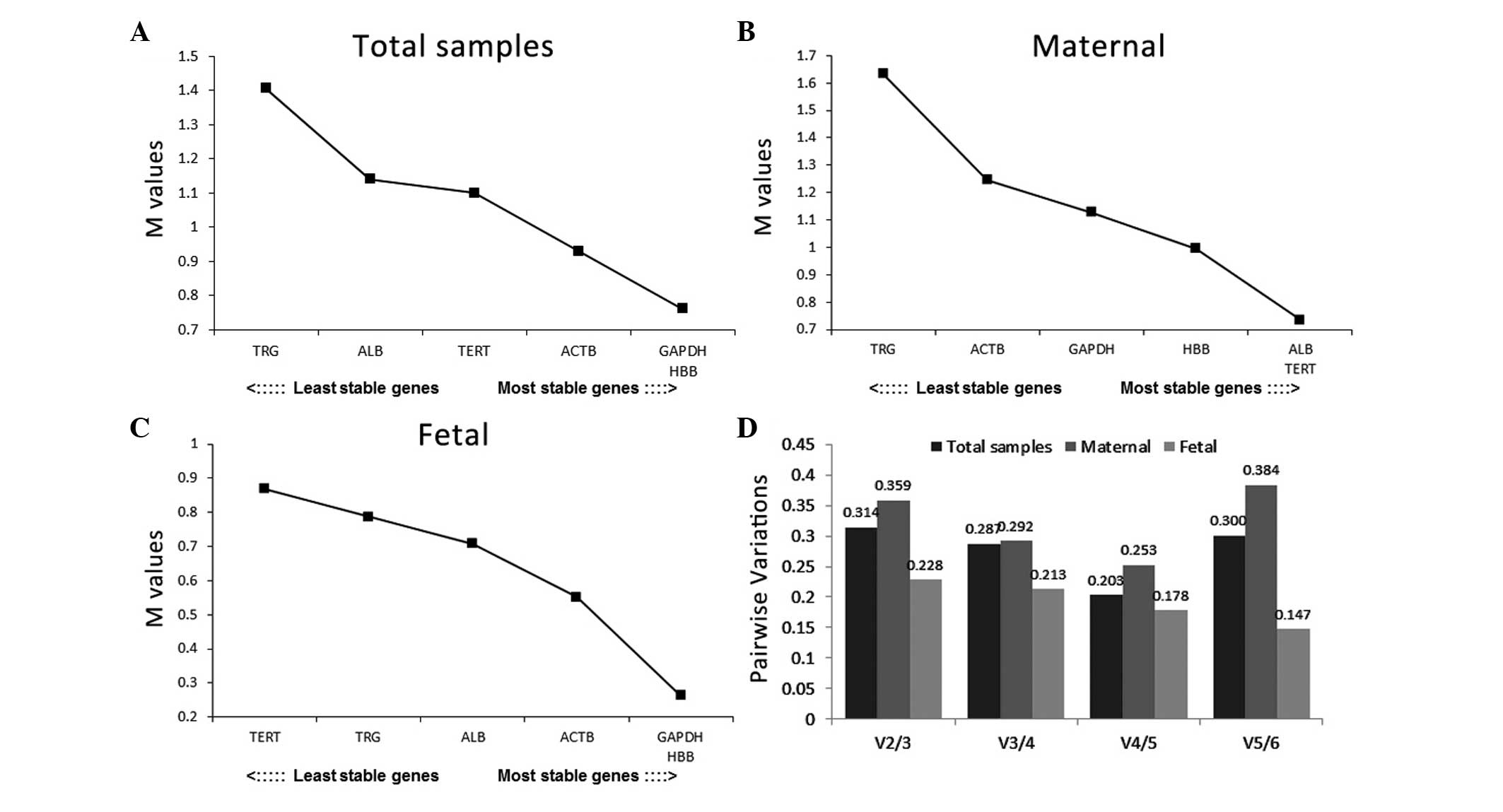
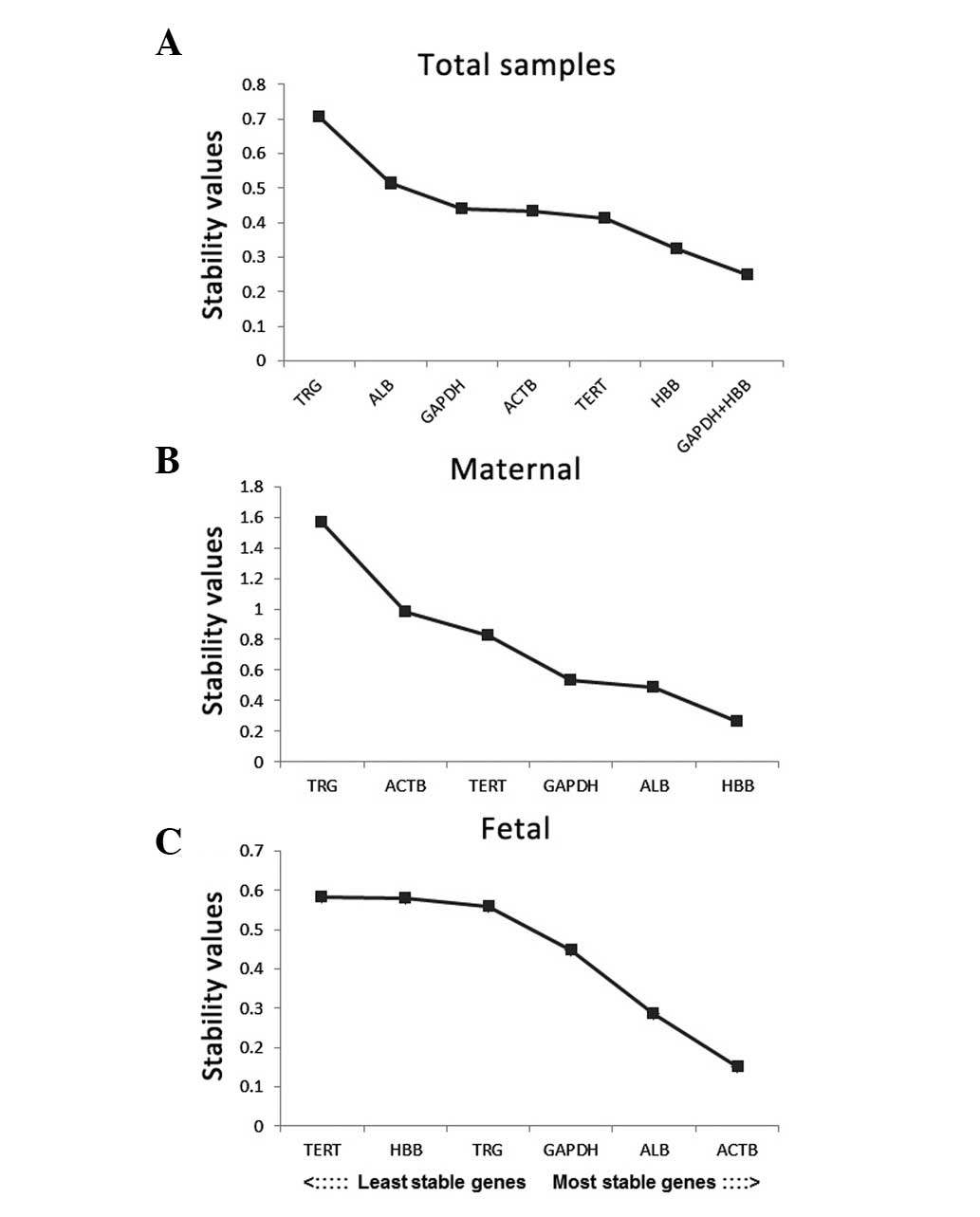
|
1
|
Lo YM, Corbetta N, Chamberlain PF, Rai V,
Sargent IL, Redman CW and Wainscoat JS: Presence of fetal DNA in
maternal plasma and serum. Lancet. 350:485–487. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khorram Khorshid HR, Zargari M, Sadeghi
MR, Edallatkhah H, Shahhosseiny MH and Kamali K: Early fetal gender
determination using real-time PCR analysis of cell-free fetal DNA
during 6th–10th weeks of gestation. Acta Med Iran.
