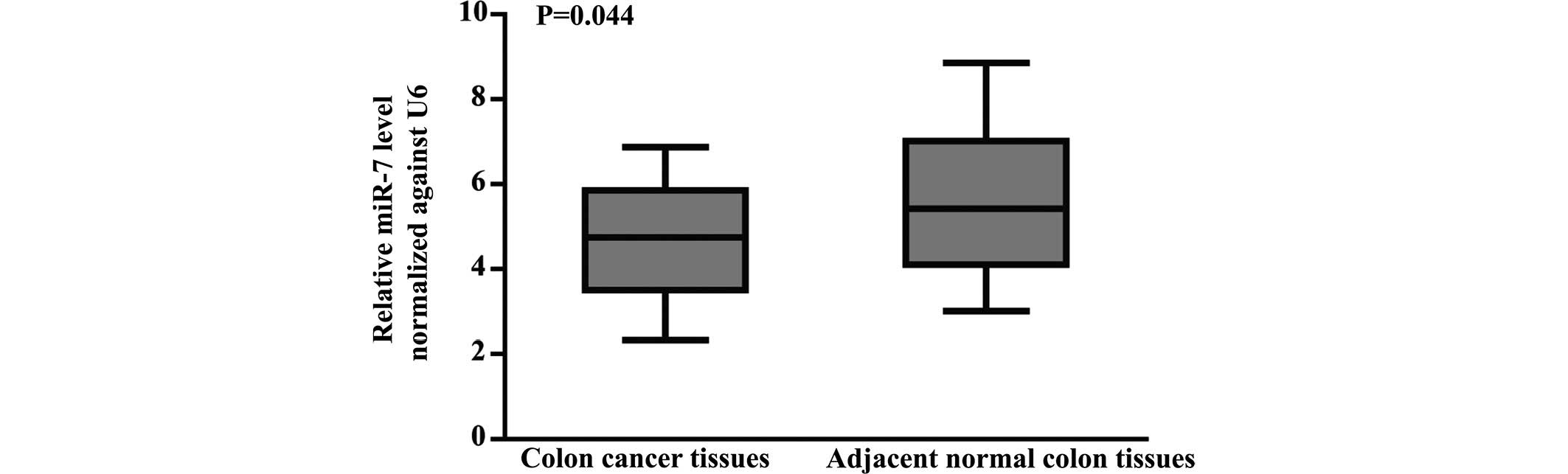
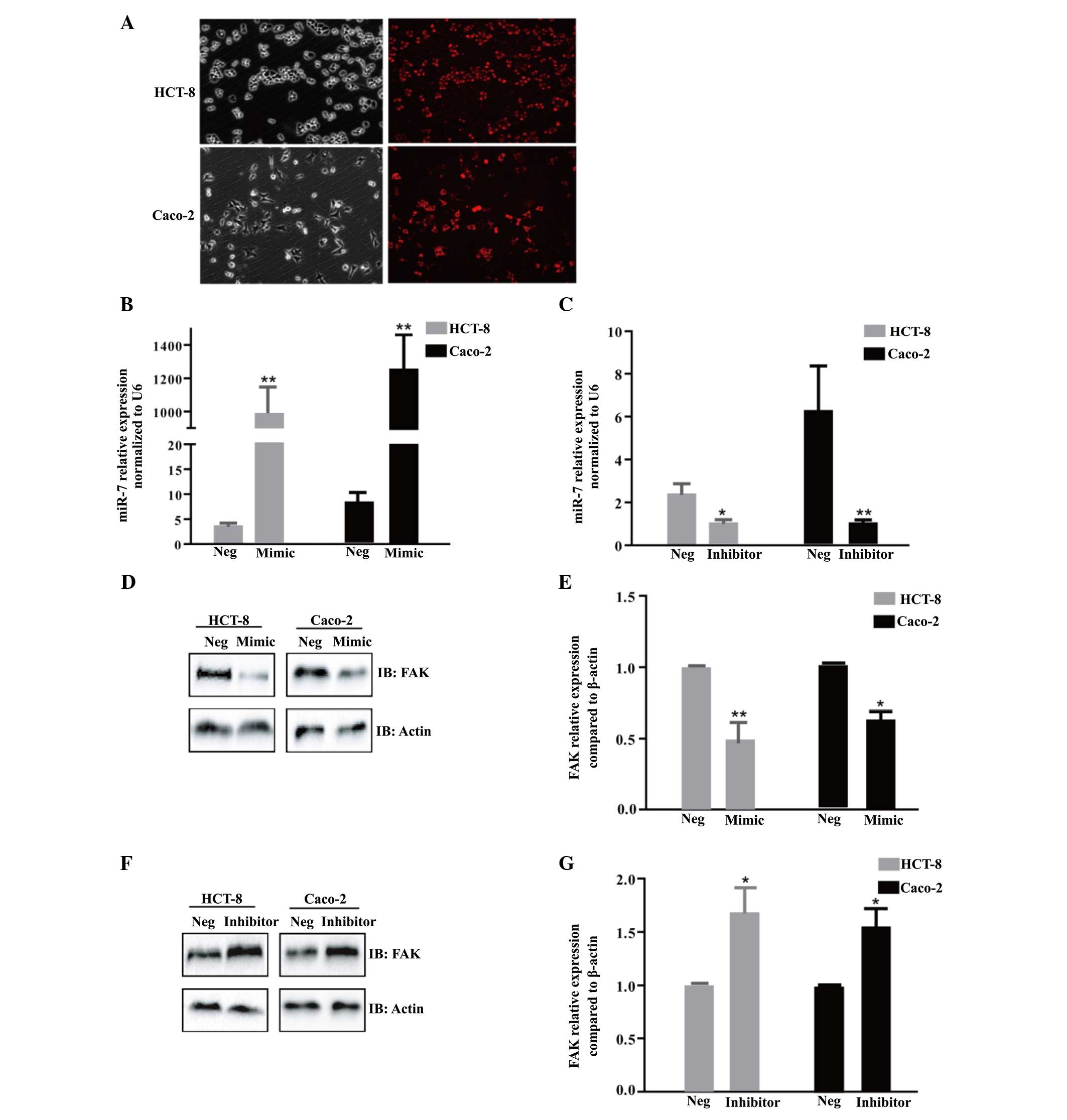
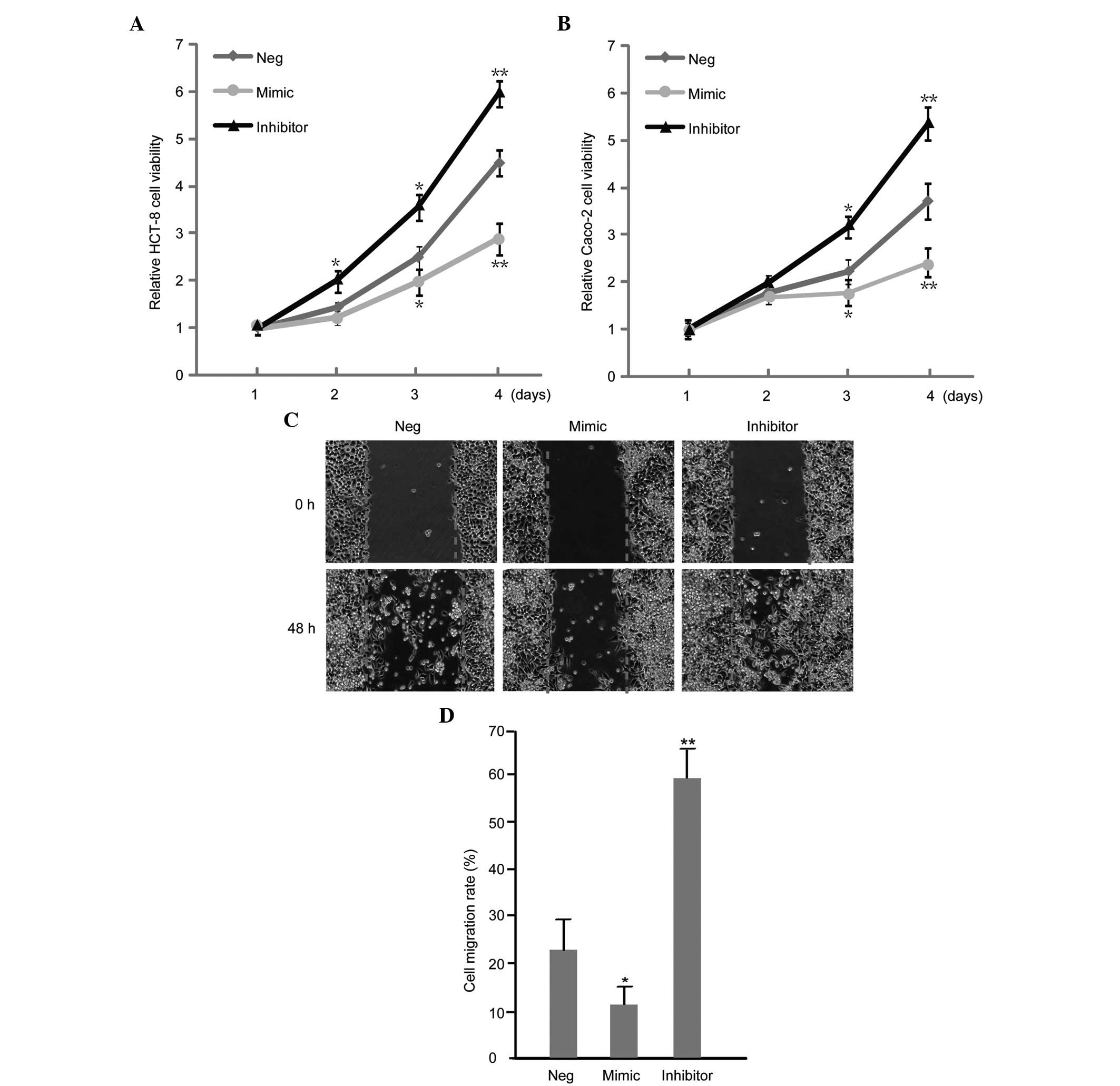
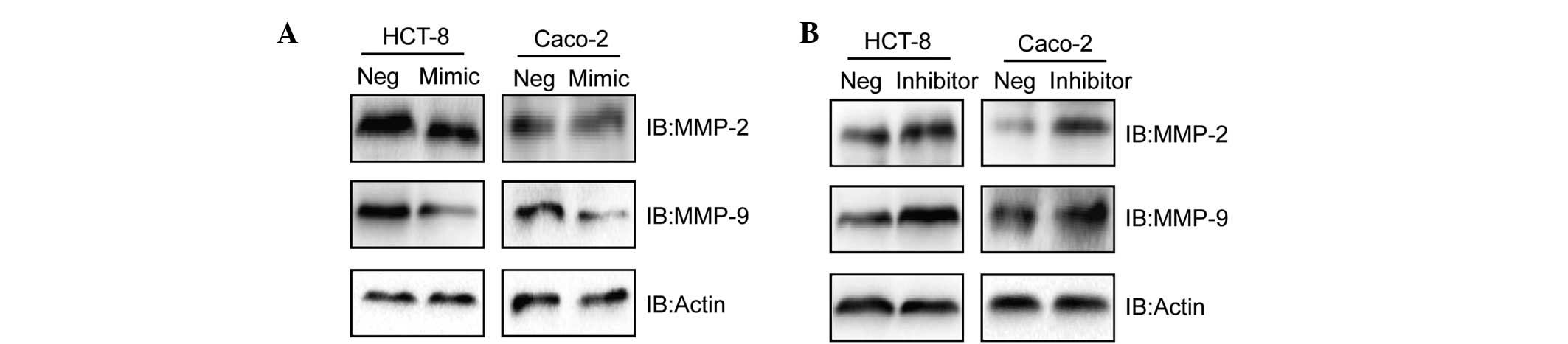
|
1
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cunningham D, Atkin W, Lenz HJ, Lynch HT,
Minsky B, Nordlinger B and Starling N: Colorectal cancer. Lancet.
375:1030–1047. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H,
Zou X and He J: Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010.
Chin J Cancer Res. 26:48–58. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cromheecke M, de Jong KP and Hoekstra HJ:
Current treatment for colorectal cancer metastatic to the liver.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 25:451–463. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Warden C, Stupart D and Goldberg P:
Stenting as first-line management for all patients with
nonperforating left-sided obstructing colorectal cancer. Colorectal
Dis. 15:e389–e395. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mitra SK, Hanson DA and Schlaepfer DD:
Focal adhesion kinase: In command and control of cell motility. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:56–68. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sein TT, Thant AA, Hiraiwa Y, Amin AR,
Sohara Y, Liu Y, Matsuda S, Yamamoto T and Hamaguchi M: A role for
FAK in the Concanavalin A-dependent secretion of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and -9. Oncogene. 19:5539–5542. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cance WG, Harris JE, Iacocca MV, Roche E,
Yang X, Chang J, Simkins S and Xu L: Immunohistochemical analyses
of focal adhesion kinase expression in benign and malignant human
breast and colon tissues: Correlation with preinvasive and invasive
phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res. 6:2417–2423. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rovin JD, Frierson HF Jr, Ledinh W,
Parsons JT and Adams RB: Expression of focal adhesion kinase in
normal and pathologic human prostate tissues. Prostate. 53:124–132.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu DG, Wang YY, Fan LG, Luo H, Han B, Sun
LH, Wang XF, Zhang JX, Cao L, Wang XR, et al: MicroRNA-7 regulates
glioblastoma cell invasion via targeting focal adhesion kinase
expression. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:2616–2621. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Fang Y, Xue JL, Shen Q, Chen J and Tian L:
MicroRNA-7 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by targeting the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 55:1852–1862. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reddy SD, Ohshiro K, Rayala SK and Kumar
R: MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase
1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res. 68:8195–8200. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiong S, Zheng Y, Jiang P, Liu R, Liu X
and Chu Y: MicroRNA-7 inhibits the growth of human non-small cell
lung cancer A549 cells through targeting BCL-2. Int J Biol Sci.
