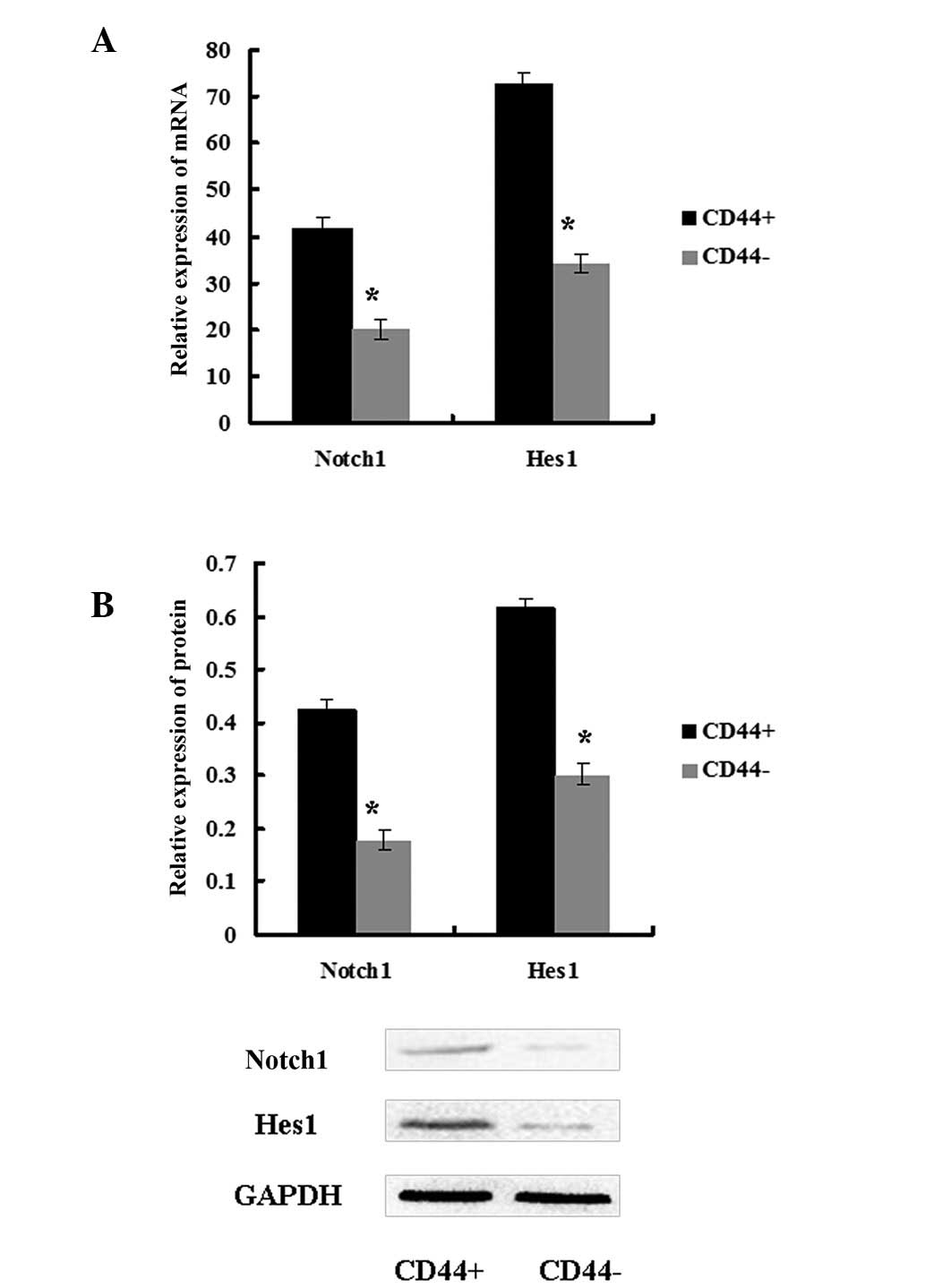
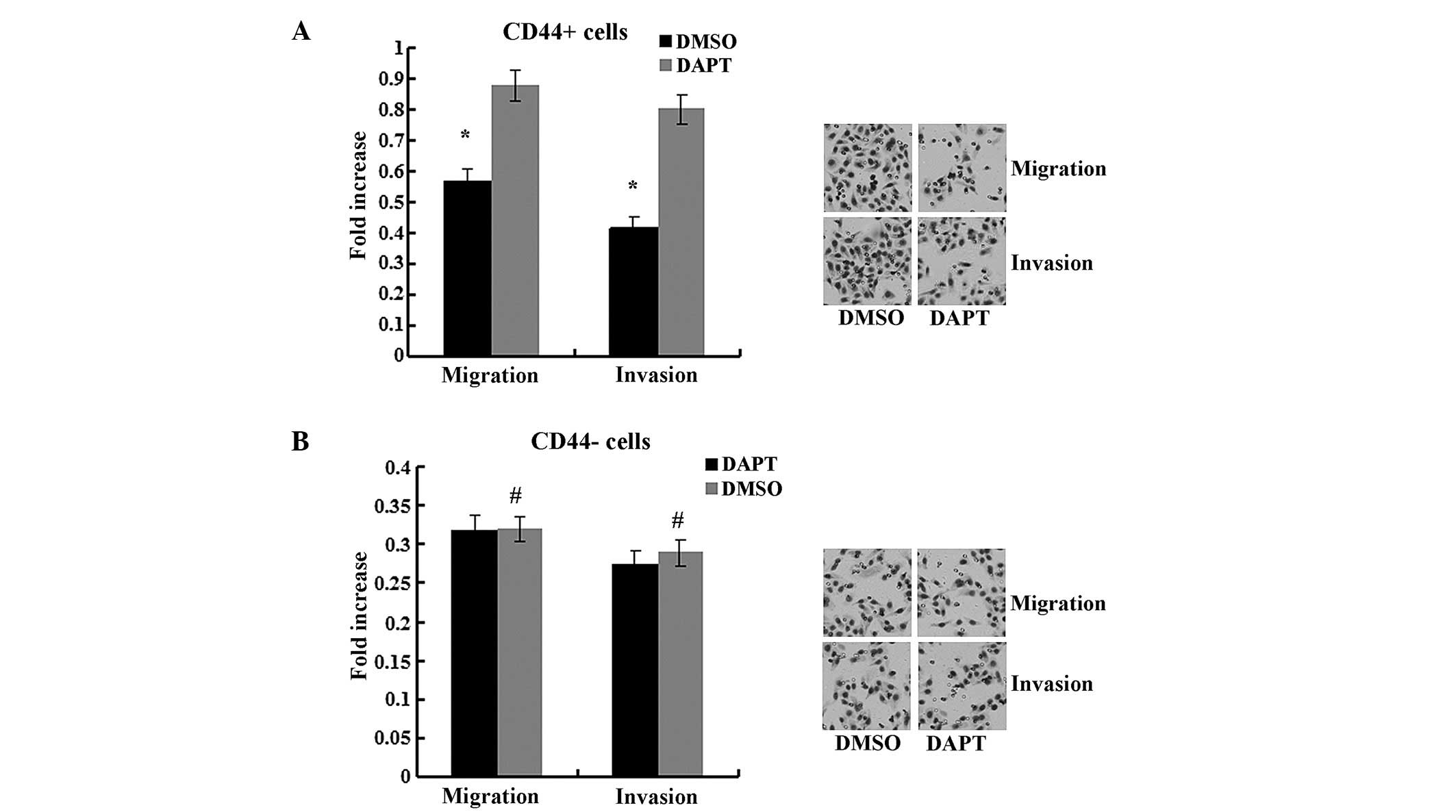
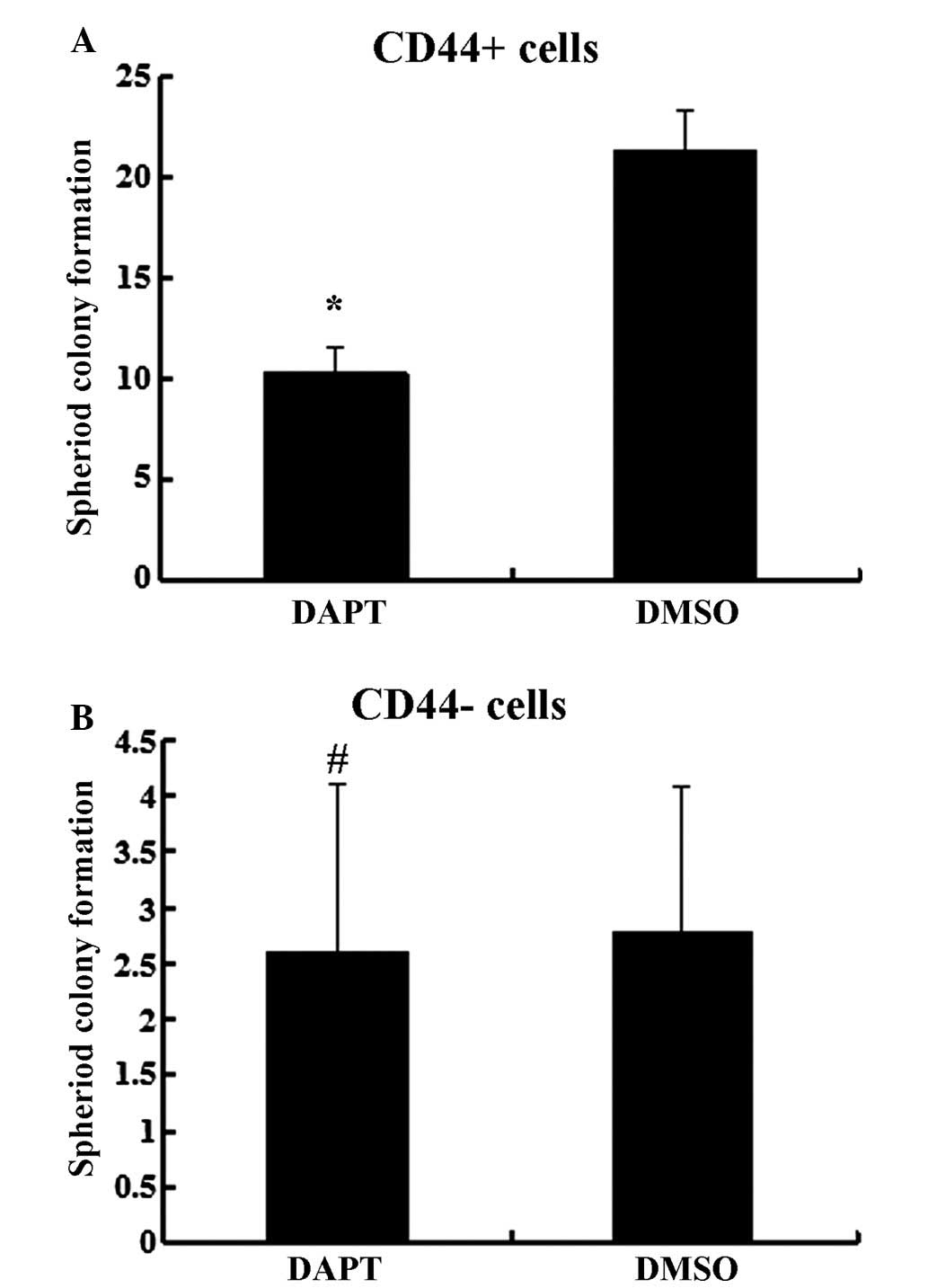
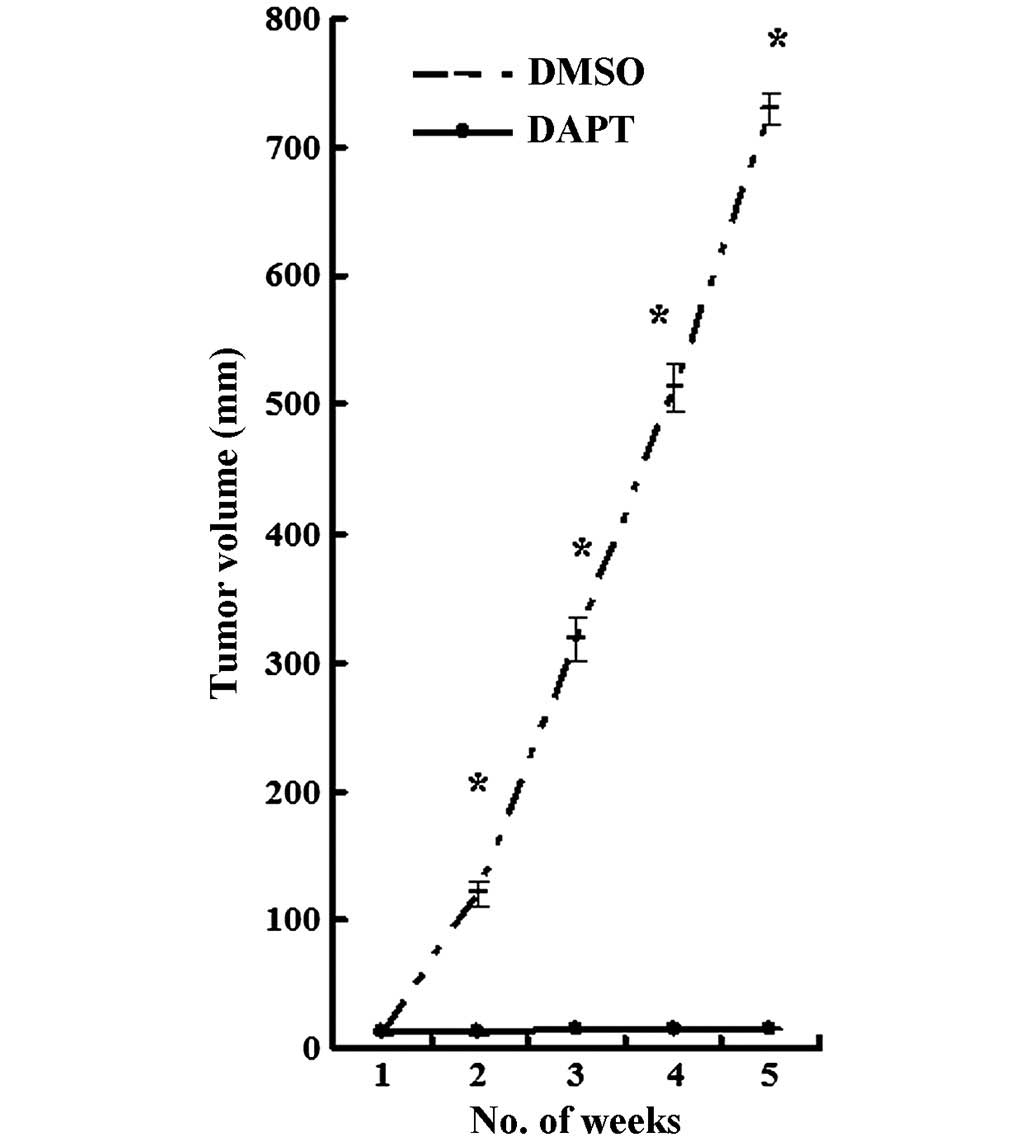
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wagner AD, Unverzagt S, Grothe W, et al:
Chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer. Cochrane Database Syst
Rev. 3:CD0040642010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen J, Kesari S, Rooney C, et al:
Inhibition of notch signaling blocks growth of glioblastoma cell
lines and tumor neurospheres. Genes Cancer. 1:822–835. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takebe N, Harris PJ, Warren RQ and Ivy SP:
Targeting cancer stem cells byinhibiting Wnt, Notch and Hedgehog
pathways. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:97–106. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Visvader JE and Lindeman GJ: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumours: Accumulating evidence and unresolved
questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:755–768. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brzozowa M, Mielańczyk L, Michalski M, et
al: Role of Notch signaling pathway in gastric cancer pathogenesis.
Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 17:1–5. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Piazzi G, Fini L, Selgrad M, et al:
Epigenetic regulation of Delta-Like1 controls Notch1 activation in
gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2:1291–1301. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pannuti A, Foreman K, Rizzo P, et al:
Targeting Notch to target cancer stem cells. Clin Cancer Res.