51:209–214. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Teitelbaum L, Metcalfe A, Clarke G,
Parboosingh JS, Wilson RD and Johnson JM: Costs and benefits of
non-invasive fetal RhD determination. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol.
45:84–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xiong L, Barrett AN, Hua R, Tan TZ, Ho SS,
Chan JK, Zhong M and Choolani M: Non-invasive prenatal diagnostic
testing for β-thalassaemia using cell-free fetal DNA and next
generation sequencing. Prenat Diagn. 35:258–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Alberry M, Maddocks D, Jones M, Abdel Hadi
M, Abdel-Fattah S, Avent N and Soothill PW: Free fetal DNA in
maternal plasma in anembryonic pregnancies: Confirmation that the
origin is the trophoblast. Prenat Diagn. 27:415–418. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chan KC, Zhang J, Hui AB, Wong N, Lau TK,
Leung TN, Lo KW, Huang DW and Lo YM: Size distributions of maternal
and fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Clin Chem. 50:88–92. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Zimmermann B, Rusterholz C, Kang A,
Holzgreve W and Hahn S: Size separation of circulatory DNA in
maternal plasma permits ready detection of fetal DNA polymorphisms.
Clin Chem. 50:1002–1011. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Papageorgiou EA, Fiegler H, Rakyan V, Beck
S, Hulten M, Lamnissou K, Carter NP and Patsalis PC: Sites of
differential DNA methylation between placenta and peripheral blood:
molecular markers for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of
aneuploidies. Am J Pathol. 174:1609–1618. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lun FM, Tsui NB, Chan KC, Leung TY, Lau
TK, Charoenkwan P, Chow KC, Lo WY, Wanapirak C, Sanguansermsri T,
Cantor CR, Chiu RW and Lo YM: Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of
monogenic diseases by digital size selection and relative mutation
dosage on DNA in maternal plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:19920–19925. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fan HC, Blumenfeld YJ, Chitkara U, Hudgins
L and Quake SR: Noninvasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by
shotgun sequencing DNA from maternal blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:16266–16271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhong Q, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Qi J, Chen Y, Li
S, Sun Y, Li C and Lan X: Expression profiling and validation of
potential reference genes during Paralichthys olivaceus
embryogenesis. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 10:310–318. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dheda K, Huggett JF, Bustin SA, Johnson
MA, Rook G and Zumla A: Validation of housekeeping genes for
normalizing RNA expression in real-time PCR. Biotechniques.
37:112–114. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Steinau M, Rajeevan MS and Unger ER: DNA
and RNA references for qRT-PCR assays in exfoliated cervical cells.
J Mol Diagn. 8:113–118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Q, Ali HA, Yu S, Zhang L, Li X, Du Z
and Zhang G: Evaluation and validation of the suitable control
genes for quantitative PCR studies in plasma DNA for noninvasive
prenatal diagnosis. Int J Mol Med. 34:1681–1687. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li X, Yang Q, Bai J, Xuan Y and Wang Y:
Identification of appropriate reference genes for human mesenchymal
stem cell analysis by quantitative real-time PCR. Biotechnol Lett.
37:67–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li X, Yang Q, Bai J, Yang Y, Zhong L and
Wang Y: Identification of optimal reference genes for quantitative
PCR studies on human mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep.
11:1304–1311. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F,
Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A and Speleman F: Accurate
normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric
averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol.
3:RESEARCH00342002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Andersen CL, Jensen JL and Ørntoft TF:
Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR
data: A model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes
suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data
sets. Cancer Res. 64:5245–5250. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C and
Neuvians TP: Determination of stable housekeeping genes,
differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity:
BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations.
