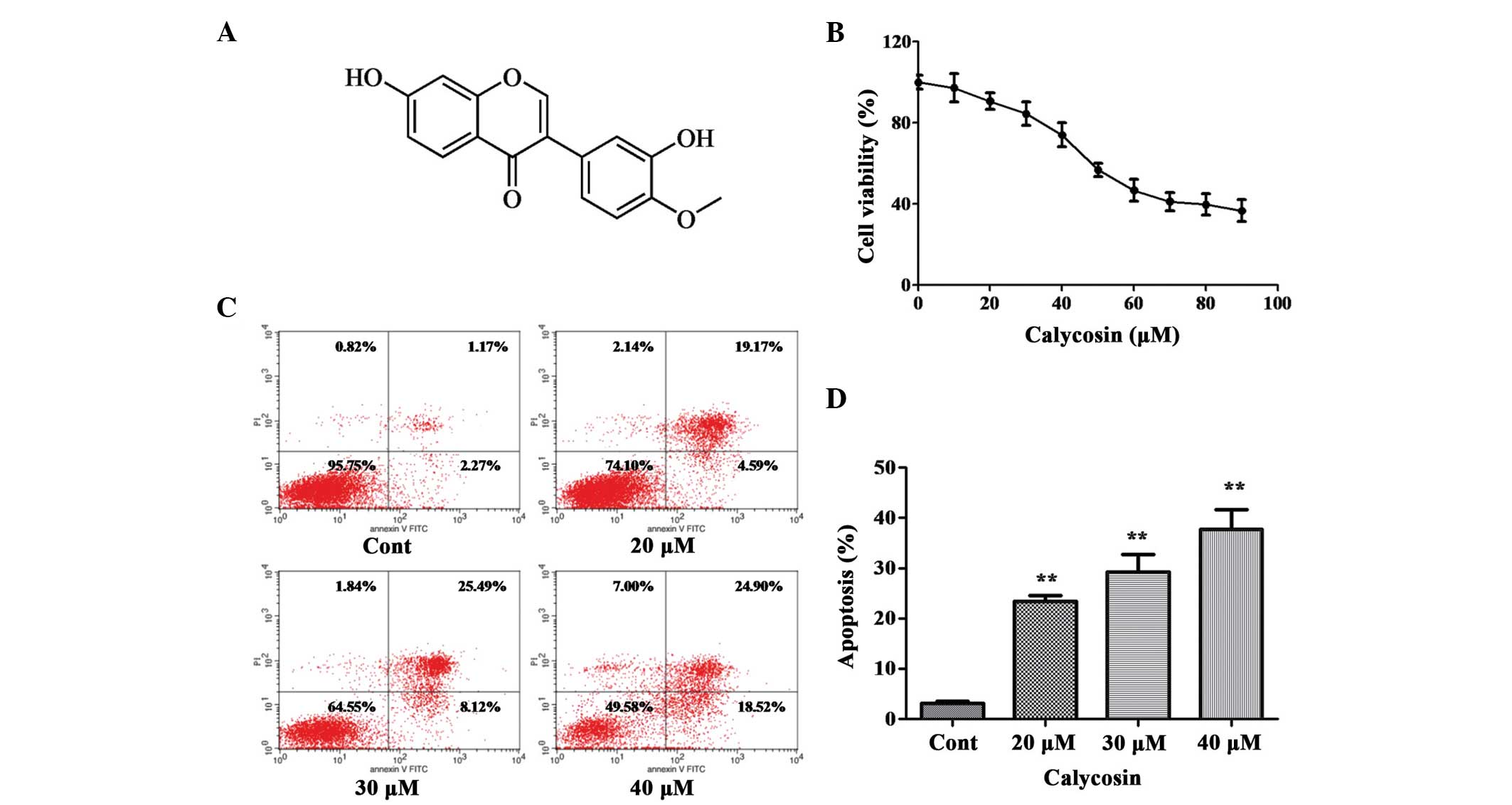
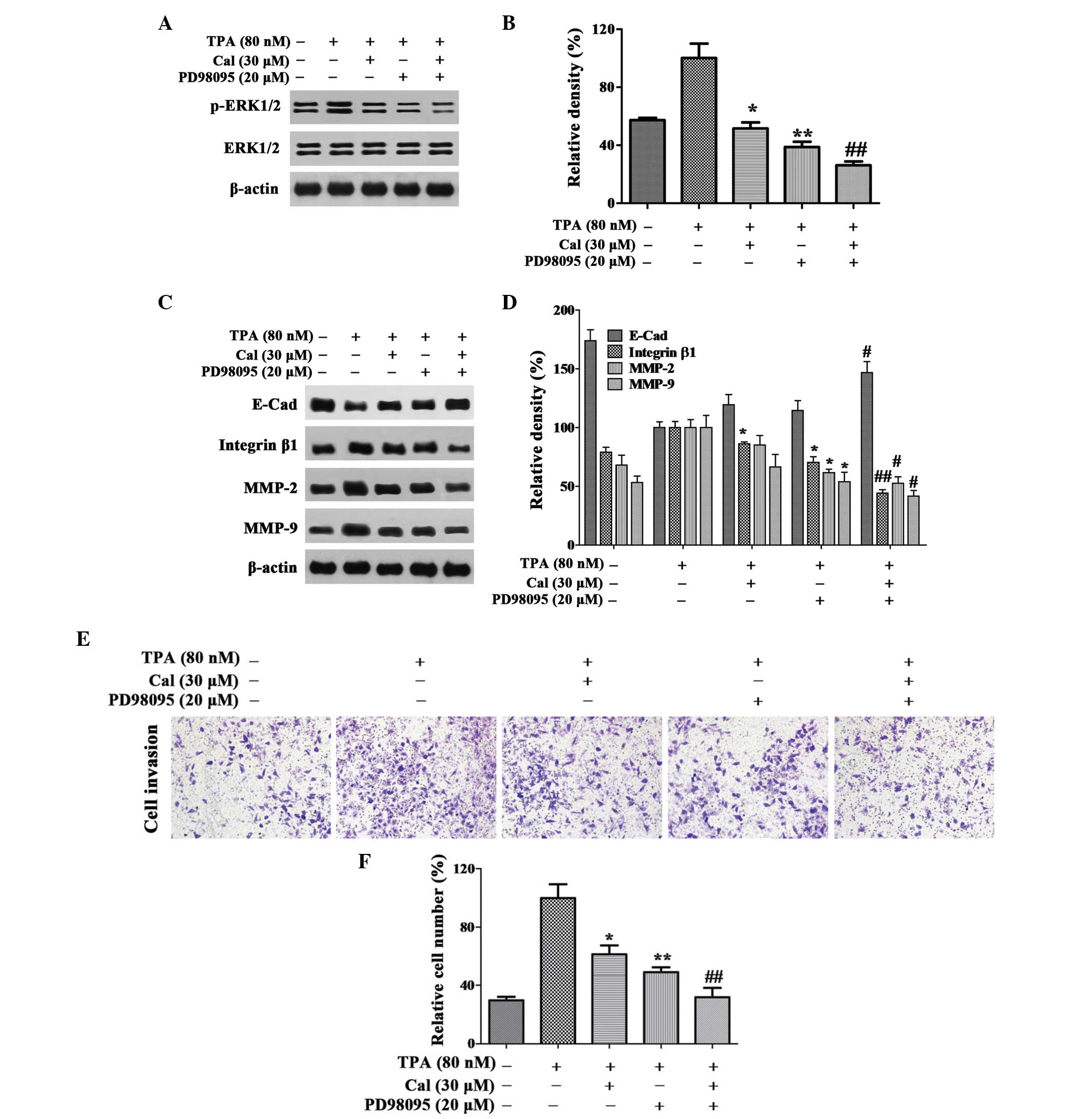
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shiono S, Kanauchi N, Yanagawa N, Abiko M
and Sato T: Stage II–IV lung cancer cases with lymphovascular
invasion relapse within 2 years after surgery. Gen Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 62:112–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lai CS, Boshoff C, Falzon M and Lee SM:
Complete response to erlotinib treatment in brain metastases from
recurrent NSCLC. Thorax. 61(91)2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huo XW, Li SN, Shi TT, Suo AL, Ruan ZP and
Yao Y: Tripartite motif 16 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis by downregulating sonic hedgehog pathway
in non-small cell lung cancer cells. BBRC. 460(1021)2015.