7:805–814. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao X, Dou W, He L, Liang S, Tie J, Liu
C, Li T, Lu Y, Mo P, Shi Y, et al: MicroRNA-7 functions as an
anti-metastatic microRNA in gastric cancer by targeting
insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor. Oncogene. 32:1363–1372.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang N, Li X, Wu CW, Dong Y, Cai M, Mok
MT, Wang H, Chen J, Ng SS, Chen M, et al: microRNA-7 is a novel
inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis.
Oncogene. 32:5078–5088. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Luo J, Cai Q, Wang W, Huang H, Zeng H, He
W, Deng W, Yu H, Chan E, Ng CF, et al: A microRNA-7 binding site
polymorphism in HOXB5 leads to differential gene expression in
bladder cancer. PLoS One. 7:e401272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chan KK, Dassanayake B, Deen R,
Wickramarachchi RE, Kumarage SK, Samita S and Deen KI: Young
patients with colorectal cancer have poor survival in the first
twenty months after operation and predictable survival in the
medium and long-term: Analysis of survival and prognostic markers.
World J Surg Oncol. 8:822010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bannazadeh Amirkhiz M, Rashtchizadeh N,
Nazemieh H, Abdolalizadeh J, Mohammadnejad L and Baradaran B:
Cytotoxic effects of alcoholic extract of dorema glabrum seed on
cancerous cells viability. Adv Pharm Bull. 3:403–408.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maruta M and Maeda K: Trends in the
treatment for liver metastasis of colorectal cancer in Japan. Rozhl
Chir. 90:669–673. 2011.
|
|
25
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Balaguer F, Link A, Lozano JJ, Cuatrecasas
M, Nagasaka T, Boland CR and Goel A: Epigenetic silencing of
miR-137 is an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Res.
70:6609–6618. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kulda V, Pesta M, Topolcan O, Liska V,
Treska V, Sutnar A, Rupert K, Ludvikova M, Babuska V, Holubec L Jr
and Cerny R: Relevance of miR-21 and miR-143 expression in tissue
samples of colorectal carcinoma and its liver metastases. Cancer
Genet Cytogenet. 200:154–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yamakuchi M, Lotterman CD, Bao C, Hruban
RH, Karim B, Mendell JT, Huso D and Lowenstein CJ: P53-induced
microRNA-107 inhibits HIF-1 and tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:6334–6339. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Foekens JA, Sieuwerts AM, Smid M, Look MP,
de Weerd V, Boersma AW, Klijn JG, Wiemer EA and Martens JW: Four
miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative,
estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13021–13026. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saydam O, Senol O, Wurdinger T, Mizrak A,
Ozdener GB, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Yi M, Stephens RM, Krichevsky
AM, Saydam N, et al: miRNA-7 attenuation in Schwannoma tumors
stimulates growth by upregulating three oncogenic signaling
pathways. Cancer Res. 71:852–861. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, Li Y,
Abounader R, Hawkinson M, Lee J, Fine H, Chiocca EA, Lawler S and
Purow B: microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor
and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer
Res. 68:3566–3572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu TJ, LaFortune T, Honda T, Ohmori O,
Hatakeyama S, Meyer T, Jackson D, de Groot J and Yung WK:
Inhibition of both focal adhesion kinase and insulin-like growth
factor-I receptor kinase suppresses glioma proliferation in vitro
and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1357–1367. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lacoste J, Aprikian AG and Chevalier S:
Focal adhesion kinase is required for bombesin-induced prostate
cancer cell motility. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 235:51–61. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kong X, Li G, Yuan Y, He Y, Wu X, Zhang W,
Wu Z, Chen T, Wu W, Lobie PE and Zhu T: MicroRNA-7 inhibits
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast
cancer cells via targeting FAK expression. PLoS One. 7:e415232012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|