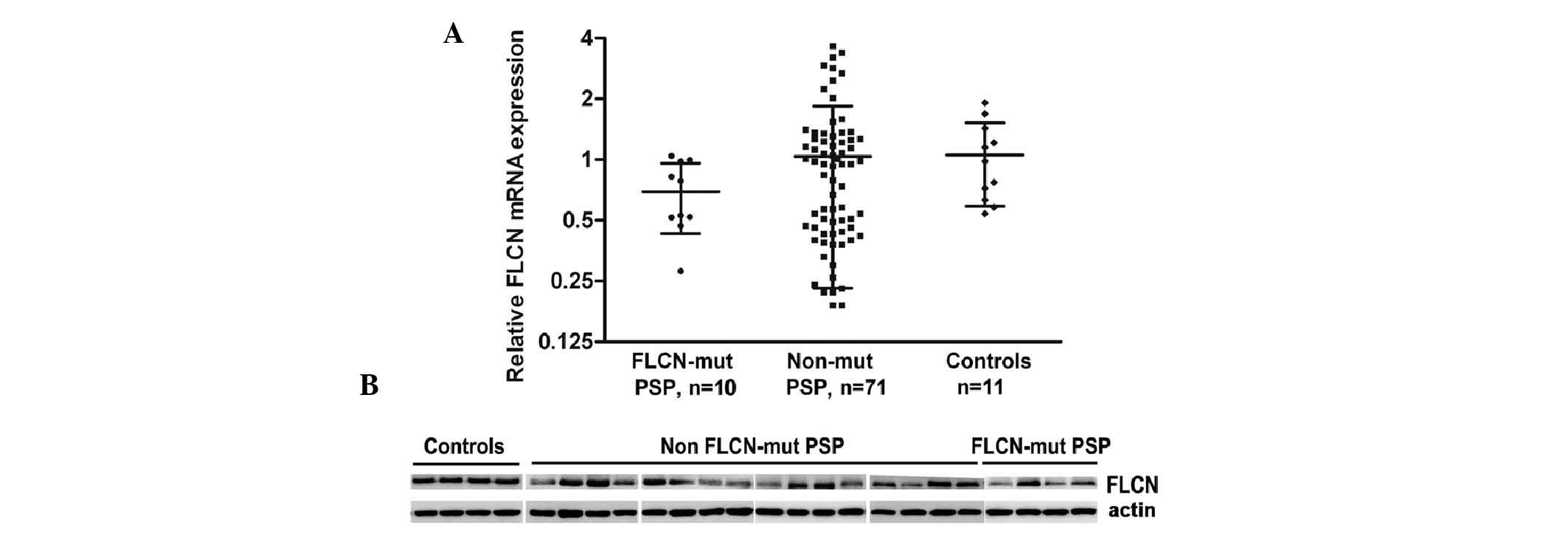
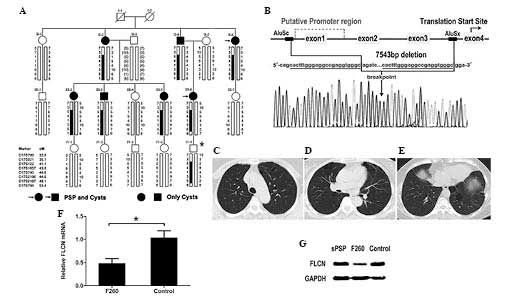
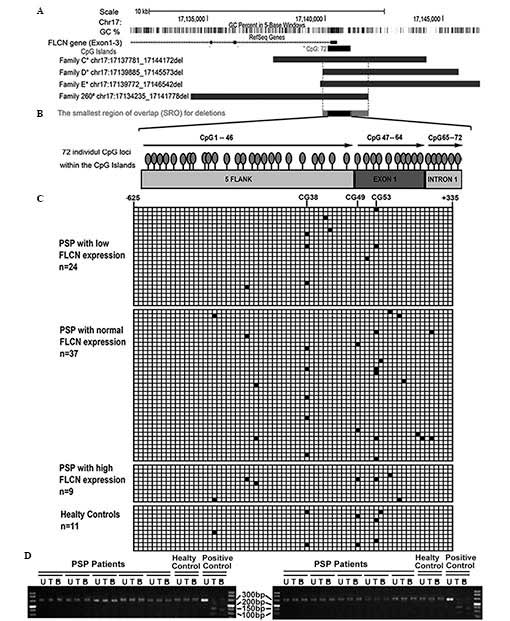
|
1
|
Graham RB, Nolasco M, Peterlin B and
Garcia CK: Nonsense mutations in folliculin presenting as isolated
familial spontaneous pneumothorax in adults. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 172:39–44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ren HZ, Zhu CC, Yang C, Chen SL, Xie J,
Hou YY, Xu ZF, Wang DJ, Mu DK, Ma DH, et al: Mutation analysis of
the FLCN gene in Chinese patients with sporadic and familial
isolated primary spontaneous pneumothorax. Clin Genet. 74:178–183.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nickerson ML, Warren MB, Toro JR,
Matrosova V, Glenn G, Turner ML, Duray P, Merino M, Choyke P,
Pavlovich CP, et al: Mutations in a novel gene lead to kidney
tumors, lung wall defects and benign tumors of the hair follicle in
patients with the Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Cancer Cell. 2:157–164.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Menko FH, van Steensel MA, Giraud S,
Friis-Hansen L, Richard S, Ungari S, Nordenskjöld M, Hansen TV,
Solly J, Maher ER, et al: Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: Diagnosis and
management. Lancet Oncol. 10:1199–1206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Painter JN, Tapanainen H, Somer M,
Tukiainen P and Aittomäki K: A 4-bp deletion in the Birt-Hogg-Dubé
gene (FLCN) causes dominantly inherited spontaneous pneumothorax.