|
|
6
|
Jo E, Park SJ, Choi YS, Jeon WK and Kim
BC: Kaempferol suppresses transforming growth factor-β1-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration of A549 lung
cancer cells by inhibiting Akt1-mediated phosphorylation of Smad3
at threonine-179. Neoplasia. 17(525)2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu ZL, Zhu WR, Zhou WC, Ying HF, Zheng L,
Guo YB, Chen JX and Shen XH: Traditional Chinese medicinal herbs
combined with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Integr Med. 12:346–358. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang XB, Wu WY, Long SQ, Deng H and Pan
ZQ: Effect of gefitinib plus Chinese herbal medicine (CHM) in
patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective
case-control study. Complement Ther Med. 22:1010–1018. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou ZY, Xu L, Li HG, Tian JH, Jiao LJ,
You SF, Han ZF, Jiang Y, Guo HR and Liu H: Chemotherapy in
conjunction with traditional Chinese medicine for survival of
elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: protocol
for a randomized double-blind controlled trial. J Integr Med.
12:175–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma X, Zhang T, Wei Y, Tu P, Chen Y and Ito
Y: Preparative isolation and purification of calycosin from
Astragalus membranaceus Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao by
high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Chromatogr A.
962:243–247. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao J, Liu ZJ, Chen T and Zhao D:
Pharmaceutical properties of calycosin, the major bioactive
isoflavonoid in the dry root extract of Radix astragali. Pharm
Biol. 52:1217–1222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang D, Wang S, Zhu L, Tian Y, Wang H,
Zhuang Y, Li Y and Wang D: Profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma
cell cycle regulating genes targeted by calycosin. Biomed Res Int.
2013(317926)2013.
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Dong X, Li Z, Wang W, Tian J and
Chen J: Downregulated RASD1 and upregulated miR-375 are involved in
protective effects of calycosin on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
rats. J Neurol Sci. 339:144–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li W, Sun YN, Yan XT, Yang SY, Kim S, Lee
YM, Koh YS and Kim YH: Flavonoids from Astragalus membranaceus and
their inhibitory effects on LPS-stimulated pro-inflammatory
cytokine production in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Arch
Pharm Res. 37:186–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, He J, Chen X, Li J, Shen M, Yu W,
Yang Y and Xiao Z: The Proapoptotic Effect of Formononetin in Human
Osteosarcoma Cells: Involvement of Inactivation of ERK and Akt
Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:637–645. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tian J, Duan YX, Bei CY and Chen J:
Calycosin induces apoptosis by upregulation of RASD1 in human
breast cancer cells MCF-7. Horm Metab Res. 45:593–598. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang KP: Role of protein kinase C in
cellular regulation. Biofactors. 2:171–178. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Konopatskaya O and Poole AW: Protein
kinase Calpha: Disease regulator and therapeutic target. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 31:8–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Hwang YP, Yun HJ, Kim HG, Han EH, Choi JH,
Chung YC and Jeong HG: Suppression of
phorbol-12-my-ristate-13-acetate-induced tumor cell invasion by
piperine via the inhibition of PKCα/ERK1/2-dependent matrix
metallopro-teinase-9 expression. Toxicol Lett. 203:9–19. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin CW, Shen SC, Chien CC, Yang LY, Shia
LT and Chen YC: 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced
invasion/migration of glioblastoma cells through activating
PKCalpha/ERK/NF-kappaB-dependent MMP-9 expression. J Cell Physiol.