Biotechnol Lett. 26:509–515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jorgez CJ and Bischoff FZ: Improving
enrichment of circulating fetal DNA for genetic testing: Size
fractionation followed by whole gene amplification. Fetal Diagn
Ther. 25:314–319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Galbiati S, Smid M, Gambini D, Ferrari A,
Restagno G, Viora E, Campogrande M, Bastonero S, Pagliano M, Calza
S, et al: Fetal DNA detection in maternal plasma throughout
gestation. Hum Genet. 117:243–248. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lo YM, Tein MS, Lau TK, Haines CJ, Leung
TN, Poon PM, Wainscoat JS, Johnson PJ, Chang AM and Hjelm NM:
Quantitative analysis of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and serum:
Implications for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. Am J Hum Genet.
62:768–775. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lo YM, Zhang J, Leung TN, Lau TK, Chang AM
and Hjelm NM: Rapid clearance of fetal DNA from maternal plasma. Am
J Hum Genet. 64:218–224. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aghanoori MR, Vafaei H, Kavoshi H,
Mohamadi S and Goodarzi HR: Sex determination using free fetal DNA
at early gestational ages: A comparison between a modified mini-STR
genotyping method and real-time PCR. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
207:202.e1–e8. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lim JH, Park SY, Kim SY, Kim do J, Choi
JE, Kim MH, Choi JS, Kim MY, Yang JH and Ryu HM: Effective
detection of fetal sex using circulating fetal DNA in
first-trimester maternal plasma. FASEB J. 26:250–258. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yenilmez ED, Tuli A and Evrüke IC:
Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis experience in the Çukurova Region of
Southern Turkey: Detecting paternal mutations of sickle cell anemia
and β-thalassemia in cell-free fetal DNA using high-resolution
melting analysis. Prenat Diagn. 33:1054–1062. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gao T, Nie Y, Hu H and Liang Z:
Hypermethylation of IGSF4 gene for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis
of thalassemia. Med Sci Monit. 18:BR33–BR40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Scheffer PG, van der Schoot CE,
Page-Christiaens GC and de Haas M: Noninvasive fetal blood group
genotyping of rhesus D, c, E and of K in alloimmunised pregnant
women: Evaluation of a 7-year clinical experience. BJOG.
118:1340–1348. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gutensohn K, Müller SP, Thomann K, Stein
W, Suren A, Körtge-Jung S, Schlüter G and Legler TJ: Diagnostic
accuracy of noninvasive polymerase chain reaction testing for the
determination of fetal rhesus C, c and E status in early pregnancy.
BJOG. 117:722–729. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Orzinska A, Guz K, Brojer E and Zupanska
B: Preliminary results of fetal Rhc examination in plasma of
pregnant women with anti-c. Prenat Diagn. 28:335–337. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsaliki E, Papageorgiou EA, Spyrou C,
Koumbaris G, Kypri E, Kyriakou S, Sotiriou C, Touvana E, Keravnou
A, Karagrigoriou A, et al: MeDIP real-time qPCR of maternal
peripheral blood reliably identifies trisomy 21. Prenat Diagn.
32:996–1001. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Della Ragione F, Mastrovito P, Campanile
C, Conti A, Papageorgiou EA, Hultén MA, Patsalis PC, Carter NP and
D'Esposito M: Differential DNA methylation as a tool for
noninvasive prenatal diagnosis (NIPD) of X chromosome aneuploidies.
J Mol Diagn. 12:797–807. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Peters IR, Peeters D, Helps CR and Day MJ:
Development and application of multiple internal reference
(housekeeper) gene assays for accurate normalisation of canine gene
expression studies. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 117:55–66. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang E, Shi S, Liu J, Cheng T, Xue L,
Yang X, Yang W, Lan Q and Jiang Z: Selection of reference genes for
quantitative gene expression studies in Platycladus orientalis
(Cupressaceae) Using real-time PCR. PLoS One. 7:e332782012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Marques TE, de Mendonca LR, Pereira MG, de
Andrade TG, Garcia-Cairasco N, Paçó-Larson ML and Gitaí DL:
Validation of suitable reference genes for expression studies in
different pilocarpine-induced models of mesial temporal lobe
epilepsy. PLoS One. 8:e718922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liman M, Wenji W, Conghui L, Haiyang Y,
Zhigang W, Xubo W, Jie Q and Quanqi Z: Selection of reference genes
for reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR normalization
in black rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli). Mar Genomics. 11:67–73.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|