Am J Hum Genet. 76:522–527. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gunji Y, Akiyoshi T, Sato T, Kurihara M,
Tominaga S, Takahashi K and Seyama K: Mutations of the
Birt-Hogg-Dube gene in patients with multiple lung cysts and
recurrent pneumothorax. J Med Genet. 44:588–593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kunogi M, Kurihara M, Ikegami TS,
Kobayashi T, Shindo N, Kumasaka T, Gunji Y, Kikkawa M, Iwakami S,
Hino O, et al: Clinical and genetic spectrum of Birt-Hogg-Dube
syndrome patients in whom pneumothorax and/or multiple lung cysts
are the presenting feature. J Med Genet. 47:281–287. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abdala OA, Levy RR, Bibiloni RH, Viso HD,
De Souza M and Satler VH: Advantages of video assisted thoracic
surgery in the treatment of spontaneous pneumothorax. Medicina (B
Aires). 61:157–160. 2001.In Spanish.
|
|
9
|
Chen YJ, Luh SP, Hsu KY, Chen CR, Tsao TC
and Chen JY: Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) for
bilateral primary spontaneous pneumothorax. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B.
9:335–340. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Toro JR, Pautler SE, Stewart L, Glenn GM,
Weinreich M, Toure O, Wei MH, Schmidt LS, Davis L, Zbar B, et al:
Lung cysts, spontaneous pneumothorax and genetic associations in 89
families with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
175:1044–1053. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Toro JR, Wei MH, Glenn GM, Weinreich M,
Toure O, Vocke C, Turner M, Choyke P, Merino MJ, Pinto PA, et al:
BHD mutations, clinical and molecular genetic investigations of
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: A new series of 50 families and a review
of published reports. J Med Genet. 45:321–331. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sahn SA and Heffner JE: Spontaneous
pneumothorax. N Engl J Med. 342:868–874. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grant LA, Babar J and Griffin N: Cysts,
cavities and honeycombing inmultisystem disorders: Differential
diagnosis and findings on thin-section CT. Clin Radiol. 64:439–448.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guimaraes CV, Donnelly LF and Warner BW:
CT findings for blebs and bullae in children with spontaneous
pneumothorax and comparison with findings in normal age-matched
controls. Pediatr Radiol. 37:879–884. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jordan KG, Kwong JS, Flint J and Müller
NL: Surgically treated pneumothorax. Radiologic, pathologic
findings. Chest. 111:280–285. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shih CH, Yu HW, Tseng YC, Chang YT, Liu CM
and Hsu JW: Clinical manifestations of primary spontaneous
pneumothorax in pediatric patients: An analysis of 78 patients.
Pediatr Neonatol. 52:150–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lim DH, Rehal PK, Nahorski MS, Macdonald
F, Claessens T, Van Geel M, Gijezen L, Gille JJ, Giraud S, Richard
S, et al: A new locus-specific database (LSDB) for mutations in the
folliculin (FLCN) gene. Human Mutat. 31:E1043–E1051. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nahorski MS, Reiman A, Lim DH, Nookala RK,
Seabra L, Lu X, Fenton J, Boora U, Nordenskjöld M, Latif F, et al:
Birt Hogg-Dubé syndrome-associated FLCN mutations disrupt protein
stability. Hum Mutat. 32:921–929. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Benhammou JN, Vocke CD, Santani A, Schmidt
LS, Baba M, Seyama K, Wu X, Korolevich S, Nathanson KL, Stolle CA
and Linehan WM: Identification of intragenic deletions and
duplication in the FLCN gene in Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Genes
chromosomes cancer. 50:466–477. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Khoo SK, Kahnoski K, Sugimura J, Petillo
D, Chen J, Shockley K, Ludlow J, Knapp R, Giraud S, Richard S, et
al: Inactivation of BHD in sporadic renal tumors. Cancer Res.
63:4583–4587. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gatalica Z, Lilleberg SL, Vranic S,
Eyzaguirre E, Orihuela E and Velagaleti G: Novel intronic germline
FLCN gene mutation in a patient with multiple ipsilateral renal
neoplasms. Human pathol. 40:1813–1819. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hasumi Y, Baba M, Ajima R, Hasumi H,
Valera VA, Klein ME, Haines DC, Merino MJ, Hong SB, Yamaguchi TP,
et al: Homozygous loss of BHD causes early embryonic lethality and
kidney tumor development with activation of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:18722–18727. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hansmann T, Pliushch G, Leubner M, Kroll
P, Endt D, Gehrig A, Preisler-Adams S, Wieacker P and Haaf T:
Constitutive promoter methylation of BRCA1 and RAD51C in patients
with familial ovarian cancer and early-onset sporadic breast
cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 21:4669–4679. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
da Silva NF, Gentle D, Hesson LB, Morton
DG, Latif F and Maher ER: Analysis of the Birt-Hogg-Dubé (BHD)
tumour suppressor gene in sporadic renal cell carcinoma and
colorectal cancer. J Med Genet. 40:820–824. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
El-Osta A and Wolffe AP: DNA methylation
and histone deacetylation in the control of gene expression: Basic
biochemistry to human development and disease. Gene Expr. 9:63–75.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kahnoski K, Khoo SK, Nassif NT, Chen J,
Lobo GP, Segelov E and Teh BT: Alterations of the Birt-Hogg-Dubé
gene (BHD) in sporadic colorectal tumours. J Med Genet. 40:511–515.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|