225:472–481. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang MY, Hsu LS, Peng CH, Shi YS, Wu CH
and Wang CJ: Polyphenol-rich extracts from Solanum nigrum
attenuated PKC alpha-mediated migration and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Agric Food Chem. 58:5806–5814.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lau GT, Huang H, Lin SM and Leung LK:
Butein downregulates phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate-induced COX-2
transcriptional activity in cancerous and non-cancerous breast
cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 648:24–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Roskoski R Jr: ERK1/2 MAP kinases:
Structure, function and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 66:105–143.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou X, Liu Y, You J, Zhang H, Zhang X and
Ye L: Myosin light-chain kinase contributes to the proliferation
and migration of breast cancer cells through cross-talk with
activated ERK1/2. Cancer Lett. 270:312–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang JY, Li S, Li ZH, Zhang ZJ, Hu G,
Cheang LC, Alex D, Hoi MP, Kwan YW, Chan SW, et al: Calycosin
promotes angiogenesis involving estrogen receptor and
mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in
zebrafish and HUVEC. PLoS One. 5:e118222010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Hou R, Zhang X, Ye Y, Wang Y and
Tian J: Calycosin suppresses breast cancer cell growth via
ERβ-dependent regulation of IGF-1R, p38 MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways.
PLoS One. 9:e912452014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liao YC, Shih YW, Chao CH, Lee XY and
Chiang TA: Involvement of the ERK signaling pathway in fisetin
reduces invasion and migration in the human lung cancer cell line
A549. J Agric Food Chem. 57:8933–8941. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shieh JM, Chiang TA, Chang WT, Chao CH,
Lee YC, Huang GY, Shih YX and Shih YW: Plumbagin inhibits
TPA-induced MMP-2 and u-PA expressions by reducing binding
activities of NF-kappaB and AP-1 via ERK signaling pathway in A549
human lung cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 335:181–193. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu B, Wang G, Yang J, Pan X, Yang Z and
Zang L: Berberine inhibits human hepatoma cell invasion without
cytotoxicity in healthy hepatocytes. PLoS One. 6:e214162011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Noda M and Takahashi C: Recklessness as a
hallmark of aggressive cancer. Cancer Sci. 98:1659–1665. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu Y, Feng L, Wang S, Zhu Q, Zheng Z,
Xiang P, He B and Tang D: Calycosin protects HUVECs from advanced
glycation end products-induced macrophage infiltration. J
Ethnopharmacol. 137:359–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu Y, Feng L, Wang S, Zhu Q, Lin J, Lou C,
Xiang P, He B, Zheng Z, Tang D and Zuo G: Phytoestrogen
calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucop yranoside ameliorates advanced glycation
end products-induced HUVEC damage. J Cell Biochem. 112:2953–2965.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lokeshwar BL, Selzer MG, Zhu BQ, Block NL
and Golub LM: Inhibition of cell proliferation, invasion, tumor
growth and metastasis by an oral non-antimicrobial tetracycline
analog (COL-3) in a metastatic prostate cancer model. Int J Cancer.
98:297–309. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu C, Yi C, Hao Z, Cao S, Li H, Shao X,
Zhang J, Qiao T and Fan D: The effect of somatostatin and SSTR3 on
proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells. Cancer Biol
Ther. 3:726–730. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qiu R, Ma G, Zheng C, Qiu X, Li X, Li X,
Mo J, Li Z, Liu Y, Mo L, et al: Antineoplastic effect of calycosin
on osteosarcoma through inducing apoptosis showing in vitro and in
vivo investigations. Exp Mol Pathol. 97:17–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen J, Zhao X, Ye Y, Wang Y and Tian J:
Estrogen receptor beta-mediated proliferative inhibition and
apoptosis in human breast cancer by calycosin and formononetin.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:1790–1797. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Trepat X, Chen Z and Jacobson K: Cell
migration. Compr Physiol. 2:2369–2392. 2012.