16:3141–3152. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Palagani V, El Khatib M, Kossatz U, et al:
Epithelial mesenchymal transition and pancreatic tumor initiating
CD44+/EpCAM+ cells are inhibited by γ-secretase inhibitor IX. PLoS
One. 7:e465142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin B, Zeng Y, Liu G, Wang X, Wang P and
Song Y: MAGE-A3 is highly expressed in a cancer stem cell-like side
population of bladder cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:2934–2941. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ailles LE and Weissman IL: Cancer stem
cells in solid tumors. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 18:460–466. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alison MR, Murphy G and Leedham S: Stem
cells and cancer: A deadly mix. Cell Tissue Res. 331:109–124. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan S, Chen JS, Sun LJ and Yao HR:
Selective enrichment of hepatocellular cancer stem cells by
chemotherapy. J Int Med Res. 37:1046–1056. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han ME, Jeon TY, Hwang SH, Lee YS, Kim HJ,
Shim HE, Yoon S, Baek SY, Kim BS, Kang CD and Oh SO: Cancer spheres
from gastric cancer patients provide an ideal model system for
cancer stem cell research. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:3589–3605. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen T, Yang K, Yu J, Meng W, Yuan D, Bi
F, Liu F, Liu J, Dai B, Chen X, et al: Identification and expansion
of cancer stem cells in tumor tissues and peripheral blood derived
from gastric adenocarcinoma patients. Cell Res. 22:248–258. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang J, Zhang Y, Chuai S, Wang Z, Zheng
D, Xu F, Zhang Y, Li C, Liang Y and Chen Z: Trastuzumab (herceptin)
targets gastric cancer stem cells characterized by CD90 phenotype.
Oncogene. 31:671–682. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang C, Li C, He F, Cai Y and Yang H:
Identification of CD44+CD24+ gastric cancer stem cells. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 137:1679–1686. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu G, Shen J, Ou Yang X, Sasahara M and Su
X: Cancer stem cells: The 'heartbeat' of gastric cancer. J
Gastroenterol. 48:781–797. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Teng Y, Wang X, Wang Y and Ma D:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulates cancer stem cells in lung
cancer A549 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 392:373–379. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song Z, Yue W, Wei B, Wang N, Li T, Guan
L, Shi S, Zeng Q, Pei X and Chen L: Sonic hedgehog pathway is
essential for maintenance of cancer stem-like cells in human
gastric cancer. PLoS One. 6:e176872011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koch U and Radtke F: Notch signaling in
solid tumors. Curr Top Dev Biol. 92:411–455. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oh P, Lobry C, Gao J, et al: In vivo
mapping of notch pathway activity in normal and stress
hematopoiesis. Cell Stem Cell. 13:190–204. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng HC, Takahashi H, Li XH, et al:
Downregulated parafibromin expression is a promising marker for
pathogenesis, invasion, metastasis and prognosis of gastric
carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 452:147–155. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li LC, Peng Y, Liu YM, Wang LL and Wu XL:
Gastric cancer cell growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
are inhibited by γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT. Oncol Lett.
7:2160–2164. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan B, Liu L, Zhao Y, et al: Xiaotan
Sanjie decoction attenuates tumor angiogenesis by manipulating
Notch-1-regulated proliferation of gastric cancer stem-like cells.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:13105–13118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ischenko I, Seeliger H, Kleespies A,
Angele MK, Eichhorn ME, Jauch KW and Bruns CJ: Pancreatic cancer
stem cells: New understanding of tumorigenesis, clinical
implications. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 395:1–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tang SN, Singh C, Nall D, Meeker D,
Shankar S and Srivastava RK: The dietary bioflavonoid quercetin
synergizes with epigallocathechin gallate (EGCG) to inhibit
prostate cancer stem cell characteristics, invasion, migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Mol Signal. 5:142010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Abell AN and Johnson GL: Implications of
mesenchymal cells in cancer stem cell populations: relevance to
EMT. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2:21–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shankar S, Nall D, Tang SN, Meeker D,
Passarini J, Sharma J and Srivastava RK: Resveratrol inhibits
pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics in human and KrasG12D
transgenic mice by inhibiting pluripotency maintaining factors and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 6:e165302011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo W: Concise review: breast cancer stem
cells: regulatory networks, stem cell niches, and disease
relevance. Stem Cells Transl Med. 3:942–948. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dave B, Mittal V, Tan NM and Chang JC:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cancer stem cells and treatment
resistance. Breast Cancer Res. 14:2022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|