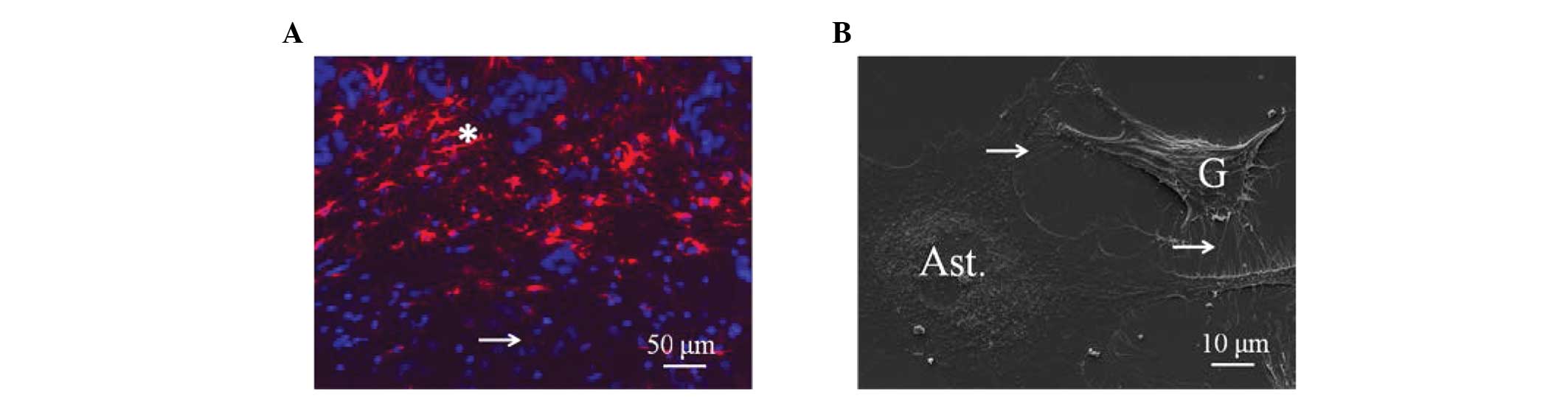
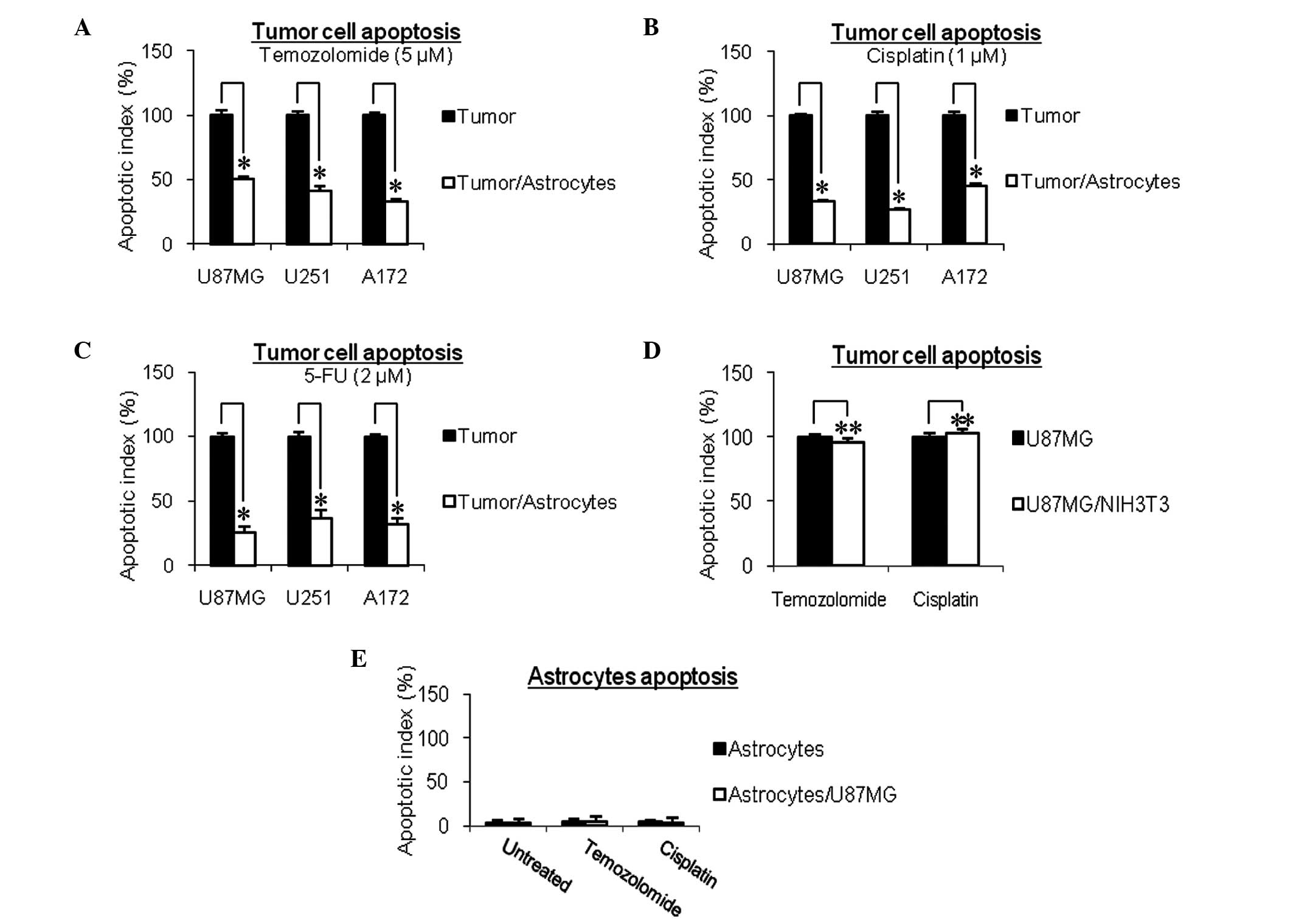
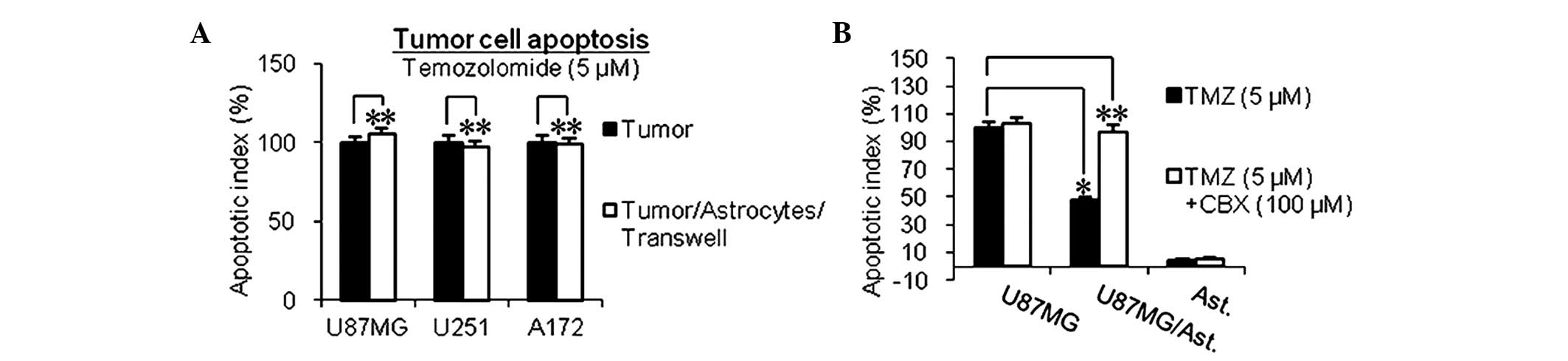
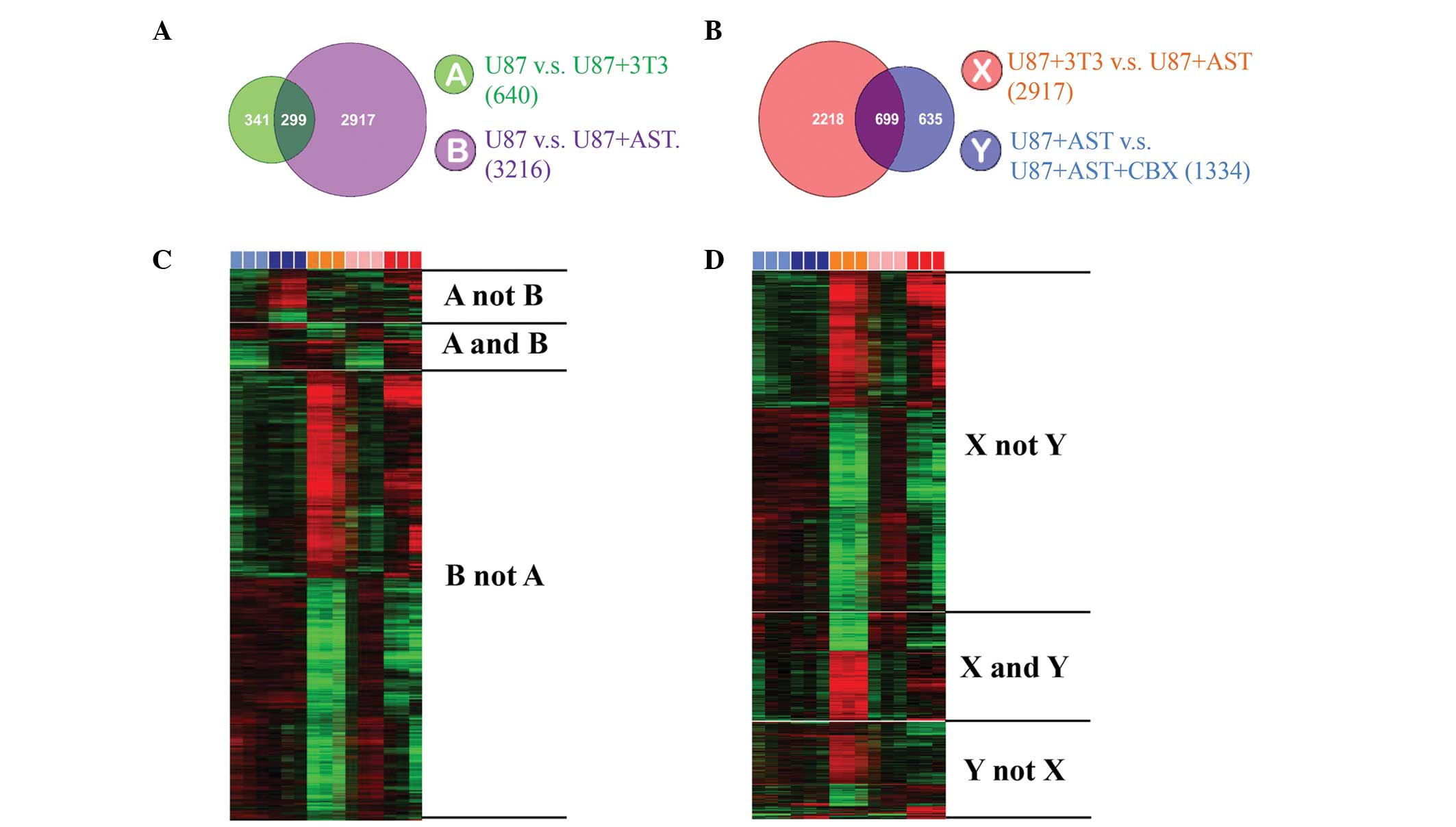
|
1
|
Wrensch M, Minn Y, Chew T, Bondy M and
Berger MS: Epidemiology of primary brain tumors: Current concepts
and review of the literature. Neuro Oncol. 4:278–299.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fisher JL, Schwartzbaum JA, Wrensch M and
Wiemels JL: Epidemiology of brain tumors. Neurol Clin. 25:867–890.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lévy S, Chapet S and Mazeron JJ:
Management of gliomas. Cancer Radiother. 18:461–467. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ashmore SM, Thomas DG and Darling JL: Does
P-glycoprotein play a role in clinical resistance of malignant
astrocytoma? Anticancer Drugs. 10:861–872. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jennings MT and Iyengar S: The molecular
genetics of therapeutic resistance in malignant astrocytomas. Am J
Pharmacogenomics. 1:93–99. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shapiro WR and Shapiro JR: Principles of
brain tumor chemotherapy. Semin Oncol. 13:56–69. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mousseau M: Chemotherapy of brain tumors:
Biological basis of its limited efficacy. Bull Cancer. 81:414–424.
1994.In French. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stewart DJ: A critique of the role of the
blood-brain barrier in the chemotherapy of human brain tumors. J
Neurooncol. 20:121–139. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang RD, Price JE, Fujimaki T, Bucana CD
and Fidler IJ: Differential permeability of the blood-brain barrier
in experimental brain metastases produced by human neoplasms
implanted into nude mice. Am J Pathol. 141:1115–1124.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hoelzinger DB, Demuth T and Berens ME:
Autocrine factors that sustain glioma invasion and paracrine
biology in the brain microenvironment. J Natl Cancer Inst.