|
|
38
|
Canel M, Serrels A, Frame MC and Brunton
VG: E-cadherin-integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and
metastasis. J Cell Sci. 126:393–401. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rodriguez-Teja M, Gronau JH, Minamidate A,
Darby S, Gaughan L, Robson C, Mauri F, Waxman J and Sturge J:
Survival outcome and EMT suppression mediated by a lectin domain
interaction of endo180 and CD147. Mol Cancer Res. 13:538–547. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Barbosa LA, Goto-Silva L, Redondo PA,
Oliveira S, Montesano G, De Souza W and Morgado-Díaz JA:
TPA-induced signal transduction: A link between PKC and EGFR
signaling modulates the assembly of intercellular junctions in
Caco-2 cells. Cell Tissue Res. 312:319–331. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hou M, Cui J, Liu J, Liu F, Jiang R, Liu
K, Wang Y, Yin L, Liu W and Yu B: Angiopoietin-like 4 confers
resistance to hypoxia/serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through
PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cells.
PLoS One. 9:e858082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang H, Wu C, Wan S, Zhang H, Zhou S and
Liu G: Shikonin attenuates lung cancer cell adhesion to
extracellular matrix and metastasis by inhibiting integrin β1
expression and the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Toxicology.
308:104–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Willis AL, Sabeh F, Li XY and Weiss SJ:
Extracellular matrix determinants and the regulation of cancer cell
invasion stratagems. J Microsc. 251:250–260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen K, Zhang S, Ji Y, Li J, An P, Ren H,
Liang R, Yang J and Li Z: Baicalein inhibits the invasion and
metastatic capabilities of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via
downregulation of the ERK pathway. PLoS One. 8:e729272013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Shi MD, Shih YW, Lee YS, Cheng YF and Tsai
LY: Suppression of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced
MCF-7 breast adenocarcinoma cells invasion/migration by α-tomatine
through activating PKC α/ERK/NF-κB-dependent MMP-2/MMP-9
expressions. Cell Biochem Biophys. 66:161–174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang Y, Yang H, Liu H, Huang J and Song X:
Effect of staurosporine on the mobility and invasiveness of lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells: An in vitro study. BMC Cancer.
9:174–186. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Park SH, Kim JH, Lee DH, Kang JW, Song, Oh
SR and Yoon DY: Luteolin 8-C-β-fucopyranoside inhibits invasion and
suppresses TPA-induced MMP-9 and IL-8 via ERK/AP-1 and ERK/NF-κB
signaling in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochimie. 951:2082–2090.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zucchini-Pascal N, Peyre L and Rahmani R:
Crosstalk between beta-catenin and snail in the induction of
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocarcinoma: Role of
the ERK1/2 pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 1410:20768–20792. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chen CC, Chen JJ and Chou CY: Protein
kinase calpha but not p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase, p38,
or c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase is required for intercellular
adhesion molecule-1 expression mediated by interleukin-1beta:
Involvement of sequential activation of tyrosine kinase, nuclear
factor-kappaB-inducing kinase and IkappaB kinase 2. Mol Pharmacol.
58:1479–1489. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Capsoni F, Ongari AM, Reali E, Bosè F and
Altomare GF: The protein kinase C inhibitor AEB071 (sotrastaurin)
modulates migration and superoxide anion production by human
neutrophils in vitro. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 25:617–626.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cheng X, Gu J, Zhang M, Yuan J, Zhao B,
Jiang J and Jia X: Astragaloside IV inhibits migration and invasion
in human lung cancer A549 cells via regulating PKC-α-ERK1/2-NF-κB
pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 23:304–313. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ren W, Liu Y, Wan S, Fei C, Wang W, Chen
Y, Zhang Z, Wang T, Wang J, Zhou L, et al: BMP9 inhibits
proliferation and metastasis of HER2-positive SK-BR-3 breast cancer
cells through ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT pathways. PLoS One. 9:e968162014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Karroum A, Mirshahi P, Benabbou N, Faussat
AM, Soria J, Therwath A, Mirshahi M and Hatmi M: Matrix
metallo-proteinase-9 is required for tubular network formation and
migration of resistant breast cancer cells MCF-7 through PKC and
ERK1/2 signalling pathways. Cancer Lett. 295:242–251. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|