99:1583–1593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: The 'seed and soil' hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L and Hansson E:
Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 7:41–53. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fields RD and Stevens-Graham B: New
insights into neuron-glia communication. Science. 298:556–562.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bullock TH, Bennett MV, Johnston D,
Josephson R, Marder E and Fields RD: Neuroscience: The neuron
doctrine, redux. Science. 310:791–793. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miller G: Neuroscience: The dark side of
glia. Science. 308:778–781. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Allen NJ and Barres BA: Neuroscience:
Glia-more than just brain glue. Nature. 457:675–677. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sofroniew MV: Reactive astrocytes in
neural repair and protection. Neuroscientist. 11:400–407. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Crooks DA, Scholtz CL, Vowles G, Greenwald
S and Evans S: The glial reaction in closed head injuries.
Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 17:407–411. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mahesh VB, Dhandapani KM and Brann DW:
Role of astrocytes in reproduction and neuroprotection. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 246:1–9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen LW, Yung KL and Chan YS: Reactive
astrocytes as potential manipulation targets in novel cell
replacement therapy of Parkinson's disease. Curr Drug Targets.
6:821–833. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Krysko DV, Leybaert L, Vandenabeele P and
D'Herde K: Gap junctions and the propagation of cell survival and
cell death signals. Apoptosis. 10:459–469. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin JH, Weigel H, Cotrina ML, Liu S, Bueno
E, Hansen AJ, Hansen TW, Goldman S and Nedergaard M:
Gap-junction-mediated propagation and amplification of cell injury.
Nat Neurosci. 1:494–500. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rouach N, Avignone E, Même W, Koulakoff A,
Venance L, Blomstrand F and Giaume C: Gap junctions and connexin
expression in the normal and pathological central nervous system.
Biol Cell. 94:457–475. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang W, Couldwell WT, Simard MF, Song H,
Lin JH and Nedergaard M: Direct gap junction communication between
malignant glioma cells and astrocytes. Cancer Res. 59:1994–2003.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou B, Bu G, Zhou Y, Zhao Y, Li W and Li
M: Knockdown of CDC2 expression inhibits proliferation, enhances
apoptosis and increases chemosensitivity to temozolomide in
glioblastoma cells. Med Oncol. 32:3782015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chai KM, Wang CY, Liaw HJ, Fang KM, Yang
CS and Tzeng SF: Downregulation of BRCA1-BRCA2-containing complex
subunit 3 sensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide. Oncotarget.
5:10901–10915. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Langley RR, Fan D, Guo L, Zhang C, Lin Q,
Brantley EC, McCarty JH and Fidler IJ: Generation of an
immortalized astrocyte cell line from H-2Kb-tsA58 mice to study the
role of astrocytes in brain metastasis. Int J Oncol. 35:665–672.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grossman R, Brastianos H, Blakeley JO,
Mangraviti A, Lal B, Zadnik P, Hwang L, Wicks RT, Goodwin RC, Brem
H and Tyler B: Combination of anti-VEGF therapy and temozolomide in
two experimental human glioma models. J Neurooncol. 116:59–65.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Peng Q, Moan J, Ma LW and Nesland JM:
Uptake, localization and photodynamic effect of meso-tetra
(hydroxyphenyl) porphine and its corresponding chlorin in normal
and tumor tissues of mice bearing mammary carcinoma. Cancer Res.
55:2620–2626. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weihua Z, Tsan R, Huang WC, Wu Q, Chiu CH,
Fidler IJ and Hung MC: Survival of cancer cells is maintained by
EGFR independent of its kinase activity. Cancer Cell. 13:385–393.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hinkerohe D, Wolfkühler D, Haghikia A,
Meier C, Faustmann PM and Schlegel U: Dexamethasone differentially
regulates functional membrane properties in glioma cell lines and
primary astrocytes in vitro. J Neurooncol. 103:479–489. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang B, Feng X, Wang J, Xu X, Liu H and
Lin N: Adenovirus-mediated delivery of bFGF small interfering RNA
increases levels of connexin 43 in the glioma cell line, U251. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:32010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goldberg GS, Moreno AP, Bechberger JF,
Hearn SS, Shivers RR, MacPhee DJ, Zhang YC and Naus CC: Evidence
that disruption of connexin particle arrangements in gap junction
plaques is associated with inhibition of gap junctional
communication by a glycyrrhetinic acid derivative. Exp Cell Res.
222:48–53. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guan X, Wilson S, Schlender KK and Ruch
RJ: Gap-junction disassembly and connexin 43 dephosphorylation
induced by 18 beta-glycyrrhetinic acid. Mol Carcinog. 16:157–164.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fidler IJ, Balasubramanian K, Lin Q, Kim
SW and Kim SJ: The brain microenvironment and cancer metastasis.
Mol Cells. 30:93–98. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|